当前中国农村空心化、城乡差距大、“乡村病”等问题日趋严峻。乡村振兴战略的提出,目的在于夯实农业基础、改善农村发展不充分的现状[1]。特色村镇的建设和发展,是实现共同富裕目标的重要途径之一,也是新型城镇化和乡村振兴的关键内容[1]。与东部沿海发达地区的村镇相比,由于受到地理区位、政策和资本等因素制约,西部边远欠发达地区的村镇发展缓慢,导致了中国区域间村镇发展不平衡的局面[2,3]。虽然东部地区市场化水平显著高于西部地区,但西部地区拥有更丰富的自然资源[4]。如何利用西部地区自然资源禀赋,推进农业现代化,从而带动区位交通条件、投资环境的改善,促进村镇的建设,为更多欠发达地区的可持续发展提供参考借鉴,是值得关注的议题。
在城乡地域系统中,村镇由县城、重点镇、中心镇以及中心村(社区)等不同空间体系构成[5]。村镇建设指的是地方行为主体在评判资源禀赋、产业基础后,整合和配置土地、人力资源等物质和非物质要素,培育农业和非农产业,重构村镇生活、生产、生态和文化空间[5,6]。国外关于乡村振兴、村镇发展的研究和实践始于20世纪50年代,美国和日本尝试通过乡村产业化来减缓乡村衰退、农村人口流失等问题[7,8]。国内学界在改革开放后也逐渐展现出对乡村、村镇建设的关注[9,10],同样认为产业是实现村镇发展、乡村振兴的内生动力和重要基础[7,11]。在中国,村镇建设和发展模式受自然资源、经济发展、生产力水平、历史传统和政府行为等多种因素影响[12]。根据发展动力的差异,村镇发展模式可分为内生发展型、外部驱动型和内外综合驱动型[5,13]。关于内生发展型,学界普遍认为农业专业化和产业化是村镇的内生发展动力之一,因为农民在分散性较强的小农经济中获益较低,而农业产业化能提高生产水平、升级产业结构[14],从而提高农民经济收入。农业专业化和产业化的特征为村镇根据本地资源特色开展专业化种植(养殖)、加工与产业化经营[5]。自然资源禀赋是一个地区形成特色农业的基础和前提,也是其取得比较优势的重要要素条件[15]。因此,中国西部地区自然资源丰富的村镇往往会把开发利用自然资源、扩大基础产业规模作为当地产业发展和经济增长的核心思路[16]。
在村镇建设和发展过程中,茶产业所发挥的作用与其他产业具有共性,也有其特性。从共性方面来看,茶产业是劳动密集型产业[17],在采茶和制茶的过程中需要投入充足的劳动力,因此发展茶产业和其他产业的相同之处在于能在本地提供大量就业岗位,减缓农村劳动力流失,甚至还能吸引外地劳动力,实现人口增长。从特性方面来看,首先,茶产业中最重要的茶树既是可再生的自然资源,也是经济作物,主要受地理区位和自然资源禀赋的影响[18]。那么茶叶的生产就会局限在特定的地区,使得拥有茶树资源的村镇能实现茶产业的可持续发展,且具有更强的竞争力和主导性。其次,茶产业的产业链由茶叶种植、加工、流通、销售等环节构成[19],涉及的经济部门多,且具有自然和文化双重属性[20]。因此,除经济收益(提供就业岗位、维持农民生计、赚取外汇)外,发展茶产业对村镇的文化和生态都有潜在的正向外部效应[17,19]——例如茶文化传播、打造与茶相关的艺术和手工艺品;固碳、减缓水土流失。
茶产业对村镇发展产生的最直接影响在于经济方面,因此国内大部分的研究从产业经济和管理科学的角度切入[21],也有部分研究从村镇景观的空间演变、茶文化和茶旅游等方面展开分析。在发展茶产业促进经济增长方面,一般认为茶叶生产、加工需要突出其特色或打造特色品牌、实现标准化生产、形成区域集聚,由此实现茶叶生产和加工的产业化与专业化,并在此过程中通过吸引外来投资、增加就业机会、完善基础设施,增加村镇的经济和社会收益[15,22,23]。在景观空间演变方面,研究发现民居建筑、村镇街巷的功能和空间会随着与茶叶生产相关的活动改变而发生变化[24,25]。在茶文化和茶旅游方面,研究指出茶叶的生产、加工、销售和茶文化、茶旅游形成了互相促进的良性关系,因此弘扬茶文化、发展茶旅游有助于提高茶叶产品的附加值,同时还能带动村镇的服务业发展[19,26]。然而,茶叶生产和加工要形成产业化和专业化,需要投入大量的原材料、资金、土地、技术和劳动力,还会受到市场需求和交通条件等因素的影响。因此,在中国东部较为发达的村镇内形成的现代茶产业实践未必能复制到西部地区,目前已有的基于东部地区开展的关于茶产业如何促进村镇发展的研究,对西部地区的参考和借鉴意义也存在一定的局限性。首先,从茶树资源来看,受到毁林开荒、种植高产的台地茶、过度采摘等影响,部分地区古茶树园面积大幅度缩小[27],古茶树茶叶供应量难以满足农业现代化生产的需求。其次,从供需关系来看,现有研究更多关注的是茶叶生产和加工的产业建设、产品供给方面,较少从市场需求层面来看其对茶资源、茶产品与茶产业的影响。在本研究案例地易武镇,古树普洱茶原料一直处于供不应求的状态,旺盛的市场需求对茶产业的发展有着非常重要的推动作用。最后,在“企业+农户”的生产组织模式中,因农产品的增值利润被龙头企业截留导致农民收入增长受到限制[28]的情况并没有在易武镇出现,然而这些现象及其成因并没有得到深入研究和讨论。在产业发展过程中,各生产主体如何选择生产组织模式和利益分配方式,以及在此过程中对村镇的可持续发展产生了什么样的影响,对该问题的讨论具有重要的理论价值和现实意义,但现有研究对农业生产组织模式中各主体之间的利益关系或农民收入问题还缺乏深度分析[29]。
在村镇的建设过程中,产业是促进村镇可持续发展最核心的动力。在产业中形成的不同的生产组织模式会对各主体间利益分配和使用产生影响,再通过各种自然资源、劳动力、技术等生产要素作用于产业的再生产,同时也会改变村镇的土地利用结构、人口结构等,最终导致村镇的生活、生产和生态功能产生演化。本文从产业和村镇社会经济视角出发,对云南省西双版纳傣族自治州勐腊县易武镇进行案例研究,揭示此区位偏远、交通条件较差的西部山区镇各生产主体如何凭借其优势的普洱茶资源促进茶产业的复兴,以及带动商贸业和旅游业的发展,从而在产业、土地和人口三方面推动乡村振兴,以丰富当前村镇发展模式与动力机制的相关研究。
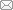
1 研究思路与框架
图1
图1
茶产业助推乡村振兴的分析框架
Fig. 1
The analysis framework of the tea industry promoting rural revitalization
从村镇社会经济视角来看,村镇可被视为在一定地域范围内由自然禀赋、区位条件、经济基础、人力资源、文化习俗等要素交互作用构成的复合系统[31]。在此系统中还包括了要素、结构和功能三个概念[32]。对于村镇系统而言,人口、土地、产业是三大核心要素[33],也是科学推进村镇经济、社会、文化、生态协调发展、实现乡村有效振兴的动力要素[1]。从结构层面来看,结构反映了要素组织的规则和逻辑关系[34],即各要素相互联系、相互作用的内在方式[35]。在易武镇的村镇系统建设和发展的过程中,其结构可分为主体和客体子系统[1,33]。主体子系统包括政府、乡贤精英、茶企和茶农等要素;客体子系统包括村镇自然资源、区位条件、茶产业基础等要素。在此结构里,各主体能通过整合易武村镇系统内外各种要素,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的总要求,协调各子系统[33]的发展,实施乡村振兴战略。从功能层面来看,功能取决于系统的要素组合和结构[33]。在传统的乡村中,居住和农业生产功能是其初始职能[33];而交易则是镇的主要功能之一。但随着乡村内外部要素和环境的变化,乡村也开始承担休闲服务、保护生态等功能[31,36,37]。
