1949年以来,党和政府始终高度关注城乡发展问题并针对特定时期展开系列政策性探索[1⇓-3]。由最初城是“城”、乡是“乡”割裂式发展转变为“城融乡”“乡融城”融合式发展,体现出国家发展的重要战略需求和高超的国家治理智慧[4,5]。在社会经济发展过程中,中国城市和乡村发展均取得历史性成就。乡村振兴战略是党的“十九大”提出的重大战略之一,主要解决中国农业农村发展动力不足、城乡发展不均衡不充分等问题,强调乡村产业、人才、文化、生态、组织等多方面振兴,旨在推动中国农业全面升级、农村全面进步、农民全面发展[6]。新型城镇化战略是党的“十八大”提出的重要理论之一,主要解决传统城镇化发展以经济、土地为本思想,强调以人为核心,高质量发展的城镇化,旨在推动城镇化科学高质量协调发展[7]。国家“十四五”规划明确提出要健全城乡要素平等交换、双向流动政策体系,强化以工补农、以城带乡,推动形成工农互促、城乡互补、协调发展、共同繁荣的新型城乡关系,从辩证法角度对乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展协调机制进行了系统阐述。马克思在城乡融合理论中认为城市与乡村的对立性可以消灭,社会经济发展必须依赖城市与乡村在更高形态上的深度融合[2,8]。因而坚持协调推进乡村振兴战略与新型城镇化战略,将有效促进城乡融合一体化发展,破解社会主要矛盾。
国外关于城市与乡村关系的研究相对较早,如莫尔“乌托邦”、欧文“新协和村”、霍华德“田园城市”等均在一定程度上反映了城乡关系发展的早期理论构想[9]。此后,西方城乡关系发展经历了二元经济结构理论、增长极理论、核心—边缘理论、城市偏向理论等[10],这时期学者们秉持的理论预设是区域发展从城市核心区开展,通过扩散效应,实现城乡共同发展。20世纪中后期,“次级城市发展战略”“城乡有机体系统”“城乡联系与交流”等思想将城市与乡村发展关系推向发展高峰。随后,“流”“流空间”等概念不断丰富城乡发展理论,研究视野也不断拓展趋于多元化[9]。总体来看,国外城乡关系发展呈现以下特点:一是受工业化发展影响,城乡关系主要体现为城市辐射带动周边乡村发展的城市偏向主义;二是分析维度逐渐多元化,由单一研究维度转为多维结合研究角度;三是注重城乡关系均衡发展,实现城市与乡村协调共同发展。国内学者对乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展关系的研究目前已形成较多优秀成果,梳理总结大致分为以下几点:第一,注重两者协同发展与实现路径的理论思考,包括强化基础设施建设与推动公共服务均等化[11]、构建城乡统一要素市场[12]、建立城乡融合发展体制机制[13]等。如学者认为新时代城乡融合发展可通过乡村振兴与新型城镇化“战略耦合”实现[14],也有学者认为可通过数字技术与数字经济助力城乡融合发展[15]。刘春芳等[16]在对城乡发展关系归纳总结基础上提出城乡融合分析框架,指出城乡融合重点方向、流动机制及格局效应等。另有学者对改革开放以来中国城乡发展演变脉络进行梳理分析,提出未来城乡共治发展的针对性建议[17]。第二,注重两者协调发展的影响因素及驱动方式探究。如学者认为城镇化和农业规模化经营是城乡协调发展的影响因素[18],也有学者认为是社会服务设施的等值配置[19]。协调发展动力可归纳为由县域城镇化通过吸纳乡村剩余劳动力撬动城乡发展的“自下而上”型和以现代化城市群引领城乡区域协同发展的“自上而下”型两类驱动方式。第三,关于两者发展水平测度、结构及格局研究。以乡村振兴和新型城镇化发展目标为出发点,构建多维评价指标体系,采用耦合协调模型等对两者发展水平进行测度,也有学者采用城乡相对发展模型进行协调水平测度。如徐维祥等[4]发现中国乡村振兴与新型城镇化的耦合协调度呈现“东部高、西南低”的分布特征,并对耦合协调度影响因素进行分析探讨。蒋正云等[20]对中部地区农业现代化与新型城镇化耦合协调机制和时空演化特征进行分析,发现两者高度耦合相关但综合效益较低,经济发展是驱动两者协调发展的主要动力。综上,学者基于乡村振兴与新型城镇化的研究已相对成熟,但基于县域尺度的两者协同发展研究相对较少。习近平总书记强调要将县域作为城乡融合发展的重要切入点,因而开展县域单元的城乡协同发展研究意义非凡。
在构建新型城乡关系、实现城乡融合发展背景下,亟待展开欠发达地区县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展研究。甘肃省城乡发展水平与全国相比仍存在一定的差距,城乡要素自由流动不畅、二元经济结构突出、公共资源配置不合理等问题制约其城乡一体发展进程。那么,当前全省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化水平究竟如何?两者协调发展过程中空间结构特征如何?存在哪些影响因素?鉴于此,本文构建县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化综合评价指标体系,对甘肃省86个县域单元2013—2019年乡村振兴与新型城镇化水平进行评价,运用LISA时间路径、LISA时空跃迁进行耦合协调度局部空间结构特征分析,运用GWR模型进行耦合协调度影响因素分析,最后结合实际提出不同区域实施乡村振兴与新型城镇化协调发展的对策建议。
1 乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调作用机理
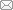
“耦合”引于物理学概念,指两个及以上系统间相互作用、相互影响,进而通过系统内部各种内在机制,形成系统协同一体化发展的现象。当其中某个子系统发生变化时,影响其他子系统也发生类似变化,形成共生发展现象[21]。乡村振兴与新型城镇化是国家经济社会发展的重要战略,在社会发展进程中存在着客观的共生关系,具有相互影响、协同发展属性。乡村振兴与新型城镇化是共生共存的发展共同体,两者协同发展是中国社会主义城乡关系演变的根本趋向,也是新时代中国式现代化发展的必然要求。乡村振兴离不开新型城镇化的带动与辐射,新型城镇化离不开乡村振兴的繁荣与支撑,两者如车之双轮、鸟之双翼。因而需促进乡村振兴与新型城镇化良性耦合,促使乡村振兴与新型城镇化双向赋能,实现新时代中国城乡协调发展新局面。乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合系统作为具有综合性、开放性等特征的复杂巨系统,可以看成是由乡村振兴系统与新型城镇化系统两者构成。乡村振兴系统包含产业、人才、文化与组织、生态等其他多个子系统,新型城镇化系统则包含人口、经济、社会、绿色等其他多个子系统(图1)。系统的各个子系统中又包含多个要素,可分为核心要素与非核心要素(核心要素用图中大圆点表示,非核心要素用小圆点表示)。各个子系统之间通过连线来表示与其他子系统之间发生交互耦合作用及产生耦合关系,共同作用于乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合系统,决定着系统的整体发展与演进方向。
图1
图1
乡村振兴与新型城镇化多要素耦合发展
Fig. 1
Multi-factor coupling development of rural revitalization and new urbanization
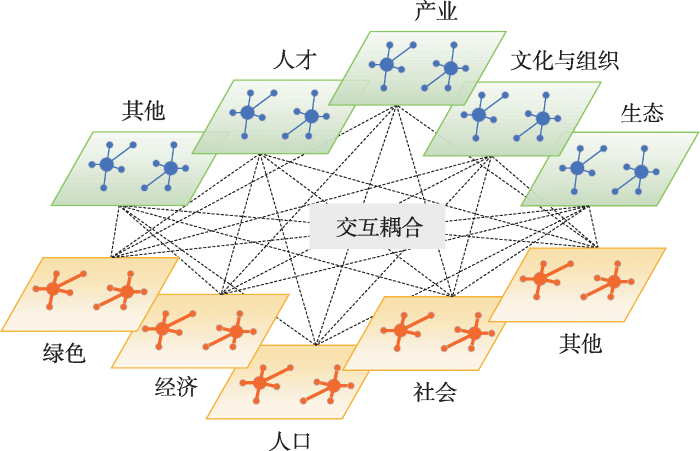
一方面,新型城镇化进程中吸纳大量乡村人口不断向城镇转移,乡村人口数量下降,乡村人均耕地面积占有量增加,有利于乡村开展规模化经营和机械化生产方式,有利于合作社等新型乡村经营主体的培育[22,23],刺激乡村地区消费市场,释放乡村发展消费潜力。新型城镇化通过乡村提供的大量土地、原料等产品供给扩大乡村地域消费市场,推动城乡协调发展功能主动衔接[4],尤其是城市周边乡村地域为城市生态宜居宜业提供绿色发展空间与生态环境保障。新型城镇化发展在维护城市周边乡村区域良好生态环境的同时,践行生态文明思想,打造生态宜居的智慧城市,与乡村振兴战略中建设生态宜居的美丽乡村思想相匹配。城镇人口数量的增加在更大程度上激发城镇对农副产品的需求,乡村人口数量的减少又要求乡村产业结构不断调整优化,通过农业供需两侧结构性改革积极调整农副产品结构,从而提高乡村居民收入。新型城镇化为乡村振兴提供优势发展机遇,促进城市资金、技术、人才等要素向乡村流动,实现城乡要素交互流动,促进资源要素合理配置[24],进而促进乡村振兴发展。新型城镇化的不断推进使得城镇为乡村提供更多就业机会,解决乡村转移人口就业问题,保障乡村人口工资性收入来源稳定。
另一方面,乡村振兴是新型城镇化发展的重要支撑,也是新型城镇化战略顺利推进的重要基础。乡村消费潜力可成为城镇经济增长的重要拉动力,乡村巨大消费潜力逐步释放,乡村消费性市场不断扩展,刺激区域消费增长[25]。乡村是区域发展的绿色生态基底,乡村区域山水林田湖草有机深度融合,造就生态宜居美丽乡村,为城镇居民提供休闲休憩绿色空间[26]。乡村人口在城镇寻求就业机会使居民工资性收入不断提高,部分资金回流乡村参与家庭住房建设及改变家庭生产生活方式等,提高乡村振兴发展实施成效。乡村为城镇发展提供生产、生活资料支持,不断提升优化农副产品供给质量,为城镇发展提供高质量原材料和生活必需资料。乡村地域通过强化原生态农产品供给,转变乡村发展生态优势为乡村生态经济优势,提供更优质的绿色无公害农副生态产品来满足城市居民高品质生活的需求。乡村人口向城镇流动导致农户自留地及农村集体建设用地资源闲置[27],通过发展数字农业及规模农业实现智慧农业,从而提高乡村居民经济收入水平。在乡村现代化发展进程中,农业机械化水平的不断提高导致乡村对农业劳动力的需求下降,农村剩余劳动力不断向城镇转移并逐步实现市民化[28],为城镇发展提供了劳动力支持。同时随着国家新型城镇化的稳步推进,城镇社会经济取得了良好发展,反过来为乡村振兴发展提供更多物力财力支持,促进乡村振兴高质高效发展(图2)。
图2
图2
乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调作用机理
Fig. 2
The coupling coordination mechanism of rural revitalization and new urbanization
总而言之,乡村振兴体系为新型城镇化提供重要的发展支撑,而新型城镇化体系又是推动乡村振兴重要的动力引擎,需坚持乡村振兴与新型城镇化两域协调发展,通过驱动—响应机制形成乡村振兴—新型城镇化耦合系统,共同驱动系统高级演化发展,最终实现两者统筹融合发展、协同一体发展、共生持续发展、高质高效发展。
2 研究方法与数据来源
2.1 研究区概况
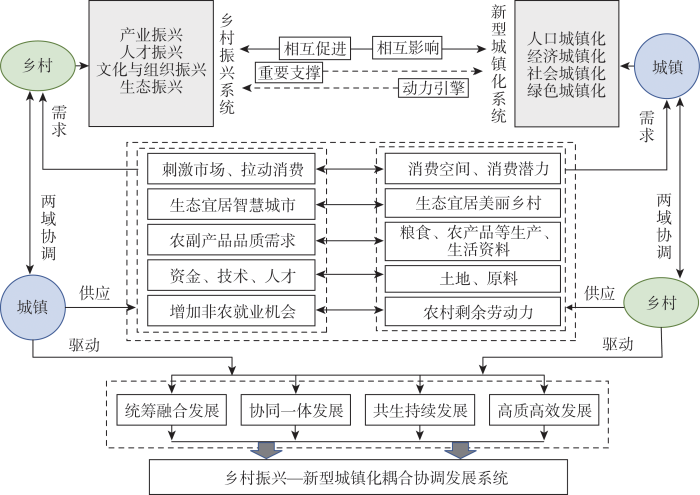
甘肃省地处青藏高原、黄土高原和内蒙古高原交汇地带,是丝绸之路经济带上重要省份,也是中国西部地区重要的生态保护屏障和进疆入藏的战略通道。截至2019年末,甘肃省农村人口为1363.69万人,占全省总人口的51.51%。全省农业总产值为1306.41亿元,占全省GDP值的14.98%,农村人均居民纯收入和人均生活消费支出分别为9629元和9694元,农村居民生活得到大幅改善。但是,整体上仍然落后于全国平均水平。全省城镇人口为1283.74万人,城镇化率达到48.49%,城镇居民人均可支配收入32323元,人均消费支出24454元,与全国其他省份相比甘肃省城镇发展水平仍相对落后。本文所选的86个研究单元包括16个市辖区、5个县级市、7个自治县、57个县和1个地级市(因安宁区无农业户籍人口,故剔除不在研究范围内,嘉峪关市无下辖县、区,因而整体纳入一个研究单元)(图3)。依据甘肃省“十四五”发展规划 [甘政发〔2021〕18号],将甘肃省划分为河西地区(嘉峪关市、酒泉市、张掖市、金昌市、武威市)、陇中地区(兰州市、白银市、定西市、临夏州)、陇东南地区(庆阳市、平凉市、天水市、陇南市、甘南州)。
图3
图3
研究区
注:图中重复数字为县域飞地;本图基于自然资源部标准地图服务系统下载的标准地图制作,底图无修改,下同。
Fig. 3
Study area (Gansu province)
2.2 综合评价指标体系构建
乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展是解决城乡发展不平衡、农村发展不充分的关键路径。新时期乡村振兴涉及产业、人才、文化、生态和组织等多方面的全面振兴,是符合新时期人民追求美好生活需求愿望的重要实践。乡村组织与文化之间关系紧密,相互联系、相互影响,两者之间具有较高的关联度,形成一个具有复杂特定功能的社会关系复合系统。由于两者自身定量表征难度较大,并考虑县域层面乡村文化与组织数据的易获取性、时效性等问题,同时借鉴已有乡村振兴评价指标体系[29],从产业振兴、人才振兴、文化与组织振兴和生态振兴四个维度构建县域乡村振兴综合评价指标体系。新型城镇化“新”在以人为本,突出以人为本、资源节约理念,强调“人的城镇化”,更加强调生态环境保护和统筹城乡协调发展。新型城镇化是推动国家经济社会高质量发展的强大动力,其相关研究成果相对较为丰富。参考前人相关研究[30],从人口城镇化、经济城镇化、社会城镇化和绿色城镇化四个维度构建新型城镇化综合评价指标体系。遵循系统性、全面性及可操作性原则,构建了甘肃省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展评价指标体系(表1)。
表1 县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展评价指标体系
Table 1
| 目标层 | 准则层 | 指标层 | 指标解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乡村振兴 | 产业振兴 | 集约化经营水平 | 农业土地产出率 |
| 机械化水平 | 农作物耕种收综合机械化率 | ||
| 机械处理保障水平 | 万人农田基本设施建设及畜牧养殖机械设备数 | ||
| 农机建设规模投入程度 | 单位耕地面积农业机械总动力 | ||
| 人才振兴 | 现代服务业从业情况 | 从事现代服务业人员占比 | |
| 农业专业人才发展情况 | 农民专业化从业人员占农林渔牧业从业人员比例 | ||
| 乡村人口受教育情况 | 乡村高中及以上学历人数比例 | ||
| 乡村经济管理人才情况 | 万人乡村经济管理人员 | ||
| 文化与组织振兴 | 文化设施支撑情况 | 村均图书馆及文化馆数量 | |
| 教育文化娱乐消费情况 | 乡村居民教育文化娱乐支出占比 | ||
| 组织专业化发展情况 | 万人农民专业合作社及农机专业合作社数量 | ||
| 组织服务化发展情况 | 万人农业技术服务机构数量 | ||
| 生态振兴 | 生活垃圾处理化水平 | 生活垃圾得到治理的村占比 | |
| 生态修复治理情况 | 荒山荒沙地造林及水土流失生态治理面积占比 | ||
| 耕地绿色发展情况 | 单位耕地面积化学肥料使用强度 | ||
| 新型城镇化 | 人口城镇化 | 人口数量结构 | 年末城镇人口占总人口比例 |
| 人口承载情况 | 建成区人口密度 | ||
| 人口就业吸纳情况 | 第二、三产业从业人员占总就业人员比例 | ||
| 经济城镇化 | 经济发展情况 | 人均GDP | |
| 产业结构优化情况 | 第二、三产业产值占GDP比例 | ||
| 经济运行状况 | 城镇社会消费品零售总额 | ||
| 社会城镇化 | 公用设施建设情况 | 人均城市道路面积 | |
| 居民生活水平情况 | 城镇居民人均可支配收入 | ||
| 公共服务设施情况 | 万人卫生医疗机构床位数 | ||
| 绿色城镇化 | 城市绿地建设情况 | 建成区绿化覆盖率 | |
| 城市绿化环境情况 | 人均公园绿地面积 | ||
| 城市整洁情况 | 生活垃圾无害化集中处理率 |
2.3 研究方法
2.3.1 熵权法
熵权法是利用评价指标的变异程度来判别指标的效用价值,在一定程度上避免了主观因素带来的偏差,使用熵权法测度县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展综合指数,具体计算过程与步骤见文献 [31]。
2.3.2 耦合协调度测算模型
“耦合”借鉴物理学系统耦合概念,将其引用表示两个及以上系统相互作用及相互影响的关系[32]。运用耦合协调度探索乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展之间的可能关系,采用耦合度反映两者之间相互作用、相互影响程度,采用协调度反映两者协同发展、协同演化程度。耦合度计算公式如下:
耦合度C虽能够判断甘肃省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合作用的强弱程度,但可能会出现子系统发展水平低而耦合度高的情况,无法真实反映乡村振兴与新型城镇化系统之间的综合协调水平,因而引入耦合协调度。公式如下:
表2 乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调类型划分
Table 2
| 类型 | 耦合协调度 | 亚类型 | U1与U2界定 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高级协调 | 0.80<D≤1.00 | 高级协调—乡村振兴发展滞后 高级协调—新型城镇化发展滞后 高级协调 | U2-U1>0.1 U1-U2>0.1 0≤|U1-U2|≤0.1 |
| 基本协调 | 0.50<D≤0.80 | 基本协调—乡村振兴发展滞后 基本协调—新型城镇化发展滞后 基本协调 | U2-U1>0.1 U1-U2>0.1 0≤|U1-U2|≤0.1 |
| 基本失调 | 0.30<D≤0.50 | 基本失调—乡村振兴发展滞后 基本失调—新型城镇化发展滞后 基本失调 | U2-U1>0.1 U1-U2>0.1 0≤|U1-U2|≤0.1 |
| 严重失调 | 0<D≤0.30 | 严重失调—乡村振兴发展滞后 严重失调—新型城镇化发展滞后 严重失调 | U2-U1>0.1 U1-U2>0.1 0≤|U1-U2|≤0.1 |
2.3.3 探索性时空数据分析
将时间维度和空间维度有效整合在传统探索性空间分析框架中,实现时空交互联动分析,可以更好地弥补探索性空间数据分析在时间维度测量的不足[33]。运用探索性时空数据分析描述甘肃省县域单元乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度的时空结构特征,进一步系统分析研究期内时序行为的空间结构、分布、模式的时间演化特征。
(1)LISA时间路径
式中:N表示研究单元数(个);T表示研究期时间间隔;Li,t为i研究单元t年份在Moran's I散点图中的位置;d(Li,t, Li,t+1) 为第t年到第t+1年i研究单元移动距离。li>1则表示i研究单元乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度呈现动态局部空间结构,反之亦然;φi>1则表示研究单元乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度局部空间依赖变化过程更具波动性,反之亦然;θi为i研究单元研究期内年际平均移动方向,同时将其分为四类:0~90°和180°~270°分别表示研究单元自身及周边耦合协调度具有高增长趋势和低增长趋势;90°~180°或270°~360°则表示研究单元耦合协调度呈现低或高的增长趋势,而相邻单元则保持高或低的增长趋势。
(2)LISA时空跃迁
LISA时空跃迁可以揭示不同局部空间中邻域间的空间关系,常用于测度不同时间段各研究单元间Local Moran's I散点图局部空间关联类型的演化过程和转移情况[37]。将LISA时空跃迁类型划分为四种类型:即Type 0,Type Ⅰ,Type Ⅱ和Type Ⅲ。Type Ⅰ表示仅县域单元自身发生跃迁,跃迁类型包括HHt➝LHt+1、LHt➝HHt+1、HLt➝LLt+1、LLt➝HLt+1四种;Type Ⅱ表示仅邻近县域单元发生跃迁,跃迁类型包括HHt➝HLt+1、LHt➝LLt+1、HLt➝HHt+1、LLt➝LHt+1四种;Type Ⅲ表示县域单元自身及邻近县域单元均发生了跃迁,跃迁类型分为跃迁方向一致型(HHt➝LLt+1、LLt➝HHt+1)和跃迁方向相反型(LHt➝HLt+1、HLt➝LHt+1)。Type 0型即县域单元自身与相邻县域单元之间未发生空间关联形态的转移,所有县域单元均保持原有状态仍处于同一象限,没有发生跃迁,即Local Moran's I散点图概率转移矩阵的对角线类型。采用时空凝聚来揭示甘肃省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度的空间稳定性,公式为:
式中:Lt表示在时间段内Type 0类型的跃迁总数(个);m为所有可能存在发生跃迁的单元数(个)。SC值在0~1之间,值越大,说明县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度空间稳定性越强。
2.3.4 地理加权回归模型
地理加权回归模型是基于研究样点地理空间位置的局部分析方法,将局部范围内的解释变量与因变量进行合并,可得到单个样点各个解释变量的回归系数[38],故采用地理加权回归模型进行县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度影响因素探讨。为更有效处理研究区内各研究数据间的空间异质性和空间依赖性问题,采用最小二乘法构建GWR模型:
式中:yi表示第i个县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化的耦合协调度;xij表示在第i个县域的第j个解释变量的值;(ui, vi) 分别表示i县域的经纬度坐标;β0(ui, vi) 表示第i个县域统计回归的常数值;βj(ui, vi) 表示第i个县域上的第j个解释变量的回归系数值;k为解释变量的个数(个);αi为i县域的误差。
由地理学第一定律可知空间地理位置越近的地理要素之间联系越紧密,地理加权回归模型的参数估计值根据加权最小二乘法将与位置邻近的局部区域加权求得,公式如下:
式中:X表示解释变量的矩阵;W(ui, vi) 表示i县域的空间权重矩阵,采用高斯距离权重计算法计算矩阵权重,如下:
式中:dig表示i县域和g县域之间的距离;b表示带宽,通过最小化CV值计算b的最优值。
2.4 数据来源
研究时段为2013—2019年,所需数据主要来源于:《中国县域统计年鉴》《中国县城建设统计年鉴》等国家级统计年鉴、《甘肃统计年鉴》《甘肃农村年鉴》等省级统计年鉴、《定西统计年鉴》《庆阳统计年鉴》等地级统计年鉴、《皋兰年鉴》《康乐年鉴》等县级统计年鉴及甘肃省各地级市国民经济与社会发展统计公报,部分数据在甘肃省相关单位官方网站依申请公开获得。
3 结果分析
3.1 乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展评价
3.1.1 乡村振兴发展水平
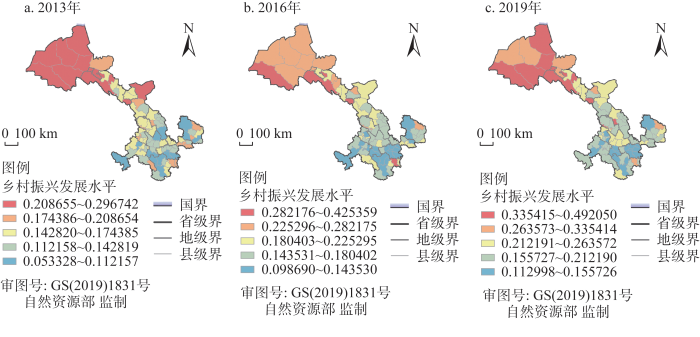
乡村振兴发展水平在空间上存在显著差异,呈现出“西北高、东南低”的发展态势。以各年份全部县域乡村振兴指数平均值反映研究区域整体情况,发现2013—2019年全省乡村振兴指数由2013年的0.157增长到2019年的0.221,各县域整体均呈现增长态势但增幅较慢,说明全省乡村振兴发展水平相对较为迟滞,总体效果欠佳。从综合得分看最高县域与最低县域差距较大,2019年相较2013年差距拉大0.136,说明随着时间的变化县域乡村振兴发展差距变大。河西地区乡村振兴指数为全省最高,其次是陇中地区,陇东南地区则处于末位。值得注意的是,对于陇东南狭长地形来说,区域乡村振兴发展存在较大差异,甘南及陇南地区乡村振兴水平明显低于相近的平凉及天水地区。县域乡村振兴综合得分排名较前的县域集中在河西地区,排名较后的县域大部分集中在陇东南地区的陇南与甘南两地(图4)。可见,乡村振兴发展水平较高的县域往往集中在城镇化率较高的地区,乡村振兴水平发展水平较低的县域往往受地形区位和交通设施条件影响显著,陇南及甘南地区农村社会经济发展相对缓慢,自然区位、交通条件等因素进一步限制区域高质量发展,导致乡村振兴发展难度较大。
图4
图4
县域乡村振兴发展水平空间分异
Fig. 4
The spatial differentiation of the development level of rural revitalization at county level
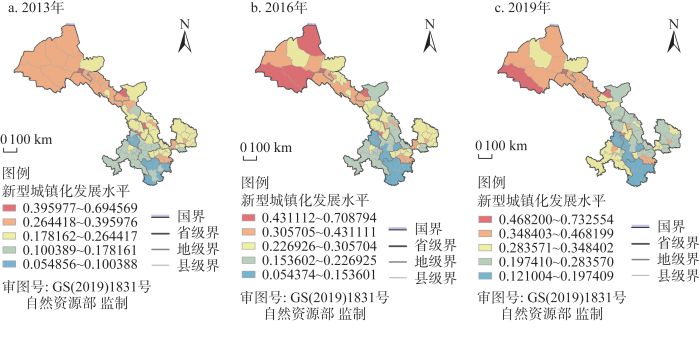
3.1.2 新型城镇化发展水平
新型城镇化发展水平在空间分布上差异较大,呈现出“西北高、东南低”的发展特征,其空间分布特征基本与乡村振兴空间发展特征一致。以各年份全部县域新型城镇化指数平均值来反映研究区域整体情况,发现2013—2019年全省新型城镇化指数由2013年的0.223增长到2019年的0.297,新型城镇化指数得到一定程度的增长,但仍可看出全省大部分县域新型城镇化发展增速相对缓慢。从综合得分来看,2013年发展指数最高的县域和最低的县域相差0.146,而2019年差值则拉大为0.611,新型城镇化发展差距逐渐拉大。河西地区新型城镇化指数在研究期内处于全省第一,陇东南地区新型城镇化水平则处于全省末位。综合得分排名较前的县域分布在兰州市主城区及嘉峪关市、酒泉市、金川区及白银区等地,这部分县城城镇化率较高且均处于全省前列,经济社会发展水平较高,县城城镇化建设水平相对较高。排名末尾的县域集中在临夏及陇南部分地区。由图5可知,陇东南新型城镇化水平内部差异较大,尤其是陇南及甘南等地,仅有个别城市发展水平较高,且主要为地级市驻地,说明这部分城市在城镇化过程中辐射带动作用还需进一步加强。
图5
图5
县域新型城镇化发展水平空间分异
Fig. 5
The spatial differentiation of the development level of new urbanization at county level
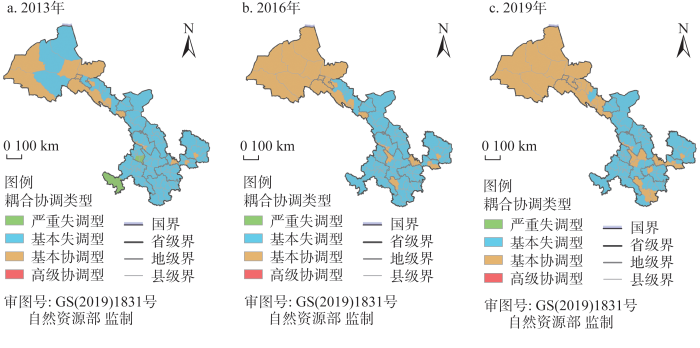
3.2 乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展分析
以全部县域耦合协调度平均值来反映研究区整体协调发展状况,发现耦合协调度由2013年的0.421增长到2016年的0.454再到2019年的0.497,协调发展程度整体呈现良性发展态势(图6)。研究期内全省县域耦合协调类型绝大部分处于基本失调状态。2013年全省耦合协调度处于严重失调状态的县域有4个,占比4.65%;2019年则不存在处于严重失调状态的县域,也印证了研究期内全省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化均得到积极发展。2013年全省耦合协调度处于基本协调状态的县域有14个,2019年增加至27个,分布在兰州市主城区、嘉峪关、酒泉及定西和平凉部分县域,而这部分县域主要为各地级市驻地城市及县域城镇化水平较高地区。2013年全省高于平均协调度的县域为41个,2019年则变为32个,说明县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展差距加大,整体发展水平仍较低,两者协同发展、协同演化水平也还需进一步加深。对全省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调类型进行划分,发现各县域亚分类划分存在异质性,2013年全省63个县域单元乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展速度基本保持一致,2019年则减少为53个县域。在基本失调类型和基本协调类型中乡村振兴滞后型均占大多数。甘南及陇南地区乡村振兴与新型城镇化两者失调程度相对较严重,且处于乡村振兴发展滞后型。总的来看,全省不存在新型城镇化发展滞后型,即说明甘肃省在社会发展过程中乡村发展缓慢且低于新型城镇化发展速度,乡村发展应尽快调整发展路径与发展策略,加快发展速度与新型城镇化协同高质量并行发展。
图6
图6
县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展类型
Fig. 6
Classification of coupling coordination degree of rural revitalization and new urbanization at county level
3.3 乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度空间演化格局
采用GeoDa计算研究期内县域耦合协调度的Moran's I来刻画两者耦合协调度的空间集聚特征,计算得到莫兰指数由2013年的0.113增长到2019年的0.161,Moran's I值均为正值且通过显著性检验,表明研究期内全省县域耦合协调度呈现显著的正相关关系。
3.3.1 LISA时间路径的空间特征
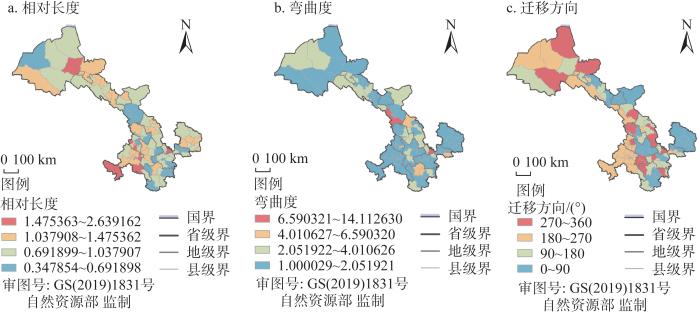
运用ArcGIS自然断点法将全省县域耦合协调度的LISA时间路径相对长度与弯曲度断裂划分为四个等级(图7),将LISA时间路径相对长度划分为:低相对长度、较低相对长度、较高相对长度和高相对长度。同理,将LISA时间路径弯曲度划分为:低弯曲度、较低弯曲度、较高弯曲度和高弯曲度。
图7
LISA时间路径相对长度能够体现出甘肃省县域各个单元乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度的局部空间结构动态性。研究期内全省LISA时间路径低相对长度的县域单元有19个,占总数的22.09%;较低相对长度的县域单元有35个,占总数的40.70%。低相对长度和较低相对长度县域单元占总数的62.79%,表明全省乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度空间格局具有一定的平稳性。甘南州玛曲县、迭部县及临潭县和玉门市、庄浪县、积石山县的LISA时间路径相对长度较大,说明这些城市近年来城镇化发展水平呈先慢后快的发展趋势,导致乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度动态变化相对较为明显。陇南部分县域及武威市LISA时间路径相对长度较小,说明这部分城市耦合协调发展关系的空间格局相对较为稳定。
LISA时间路径弯曲度能够反映出甘肃省各县域单元乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度局部空间依赖和增长过程的波动性。县域LISA时间路径弯曲度均大于1,移动路径呈现出非线性变化,说明全省各县域耦合协调度具有迁移变化特征,局部空间依赖方向更具有波动性特征。LISA时间路径低弯曲度的县域单元有57个,占总数的66.28%;较低弯曲度的县域单元有21个,占总数的24.42%。低弯曲度和较低弯曲度的县域单元占比达到90.70%,表明全省县域耦合协调度在局部空间依赖方向和空间增长过程中具有波动性较弱特征,但同时又可看到各县域自身耦合协调度受相邻县域的溢出效应影响程度较小。从LISA时间路径弯曲度空间分布格局来看,全省县域城镇化水平较高的地区,尤其各市驻地城市,弯曲度变化均不显著。庄浪县和天祝县LISA时间路径弯曲度变化最大,表明这两地耦合协调度在空间依赖上波动较强,可能的原因在于这两地城镇及乡村发展受周边发展较好城市社会经济发展影响较大。总体来看,全省县域耦合协调度LISA时间路径低弯曲度分布范围广占比大,耦合协调度空间格局相对较稳定,受周边邻近城市溢出效应或虹吸效应相对较弱。
3.3.2 LISA时间路径的迁移方向
LISA时间路径迁移方向能够反映出甘肃省县域各单元乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度发展的局部空间格局演变的整合性。研究期内全省县域耦合协调的LISA时间路径迁移方向呈现出协同增长的县域有52个,占全部城市的60.47%,表明甘肃省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展空间格局演化具有较强空间整合性,即县域单元及相邻县域耦合协调度整体呈现出的高增长或低增长趋势较为明显。其中,全省正向协同发展的县域有30个,占协同增长城市单元的57.69%,主要分布在庆阳市、金昌市与张掖市、定西市和陇南部分县域,与邻近县域城市表现出正向协同增长的跃迁方式。负向协同发展的县域有22个,占协同增长城市单元的42.31%,主要分布在甘南州及酒泉市和临夏州部分县域,与相邻县域表现出负向协同增长的跃迁方向,而其他县域单元都与其临近县域城市的跃迁方向相反。
3.3.3 LISA时空跃迁分析
前文中所采用的LISA时间路径分析方法可以揭示甘肃省各县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度LISA坐标变化的大小及趋势,但无法反映在莫兰指数散点图中局部空间发生关联类型相互转移情况。LISA时空跃迁则能够反映出甘肃省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调的莫兰指数散点图中坐标变化的时空演变格局,从而进一步刻画出甘肃省不同县域单元乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度的局部空间结构概率转移特征。由表3知,在Local Moran's I散点图的转移概率矩阵中,对角线元素跃迁概率远大于非对角线元素,表明甘肃省各县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度的局部空间关联格局保持在一定的稳定态势。具体来看,Moran's I散点保持在同一象限内的概率为83.91%,即Moran's I散点图的时空凝聚为0.839,说明研究期内全省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度的LISA并没有发生显著的时空跃迁,即空间关联格局保持一定的稳定态势。2013—2019年县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度进行了四种类型转移跃迁,其时空跃迁发生的概率大小排列为Type 0型>Type Ⅱ型>Type Ⅰ型>Type III型,即未发生空间关联形态转移的Type 0型是最普遍的跃迁类型。Type Ⅰ型中LHt➝HHt+1转移跃迁概率最大,概率为13.8%;Type Ⅱ型中HLt➝HHt+1转移跃迁概率最大,概率为12.5%;这揭示出甘肃省县域耦合协调度表现为由低向高的转移跃迁态势,也表明甘肃省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调正在朝着积极方向发展。Type III型中HLt➝LHt+1转移跃迁概率最大,概率为3.1%,表明研究期内甘肃省县域耦合协调度也部分存在由低向高与由高向低并存的跃迁态势。以上分析反映出全省多数县域未发生时空跃迁,乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度空间格局呈现出一定的转移惰性与路径依赖特征。
表3 Local Moran's I散点图的转移概率矩阵
Table 3
| t\t+1 | HH | LH | LL | HL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HH | Type 0(0.909) | Type I(0.023) | Type III(0.000) | Type II(0.068) |
| LH | Type I(0.138) | Type 0(0.828) | Type II(0.034) | Type III(0.000) |
| LL | Type III(0.014) | Type II(0.116) | Type 0(0.797) | Type I(0.073) |
| HL | Type II(0.125) | Type III(0.031) | Type I(0.063) | Type 0(0.781) |
3.4 乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调空间集聚类型
县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度的空间依赖性随着时间的变化而发生变化,主要是通过空间极化类型与空间均衡类型之间的转化,从而在空间上呈现出不同的集聚态势。通过对比各县域LISA时间路径移动特征,并结合空间结构局部关系类型,甘肃省县域耦合协调度空间集聚过程大致可分为稳定型(LL➝LL、HH➝HH、LH➝LH、HL➝HL)、极化➝均衡型(HL➝LL、LH➝LL、HL➝HH、LH➝HH)、均衡➝极化型(LL➝HL、LL➝LH、HH➝HL、HH➝LH)、同步均衡性型(LL➝HH)四种状态(表4)。县域耦合协调度空间集聚稳定型的共有65个,占比达到75.58%,说明全省县域耦合协调度整体上表现为稳定的空间结构特征。极化➝均衡型县域单元有6个,占总数的6.98%,其中静宁县(HL➝HH)、西峰区(HL➝HH)、安定区(HL➝HH)、永登县(LH➝HH)、泾川县(LH➝HH)由极化到高水平均衡演化,表明静宁、西峰等五地与周边县域单元的发展协调度不断提升;而卓尼县(HL➝LL)则由极化向低水平均衡演化,即说明卓尼县耦合协调度发展还存在欠缺,未来需要进一步注重乡村与城镇同步迈向高水平协调均衡发展。均衡➝极化型县域单元有12个,占总数的13.95%,其中宕昌县(HH➝HL)、榆中县(HH➝LH)、迭部县(HH➝LH)由高水平均衡状态转向极化发展状态,而其他地区则由低水平均衡状态转向极化发展状态。同步均衡型县域单元有3个,即陇西县、宁县和庆城县,演化类型均为LL➝HH,可以发现这三个城市均由低水平均衡发展迈向高水平均衡发展,也反映出这些城市近年来注重乡村振兴与城镇化协同发展,坚持乡村振兴和新型城镇化双轮驱动,双轨并行。
表4 县域单元空间集聚演化类型
Table 4
| 演化状态 | 演化类型 | 县域单元 |
|---|---|---|
| 稳定型 | LL➝LL、HH➝HH、LH➝LH、HL➝HL | 白银区、靖远县、景泰县、秦州区、麦积区、清水县、凉州区、民勤县、古浪县、通渭县、西和县、徽县、两当县、临夏市、临夏县、康乐县、广河县、和政县、东乡县、积石山县、合作市、临潭县、玛曲县、碌曲县、夏河县、红古区、嘉峪关市、肃南县、民乐县、临泽县、高台县、山丹县、灵台县、崇信县、华亭市、肃州区、金塔县、瓜州县、肃北县、阿克塞县、玉门市、敦煌市、康县、永昌县、会宁县、天祝县、甘州区、崆峒区、合水县、镇原县、文县、礼县、永靖县、舟曲县、城关区、七里河区、西固区、皋兰县、金川区、平川区、甘谷县、庄浪县、渭源县、临洮县、武都区 |
| 极化➝均衡型 | HL➝LL、LH➝LL、HL➝HH、LH➝HH | 卓尼县、静宁县、西峰区、安定区、永登县、泾川县 |
| 均衡➝极化型 | LL➝HL、LL➝LH、HH➝HL、HH➝LH | 环县、漳县、岷县、成县、秦安县、武山县、张家川县、华池县、正宁县、宕昌县、榆中县、迭部县 |
| 同步均衡型 | LL➝HH | 陇西县、宁县、庆城县 |
3.5 乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度影响因素
3.5.1 驱动因素及变量选取
乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调受多种因素影响,为清楚阐述甘肃省县域耦合协调发展影响因素,首先以2019年的截面数据减去2013年对应的指标值,对新得到的数据进行标准化处理,将驱动因素的变化值作为解释变量,将耦合协调度变化值作为被解释变量,探究影响两者耦合协调发展的影响因素。(1)城乡收入差距。缩小城乡收入差距能调动农民生产生活积极性,有助于城乡要素畅通流动,进而推动区域城乡协调发展与共同富裕。城乡收入差距过高不利于社会经济稳定发展,制约区域乡村振兴系统和新型城镇化系统发展进程,不利于两者耦合协调发展。选取城乡居民人均可支配收入比表征城乡收入差距。(2)城乡消费差距。消费和收入呈正相关关系的经济学基本原理说明消费需求随着收入的增长而增加,缩小城乡消费差距可以避免城市居民与乡村居民消费断层,以免导致高档消费与低档消费难以衔接。另外,城乡居民收入差距加大也意味着城乡居民消费结构存在差异,与城乡协调发展要求相悖,不利于乡村与城镇高质高效协同发展。选取城乡居民人均消费比表征城乡消费差距。(3)产业二元性水平。产业二元性在一定程度上能反映地区二三产业与传统农业发展差异程度,低产业二元性会为地区国民经济发展积累资金,反过来支援和促进农村传统农业发展,同时也推动和吸引农村传统产业的创新与改造,缩小乡村与城镇发展差距。高产业二元性会拉大二三产与一产发展差距,难以实现城乡统筹发展,影响区域整体经济健康发展与可持续发展进程,进而影响乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展。选取(第二、三产业产值/二三产业就业人员数)/(第一产业产值/第一产业就业人员数)表征产业二元性水平。(4)经济发展水平。经济发展是区域城乡协调发展的有效推动力,对乡村与城市子系统产生重要影响。一般来讲,区域经济发展水平越高,对区域乡村与城镇协调发展也就具有更高程度的重视与要求,即会促进区域城乡协调发展水平提高和质量提升。选取国内生产总值表征经济发展水平。(5)政府调控水平。政府调控能够弥补区域经济市场及实体经济的不足,适度政府调控对区域经济社会文化发展具有显著正向影响,政府能够通过财政倾斜、鼓励创新、制定发展战略与规划等手段对城乡发展要素进行合理调配,以促进乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展程度。但需要指出,政府调控是一把双刃剑,过度调控也会不利于区域经济社会发展,甚至会加剧地区经济社会发展下行速度[39],进一步影响或加剧区域城市与乡村发展差距,不利于两者协调发展。财政支出被认为是政府干预的主要手段[40],选取公共财政支出占GDP比例表征政府调控水平。通过构建OLS线性回归模型研究自变量对因变量的影响程度与显著性水平,各变量VIF最大值小于3,即各变量之间不存在多重共线性问题。又考虑到OLS模型只能研究全局回归系数的局限性,故进一步构建GWR模型分析县域耦合协调度影响因素的局部效应。从对比结果看,OLS模型调整后的R2为0.498,GWR模型调整后的R2为0.552,GWR模型拟合优度明显高于OLS模型,即使用GWR模型能够更好地解释乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调影响因素。
3.5.2 GWR模型结果分析
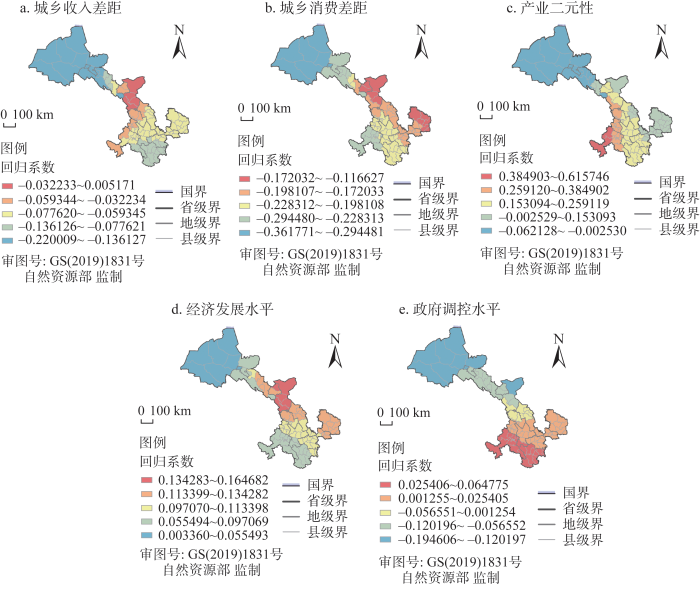
基于GWR模型的五个自变量回归系数在地理空间的分布情况可以更好地刻画自变量因素对耦合协调度影响程度的空间差异。由图8可知,县域耦合协调度的影响因素在空间上差异较大,总体上呈块状分布发展态势。城乡收入差距、城乡消费差距、产业二元性水平影响力系数为负,经济发展水平、政府调控水平影响力系数为正。
图8
图8
县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度影响因素
Fig. 8
Influencing factors of coupling coordination degree between rural revitalization and new urbanization at county level
城乡收入差距对耦合协调度影响的空间分布特征表现为中间高两头低。城乡收入差距的回归系数为负,说明城乡收入差距对耦合协调度的提升呈负相关关系,城乡收入差距增大不利于耦合协调度的提升。回归系数低值区位于河西地区,高值区位于兰州、白银、武威、金昌等地,这部分地区受城乡收入差距变化影响较大,其主要原因在于兰白都市圈、金武城镇圈近年来经济社会发展形势较好,其发展过程中难免会出现注重城镇而忽视乡村的发展方式,出现城市不断开发扩张、农村人口不断向城镇转移、农业占比不断下降、农村发展相对萎缩等现象,进一步造成城乡居民收入差距加大,从而影响乡村与城镇耦合协调发展。城乡消费差距的回归系数为负,说明城乡消费差距对耦合协调度具有负相关性。回归系数最大的是民勤县,最小的是敦煌市。回归系数高值区主要分布在金昌、武威、白银及陇东地区,低值区分布在酒泉、甘南及张掖部分县域,空间布局整体呈现出西低东高的发展特征。城乡消费差距增大影响区域经济发展水平,制约乡村与城镇发展进程,使得区域协调发展受到一定程度的阻碍。产业二元性水平对耦合协调度的回归系数为有正有负,说明产业二元性对耦合协调度的影响具有不确定性。回归系数最大的是玛曲县,最小的是金塔县,回归系数正值区主要分布在甘南地区及临夏部分县域,与耦合协调度呈正相关关系,而其余城市产业二元性回归系数均为负值,说明产业二元性的提高对耦合协调度的影响不显著,亦或可能导致耦合协调度水平下降。河西地区酒泉市、嘉峪关、张掖市等地及庆阳市耦合协调的回归系数为负值,产业二元性水平加大会使乡村与城镇产业发展差距加大,不利于耦合协调度的提升。这部分城市主要是能源工业型城市,可能在发展路径上存在依赖,从而导致其城乡协调发展中无法进行产业创新或产业更新以带动乡村发展,因而在耦合协调度提升方面不能单纯考虑产业二元性水平的影响。经济发展水平对耦合协调度的回归系数为正,说明经济发展水平对耦合协调度存在正相关关系,即经济发展水平的提升在一定程度上会提高耦合协调度。回归系数最大的是民勤县,最小的是瓜州县,回归系数高值区主要分布在河西地区武威、金昌、张掖部分县域及庆阳、白银等地,低值区主要分布在甘南、陇南、酒泉、嘉峪关等地,经济发展水平对耦合协调度提升的拉动作用受限,应从根本上考虑更加综合性的提升手段。政府调控水平对耦合协调度的回归系数有正有负,说明适度政府调控水平将有利于部分地区耦合协调度提升,过度政府调控也可能会在一定程度上阻碍乡村与城镇耦合协调发展,造成区域发展失调。回归系数最大的县域是玛曲县,最小的是敦煌市,回归系数低值区主要位于酒泉、嘉峪关及张掖,表明这些地区政府调控程度对耦合协调度的带动作用有限,同时需注重度的把握。地方政府财政支农程度在一定程度上影响着当地乡村发展水平与进程,进而影响乡村振兴与新型城镇化的协调发展。
4 结论与讨论
4.1 主要结论
(1)县域乡村振兴水平与新型城镇化水平在空间上差异显著,但均呈现“西北高、东南低”的发展态势。河西地区乡村振兴指数最高,陇南、甘南乡村振兴指数处于全省末位。指数得分最高与最低县域差距明显,乡村振兴发展水平优劣不等,层级分异较为明显。河西地区新型城镇化水平处于全省前列,陇南地区及甘南高原新型城镇化水平处于中等偏下水平。全省各县域亚分类划分存在异质性,在基本失调类型和基本协调类型中乡村振兴滞后型占大多数,全省不存在新型城镇化发展滞后型。河西地区乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度处于全省第一,陇中地区与陇东南地区耦合协调度相对较低。
(2)研究期内县域耦合协调度的空间格局具有一定的平稳性,在局部空间依赖方向和空间增长过程中具有波动性较弱特征,受周边邻近城市溢出效应或虹吸效应相对较弱。县域自身耦合协调度受相邻县域的溢出效应影响程度较小,整体呈现出的高增长或低增长趋势较为明显。耦合协调度的局部空间关联格局保持在一定的稳定态势,多数县域未发生跃迁,空间格局呈现出一定的转移惰性与路径依赖特征。
(3)甘肃省县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度的影响因素在空间上差异较大,总体上呈现块状分布发展态势。城乡收入差距、城乡消费差距、产业二元性水平影响系数为负,经济发展水平、政府调控水平影响力系数为正。推进县域乡村振兴战略有效实施和新型城镇化稳步建设,需倡导内涵式集约型发展模式,全省各县域结合自身资源禀赋与发展优势,制定极具地域特色的发展规划。
4.2 讨论
开展欠发达地区县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调研究可为区域高质量协同发展提供决策支撑和理论参考,对面临乡村发展滞后、乡村发展动力不足的西北地区统筹城乡协同发展方面具有重要指导意义。甘肃省乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展水平相对较低,乡村发展创新动力不足、部分地区建设难度大、任务艰巨,新型城镇化快于乡村振兴但仍处于全国末位,加之近年来经济社会发展缓慢、基础设施配置不均、创新发展后劲不足等原因,全省城乡发展不均衡,乡村振兴与新型城镇化协调发展难度加大。未来需要更加重视乡村与城镇协同发展,一方面继续加强新型城镇化发展质量,更加突出以人为核心的城镇化,以现代化城市群和都市圈发展带动周边县域经济快速发展,以县域发展引领乡村高质量发展。另一方面着力提升乡村振兴发展水平,进一步提高农业农村创新发展现代化水平,加大财政支农倾向,以县域经济发展吸引乡村剩余劳动力撬动乡村经济发展。河西地区未来应持续推动乡村振兴与新型城镇化良性耦合协调发展,夯实区域发展生态基底,推动现代丝路寒旱农业智能化、机械化、设施化发展,持续推进以人为本、注重质量的城镇化建设,着力构建河西地区城乡协同发展新样板。陇中地区需持续改善区域发展生态基底,打造“两山”理念实践典范,建设人与自然和谐共生发展新模式。注重发挥中心城市对周边乡镇发展的辐射带动作用,促进经济发展及政府宏观调控对区域城乡协同发展的拉动作用。陇南地区及甘南高原需要进一步加大地方政府财政支农倾向以强化政府调控能力,提升政府在推进乡村振兴与促进新型城镇化发展进程中优化调控、合理引导两者协调高质高效发展能力。进一步强化乡村地区基础设施建设,尤其需提升乡村基层组织、教育服务水平,补齐乡村在产业发展、基础设施、公共服务等方面的发展短板。
总体来讲,乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展研究仍然任重道远,对二者协调发展路径、机制还需进一步探索。乡村振兴与新型城镇化发展内涵宽泛,是涉及多要素之间的复杂地域系统,同时乡村振兴与新型城镇化具有共生效应,涉及自然、经济、人文、历史等多方面,两者间如何进行良性耦合和协同发展目前仍处于摸索阶段。面向中国式现代化城乡融合发展,未来既需要在顶层设计上厘清两者协调发展逻辑思路,也需要注重省市县乡村五级政府政策衔接与具体实施,将理论与实际相结合。县域乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调发展需要更多地考虑如何以县域为载体构建新型工农城乡关系,破解城乡二元经济结构,实现城乡要素逐步协同融合发展。下一步研究中还需优化评价指标体系,实地调研并结合大数据平台获取更加详细的研究数据,以期更深层次地揭示二者耦合协调发展驱动因素及关联机制,为甘肃省乡村振兴战略与新型城镇化战略协同并进发展提供重要参考意义。
参考文献
新中国70年乡村发展与城镇化的政策演变及其态势
Evolving relationship between rural development and urbanization in China since 1949
新时代乡村振兴与新型城镇化融合发展的理论依据与实现路径
The theoretical basis and realization path of the combination of rural revitalization and new type of urbanization in the New Era
China's urban-rural relationship: Evolution and prospects
DOI:10.1108/CAER-02-2018-0038
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In the 69 years since the founding of the People’s Republic of China, especially the 40 years since the reform and opening-up, the relationship between urban and rural areas has undergone profound change. When the deepening reform of the urban-rural relationship is entering a critical period, it is necessary to reassess the evolution of the urban-rural relationship in China and draw a picture for that relationship in the future. The paper aims to discuss these issues.
乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调的动态演进及其驱动机制
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200902
[本文引用: 4]

