“十四五”是实现2035年“美丽中国建设”目标的关键时期,进一步加快推动自然资源资产负债表编制制度,是深刻把握中国生态文明建设及生态环境形势、提高生态环境治理能力现代化的重要体现。第九次全国森林资源连续清查统计数据显示,森林资源占国土面积的21.63%,2018年生态服务价值为15.88万亿元,GDP总值为91.93万亿元,其生态服务价值占GDP总值的17.27%,这表明森林资源是自然资源的重要构成和经济社会发展的物质基础,在生态文明建设中承担着不可替代的历史使命。近年来中国林地、林木资产稳步增长,但是森林资源消耗形式依然严峻,缺林少绿的总体状况仍未得到根本改善,森林质量不高,生态服务功能不强,森林资源消耗压力依然很大[1]。通过积极探索编制森林资源资产负债表,将有助于进一步完善森林资源有偿使用和生态补偿制度,实现对森林资源资产的有效保护与合理利用。自“十八届三中全会”以来,中国学者已在核算内容与报表形式等方面取得诸多成果,但在负债与生态产品价值计量方面仍缺乏共识[2],严重降低了报表制度的试点效果与推行速度。因此,本文在总结现有森林资源核算研究的基础上,对森林资源核算内容进行补充完善,并对报表编制思路与报送流程做了详细描述,力求构建“高质、务实、管用”的森林资源资产负债表体系。
1 森林资源资产负债表研究进展及评析
1.1 研究进展
探索编制自然资源资产负债表是具有中国特色的重大理论创新[2],旨在采用国家资产负债表的方法,以报表形式核查全国范围内某一时点自然资源的存量,反映一段时期内资源资产变动情况[3]。其本质上是将会计理论运用于政府管理,通过计算资源环境的资产存量与负债消耗量,合理评估政府在资源环境的管理绩效,引导和约束官员行为,以推动资源的合理利用与生态环境的保护。从名称和作用上来看,自然资源资产负债表是基于环境会计理论的一种衍生与应用[4]。因此,森林资源的资产负债表至少应包含资产、负债、所有者权益三部分。但与之不同的是,森林等自然资源负债表不仅需呈现货币价值,更要呈现实物数量,这是由国家资产负债表盘查“家底”的性质决定,且在现有浙江湖州等地的试点中已经达成了共识——遵循先实物后价值、先存量后流量的编制原则[5]。然而,在森林资源的编制方面仍存在一些争议。
首先是森林资源的资产内涵应该包含哪些内容。根据联合国《2012年环境经济核算体系:中心框架》(SEEA-2012)的核算内容,森林资源资产价值包含林地与林木两部分[6],而联合国粮农组织发布的《林业环境经济核算指南——跨部门政策分析工具》(FAO-2004),把研究对象从林地与林木价值扩展到森林生态服务的价值上[4],2013年英国国家统计局也完成了森林资源生态服务价值账户的初步编制;2021年《环境经济核算体系:生态系统核算》(SEEA-EA)发布,各国纷纷开展生态系统核算。森林资源的价值不仅在于提供了林木、林地等实物产品,更重要的是其提供的固碳释氧、调节气候等生态产品为人类创造了赖以生存的生态环境,其对生态环境的作用理应被揭示。所以结合国际经验,森林资源资产至少应包含林地、林木以及生态产品三部分。
其次是森林资源负债是否存在以及如何确定。最早开展绿色资源核算的学者们依据SEEA的框架对负债不予确认[7],即认为不存在资源负债,虽然这样做比较符合国际核算惯例,但缺少负债的报表并不是真正意义上的资产负债表。目前来看,多数学者承认负债的存在并积极探讨其内涵:(1)从资源使用的角度,认为负债是核算期内的资源耗减量[3,8,9],该观点存在两个问题,首先资产的减少并不意味着负债的增加,其次“资源的减少”与“森林资源资产的变动减少”概念易混淆,操作较困难;(2)把资源消耗超过政策红线或自然承载力的部分作为负债[2,10,11],该观点相对合理,但自然承载力如何测量又会增添新的挑战;(3)把污染治理成本、环境保护成本计入负债[12],首先从会计学上说,成本是当期损益,而负债是现时义务,成本不能等同于负债,其次污染的产生与治理范围较难界定,很难区分清楚是由哪种自然资源直接产生;(4)还有学者认为资源质量变化[10]、生态效益减少[3]即是负债,也同样存在难界定、难操作的问题。