2 案例地概况与数据来源
2.1 案例地概况
易武是云南省西双版纳傣族自治州勐腊县北部的一个山区镇,于2015年7月撤乡设镇。尽管地理位置偏远、交通较为不便,但是易武在清末民初就已经成为重要的茶叶加工和出口基地,是茶马古道的起点,茶文化历史深厚。易武镇的自然环境适宜种植茶树,年均降雨量在1700~2200 mm之间,境内土壤以红壤、赤红壤为主,酸碱度pH值在4.5~6.5之间。
易武镇下辖易武、纳么田、麻黑、曼腊、曼乃、倮德6个村委会,73个村民小组,17个茶胶队。易武镇的经济结构以农业为主,其中又以茶叶种植为主。全镇茶叶种植面积达9.8万亩(1亩≈667 m2)(有证面积4.58万亩),其中古茶园面积7.28万亩;2018年干毛茶总产量2000 t,总产值2.6亿元。以茶叶为主要经济收入的人口数达到10859人(占比达59.45%);农民人均可支配收入达8657元,其中80%以上的经济收入来自茶叶。全镇有生产许可的茶厂数量达62个,还有茶叶协会1个、农民茶叶专业合作社6个。
2.2 数据获取
研究数据分别来自半结构式访谈调研和文献资料及地方政府工作报告的二手数据。第一次调研时间为2002年8月,主要访问了老乡长张先生,访谈后预测易武会因古树普洱茶重新被市场认可而复兴。第二次调研时间为2015年7月16-20日,调研范围为易武镇全镇,访谈人数16人(其中政府官员2人、外地茶商5人、本地茶农9人),访谈内容主要为易武的社会、生态、经济等方面的发展成就,茶园空间分布概况和茶产业发展现状。第三次调研时间为2015年12月19-28日,调研范围为易武镇全镇,访谈人数31人(其中政府官员3人、本地茶厂老板9人、外地茶商3人、本地茶农16人),访谈内容包括茶产业发展历史及现状、茶叶具体生产过程、茶农对本地历史和当前生活质量的认知。第四次调研时间为2019年7月16-20日,调研范围为易武镇主街和麻黑村,访谈人数15人(其中政府官员3人、本地茶厂老板7人、本地茶农3人、外来员工2人),访谈内容为有关易武镇的历史文化及社会经济发展、村民种植和加工茶叶、茶厂及茶园经营情况更新。
3 易武镇普洱茶产业生产组织和利益分配模式
3.1 普洱茶产业发展历史
根据茶叶产量的变化,易武镇普洱茶产业的发展可划分为“兴盛—衰落—复兴”三个阶段。(1)清初—民初兴盛期。清朝时期,易武镇普洱茶被列为贡茶,当地政府召集顶级茶农和茶叶专家到易武种植普洱茶树,使得易武正山成为古六大茶山中茶园面积最大、茶叶产量最大的茶山。为方便运送贡茶,当地政府还组织修建了一条始于易武的石板道,现被称为“茶马古道”。民国时期,易武的茶叶贸易拓展到了国外市场,并成为通往东南亚的陆路出口口岸。在此期间,易武茶产量达到顶峰,据《镇越县新志稿》,清嘉庆至道光年间易武山年均产干茶7万余担。(2)近现代衰落期(抗日战争时期至1994年)。此阶段战乱频繁,20世纪30年代易武发生兵乱事件,导致茶产量减产至30担。1949年后,实行计划经济体制,茶叶只能在供销社内进行统购统销,压缩了茶农的获利空间,茶农对茶叶种植和生产的积极性并不高。20世纪80年代实行林权分配,各家依据人口数进行了茶树分配,因此每家每户都拥有一定数量的茶树。(3)现代复兴期(1994年至今)。1994年,台湾著名茶叶爱好者吕礼臻和邓时海等人赴易武考察,并向时任易武乡长的张毅定制传统手工普洱茶饼。于是张毅向掌握传统制茶技术的老人学习具体的工艺流程,同时还邀请了大量易武的茶农加入到这个生产过程中进行协助和学习。在张毅的影响下,更多农户也参与到传统制茶手法的复兴中来,易武的传统茶叶生产、加工技术由此得以恢复,“具备传统工艺、高质量原料”的易武普洱茶形象和品牌被建构起来。越来越多茶农恢复种植茶树,易武镇茶园面积和产量逐年增加(表1)。
表1 2011—2018年易武镇茶园面积及产量
Table 1
| 年份 | 茶园面积/亩 | 干毛茶产量/kg |
|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 42711 | 842000 |
| 2012 | 42681 | 868000 |
| 2013 | 42686 | 926000 |
| 2014 | 51633 | 1100000 |
| 2015 | 52633 | 1242178 |
| 2016 | 53628 | 1598971 |
| 2017 | 62717 | 1751765 |
| 2018 | 98784 | 2150854 |
注:数据来源于易武镇政府。
易武的优质普洱茶主要由不施洒农药、富含茶多酚的古茶树生产、加工而成,年均产量不高,且具有“越陈越香”的特性;加之茶马古道、贡茶之乡的文化意义,使得易武普洱茶既能满足大众消费者对健康、营养、个性化口感的茶产品需求,也能满足茶文化精英或消费能力较强的人的收藏需求。
3.2 普洱茶产业生产组织模式
在易武普洱茶产业现代复兴阶段,茶产业生产组织模式主要有三种,分别为“原料生产茶农+小型加工茶厂”“原料生产茶农+现代大型茶企”“散户茶商+自产自销茶农”。根据生产组织模式的不同,易武普洱茶产业的生产主体可分为四类:(1)原料生产茶农。此类型茶农拥有茶树,但只种植和采摘茶叶原料,或再对茶叶进行最基本的杀青晒青加工制成毛茶,销售茶叶原料和毛茶。(2)小型加工茶厂。部分能力较强的原料生产茶农实现最初的资本积累、技术学习后进一步开设小型茶叶初制厂并成为茶厂主。此类型茶厂拥有一定规模的茶园和厂房,能够对茶叶原料进行更高级的加工,如干燥、压饼等初加工或发酵加工,制成茶饼后进行销售。目前,易武镇内不同茶厂的规模大小存在差异,但都处于不断扩大的阶段中。(3)现代大型茶企。此类型茶企拥有较大规模的茶园和厂房,同时还会与茶农合作收购其茶叶原料;通过机器对茶叶进行规模化加工,制成和销售的茶叶产品更多元化,是易武镇普洱茶产业现代化和产业化的主要模式。现代大型茶企于2014年前后进驻,由外地资本进行投资建设;本地大型茶企数量相对较少,仍处于成长阶段。另一方面,受限于土地政策,无论是本地还是外地的现代大型茶企难以取得更多建设用地,厂房面积和规模较难进一步扩大。部分茶企选择在易武镇内开设门店以展示产品、宣传品牌和吸引散户茶商交流为主要目的,而实际加工生产的厂房则设在其他县;或者把用以加工的厂房建设在易武镇周边而非镇内。(4)自产自销茶农。此类型茶农拥有茶树,除了生产茶叶原料,还能通过传统的手工制茶工艺生产个性化茶饼,直接销售给散户茶商。
3.3 普洱茶产业生产要素投入