重构乡村振兴与新型城镇化的指标体系,采用耦合协调度模型、空间马尔可夫链以及地理加权回归模型,分析了2005—2017年中国30个省(市、自治区)乡村振兴与新型城镇化的耦合协调水平、时空分异格局、空间动态演进以及驱动机制。研究发现:(1)乡村振兴与新型城镇化的耦合协调度呈现“东部高、西南低”的分布特征,中级协调区域逐步向中部扩散,高级协调区域数量不断增加;高级协调类型省(市、自治区)中“乡村振兴滞后型”占大多数,初级协调和濒临失调类型省(市、自治区)中“新型城镇化发展滞后型”居多。(2)耦合协调度的动态演进呈现维持原有状态稳定性的特征,较难实现跨越式转移,处于高级协调阶段的省(市、自治区)存在“俱乐部趋同”现象。向上转移的省(市、自治区)主要集中在中部,向下调整的以北方省(市、自治区)居多;耦合协调较高的省(市、自治区)对邻近省(市、自治区)具有正向溢出效应,而耦合协调度低的省(市、自治区)对周围产生负向效应,且这种影响是不对称的。(3)影响乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调度变化的驱动力空间差异显著,表现出层级带状分布的发展态势。政府驱动、投资驱动、人口驱动呈现南北层级带状分布。消费驱动、收入驱动、产业驱动呈现东西层级带状分布。
The dynamic evolution and its driving mechanism of coordination of rural rejuvenation and new urbanization
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200902 URL [本文引用: 4]
城乡关系研究进展及其对乡村振兴的启示
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180880
[本文引用: 1]