再者是森林资源资产负债表的具体形式。现有的研究较多是将其作为自然资源资产负债表框架下的一个子项目,从某种程度上说,自然资源负债表的编制情况即代表了森林资源资产负债表的现状。通过文献梳理发现,中国学者从核算项目、账户类型、价值量化、报表样式等方面进行了较为全面的研究[13],根据编制原则及特点主要可以分为五类。由表1可知,有两类报表不考虑负债的计量,而包含负债计量的报表多以“资源的耗减量”作为计量标准,并没有涉及更丰富的负债内涵;同时关于生态价值方面的研究也相对较少;另外这些报表的研究主要停留在理论探索阶段,报表编制的主体以及编制周期等模糊不清,在中国目前开展的地方试点中应用性并不高。由表2可知,试点地区的报表多以林地、林木资产的核算为主,相对突出的是在呼伦贝尔市、深圳宝安区的试点中尝试对负债进行计量,在湖州市的试点尝试建立生态账户核算森林资源生态系统功能,这从另一方面验证了研究资源负债与生态产品价值的科学性与必要性。
表1 五种森林资源资产负债表理论类型
Table 1
表2 试点地区森林资源资产负债表编制情况
Table 2
| 省(自治区) | 整体编制情况 | 森林资源方面的主要特征 |
|---|---|---|
| 内蒙古 | 率先在呼伦贝尔市、赤峰市开展试点,主要从草原、林地、湿地三方面开始探索。2014—2015年,主要编制《自然资源资产账户(实物量)》调查表,包含森林、草原等实物量资产账户;之后开始尝试探索估值技术,实现对实物账户的价值量化;2017年下半年到2018年,全面完成资源资产负债表编制工作 | 森林资源资产负债表主要统计林地及林木资产的实物量,包括“使用”与“来源”两种统计口径。其中使用方即资源与资产的存量,为时点数;来源方即资源与资产当期消耗量,为时期数。还特别提出负债与权益转换的概念,即当政府的出资部门与自然资源产权管理部门完成产权交接时,该部分负债便转为权益 |
| 贵州 | 主要在赤水市和荔波县进行试点,该试点结合本地自然资源的实际情况,现已完成土地、森林、水资源三份单项资产方案,以及自然资源资产负债表编制方案 | 确立了省级林业资产负债表(实物量表)的内容,分为林地、森林、湿地三类资源账户,包括林地面积等七个一级指标,并在此基础上进一步划分出对应的23个二级指标 |
| 广东 | 在深圳市大鹏新区和宝安区进行试点,其中大鹏新区侧重于生态环境保护,宝安区侧重于工业发展对资源环境的影响,已初步建立自然资源资产价值评估方法体系,包括自然资源资产实物量表、存量表、流量表、价值表、负债表、负债损益表等七大类 | 参照绿色GDP核算中相似替代的计算方法,计算出森林资源资产的货币价值,但是整体报表的编制仍然以实物数量为主 |
| 湖北 | 鄂州市是湖北省唯一的全面改革示范区,主要对土地、林木和水资源进行探索研究。另外在梁子湖区进行生物资源资产负债表编制工作,尝试对生态系统服务价值进行计量 | 林木资源数据方面,结合全国森林资源二类调查结果、历年林地更新情况,通过林地生产模块和档案更新,推算获得非普查年份数据,已完成2011—2015五个年度村级林木资源资产账户 |
| 浙江 | 湖州市已编制完成市及各县区2010—2013年自然资源资产负债表,主要包含土地、水、矿产、林木四类资产账户,对每一类资源均按照存量、流量和质量进行核算 | 将森林资源分属不同的核算账户,在资源账户分别核算土地与林木实物量,尝试在生态账户核算森林资源生态系统功能价值 |