任何企业的生产经营都涉及两个层次的决策:一是对生产经营组织模式的选择;二是在既定的生产组织模式下对资源配置的决策[38]。对于易武镇的普洱茶生产主体而言,选择何种生产组织模式需要评估其所拥有的资源禀赋,以及如何通过优势生产要素的投入来实现资源价值和可获利润的最大化。易武镇普洱茶的生产加工环节主要为:鲜叶采摘—杀青揉捻—晒青(毛茶干燥)—蒸压制成茶饼(茶砖、沱茶)。在各生产环节中,不同生产主体投入的原料、劳动力、技术和资本等生产要素均不相同,最终面向市场销售的渠道也有所差异(表2)。首先,在原料方面,四类产业主体都拥有部分茶园的产权,但是所占比例不同。原料生产、自产自销茶农的茶叶原料主要来自其拥有产权的茶园,少部分会与其他茶农或茶厂协调承包收茶;小型加工茶厂往往会与其他茶农合作,承包其部分茶园,以满足自身的加工需求;现代大型茶企拥有部分茶园,同时还会通过现场考察茶叶质量来决定提供原料的茶农,没有长期固定的收购对象。其次,在劳动力方面,因鲜叶采摘只能通过人工采摘,而杀青、晒青和压制等环节均可采用人工或机器的加工方式。因此,在产茶时节,除少数茶农会以承包的形式代为收取之外,四类生产主体都会在收茶季节雇佣劳动力进行收茶。雇佣对象往往比较固定,且一般选择搬迁下山的苗族人。部分茶企也会从外地调配专业人员收茶。第三,在技术方面,易武传统手工制茶工艺是其区别于其他地区茶产品的核心要素之一,也是其竞争优势所在。传统手工制茶对技术要求较低,导致大茶企相对于规模较小的茶叶加工厂而言并无明显的技术优势,茶企的优势主要在于加工效率、技术规范和卫生标准方面。在销售环节,大部分茶农和茶厂主要通过熟人交易;还有的茶农、茶厂的生产过程由买家定制,到了收茶时节,买家就会来到易武收茶,而后运到经济发达的地区如珠三角、长三角等地区;现代大型茶企通常有其固定的销售渠道销往海内外市场。
表2 易武镇普洱茶各生产主体的生产要素投入情况
Table 2
| 生产主体 | 原料 | 劳动力 | 技术 | 资本 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自产自销茶农 | 基本自给,少量承包 | 雇佣当地人 | 传统技术 | 原始积累 |
| 原料生产茶农 | 基本自给,少量承包 | 雇佣当地人 | 传统技术 | 原始积累 |
| 小型加工茶厂 | 自给和承包并存 | 雇佣当地人 | 传统技术为主,少量先进技术 | 原始积累 |
| 现代大型茶企 | 承包和收购并存 | 雇佣当地人或外地调配 | 传统和先进技术并存 | 外地茶企以外来投资为主;本地茶企以原始积累为主 |
注:作者根据访谈内容整理。
3.4 普洱茶产业利益分配方式
各生产主体因其资源禀赋差异而选择不同的生产合作方式,从而形成不同的利益分配关系。科学、合理的利益分配关系,对各主体在生产环节上实现利益平衡极其重要[40]。从利益分配方式来看,各生产主体在不同的生产组织模式中参与的生产环节、拥有的资源禀赋各有差异,但参与的环节越多、拥有的资源越稀缺,获利能力就会越强。(1)在“散户茶商+自产自销茶农”模式中,稀缺的古茶树资源完全属于茶农,且茶农掌握了传统制茶工艺,能够参与茶叶生产的全过程,也因此对茶叶产品的销售具有最大的话语权;此外,散户茶商与茶农直接交易,缩短了中间流通环节,双方交易信息透明度最高。因此,茶农能够获得最直接的收入和利润,完成资本的积累和交流能力的提升。(2)在“小型加工茶厂+原料生产茶农”模式中,茶农拥有茶树,但仅参与鲜叶采摘到晒青环节,通过提供原料获得相应收入,可获利的空间相对较小;而茶厂能参与茶饼生产和加工的环节,获利能力比茶农更强,销售茶产品获得的收入和利润能投入到本地茶业的再生产中。(3)在“现代大型茶企+原料生产茶农”模式中,茶农也仅能获得原料或初制加工成品的较低收入;而茶企在茶叶产品种类生产、包装等方面更齐全,销售渠道更成熟,获得的收入和利润占比更高。另一方面,茶企能通过其品牌效应提升易武古树普洱茶的竞争力,助推茶叶原料收购价格的进一步增长,为茶农带来更多收益。总的来说,在获利能力方面,存在现代大型茶企>小型加工茶厂>原料生产茶农的基本情况。另一方面,在普洱茶产业中,古茶树是最稀缺的资源。因此,拥有古茶树、能够自产自销的茶农,无论是在与小型茶厂、大型茶企合作还是与散户茶商直接交易的过程中,都拥有极强的议价和获利能力。
4 普洱茶产业助推乡村振兴的过程与机制
4.1 普洱茶产业助推乡村振兴的过程
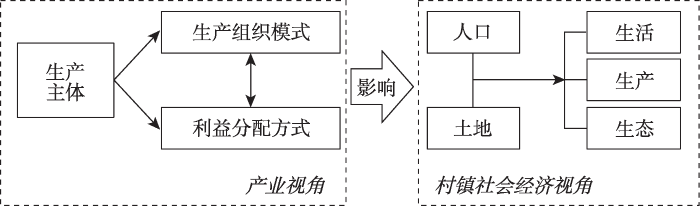
在易武镇的普洱茶产业复兴过程中,四类生产主体把所得经济收入投入到不同的生活、生产和生态场景中并实现其功能,由茶产业的发展带动了村镇系统结构的改变,为当地土地和人口带来正外部性,从而促进了乡村振兴的实现,主要表现在以下三个方面(图2)。
图2
图2
易武普洱茶产业复兴助推乡村振兴的过程
Fig. 2
The process of the tea industry promoting the rural revitalization of Yiwu
(1)促进了茶产业、商贸业和服务业的发展。在茶产业方面,易武镇茶园面积及茶叶产量快速增长(表1),茶厂和茶企通过升级加工设备、扩建厂房、雇佣劳动力来扩大产业规模,具有规模的茶厂和茶企数从54家(2015年)增长到62家(2018年)①(①数据来源:易武镇政府。);茶农也通过雇佣外来劳动力和传承传统制茶工艺提高自身的生产水平。在茶业恢复增长的同时,商贸业和旅游业也得到了发展。由于现在普洱茶的生产仍缺乏统一的质量监测标准和机械化生产标准;古树茶年均产量不高,无法满足日益增长的市场需求;且普洱茶的品质极大程度取决于古树茶的质量和制茶者的生产经验与专业程度[41]。因此,虽然现代物流业非常发达,但出于对易武原产地古树茶的辨识、对传统制茶工艺的要求以及对茶叶品质和独特口味的追求,大部分散户茶商选择亲自来到易武镇的各个村里与茶农面对面交流、交易,而非简单地通过线上或者与第三方供应商交易。于是,生产和交易功能同时发生在村域,原本“镇”的交易功能下沉到乡村,促进了茶农对其居住空间的改造,例如茶农会在自己居住的房子里增设住宿设施和参观茶叶加工的空间。除此之外,茶农还在易武镇的主街开设各种类型的商铺,服务于外地茶商和本地居民;易武镇也凭借其“贡茶之乡”的品牌和普洱茶文化吸引了大量茶游客,商贸业和旅游业逐渐发展。2018年,在易武镇新街沿边173家店铺中,零售(42家)、茶店(35家)、餐饮(26家)、住宿(17家)②(②数据来源:作者实地调研整理。)业态类型合计占比达到了70%。当镇上或者村里出现道路损坏时,为了不影响茶叶交易,同时考虑到政府财力有限,茶农会自发地、主动地维修道路而不是等政府来维护,完善交通设施又能进一步促进商贸业和旅游业的发展。
(2)保护了农业用地。从土地利用类型来看,《勐腊县土地利用总体规划(2010—2020年)》中制定易武的城镇村建设用地仅为125.08 hm2(约1.25 km2),大型茶企无法申请到更多建设用地,制约其进一步扩张,一定程度上反而保护了易武镇的小型加工茶厂。另一方面,意识到古树茶带来的极高经济价值,茶农会自发保护古茶树,从而保护了农业用地。
(3)吸引了外地人口流入、茶农身份得到转变。在采茶季节或茶叶交易旺季,各生产主体皆需从外地招募劳动力进行茶叶的采摘、初制加工等。2018年,易武镇吸引了县外外来务农人员1361人、外来从事二产人员121人、外来从事三产人员592人③(③数据来源:易武镇政府。)。另一方面,自产自销型茶农通过进入茶叶加工流通和销售环节分享利润从而增加收入,同时还创造了改变身份和地位的条件——由单纯务农身份转变为拥有加工和销售茶叶产品能力的经营者。
在实现基本的土地保护、人口流入、产业多元化发展之后,各生产主体能完成资源要素的原始积累,继续根据各自生产需求投入不同的生产要素,开始新一轮循环。
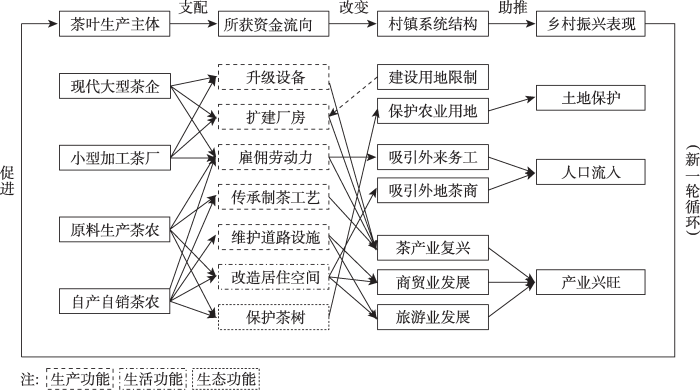