随着乡村振兴战略的实施,我国已经进入城乡关系变革及乡村发展快速转型的关键时期。科学认知国内外城乡关系理论发展和演变规律对实施乡村振兴战略、缩小城乡差距、调整城乡结构和优化城乡格局具有重要意义。本文在系统梳理国外城乡关系理论及我国乡村发展与城乡关系演进的阶段性特征的基础上,从经济、社会、生态及文化的视角阐述了我国乡村发展与城乡关系研究的相关进展,并在此基础上探讨了未来重点的研究领域和方向。乡村发展思维应由生产主义导向转向后生产主义,关注乡村多元价值,深化基于乡村多功能转型理论的乡村振兴机制、区域路径与模式研究;在科技迅速发展,新事物新因素大量涌现的新时代,应关注特色小镇、田园综合体、民宿及乡村电子商务等新兴乡村转型发展形态的形成机制;同时,基于不同地域类型的乡村振兴的机制与模式研究也应得到重视,结合国际乡村地理学前沿,深入开展发达地区乡村的混杂性研究。广泛的城乡空间重构进程对乡村地区产生剧烈的影响与挑战,对于乡村振兴视角下城乡空间重构的动力机制与模式的研究仍需持续关注;根据我国的特殊国情,创新适合我国基本国情与发展实际的乡村振兴理论与实现路径,推动城乡融合发展。
Research progress of urban-rural relations and its implications for rural revitalization
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180880
[本文引用: 1]