1.2 研究评述
综上所述,在森林等自然资源负债表的编制方面,无论是理论研究还是实践探索均已取得初步成果,但从总体上来看,中国在森林资源资产负债表的编制方面仍处于探索阶段,且存在三个主要问题:
(1)缺少森林资源生态方面的价值核算。中国试行的自然资源资产负债表编制制度参考SEEA框架,没有设立森林资源的专项核算,而是把林地与林木分别归属于不同的资产账户,这样的核算方式,并不能全面直观地反映森林资源的整体价值,一方面林地与林木相互依存,分属不同账户核算存在较严重的重复核算问题[6];另一方面易忽略森林资源生态产品价值,存在低估资产的风险。更重要的是,森林生态服务中净化空气等价值并不能完全进行市场交易,亦不会带来直接的经济流入,其具有公共产品的属性,应将经济价值与公益价值进行单独核算[18,19]。虽然赤水、鄂州等地尝试对森林资源整体进行研究,但重心仍是林地与林木资产核算,较少考虑森林资源的生态产品价值,更忽略了对生态产品价值中公益性价值的列示。
(2)缺少森林资源负债的价值核算。主要原因在于现有研究未能清晰且合理地界定负债的内涵。首先需要明确的是,负债是中性并非负向概念,不能简单地将资源耗减、环境污染等不好的方面归属于负债;其次负债是义务是存量概念,而资源的减少是流量并不是负债本身;再者是环境承载力、污染处理等方面的估算难度较大,可信值较低,并不能真实反映森林资源对经济的贡献度,亦不能表明关联政府对森林资源的受托责任。
(3)森林资源资产负债表编制实操性不高。一方面是报表形式目前为止主要停留在理论探索阶段,有些核算项目与计量方式过于复杂,在实务中较难实现,如权益平衡表中资源负债的多少取决于自然资源资产与资源生态权益之间变化量的比较[17];另一方面是学者们大多专注于核算内容与报表形式的研究,而在报表编制流程、责任单位、报送时间、公布周期等方面的描述不是很清晰,进而降低了报表的适用性与实用性,试点省份的报表也具有一定的区域性特点,尚未在全国范围内推广。
为进一步深化森林资源资产负债表编制的可行性与连续性,需对森林资源资产负债表体系进行再设计完善,通过细化单项报表内容与格式规范、明确编表主体与报送周期,使报表的编制真正成为森林资源动态核算的一项制度性工作。
2 森林资源资产负债表的核算内容
2.1 森林资源资产的内涵与核算
关于森林资源资产的研究,目前主要的争论在于森林资源的生态服务功能是否归属资产的核算范围。首先是产权方面,依据《森林法》第十四条规定“森林资源属于国家所有”,森林资源的生态服务功能与森林资源本身具有不可分割性,因此其生态产品也具有产权确定性;其次是可用货币计量,森林的生态服务功能如同企业的无形资产,没有具体形态却能依附于有形资产产生超越有形资产本身的价值,这些价值较难计量不等同于不用计量,2020年新修订的《森林生态系统服务功能评估规范》发布,已表明对森林生态产品进行货币计量的必要性与可行性;再者是收益方面,森林的生态服务功能具有经济性与公益性并存的特点,其提供的药材、油料等具有市场变现的可能,同时其净化的空气水源等是公益性的人类惠益,从广义的收益角度考虑,森林资源生态效益符合“能够产生预期收益”的要求。综上,森林资源的生态服务功能价值具有“产权明晰、产生收益、可靠计量”的资产属性,森林资源资产应是核算区域内能产生经济利益、生态效益和社会福祉的森林资源整体[13]。因此,其核算范围包含林地、林木实体资产以及生态产品三部分。
表3 林地资产与林木资产统计表
Table 3
| 林地资产 | 林木资产 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 用地类型 | 面积/hm2 | 树种 | 面积/hm2 | 蓄积/m3 | |