4.2 普洱茶产业助推乡村振兴的作用机制
图3
图3
易武普洱茶产业助推乡村振兴的作用机制
Fig. 3
The mechanisms of the tea industry promoting the rural revitalization of Yiwu
从村镇社会经济视角来看,当茶产业中的各生产主体在获得经济收入后,会对这些利润进行分配,分别投入到本地生产与再生产、生活和生态场景中,从而带来人口流入与土地保护的正外部性。在生产场景中,升级设备、扩建厂房、雇佣外来劳动力、改善道路设施等能够推动茶产业、商贸业和旅游业的进一步发展,促进了产业兴旺。在生活场景中,茶农改造居住空间、传承传统制茶工艺、开设商业店铺等提高了其生活水平,达成了生活富裕。在生态场景中,茶农自发保护古茶树、积极种植新茶树,保护农业用地的同时为自身创造了更宜居的自然环境,实现了生态宜居。
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
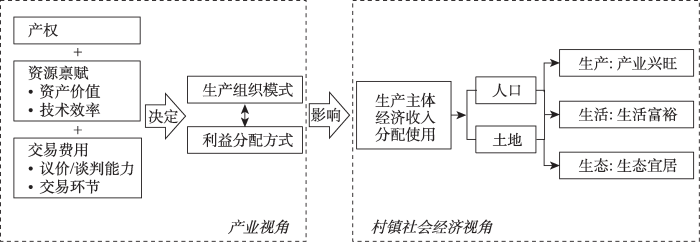
本文从产业和村镇社会经济视角分别剖析了易武镇茶产业复兴过程中茶农、小型加工茶厂、现代大型茶企等生产主体在权衡其产权、资源禀赋和交易费用的优势条件后选择不同的生产组织与利益分配模式,从而对各主体收入及使用产生影响,最终在产业、土地和人口三方面共同推动了乡村振兴的实现,主要结论如下:
(1)对于拥有资源禀赋的农业型村镇而言,可再生的、可持续发展的、无可替代的稀缺自然资源是其最重要的生产要素;对于农民而言,明确掌握这些资源的产权,能成为其维持生计、提高收入的重要保障。以往研究认为,农民作为初级农产品的提供群体,具有分散、小规模经营的特点,组织化程度低,在市场谈判和交易环境中往往处于劣势,这也是导致农民收入难以提高的重要原因之一[28]。然而,在本研究中,市场对于优质、个性化普洱茶产品的需求远远超过了供给,导致古树茶的市场价值极高;同时,茶农拥有古茶树这一稀缺资源的产权。因此,即使生产的组织化程度不高,茶农也能在与散户茶商、小型茶厂、大型茶企议价、谈判和交易中占据主导权。
(2)资源禀赋和交易费用决定了一个地方的产业主体选择何种生产组织模式和利益分配方式。易武镇尚未形成现代大型茶企集群,仍以中小型茶厂和分散式生产为主。这是由于古树茶原料产量不高,无法满足大规模的生产需求;生产加工环节较短、制茶技术相对其他茶叶较简单,且茶农可自由选择是否与其他生产主体合作,因此茶叶生产无法形成垄断;且消费者更偏好于传统制茶工艺而非机器生产的茶叶产品。因此,在现代化农业的生产和经营体系的构建中,可适当扶持更多本地茶农建设中小型加工茶厂,生产、加工普洱古树茶和台地茶,结合普洱茶文化,引导当地从农业主导转变为农业、加工业与服务业协同发展,通过多元化产业增强社会经济韧性。
(3)在发展产业促进乡村振兴中,政策应更多地倾向于明晰农户对资源的产权和提高农民自身的能力当中。研究表明,在市场需求旺盛、交易价格高昂、古茶树产权明确的前提下,相较于与茶企或茶厂合作的模式,茶农自产自销模式是一种能使农户获得最大化利润的生产组织模式。因此,可利用茶叶交易展览会等增进茶农和散户茶商、大型茶企的交流与交易,帮助茶农提高与外界沟通和议价的能力,了解市场不断变化的需求,让他们也有能力加入加工流通环节,由单纯务农身份转变为拥有加工和销售茶叶产品能力的经营者,在实现身份转变的同时提高收入。
5.2 讨论
既有研究指出解决“三农问题”的核心与难点在于如何提高农民的收入,即何种模式的农业产业化或农业发展才能提高农民的收入[29]。此外,在乡村振兴背景下农业如何促进乡村和城镇发展的研究中,往往强调提高农业生产效率、实现农业现代化和产业化、促进产业转型升级。但本文认为这些观点无法清楚地解释分散生产的普洱茶产业如何、为何成功助推易武镇实现乡村振兴。因此,基于案例研究,本文的贡献在于,除了呼应产业发展是村镇发展的核心这一观点,还强调产业发展过程中生产组织模式及利益分配模式需要重点关注村民的产权和能力提升,实现产业和村镇互促发展。乡村振兴的目的在于产业、生态、文化、人才和组织的“五大振兴”[1],要求实现产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕。易武镇通过重新培育、振兴茶产业实现了收入增长;在保护古茶园、改造居住和生产空间过程中,实现了乡村景观优化、人居环境质量改善和保护生态;在挖掘普洱茶文化和茶马古道历史文物中,传承了乡村文化,也得到政府的政策支持打造特色旅游小镇;村民积极主动发展茶产业、改造居住和生产空间、维护农村基础设施、逐渐树立对古茶树品牌保护的意识(例如班章村村民会在村口检查外来汽车,避免外来的茶叶进入班章而被包装成优质的班章茶销售);易武镇政府服务于村民,政府与村民关系融洽;村民在衣、食、住、行方面的日常生活水平得到了极大的改善和提高。总而言之,在全球化时代,易武镇融入了世界乡村发展网络体系,实现了乡村有效振兴,推进了经济、社会、文化、生态的协调与发展。
本文的局限性在于,尚未对新一轮的资源要素的积累和循环进行调查分析。初始的资源禀赋差异,例如茶农拥有的古茶树数量、传统制茶工艺的掌握程度、议价能力等导致了茶农在茶叶产品生产过程中能参与的环节、分配的利益各有不同。在再生产过程中,资源要素的积累和循环又会进一步加大这种差距[39]。茶农、小型加工茶厂和现代大型茶企在这些动态积累的过程中会出现分化,进而可能在合作过程中形成新的生产组织和利益分配模式,最终引起更明显的社会分层和分化。此外,由于普洱茶产业的复兴与特殊事件相关,具有难以复制的特殊性,未来是否同样会因市场需求的变化而对茶产业和村镇发展产生影响尚未明晰。
致谢
真诚感谢中山大学翁时秀副教授对本文提出的修改意见和建议。
参考文献
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 5]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the New Era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 5]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
Revitalize the world's countryside
DOI:10.1038/548275a URL [本文引用: 1]
新时期中国城乡发展的主要问题与转型对策
Urban-rural development problems and transformation countermeasures in the new period in China
DOI:10.2307/142020 URL [本文引用: 1]
外部治理环境对盈余质量的影响: 自然资源禀赋是“诅咒”吗
The effect of external governance environment on earnings quality: Is natural resource endowment cursing
中国村镇建设和农村发展的机理与模式研究