With the implementation of rural vitalization strategy, China has stepped into a critical period with the dramatic changes of urban-rural relations and the accelerating transformation development of rural territorial system. Scientifically understanding the research progress of urban-rural relation theory and evolution rule is of great significance for boosting rural vitalization, narrowing urban-rural disparity, adjusting urban-rural structure and optimizing urban-rural patterns. This paper elaborates the research progress of urban-rural relations and rural development in China from the dimensions of economy, society, ecology and culture based on the review of foreign urban-rural relations and the characteristics of domestic rural development, as well as the evolution of urban-rural relation. Furthermore, prospect of research focus or key fields in the future were given. Firstly, transforming the development idea from productivism oriented to post-productivism oriented and attaching importance to the multiple values of rural areas should be emphasized. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out intensive studies about the mechanism, regional path selection and development mode of rural vitalization based on the theory of rural multiple function transition. Understanding the relationship of different functions is essential for dealing with rural decline and realizing the comprehensive vitalization. Meanwhile, we should focus on the mechanism and format of rural vitalization based on different territorial types. Against the context of rural-urban integrated development, we should promote the supply-side reform and activate the forces of socio-economic growth in underdeveloped areas. As for the developed rural areas, the “hybridity” should be emphasized and further studies should be conducted. In some rural areas, the phenomenon of the hybridity of development agents, the combination of production space and living space, the mixture of rurality and modernism have emerged. Accordingly, more emphasis should be placed on the heterogeneity and diversity in the process of rural restructuring. Secondly, with the emergence of new factors or new technologies, we should focus on the new morphology of rural development, such as characteristic towns, rural complex and “Taobao village”. In recent years, China's rural areas have undergone intensive restructuring motivated by e-commerce, which has triggered a new wave of rural rejuvenation. But how e-commerce affects rural development and the characteristics of this process are still unclear, and this is important for understanding the urban-rural relations under the context of informatization. Thirdly, the mechanism and format of urban-rural spatial restructuring should be emphasized. From the perspective of urban-rural interaction, the theory of urban-rural network may be practical and meaningful for optimizing the spatial distribution of infrastructure construction and industrial development. Lastly, creating or improving the theory and improving the path of rural vitalization according to the national conditions are meaningful for realizing the strategy.
乡村振兴背景下县域农业农村创新发展评价及空间格局: 以甘肃省为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220202
[本文引用: 1]