| 1.乔木林地 | 1.用材林 | ||||
| 2.竹林地 | 2.防护林 | ||||
| 3.疏林地 | 3.特种用途林 | ||||
| 4.灌木林地 | 4.能源林 | ||||
| 4.1特殊灌木林地 | 5.经济林 | ||||
| 4.2一般灌木林地 | 6.竹林 | ||||
| 5.未成林造地 | 7.其他林木 | ||||
| 5.1未成林人工造林地 | 7.1散生木 | — | |||
| 5.2未成林封育地 | 7.2四旁树 | — | |||
| 6.迹地 | 合计 | ||||
| 6.1采伐迹地 | 乔林木 | ||||
| 6.2火烧迹地 | 1.幼龄林 | ||||
| 6.3其他迹地 | 2.中龄林 | ||||
| 7.苗圃地 | 3.近熟林 | ||||
| 合计 | 4.成熟林 | ||||
| 5.过熟林 | |||||
| 森林覆盖率% | 合计 | ||||
表4 林地资产与林木资产定价方法[1]
Table 4
| 资产类别 | 核算指标 | 核算方法 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 林地资产 | 林地 | ||
| 林木资产 | 幼龄林 | ||
| 中龄林 | |||
| 近成过熟林 | W为木材销售总收入(元);C为木材生产经营成本(包括采运成本、有关税费)(元);F为木材生产经营段利润(元) | ||
| 经济林 | A为盛产期年净收益(元/a);u为经济寿命期(a) | ||
| 竹林 | V为竹林价值(元);A为竹林的年净收益(元/a) |
(2)生态产品。与突出生态系统功能特性的生态服务价值评估不同,生态产品主要是从经济与社会意义角度出发,特指依附于森林资源实体资产、为人类提供多样化需求的最终产品或服务[18]。借鉴SEEA-EA对生态产品的分类以及生态系统生产总值(GEP)的核算项目,本文将森林资源生态产品分为供给产品②(② 为避免重复核算的问题,供给产品主要指除木材以外的其他林下经济产品。)、调节服务产品以及文化服务产品三类。森林生态产品价值是对一定时期内产品或服务的流量核算,既具有经济性也有公益性[19]。其中,药材、油料等供给产品以及生态旅游等文化服务能带来经济流入,而调节服务以及森林文化遗产等带有公共产品的属性,不具有经济价值,因此应对森林生态产品不同流量价值进行单独核算[18](表5)。另外,森林资源实体资产核算是存量价值,与生态产品的流量价值不能简单地直接相加,还需通过累计折现的方法将流量价值转化为存量价值[19](表6)。
表5 森林资源生态产品统计表
Table 5
| 生态产品类别 | 核算类别 | 价值类型 | 指标类别 | 单位 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.供给产品 | 1.1林产品供给 | 经济价值 | 干果产品 | t | |
| 森林药材 | t | ||||
| 油料 | t | ||||
| 林产工业原料 | t | ||||
| 其他林产品 | t | ||||
| 2.调节服务产品 | 2.1保育土壤 | 公益价值 | 固土 | t | |
| 保肥 | t | ||||
| 2.2涵养水源 | 调节水量 | m3 | |||
| 净化水质 | t | ||||
| 2.3固碳释氧 | 固碳 | t | |||
| 释氧 | t | ||||
| 2.4净化环境 | 吸收气体污染物 | t | |||
| 2.5森林防护 | 防风固沙 | t | |||
| 农田防护 | hm2 | ||||