The mechanism and models of villages and towns construction and rural development in China
“回得去的故乡”需要新思路
"Homelands" need new ideas
China's rural revitalization and development: Theory, technology and management
DOI:10.1007/s11442-020-1819-3 [本文引用: 3]
Rural revitalization in Japan: Spirit of the village and taste of the country
DOI:10.2307/2645373 URL [本文引用: 1]
变化中的中国乡村建设: 从半坡原始村落到烽火新村来看中国乡村建设的发展
The changing rural development: The development of rural construction in China from banpo primitive village to fenghuo new village
中国农村的经济、社会发展与村镇建设
China's rural economic and social development and village construction
Land consolidation and rural revitalization in China: Mechanisms and paths
中国区域农村发展动力机制及其发展模式
Dynamic mechanism and models of regional rural development in China
DOI:10.11821/xb200802001
[本文引用: 1]

The agriculture, rural and farmer development are the principal and radical problems in the recent economic and social process in China. Nowadays, aiming at building a moderately prosperous society in all respects and modernizing the country, the project of new socialist countryside construction was advanced at the Fifth Plenary Session of the 16th Central Committee of the Party, which means advanced production, improved livelihood, a civilized social atmosphere, clean and tidy villages and efficient management. Though many researches have been conducted on the new socialist countryside construction and given some suggestions, there have been relatively few studies on the research of rural development theory. It is an original approach to the analysis of the elements and configuration of the whole rural development system to provide theoretical basis for choosing rural development models based on the view of system theory. The results are as the follows: (1) The regional system is a urban-rural integration, so it is very necessary to study rural development problem in the general framework of the whole regional system. (2) Regional rural development system is a complicated synthesis, including regional rural development core system and regional rural development exterior system. The former is composed of rural natural system, rural economic system, rural social system and rural ecological system, and the latter consists of regional development policies, international trade circumstance, etc. The essence of rural development is the process of mutual coupling and coordination of the two sub-systems. (3) The regional rural comprehensive ability lies on two aspects including the rural development inner ability and the exterior drive of urbanization and industrialization. The interaction mechanism obeys parallelogram principle in physics. The evolvement characteristics of rural development system are different in the different combinations of the inner and exterior driving forces. (4) According to the difference of rural development driving forces, rural development models are classified into two types, namely the dominant type of rural self-development and the dominant type of the exterior drive of industrialization and urbanization, and six sub-types at the second level, which are industry driving, villages and towns construction driving, labor force transfer driving, characteristic industry driving, eco-tourism development and specialized market organization driving. In conclusion, it is a scientific approach to the exploration of regional rural sustainable development models, based on the analysis of elements, construction, and function of regional rural development system and characteristics.