实施农业农村现代化创新发展措施,将有效促使乡村振兴战略长远推进,形成我国农业农村创新发展的新局面。基于甘肃省86个县域研究单元,从创新投入、创新保障、创新效果三个维度构建了包含28个二级指标的农业农村创新发展评价指标体系,就农村地区创新发展水平进行综合评价。结果表明:(1)甘肃省农业农村整体创新发展得分呈上升趋势,但增长幅度较为缓慢。综合创新能力得分较高的县(区)主要集中在河西地区东部,得分较低的县(区)主要集中在南部民族地区。河西地区创新保障和创新效果水平处于全省前列,南部民族地区创新投入水平较低。(2)全省农业农村创新发展在东西方向上表现为西高东低,2013年以后逐渐表现出“两头高、中间低”趋势;在南北方向上表现北高南低;在东南—西北方向上呈现出西北高、东南低;在西南—东北方向上呈现出东北高、西南低。创新发展指数方向特征未发生明显变化,在空间上具有一定的锁定性。(3)创新发展热点区域集中在河西地区张掖市、武威市及金昌市,冷点区域集中分布在南部民族地区;极冷点区和极热点区数量减少,县域农业农村创新发展差距在减小。(4)多元资本投入、农业经济发展、自然地理条件及资源禀赋、农业基础设施配置、农业发展政策等通过内外因素结合创新发展供需两侧作用于甘肃省农业农村创新发展时空演化。
The evaluation and spatial pattern of agricultural and rural innovation-driven development at county level in the context of rural revitalization: Take Gansu province as an example
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220202 URL [本文引用: 1]
以人为核心的新型城镇化的基本内涵、主要指标和政策框架
Basic connotation, main indicators, and policies framework of the human-oriented urbanization
城乡融合发展的科学内涵与实现路径: 基于马克思主义城乡关系理论的思考
The scientific connotation and realization path of urban and rural integration development: Thought based on the marxist theory of urban-rural relations
城乡融合发展: 西方理论局限与中国实践嵌入
Urban-rural integration development: Western theoretical limitations and Chinese practice embeddedness
国内外城乡统筹研究进展及其地理学视角
Domestic and foreign urban and rural research progress and perspective of geography
贫困地区加快实现城乡融合发展的优化路径
The optimal path to accelerate the realization of urban-rural integrated development in poverty-stricken areas
中国城乡关系演变历程、融合障碍与支持政策
The evolution of China's urban-rural relations, fusion obstacles and supporting policies
城乡融合与乡村振兴: 理论探讨、机理阐释与实现路径
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201811001
[本文引用: 1]