| 3.文化服务产品 | 3.1森林旅游 | 经济价值 | 旅游人次 | 人 | |
| 旅游收入 | 万元 | ||||
| 3.2公益性文化服务 | 公益价值 | 人林共生时间[21] | h |
表6 生态产品价值定价方法
Table 6
| 核算内容 | 核算指标 | 计算公式 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 供给产品 | 林产品 供给 | U为森林非林木产品价值(元/a); | |
| 调节服务 产品 | 固土 | ||
| 保肥 | i为氮、磷、钾;V为林分保肥价值(t/a);D为林地与无林地的土壤侵蚀模数差 [t/(hm2·a)];S为森林面积(hm2);Wi为单位森林土壤中含氮磷钾量(%);Ti为化肥中氮磷钾的比例(%);Pi为化肥中氮磷钾的销售价格(元/t);M为单位森林土壤中有机质含量(%);P为有机质价格(元/t) | ||
| 调节水量 | G为林分年调节水量(m3/a);A为林分面积(hm2);P为林分林外降水(mm/a);E为林分蒸散量(mm/a);C为林分地表快速径流量(mm/a);U为森林年调节水量价值(元/a);Ck为水资源市场交易价格(元/m3);t为价格参数换算系数 | ||
| 净化水质 | G为林分年调节水量(m3/a);A为林分面积(hm2);P为林分林外降水(mm/a);E为林分蒸散量(mm/a);C为林分地表快速径流量(mm/a);U为林分净化水质价值(元/a);K为污水处理成本(元/m3);t为价格参数换算系数 | ||
| 固碳 | G为年固碳量(t/a);A为林分面积(hm2);R为CO2中碳的含量27.27%;B为林分年净生产力 [t/(hm2·a)];F为单位面积林分土壤年固碳量 [t/(hm²·a)];U为林分年固定碳价值(元/a);C为固碳价格(元/t);t为价格参数换算系数 | ||
| 释氧 | G为林分年释氧量(t/a);A为林分面积(hm2);U为林分年释氧价值(元/a);B为林分年净生产力 [t/(hm2·a)];C为制造氧气的价格(元/t);t为价格参数换算系数 | ||
| 吸收污染物 | i为SO2、NOx、HF;Gi为林分年吸收污染物的量(t/a);Qi为单位面积林分吸收污染物 [kg/(hm2·a)];A为林分面积(hm2);U为吸收污染物价值(元/a); | ||
| 防风固沙 | U为森林防风固沙功能的价值量(元/a);A为林分面积(hm2);K为治理沙漠出资额度 [元/(hm2·a)];t为价格参数换算系数 | ||
| 农田防护 | U为森林农田防护功能的价值量(元/a);Va为农作物、牧草价格(元/kg);ma为农作物、牧草平均增产量(kg/a);t为价格参数换算系数 | ||
| 文化服务 产品 | 森林旅游 | U为森林旅游价值(元/a);Uk为各林区旅游业与休闲产业的收入(元/a) | |
| 公益性 文化活动[21] | Vpi为区域内森林文化物理量(cy);Pi为区域人口数量(人);Fi为区域内森林覆盖率(%);Mi、Mt分别为区域内、全国单位面积森林蓄积量(m3);Tfi为区域内森林共生的基本时间(h);Vc为一年内区域森林文化价值量(元/a); | ||
| 存量价值 | 流量现 值加总[19] | P为生态产品存量价值(元); |
2.2 森林资源负债的内涵与核算