基于“潜力—支持力—恢复力”框架的村镇可持续发展能力及其类型甄别
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211205
[本文引用: 1]

科学判断村镇可持续发展能力,精准定位村镇发展类型,对于实现乡村振兴多元目标具有重要价值。以重庆市江津区为研究区,2017年为研究时点,从潜力、支持力与恢复力三个维度解析村镇可持续发展能力,从而构建评价指标体系与评价模型,分析村镇可持续发展能力空间分异特征及其类型。研究表明:(1)村镇可持续发展能力的强弱是潜力、支持力与恢复力三者共同作用的结果。(2)江津区村镇潜力呈现“北高南低”;支持力呈现“北高南低”;恢复力呈现“南高北低”;可持续发展能力呈现“西南高东北低,组团状分布”。(3)江津区村镇可划分为发展潜力挖潜型、城乡融合促进型、安全质量提升型与能力全面发展型四种可持续发展类型,进而提出差异化调控策略,以引导村镇可持续发展、增强县域综合实力。
Study on sustainable development capacity of villages and towns and its types based on the framework of potential-support-resilience
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211205
[本文引用: 1]

It is of great significance in the implementation of rural revitalization strategy and the realization of its multiple goals to scientifically evaluate the level of the sustainable development ability and determine targeted development types of villages and towns. Based on sorting out the implication of the sustainable development ability implication of villages and towns from the perspectives of potential, support and resilience, this study establishes the evaluation framework and evaluation models. Meanwhile the study takes 25 towns in Jiangjin district of Chongqing as research units to quantitatively measure the sustainable development ability of villages and towns in 2017. And then it reveals the spatio-temporal differentiation and accordingly identifies the vulnerabilities types, and proposes targeted regulation strategies. The results shows that: (1) The sustainable development ability of villages and towns is the result of the interaction of potential, support and resilience. (2) On the whole, the potential of villages and towns shows a spatial pattern of " high in the north and low in the south" in Jiangjin; the support of villages and towns shows a spatial pattern of "high in the north and low in the south" in Jiangjin; the resilience of villages and towns shows a spatial pattern of "high in the south and low in the north" in Jiangjin; the sustainable development ability of villages and towns shows a spatial pattern of "high in the southwest, low in the northeast, cluster distribution". (3) We divide the sustainable development ability of villages and towns in Jiangjin into four types, including potential enhancement type, urban-rural integration promotion type, ecological security improvement type and potential-support-resilience ability comprehensive development type. Based on the principle of "ecological priority-classified control-highlight emphasis-local adaptation", the study proposes differentiated sustainable development ability improvement strategies for different types, to guide the sustainable development of villages and towns.