缩小城乡差距,促进城乡均衡发展,实现城乡居民生活质量等值,是乡村振兴和城乡融合发展的重要目标。通过基础理论的分析,探讨了城乡融合与乡村振兴科学内涵,剖析了城乡融合与乡村振兴的相互关系,构建了城乡空间均衡模型和定义城乡等值线,提出了中国城乡融合与乡村振兴实现途径及需要深入研究的方向。结果表明:① 城乡融合发展是基于空间布局优化和制度供给创新的经济、社会、环境全面融合发展,“乡村振兴五边形”和“人—地—钱—业”是乡村振兴的核心内涵;城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相互支撑,城乡融合和乡村振兴的过程是城乡空间动态均衡的过程。② 城乡发展的空间均衡模型可以较好地阐释促进城乡融合发展、实施乡村振兴的关键问题,通过城乡要素的重新优化配置和人口的流动,城乡人均综合发展效益逐渐趋于相等;城乡等值线可以进一步解释城乡发展空间均衡的动态过程与传导机理。③ 从政策制度构建、“点轴”渐进扩散、分区分类推进、典型发展模式提炼等方面探讨乡村振兴的科学路径,可以为中国乡村振兴战略实施提供理论参考。
Urban-rural integration and rural revitalization: Theory, mechanism and implementation
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201811001
[本文引用: 1]

Rural revitalization and urban-rural integration aim at narrowing the gap between urban and rural areas, promoting balanced development and realizing the equivalent life quality between urban and rural residents. Spatial equilibrium and its quantitative expression provide a new perspective to explain the pattern, process and mechanism of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. Through the analysis of basic theory, this study discusses the scientific content and interaction between urban-rural integration and rural revitalization, sets up the urban-rural spatial equilibrium model, defines the urban-rural development isolines, works out the way to implement the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China, and addresses the potential for further research. The results show that: (1) Theory of regional system of man-land relationship and theory of spatial structure are the important theoretical basis for urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. The urban-rural integrated development depends on the all-round development of economy, society and environment with optimized spatial layout and innovative system, and rural revitalization mainly refers to the "pentagon of rural revitalization" and "people-land-capital-industry"; Urban-rural integration and rural revitalization strategy support each other, and the process of urban rural integration and rural revitalization is a dynamic equilibrium process between urban and rural areas. (2) The key issues of implementing rural revitalization and urban-rural integration can be illustrated through the urban-rural spatial equilibrium model, and the overall per capita benefits in rural areas gradually tend to be the same as that in cities by the re-optimization of urban-rural factors and population mobility; the dynamic process and mechanism of urban-rural integration spatial equilibrium is further interpreted via the urban-rural development isolines. (3) Exploring the implementation path of scientific rural revitalization strategy can achieve the goal of urban-rural integration and urban-rural spatial equilibrium development. The scientific path of rural revitalization is discussed from the perspectives of policy system construction, "pole-axis" spatial progressive diffusion, sub-area classification and typical development pattern, and it can provide theoretical reference for the strategy implementation of China's rural revitalization.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 1]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the New Era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 1]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
数字技术和数字经济助力城乡融合发展的理论逻辑与实现路径
Theoretical logic and practical path of digital technology and digital economy to promote urban-rural integration development
从城乡一体化到城乡融合: 新型城乡关系的思考
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.10.006
[本文引用: 1]

新型城镇化和乡村振兴战略的深入实施,推动城乡关系进入了一个融合发展的新阶段。采用Citespace1.0软件分析及文献归纳方法,识别了城乡关系研究热点,梳理了城乡关系研究在理论探索、影响因素、测度与评价、空间组织及推进策略等方面的研究进展。在此基础上,重点对面向城乡融合发展的新型城乡关系研究进行了总结,从理论基础与总体思路、多源数据与方法集成等方面提出了基于要素流动的城乡融合分析框架,指出了城乡融合研究的重点是基于多源数据的城乡关系测度与评价,城乡要素流动的特征、格局与效应,城乡要素融合发展的流动机制,城乡融合发展调控策略等。
From town-country integration to urban-rural integration: New thinking on the relationship between urban and rural areas
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.10.006
[本文引用: 1]

The in-depth implementation of the new urbanization and rural revitalization strategy has pushed the urban-rural relationship into a new stage of integrated development. Based on Citespace1.0 software analysis and literature induction method, the paper identified the research hotspots of urban-rural relationship, reviewed the research progress of urban-rural relationship. Which included theoretical connotation and influencing factors of urban-rural relationship, measurement and evaluation of urban-rural connection, urban-rural spatial organization and development mode, and coordinated development of urban-rural areas and promotion strategy. Combining with the social economic background of information revolution and the change of urban-rural relationship in China, we points out that the construction of urban-rural relationship in the new period needs to change the traditional urban-rural relationship centered on the city, promote the integration of urban and rural areas and the formation of a new pattern of equal development between urban and rural areas. Based on this, we puts forward and discusses the construction and overall thought of a new urban-rural relationship toward urban-rural integration development. Then we proposes a framework for urban-rural integration analysis based on elements flow, puts forward the general idea of analyzing the characteristics, pattern and mechanism of urban-rural elements flow, which is supported by flow space theory and new mobility paradigm, multi-source data and visual analysis. The paper emphasizes the importance of measurement and evaluation of urban-rural relationship and the flow of urban-rural elements. The characteristics, pattern and mechanism of urban-rural factors flow, and the regulation and control strategy of the integration development of urban-rural areas are discussed in detail. The paper also explores the construction of the urban-rural integration database, the measurement of the flow of urban-rural elements and their spatial-temporal changes, and spatial simulation and visualization expression and other methods and techniques.
迈向城乡共治:改革开放以来城乡关系演变解读
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.05.014
[本文引用: 1]

城乡关系历来是经济社会发展的重要关系及党和政府关注的重大问题。为探究城乡关系及其治理逻辑,论文借助CiteSpace软件分析改革开放以来城乡关系的研究热点,结合时代背景解读城乡关系的演变历程,进而揭示城乡关系的脉络特征与治理变革的内在逻辑。研究表明:改革开放以来城乡关系的演变经历了4个阶段,形成了“城乡关系向好发展—城乡关系再度失衡—城乡关系调整完善—城乡关系一体化发展”的演变脉络;折射出“打破城乡分割”“偏向城市领域”“统筹城乡发展”“推进城乡一体化”的治理逻辑;十九大以来,城乡关系向着城乡融合的方向发展,迈向城乡共治是新时代城乡融合发展的内在要求与治理趋势。最后,文章从废除城乡二元体制、建立新的配套体制机制,打破学科界限、融合跨学科知识和实践交叉应用,新型城镇化和乡村振兴两大战略有机结合等方面对城乡融合发展与城乡共治进行了研究展望。
Toward rural-urban co-governance: An interpretation of the change of rural-urban relationship since the reform and opening up
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.05.014
[本文引用: 1]

The relationship between urban and rural areas in China has been an important relationship for economic and social development and a major concern of the party and the government. In order to explore the relationship between urban and rural areas and its governance logic, the CiteSpace software was used to analyze the research hotspots of rural-urban relationship since the reform and opening up in the 1970s and to interpret its change based on the historical background, and then reveal the contextual characteristics of rural-urban relationship and the internal logic of governance reform. The research shows that since the reform and opening up, rural-urban relationship has gone through four stages—from an improving urban-rural relationship, to rural-urban re-separation, rural-urban relationship adjustment, and integrated rural-urban development. The process reflects the governance logic of breaking the rural-urban division, favoring the urban field, balancing rural-urban development, and promoting rural-urban integration. Since the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, the relationship between urban and rural areas has developed in the direction of rural-urban integration. Rural-urban co-governance is the internal demand and governance trend of integrated rural-urban development in the new era. Finally, the article discussed the prospect of integrated rural-urban development and rural-urban co-governance from the aspects of abolishing the rural-urban dual system and establishing new supporting systems and mechanisms, breaking disciplinary boundaries and integrating interdisciplinary knowledge and cross-application of practice, and organically combining the two strategies of new urbanization and rural revitalization.
东北三省城乡协调发展格局及影响因素
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.08.012
[本文引用: 1]

以东北三省36个地区为研究对象,系统构建了城乡协调的指标体系,采用基尼系数、空间自相关和空间回归等方法探讨了2005年、2010年和2015年东北三省城乡协调的空间格局和影响机制。研究表明:① 东北三省城乡协调度的区域差异不断扩大且具有明显的空间集聚特征,但集聚程度趋于减弱。② 不同地区城乡协调水平变化各异。研究期内,大连市和锦州市一直处于高水平城乡协调状态,朝阳市长期处于低水平城乡协调状态。鹤岗市和七台河市城乡协调度位次上升最明显,哈尔滨市和辽源市城乡协调度位次下降最显著。③ 从空间格局来看,中级城乡协调区增多且向北移动,初级城乡协调区减少且向中部集中,“南北高,中间低”的城乡协调格局基本形成。与此同时,城乡协调的冷热点均不断收缩,空间极化效应趋于减弱。④ 城镇化和农业规模化经营是促进东北城乡协调发展的主要力量,工业化并未显著促进东北城乡协调发展且与城乡协调发展负相关,农业现代化经营对城乡协调发展有正向作用,交通因素在近些年的促进作用逐渐凸显,经济发展水平与信息化水平对东北城乡协调发展的作用还不明显。
Spatial pattern of urban-rural coordination development in Northeast China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.08.012
[本文引用: 1]