会计学认为资产与负债的产生是由于不同主体之间发生了交易和事项[7]。换言之,自然资源负债的产生也必然存在于交易或事项之中,核心问题在于交易的主体是谁?“负”了谁的债?一种观点认为是经济系统与生态系统的交易,“负”了生态系统,将资源耗减、质量下降等确认为负债;另一种从代际公平与可持续发展角度出发,则认为未来人是债权人。本文认同后者,即自然资源受益者(当代人)对受损者(未来人)的负债[20],当代人在使用森林等自然资源会造成气候或环境的破坏,客观上损害了未来人对资源的开发与使用,因此需要承担补偿的义务;当代人通过在特定期限内对资产的合理利用,开发出新资源(尤其是不可再生资源)用于债务的偿还,周而复始即可实现资源的永续利用,而各级政府作为代理人行使监督与管理职责。所以,自然资源负债本质上也是特定主体需要在未来进行偿付的义务,包括主动的维护和管理成本,以及被动的治理和恢复义务。同理森林资源负债即为国家等责任主体为实现森林资源的可持续发展而需要偿付的资源管理、环境保护、生态修复和维护的现时义务,核算范围至少应包括以下四项内容,并根据“债权发生制”原则对负债事项进行计量(表7)。
表7 森林资源负债详情表
Table 7
| 负债 类型 | 事项 | 期初年 | 期初+1年 | …… | 期末-1年 | 期末年 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积 | 金额 | 面积 | 金额 | 面积 | 金额 | 面积 | 金额 | 面积 | 金额 | |||||||
| 生态 恢复 | 更新采伐迹地 | |||||||||||||||
| 更新火烧迹地 | ||||||||||||||||
| 退耕还林 | ||||||||||||||||
| 小计 | ||||||||||||||||
| 生态 维护 | 林相改造 | |||||||||||||||
| 生态补偿投入 | ||||||||||||||||
| 小计 | ||||||||||||||||
| 灾害 防治 | 护林防火及其宣传、培训等 | |||||||||||||||
| 森林病虫害防治及其宣传、培训等 | ||||||||||||||||
| 小计 | ||||||||||||||||
| 超载 补偿 | 违规占用退还 | |||||||||||||||
| 低于红线补偿 | ||||||||||||||||
| 小计 | ||||||||||||||||
| 合计 | ||||||||||||||||
(1)应付生态恢复。主要指各级林业主体及政府为恢复原有森林植被样貌和生态系统服务功能而付出的成本,包括更新采伐迹地、更新火烧迹地、退耕还林等事项所付出的全部花费。
(2)应付生态维护。主要指各级林业主体及政府定期对森林资源存续状态进行修复所需要付出的成本,包括林相改造与生态补偿性投入等。
(3)应付灾害防治。主要指各级政府为预防和补救各类森林灾害所需要付出的成本,包括护林防火、森林病虫害防治的宣传与培训等费用支出。
(4)应付超载成本。主要指各级政府需要支付的因对森林资源的不合理使用而造成的过度损耗成本,包括违规占用退还、低于政策红线补偿等。
2.3 森林资源净权益的内涵与核算
森林资源净权益是一个国家或地区所拥有的森林财富的总和,在数量上应等于森林资源资产减去森林资源负债,即森林资源资产扣除森林资源负债后由森林资源所有者持有的净资产;在经济意义上反映的是某一个地区政府投入的原始资本、森林资源资本增值与消耗后归属于国家和集体的剩余收益;其管理意义是展现某区域一定时间内对森林资源管理和培育的净成果,是反映政府管理绩效的关键指标[13],即森林净权益应包含林地、林木与生态产品权益三部分。另外,需特别说明的是,在进行报表填列时,森林资源净权益是根据产权明晰的资源存量进行填列,而林地与林木资产的实物量也是由资源存量决定,有可能出现“资产”与“净权益”在数值上完全一致的情况,显然不符合基本的记账原则。所以为实现“森林资产=森林负债+森林净权益”在报表内的勾稽平衡,本文特别设立“应补偿权益”项目[22]。该项目相当于森林净权益的备抵科目,在数值上等于森林负债中林地与林木各项支出的累计额,经济学意义为森林资源资产权益主体所必须承担和支付的那一部分现时义务。