乡村空间重构与土地利用转型耦合机制及路径分析
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220712
[本文引用: 1]

科学揭示乡村空间重构与土地利用转型的耦合发展关系,有利于为中国乡村振兴和城乡融合发展提供理论基础和实践依据。运用文献综述、理论分析阐释二者的耦合机理及驱动因子。主要结论如下:(1)重构乡村空间是对新一轮乡村转型发展要求的积极回应,土地作为乡村地域的关键发展要素,通过其利用形态的多维转化适应不同的空间重构场景。(2)乡村空间重构是土地利用转型的重要驱力,也为土地利用转型提供不竭的现实需求,土地利用的成功转型是乡村空间重构结果的显著表征,二者交互影响,存在耦合互动关系。(3)空间规划、政策制度、产业结构、利益主体及生态理念的多轮驱动机制共同对其耦合关系施加影响,不同作用机制下的作用效力、方向有所不同。(4)新时代下促进乡村空间重构与土地利用转型耦合发展的一个重要思路是全方位探寻土地利用优化转型的多维路径,总体上应立足生态文明的价值位序,以空间规划为约束机制,以产业结构升级为诱发机制,以多方利益协调为保障机制,同时创新土地政策制度机制,从而提高耦合水平,助力乡村振兴战略实施。
The driving mechanism and path analysis of the coupling development of rural spatial reconstruction and land use transformation
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220712
[本文引用: 1]

With the rapid advancement of urbanization and industrialization in China, the social structure and economic development model of rural areas and the development of spatial systems such as ecological system have changed significantly, followed by the change of land use form in different regions. Thus, revealing scientifically the coupling development relationship between rural spatial restructuring and land use transition, and discussing the coupling mechanism and optimal path are conducive to providing theoretical basis and practical basis for China's rural revitalization and urban-rural integrated development, which is meaningful both in theory and practice. This study used literature review theory to analyze and explain the coupling mechanism and driving factors of rural spatial restructuring and land use transition. The main conclusions are drawn as follows: (1) The reconstruction of rural space is a positive response to the new round of rural transformation and development requirements. As a key development element of rural region, land can adapt to different spatial reconstruction scenes through the multi-dimensional transformation of its utilization forms. (2) Rural spatial restructuring is an important driving force for land use transformation, and it also provides inexhaustible realistic demands for land use transformation. The successful land use transformation is a significant representation of the results of rural spatial restructuring, and there is a coupling interaction between the two. (3) This paper constructs a multi-wheel driving mechanism of their coupling development, the direction of the effect path is different under different action mechanisms. More specifically, spatial planning and policy system design are indispensable constraints and regulation mechanisms of coupled development; the transformation of industrial structure and the change of economic system have obvious driving and catalytic benefits in deepening the coupling relationship between the two. In addition, the coupling relationship between rural spatial restructuring and land use transformation is deeply constrained by the behavior of multiple stakeholders, so the protection and coordination of the ownership rights of relevant stakeholders should run through the coupling development from the end to the end. Finally, establishing the value order of ecological priority is of great significance to the coupling evolution process. (4) In the New Era, it is important to explore the multi-dimensional path of land use optimization to promote coupled development. On the whole, the core values of ecological civilization should be established, spatial planning should be taken as the constrained mechanism, industrial structure upgrading as the induced mechanism, multi-stakeholder coordination as the guaranteed mechanism. Meanwhile, the land policy system mechanism should be innovated. Only in this way can we improve the coupling level and facilitate the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy.
农业产业化与特色农业的发展: 以安溪茶产业发展为例
Agricultural industrialization and the development of characteristic agriculture: Taking the development of Anxi Tea Industry as an example
从比较优势到竞争优势: 建构西部地区可持续的产业发展能力
From comparative to competitive advantage: Cultivation of the ability to sustainedly develop industries in Western China
The tea industry and a review of its price modelling in major tea producing countries
Government behaviours in sustainable development of tea industry: Empirical evidence from Fujian, China
DOI:10.1504/IJSD.2021.115233 URL [本文引用: 1]
Integrating tea and tourism: A sustainable livelihoods approach
DOI:10.1080/09669582.2019.1648482 URL [本文引用: 3]
具有文化特质功能型农业的发展模式: 以茶文化与茶产业为例
Model of agriculture with culture function: A case study of tea culture and tea industry
Spatio-temporal variation and the driving forces of tea production in China over the last 30 years
DOI:10.1007/s11442-018-1472-2
[本文引用: 1]

As a daily necessity and an important cash crop in China and many other countries, tea has received increasing attention. Using production concentration index model and industry’ s barycenter theory, we analyzed the spatio-temporal distribution of tea production and barycenter movement trajectory of tea plantations and production in China between 1986 and 2015. Driving forces of the movement were also analyzed. From 1986 to 2000, tea production in China’s Mainland of grew slowly (by 210×103 t). The continuous increase in tea yield per unit area was the primary contributor (more than 60%) to the growth in tea production during this period. Since China joined the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001, tea production has grown rapidly, by 1.59×106 t between 2001 and 2015. The increase in the tea plantations area is the main contributor. Over the last 30 years, the barycenters of tea production in China have moved westward from the Dongting Lake Plain to the eastern fringe of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Guizhou, Guangxi, and Sichuan in southwestern China have gradually become regions of new concentrated tea plantations and main tea production provinces. Lower cost of land and labor in southwestern China are the main drivers of the westward movement of China’s tea industry. In addition, supportive policies and the favorable natural geographical environment contribute to the westward movement of tea industry. Our research highlights the spatio-temporal variation of China’s tea production in the last three decades. The result indicates importance to make appropriate policies to promote the development of tea industry in China.