Coordinating urban-rural coordinated development is an important foundation for achieving economic sustainable development of region. This paper selects 36 prefecture-level units in Northeast China as samples and constructed systematic index system to evaluate the level of urban-rural coordinated development. Then, the paper uses Gini coefficient, spatial autocorrelation and spatial regression to research the spatial pattern and influence mechanism of urban-rural coordinated development in Northeast China in 2005, 2010 and 2015. The result shown that: 1) The regional difference of urban-rural coordination degree in Northeast China has shown an expanding trend, and the phenomenon of spatial agglomeration is obvious, but the intensity of spatial agglomeration is declining. 2) The level of urban-rural coordination varies diferent in different regions. During the study period, Dalian and Jinzhou have always been high level of urban-rural coordinated area, and Chaoyang has always been a low level of urban-rural coordinated area. Hegang and Qitaihe were the most obvious upward cities of urban-rural coordination order, while Harbin and Liaoyuan declined most significantly. 3) From the perspective of spatial pattern, intermediate urban-rural coordination areas increased and moved northward, while primary urban-rural coordination areas decreased and concentrated in the middle. Then, formed a "north-south high, middle low" urban-rural coordination pattern. At the same time, the cold and hot spots of urban-rural coordination are shrinking, and the spatial polarization effect tends to weaken. 4) Urbanization and large-scale agricultural management have a positive effect on urban-rural coordinated development, industrialization does not significantly promote the urban-rural coordination in northeast China and is negatively related to the urban-rural coordination, agricultural modernization plays a positive role in the urban-rural coordinated development. In recent years, transportation gradually plays an positive role in urban-rural coordinated development. Economic development level and informatization level in the urban-rural coordinated development in northeast China are not obvious.
Exploring the urban-rural development differences and influencing factors in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China
DOI:10.1007/s11442-020-1802-z
[本文引用: 1]

Uneven urban and rural development is one of the main reasons for the decline of the countryside. This imbalance could be measured by the urban-rural difference index (URDI). Existing studies on urban-rural differences have focused on single dimension between urban and rural areas, and lack a systematic multi-dimensional measurement. Based on the construction of an index system and model for measuring urban-rural differences, this study took the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain (HHHP) as the study area, explores the spatial pattern of urban-rural differences in the area, and used geographical weighted regression models to identify the factors affecting urban-rural development differences. Results show that the mean value of URDI in the HHHP was 0.295, and the URDI in its western region was higher than that in the east. The average URDI was relatively high in the western counties along the Beijing-Guangzhou Railway. The low level of urban-rural “population-land-industry” development in the HHHP is an important reason for the small differences between urban and rural areas. Improvements in road transportation infrastructure have led to an increase in the urban-rural development gap. However, the driving force of the road network on urban development is greater than that on rural areas. The role of county economic agglomeration is gaining strength. In the process of rapid economic development, more attention should be paid to the development of the rural economy and the overall revitalization of the countryside. The equivalent allocation of social service facilities is an effective way to solve the problem of urban-rural imbalance. Further analysis demonstrated that terrain factors have relatively little influence on the URDI. This study provides a new perspective and measurement method for understanding the integration of urban and rural development, and provides a useful reference for guiding the urban-rural integration development and the rural revitalization.
中部地区新型城镇化与农业现代化耦合协调机制及优化路径
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210313
[本文引用: 1]

基于城乡统筹和区域协调发展的视角,构建了新型城镇化与农业现代化耦合协调发展评价指标体系,采用全局主成分分析、耦合协调度模型对2007—2017年中部地区两化的耦合协调机制及时空演化特征进行了系统研究。结果表明:(1)研究期间各省份新型城镇化与农业现代化以一定幅度的波动持续增长,但双向交互下的综合效益总体偏低,经济发展是驱动二者水平提升的主要动力;(2)中部地区新型城镇化与农业现代化表现为高度的耦合相关,2007—2017年两系统经历了“轻度失调—初级协调”的转变,耦合协调关系总体趋于不断优化,协调水平在空间格局上呈现“南高北低”的分异特征;(3)中部地区新型城镇化与农业现代化的耦合协调存在一定短板,相比之下新型城镇化的发展稍显滞后。2012年以来,在宏观政策的调控和引导下两系统发展的不平衡趋势逐步减弱,多数省份已先后实现不同协调等级的同步发展。掌握新型城镇化与农业现代化的耦合协调特征和时空演化趋势,对新时期中部地区崛起和现代化建设目标的实现有着积极的现实意义。
Coupling and coordination between new urbanization and agricultural modernization in Central China
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210313 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国区域创新能力与经济发展水平的耦合协调分析
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.09.003
[本文引用: 1]

采用协整检验和耦合协调模型方法,分析不同尺度区域创新能力与经济发展水平耦合协调状况的时空演化及差异规律。结果表明:① 中国区域创新能力与经济发展水平具有长期稳定而短期跳跃性,区域创新并不必然带来经济发展。② 2005~2014年间,两者动态的耦合协调程度具有尺度敏感性且在地级尺度上偏低,但正逐步改善,区域差异随尺度的缩小而增大。③ 耦合协调高值区在省级层面分布在北京、上海、广东等沿海省份,地级层面分布除沿海城市外,还有内陆省会城市及其周边城市,分布由分散逐渐集聚,宏观上已经形成“沿海-腹地”型大创新-经济合作区。
Coupling coordination between China's regional innovation capability and economic development
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.09.003
[本文引用: 1]

The unidirectional driving relationship between regional innovation and economic development has attracted many scholars' attention, but their bidirectional coupling relationship has been neglected. By constructing the evaluation system of regional innovation capability and economic development level on the basis of their connotations, using the technologies of cointegration test and coupling coordination model, this paper analyzes the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and the difference regularity of the coupling coordination between regional innovation capability and the economic development level on different spatial scales. It shows that: 1) In the long run, there is a stable cointegration relationship between China's regional innovation capability and economic development level, while salutatory relationship in the short-term. Regional innovation cannot necessarily bring about economic development. There is a higher degree of coupling coordination between economic development and innovation ability to the regions with a perfect regional innovation system, that is, with heterogeneous innovation actors, efficient innovation networks and innovation environment, and China's innovation-driven strategy could play a greater role. However, it is found that, during the period of 2005-2014, the degrees of coupling coordination between the two is scale-sensitive and it is generally low on the municipal scale, although increased progressively over time. It is imperative to upgrade the equilibrium relationship between the two from low to high; 2) The regional differences of the degree of coupling coordination between the two increased with the reduction of the spatial scale, however, the differences are decreasing; 3) The high-value areas of the coupling coordination at the provincial level are Beijing, Shanghai, Guangdong, Zhejiang and other South-East coastal areas in China with a scattered distribution. However, the high-value areas of the coupling coordination at the municipal level are more developed coastal cities, inland capital cities and their surrounding cities with a gathered distribution, preliminarily formed a national “coastal -hinterland” innovation-economic cooperation zone; 4) The key to China's innovation-driven strategy is to construct provincial and municipal innovation system, increase the innovation input, and promote the coupling docking and interaction feedback between the various links of government-industry-university-research cooperation.
国际视角下协调推进新型城镇化与乡村振兴的思考
Consideration on the coordination of new urbanization and rural revitalization from an international perspective
新型城镇化与乡村振兴联动: 现实背景、理论逻辑与实现路径
Linkage of new urbanization and rural revitalization: Realistic background, theoretical logic and realization path
中国省域新型城镇化、乡村振兴与经济增长质量耦合协调发展及影响因素分析
基于新型城镇化、 乡村振兴和经济增长质量的丰富内涵, 构建了新型城镇化—乡村振兴—经济增长质量耦合协调评价指标体系, 运用熵值法、 耦合协调度模型对 2011 - 2018 年中国 31 省区市新型城镇化 —乡村振兴—经济增长质量三系统综合发展水平及耦合协调度进行量化, 并结合面板 Tobit 模型对耦合协调度的影响因素进行研究。 结果表明: ①31 省区市新型城镇化—乡村振兴—经济增长质量三系统综合发展水平呈现显著的区域差异, 其中, 三系统综合水平都相对较高的省区市主要分布在东部地区, 而东北、 中部和西部地区三系统综合水平较低, 绝大多数低于全国平均水平。 ②全国三系统耦合协调度整体上偏低, 研究期内呈现缓慢上升并趋于稳定的发展趋势。 从空间演变来看, 耦合协调度具有显著的空间分异规律, 呈现 “东部> 中部 > 东北 > 西部” 的发展格局, 但耦合协调度的省际差异在逐步缩小, 均衡发展趋势有所显现。 ③在全国层面, 政府能力、 交通基础设施水平、 金融发展水平、 产业结构、 人口增长及劳动力质量对三系统耦合协调度具有显著的正向促进作用, 而城乡收入差距则不利于三系统的协调发展。 ④三系统耦合协调度的影响因素具有明显的区域异质性。
Analysis on the coupling and coordinated development and influencing factors of new urbanization, rural revitalization and economic growth quality in Chinese provinces
欠发达地区新型城镇化与乡村振兴战略协同水平的测度及影响因素: 基于政府效率和互联网发展视角
Measurement and influencing factors of synergy level of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization strategies in underdeveloped areas: From the perspective of government efficiency and internet development
甘肃省新型城镇化与乡村振兴协调水平及其影响因素
DOI:10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00136
[本文引用: 1]

在新时代脱贫攻坚任务实现的背景下,提升新型城镇化与乡村振兴协调发展水平,有利于西北地区巩固拓展脱贫攻坚成果、持续增强内生发展动力并加快融入西部大开发新格局。鉴于此,运用改进的耦合协调度模型对2013—2018年甘肃省新型城镇化与乡村振兴的协调发展程度进行量化,并结合面板Tobit模型对二者耦合协调度的影响因素进行研究。结果表明:(1)新型城镇化与乡村振兴的空间分布基本一致,大体上呈现河西地区>陇中地区>陇东南地区>南部民族地区的空间发展格局。(2)全省、河西地区、陇中地区及南部民族地区新型城镇化与乡村振兴的协调发展效应逐步增强,耦合协调发展呈现西北强东南弱的空间分异特征,河西和陇中地区耦合协调水平明显高于陇东南及南部民族地区。(3)新型城镇化与乡村振兴同步发展类型的市州较少,乡村振兴滞后型的市州明显增加,并且集中分布于陇中地区及陇东南地区。(4)政府能力、工业化及交通基础设施水平对二者耦合协调水平具有正向促进作用,而固定资产投资和城乡收入差距则不利于新型城镇化与乡村振兴的协调发展。影响二者耦合协调度的因素具有明显的区域异质性。
Measurement of coordination level between new urbanization and rural revitalization in Gansu province and its influencing factors
DOI:10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00136
[本文引用: 1]

In the context of the realization of the task of poverty alleviation in the new era, improving the coordinated development level of new urbanization and rural revitalization is conducive to consolidating and expanding the achievements of poverty alleviation in Northwest China, continuously enhancing the endogenous development power, and accelerating its integration into the new pattern of western development. In view of this, the improved coupling coordination degree model is used to quantify the coordinated development degree of new urbanization and rural revitalization in Gansu Province, and the influencing factors of their coupling coordination degree are studied combined with panel Tobit model. The results show that: (1) The spatial distribution of new urbanization and rural revitalization is basically the same, which generally presents the spatial development pattern of Hexi region > central Gansu region > southeast Gansu region > southern ethnic minority region. (2) During 2013-2018, the coordinated development effect of new urbanization and rural revitalization in the whole province, Hexi region, central Gansu region and southern ethnic areas has gradually increased. The coupling and coordinated development shows the spatial differentiation characteristics of strong northwest and weak southeast. The coupling and coordination level of Hexi and central Gansu region is significantly higher than that of southeast and southern ethnic areas. (3) There are fewer cities and prefectures with the synchronous development of new urbanization and rural revitalization, and the cities and prefectures with lagging rural revitalization have increased significantly, which are concentrated in central Gansu and southeast Gansu region. (4) Government capacity, industrialization and transportation infrastructure level play a positive role in promoting the coupling and coordination level of the two, while fixed asset investment and urban-rural income gap are not conducive to the coordinated development of new urbanization and rural revitalization. The factors affecting the coupling coordination degree of the two have obvious regional heterogeneity.
我国新型城镇化与乡村振兴协调发展趋势研究
Research on coordinated development trend of New-type urbanization and rural revitalization in China
乡村振兴战略应与新型城镇化同步推进
The common progress of the rural revitalization strategy and new urbanization
基于改进熵值TOPSIS灰色关联度模型的青海省乡村振兴评价及障碍因子分析
Evaluation and obstacle factor analysis of rural revitalization in Qinghai province based on improved entropy topsis gray correlayion model
沿海地区新型城镇化综合发展水平测度
Measure the comprehensive development level of new-type urbanization in coastal areas
基于“五大发展理念”的经济高质量发展水平测度: 广东省21个地级市的实证分析
The measurement of high-quality development level from five development concepts: Empirical analysis of 21 prefecture-level cities in Guangdong province
中国社会保障与经济发展耦合的时空特征及驱动力分析
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190493
[本文引用: 1]

利用耦合协调度模型、标准差椭圆、空间自相关等方法,研究2002—2017年中国社会保障与经济发展耦合协调的时空特征及驱动机制。结果表明:① 社会保障与经济发展之间相互适应、共同发展逐渐增强,但耦合协调度等级没有发生明显的跃迁,研究期内全国整体属于勉强耦合协调类范围,四大区域的耦合协调性呈东部地区>东北地区>中部地区>西部地区的态势。② 社会保障与经济发展的耦合协调度在东西和南北方向上收缩,向中部地区集聚的态势较明显;社会保障与经济发展的耦合协调整体上具有正的空间自相关性,局部空间自相关四种类型中,高高型集中分布在东部地区,低低型多在西部地区,高低型和低高型相对分散。③ 社会保障与经济发展的耦合协调在空间上的差异是内外部因素驱动的结果。内部驱动力中,城镇居民人均可支配收入、农村居民人均纯收入和人均GDP起到关键性作用;外部驱动力中,城镇化率和民营企业就业人数起了重要作用。
Spatio-temporal characteristics and driving force of coupling social security and economic development in China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190493
[本文引用: 1]

Entropy method, coupling coordination model, standard deviation ellipse model, spatial autocorrelation, etc., were used to measure the coupling coordination degree of social security and economic development in China from 2002-2017, and examine its spatio-temporal differentiation. At the same time, the influence degree and driving force were analyzed by grey correlation degree model and Pearson correlation coefficient. The results show that: (1) in terms of time series, the coupling coordination between social security and economic development in China is increasing, but lags behind the development of social security and the economy. The average annual coupling degree of the four major regions is Eastern region > Northeast region > Central region > Western region. (2) As for spatial aspects, the pattern of coupling and coordination between social security and economic development is solidified and dynamically changing, mainly due to the alternation of general maladjustment and forced coupling and coordination, and its spatial distribution has a tendency of aggregation. (3) In terms of driving force, five factors, namely, per capita disposable income of urban residents, per capita net income of rural residents, per capita GDP, urbanization rate and employment number of private economy, are the important driving forces of the coupling and coordination pattern of social security and economic development.
长三角城市群产业生态效率及其时空跃迁特征
Research on industrial eco-efficiency and spatio-temporal transition characteristics of the Yangtze River Delta
中国能源碳足迹时空格局演化及脱钩效应
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202101016
[本文引用: 1]

利用DMSP-OLS夜间灯光数据和碳排放统计数据,构建碳排放面板数据模型,模拟了2000—2013年中国的碳排放量。运用探索性时空数据分析(ESTDA)框架体系,从时空交互视角分析2001—2013年碳足迹的空间格局和时空依赖动态演化;利用改进的Tapio脱钩模型对3个时间段336个地级单元环境碳负荷与经济增长之间的脱钩效应进行综合分析。研究表明:① 2000—2013年,中国的碳排放在时空演变上既表现出稳中有进的总体特征,也存在快速增长的阶段特征。② 碳足迹和碳赤字均呈逐年增长趋势,年均增长率分别为4.82%和5.72%;碳足迹和碳赤字整体北方大于南方,不同的行政单元尺度下碳足迹和碳赤字空间异质性特征明显。各地级单元碳足迹变异系数逐步增大,存在极为显著的空间自相关特征。③ LISA时间路径相对长度北方大于南方,且呈由沿海地区向中西部地区递增的趋势;LISA时间路径弯曲度整体上则由沿海地区向内陆地区递减。④ 综合脱钩指数整体以弱脱钩型为主,但弱脱钩型城市数量持续减少,扩张连接、扩张负脱钩区域数量逐渐增多且向中西部及东北地区聚集分布;全国平均脱钩弹性值逐步增长,变异系数持续下降。
Spatiotemporal patterns of energy carbon footprint and decoupling effect in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202101016
[本文引用: 1]

The global environment issue resulting from carbon emissions has aroused worldwide concern for governments, the public and scientific communities. A precise measurement of the time-resolved and spatial distribution characteristics of carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon footprint as well as its long-period evolution mechanism, can help clarify the relationship between environmental carbon load and economic growth, and are critical references to the formulation of scientific carbon emission reduction targets with reasonable and differential emission reduction policies. In this study, the mainland of China is taken as the research object. According to the quantitative correlations between DMSP-OLS nighttime light image data and carbon emission statistics, the carbon emission panel data model was simulated for China's carbon emissions in the period 2000-2013, and then the spatiotemporal evolving trend and spatial distribution characteristics of carbon emissions in the 14-year research period were discussed using Theil-Sen Median trend analysis and Mann-Kendall test method. Based on the framework of exploratory spatial-temporal data analysis (ESTDA), the spatial pattern and spatiotemporal dynamic evolution of carbon footprint from 2001 to 2013 were analyzed from the perspective of spatiotemporal interaction. In the three periods, the decoupling effect between environmental carbon load and economic growth of 336 prefecture-level cities were analyzed using the improved Tapio decoupling model. The results show that the overall carbon emissions in China had been on the rise from 2000 to 2013, in which the stable-slow rise type was dominant. China's carbon footprint and carbon deficit increased year by year, and the central and western regions became the focus of the growth of carbon footprint and carbon deficit from 2001 to 2013. At different administrative city scales, the spatial distribution pattern of carbon footprint and carbon deficit show obvious administrative orientated and spatial zonal differentiation characteristics. The annual average of global Moran's I index of each level unit is 0.491, which indicates that there is a significant spatial auto-correlation feature in the carbon footprint of China's prefecture-level units. The relative length of the LISA time path is greater in the north than in the south, and it tends to increase from the coastal areas to the central and western regions. The curvature of LISA time path decreases from coastal areas to inland areas on the whole. The curvature of northeast and central regions is higher, while that of eastern and western regions is lower. There is a different trend of the decoupling effect of environmental carbon load in China. Meanwhile the expansion-connection and expansion of negative decoupling regions continuously increased and spatially agglomerated, presenting an "E"-shaped distribution pattern from the north to the south. The national average decoupling elastic value is gradually increasing, while the coefficient of variation continues to decline, and the decoupling type has a significant evolution trend. Therefore, the unbalanced trend of economic growth and carbon emissions in China will continue for a certain period.
STARS: Space-time analysis of regional systems
DOI:10.1111/gean.2006.38.issue-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Comparative spatial dynamics of regional systems
Visualizing regional income distribution dynamics
DOI:10.1007/s12076-010-0048-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于住宅价格视角的居住分异耦合机制与时空特征: 以南京为例
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704003
[本文引用: 1]

城市住宅价格空间分异,是居住空间资源非均衡配置的市场化表达,映射出不同阶层社会群体对城市住宅的选择倾向与需求差异,与居住空间分异在机制和格局上存在一定耦合关联。以南京主城区商品房社区为研究对象,构建起住宅价格特征变量指标体系,采用地理加权回归模型,分析导致房价空间差异的主要因素、组合关系及时空演变特征。研究发现:社区服务档次、学区资源、环境区位、景观稀缺等能够体现居住群体经济实力、生活方式与文化品位的因素,是影响房价分异的主导要素并随时间不断强化;南京房价总体上呈现“圈层+扇形+飞地”的空间结构,高房价主要分布在城市中心、名校学区、高档封闭社区和山水景观别墅区;房价分异与居住分异在作用机制和空间格局上表现出显著的关联耦合特征。城市房价空间分异不止于表达,同时也是推动居住空间分异与再分化的重要驱动机制,并能够预判未来一段时期内城市居住空间分异格局演变的基本走势,可以为城市社会空间研究提供具有前瞻性的观察视角和分析工具。
Coupling mechanism and spatial-temporal pattern of residential differentiation from the perspective of housing prices: A case study of Nanjing
政府干预、金融深化与行业投资配置效率
Government intervention, financial deepening and industrial investment allocation efficiency
中国旅游经济对城市绿色发展的影响及空间溢出效应
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110012
[本文引用: 1]

在“生态优先、绿色发展”战略背景下,针对旅游经济绿色产业外部性及其空间溢出的科学认识缺乏,论证中国旅游经济能否促进绿色发展并揭示其空间溢出特征具有理论和现实意义。选取绿色全要素生产率(GTFP)作为城市绿色发展水平评价指标;融合多源数据并利用EBM-GML模型测算并分解中国284个地级以上城市2005—2016年GTFP;利用空间分析方法刻画地市尺度下GTFP时空格局及聚类情况;依托空间杜宾模型揭示旅游经济对绿色发展的影响及空间溢出效应。结果表明:① 东部、中部、西部、东北城市GTFP年度均值呈现总体上升态势,但“中部塌陷”特征明显;地市尺度中国GTFP格局与经济版图存在空间错位。② 旅游经济具有良好的绿色发展效应,能够同时促进绿色技术效率和绿色技术进步,进而驱动目的地本地GTFP增长。③ 旅游经济对GTFP存在不显著的正向空间溢出,但对绿色技术效率具有显著正向空间溢出。④ 政策上应加强区域内旅游经济联动发展,构建旅游目的地创新溢出机制,推动旅游目的地与邻地产业分工协同发展,打造旅游业深度参与的区域产业生态圈和综合体等,以期强化中国旅游经济对绿色技术进步的空间溢出。
The influence and spatial spillover effects of tourism economy on urban green development in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110012
[本文引用: 1]

Ecological priority and green development has become one of China's national strategies. Additionally, the scientific understanding of the green externality of tourism economy and its spatial spillover is still insufficient. Therefore, in terms of theoretical and practical significance, it is necessary to demonstrate whether China's tourism economy can promote green development and reveal its spatial spillover characteristics. On the basis of constructing the spatial spillover mechanism of green development effect of tourism economy, this paper selects green total factor productivity (GTFP) as the evaluation index of urban green development level based on bibliometric analysis; integrates multi-source data and uses EBM-GML model to calculate and decompose the GTFP of 284 cities at prefecture level in China from 2005 to 2016; uses the spatial analysis method to describe the spatio-temporal pattern and spatial clustering of GTFP at prefecture level. Based on the spatial Durbin model, this paper reveals the impact of tourism economy on green development and spatial spillover effect. The results show that: (1) the annual average of GTFP in eastern, central, western and northeastern China showed an overall upward trend. Eastern China has the largest improvement in GTFP (accumulated growth of 48.08%), followed by the western region (accumulated growth of 44.18%) and the northeastern region (accumulated growth of 36.05%), while the central region has the lowest improvement (accumulated growth of 26.56%), so that the "Central Collapse" feature is obvious. Moreover, there is a spatial dislocation between China's GTFP pattern and its economic map at the prefecture level. (2) The tourism economy could significantly promote the growth of local GTFP in tourist destinations by simultaneously promoting green efficiency change (GEC) and green technological change (GTC). (3) The spatial spillover mechanism of tourism economy on green development is reflected in the fact that tourism economy can significantly improve the GEC in neighboring cities, but it cannot significantly promote the GTC in neighboring cities. (4) In terms of policy, it is necessary to strengthen the linkage development of tourism economy within the region, and build an innovative spillover mechanism for tourism destinations. In addition, it is feasible to promote the coordinated development of tourism destinations and neighboring industries, and create a regional industrial ecosystem and complex with deep participation in the tourism industry.