特色小城镇建设发展研究: 以青岛海青茶园小镇为例
Study on the construction and development of characteristic small towns: A case study of Qingdao Haiqing Tea Garden Town
产业链作用下的小微产业村镇“产、城关联”用地模式探讨: 以福建省茶叶加工产业村镇为例
A study on industrial-chain-based associated land use model for small industrial villages: The case of tea-processing industrial villages in Fujian province
茶叶经济对西双版纳易武古镇景观空间演变的影响
The impact of tea economy on spatial evolution of Yiwu Ancient Town in Xishuangbanna
Rural revitalization of Xiamei: The development experiences of integrating tea tourism with ancient village preservation
DOI:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2022.01.006 URL [本文引用: 1]
茶旅游发展中的茶农角色参与: 南糯山、老班章案例
The development of Pu'er Tea tourism development in the perspective of tea farmer participation: Case studies of Nannuoshan and Laobanzhang
云南古茶树资源现状与保护对策
Status quo of ancient tea tree resources of Yunnan and measures for protection
农业产业化经营和农民组织创新对农民收入的影响
The impact of agricultural vertical integrating and farmer's organizational innovation to the farmer's income
农业产业化模式、利益分配与农民收入
Agricultural industrialization model, profit distribution and farmer income
不同生产组织模式下农户技术效率研究: 基于江苏省桃农的调研数据
Research on farmers' production efficiency under different organization modes: An empirical analysis on farmers in Jiangsu province
Rural restructuring in China: Theory, approaches and research prospect
DOI:10.1007/s11442-017-1429-x
[本文引用: 2]

Rural restructuring is a process of reshaping socio-economic morphology and spatial pattern in rural territory in response to the changes of elements both in kernel system and external system of rural development, by optimally allocating and efficiently managing the material and non-material elements in the two systems. It aims at ultimately optimizing the structure and promoting the function within rural territorial system as well as realizing the coordination of structure and complementation of function between urban and rural territorial system. This paper establishes a theoretical framework of rural restructuring through elaborating the concept and connotations as well as analyzing the mechanism pushing forward rural restructuring based on the evolution of “elements-structure-function”, and probes the approaches from the three aspects of spatial restructuring, economic restructuring and social restructuring. Besides, the authors argue that the study of rural restructuring in China in the future needs to focus on the aspects of long-term and multi-scale process and pattern, mechanism, regional models, rural planning technology system and standard, policy and institutional innovations concerning rural restructuring as well as the impacts of globalization on rural restructuring, in order to serve the current national strategic demands and cope with the changes of rural development elements in the process of urban-rural development transformation.
基于系统论的土地利用多功能分类及评价指标体系研究
Research on land use functions classification and evaluation system based on system theory
乡村重构的理论认知
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.002
[本文引用: 5]

面向快速城镇化进程中乡村地域日益复杂的人地关系,乡村重构成为地理学研究的重要前沿课题。乡村重构即行为主体通过优化配置和有效管理影响乡村发展的物质和非物质要素,重构乡村社会经济形态和优化地域空间格局的过程。本文在已有研究基础上,基于乡村地域系统的“要素—结构—功能”视角,从乡村重构的行为主体、价值取向和目标定位等方面进一步阐释了乡村重构的概念内涵,剖析了由诱发机制、支撑机制、约束/促进机制、引导机制、引擎机制构成的乡村重构作用机制框架。最后,基于政府行为对推动城乡资源要素优化配置和乡村重构的引领作用,认为有必要重构乡村社会经济的政府干预框架,并对未来中国乡村重构需进一步重点关注的研究内容展开探讨。
Theoretical thinking of rural restructuring
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.002
[本文引用: 5]

With its focus on the increasingly complicated human-environment relationship under the background of rapid urbanization, rural restructuring study has become an important frontier research area of geography. Rural restructuring is a process of reshaping the socioeconomic forms and spatial patterns in rural areas in respond to the changes of factors both internal and external of the system, by optimally allocating and efficiently managing the material and non-material elements of rural development. It aims at ultimately optimizing the structures and improving the functions within rural territorial systems as well as realizing the structural coordination and functional complementation between urban and rural territorial system. Based on the perspective of "elements-structure-function" of rural territorial system, this article first elaborated the concept of rural restructuring from the aspects of behavioral mainstream, value system, and targets. Then, a framework of rural restructuring mechanism was analyzed, which consisted of inducing mechanism, supporting mechanism, constraining/promoting mechanism, guiding mechanism, and driving mechanism. Furthermore, in view of the guiding role of governments in optimal allocation of critical resources and rural restructuring, this article argued that it is necessary to restructure the contours of state intervention in rural societies and economies. Finally, the research contents of rural restructuring in the future were prospected.
基于“要素—结构—功能”的企业商业模式研究
A research on business model of "element-structure-function": An example to monternet
试论社会有机系统的要素、结构和功能
On the elements, structure and function of social organic system
城乡融合区乡村地域多功能空间分异及影响因素: 以福州东部片区为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20221015
[本文引用: 1]

乡村地域多功能是有效破解城乡二元结构、促进城乡融合发展的重要途径。本文以国家城乡融合发展试验区——福州东部片区为研究区,基于乡镇域尺度分析研究区乡村地域多功能空间分异规律与特征,使用地理探测器分析空间分异的影响因素。结果表明:(1)研究区各乡镇的乡村单一功能空间格局特征表现为农业生产功能在沿海小范围聚集,工业发展和生活保障功能主要集中分布在福州城区边缘郊区和南部乡镇,生态保育功能西部山区大于东部乡镇,而旅游休闲功能主要分布在中北部乡镇和平潭岛;(2)依据LSE模型,将研究区乡镇划分为五功能、四功能、三功能、双功能复合区和单功能主导区,其中拥有五、四功能复合区的乡镇共计58个,占比45.68%,说明研究区乡村地域多功能整体上处于较高水平,城乡融合发展基础良好;(3)乡村地域多功能的空间分异受自然环境、社会经济等内外因素的共同影响,自然环境因素塑造了乡村地域初始与特色功能,地理区位因素促进乡村功能的形成与分化,社会经济是优化乡村功能的基础因素,政策资金是推动乡村多功能转型的主导因素。研究结果为进一步推进区域城乡融合发展与乡村振兴提供科学依据。
Spatial differentiation and influencing factors of rural territorial multi-functions in urban-rural integration area: A case study of Eastern Fuzhou
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20221015 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于CiteSpace中国乡村功能研究的知识图谱分析
Knowledge structure of rural function in China: An analysis based on CiteSpace map
DOI:10.1080/00130095.1961.11729540 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于生产组织模式选择超边际分析的战略联盟稳定性边界研究
Study on the stability boundary of strategic alliances based on in framarginal analysis of production patterns
资源禀赋差异与合作利益分配: 辽宁省HS农民专业合作社案例分析
Resource endowment difference and profit distribution of cooperation: A case study of HS Farmer Specialized Cooperative in Liaoning province
对农业产业化经营利益分配机制的思考
Thoughts on the profit distribution mechanism of agricultural industrialization
Status and development trends of Pu'er Tea industrial mechanization and automation