3 森林资源资产负债表编制体系的改进
3.1 森林资源资产负债表的编制思路
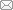
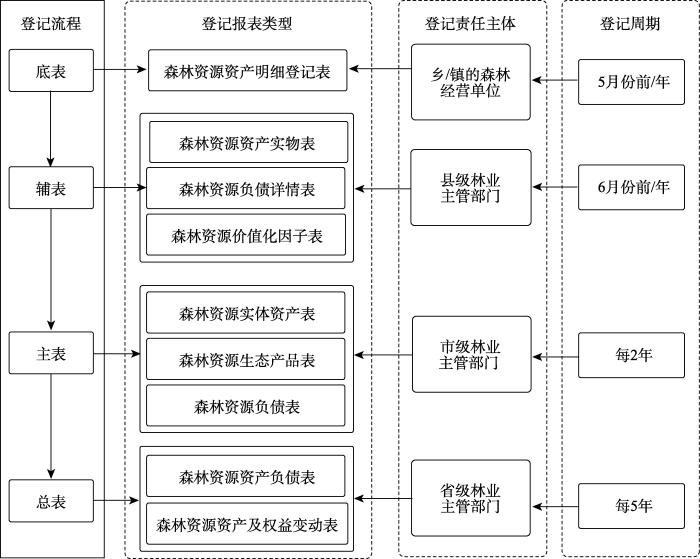
编制森林资源资产负债表应坚持“内容全、质量高、便操作”的基本要领,不仅能如实反映某地区森林资源的实际存量及变动情况,促进资源环境与社会经济实现协调发展,还要实现核算数据的集约化并展现数据的相互关系,便于报表阅读者在最短时间内了解某区域特定时点森林资源资产的管理状况,增强报表编制工作的连续性与操作性。本文依据“底表—辅表—主表—总表”的思路(图1),先对森林资源资产明细进行详细统计;而后汇总单位面积森林的实物量及其价值参数,使区域内森林资源实物能够实现货币化计量;最后在单项核算的基础上构建完整的森林资源资产负债表。
图1
3.2 森林资源资产负债表的框架体系
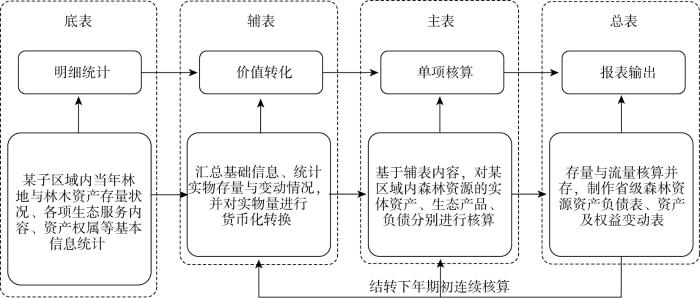
森林资源资产负债表需兼顾“清家底”和“明责任”两大功能,全面揭示政府对各类资源的占有与利用程度,科学评价领导干部任职期间生态保护责任的履行情况,引导树立经济增长与环境保护同步的新型政绩观。因此,本文将报表的编制与中国现有的行政体系结合起来,按照“国家为主导、省/市做统筹、县/乡打基础”的原则,从实物存量核实再到资产负债价值量核算,分级落实,层层推进,力求构建一个“高质、务实、管用”的森林资源资产负债表体系(图2)。
图2
(1)底表的内容及编制要求
(2)辅表的内容及编制要求
表8 森林资源实物表
Table 8
| 编制单位 年 月 日 单位:hm2、t、m3等 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 资产项目 | 单位 | 期初存量 | 本期变动量 | 期末存量 |
| 1.林地资产 | ||||
| …… | ||||
| 2.林木资产 | ||||
| …… | ||||
| 3.生态产品 | ||||
| …… | ||||
注:本期变动情况,增加时正常填列,减少时带“-”填列
表9 森林资源资产价值化因子表
Table 9
| 核算指标 | 价值量参数 | 单位 | 2022年标准 | 参数来源[1,23] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 林地 | 林地投资收益率 | % | — | 中国森林资源核算研究项目组第三次研究公布的参数,为2%~3% |
| 林木 | 林木投资收益率 | % | — | 中国森林资源核算研究项目组,乔木4.5%,竹林、经济林6% |
| 土壤保持 | 挖取单位体积土方费用 | 元/m3 | 126 | 中国森林资源核算研究项目组 |
| 保肥 | 化肥中磷酸二铵的价格 | 元/t | 4053 | 中国化肥网,磷酸二铵中氮含量14%,磷含量为15% |
| 化肥中氯化钾的价格 | 元/t | 3700 | 中国化肥网,氯化钾中钾含量为57% | |
| 水源涵养 | 水价 | 元/m3 | 1 | 中国水权交易所水权交易价 |
| 空气净化 | 二氧化硫环境保护税额 | 元/kg | 6.27 | 《中华人民共和国环境保护税法》,大气污染物税额1.2~12元/污染当量;污染当量值:二氧化硫0.95 kg、氮氧化物0.95 kg、氟化物0.87 kg;取税额中位数计算价格 |
| 氮氧化物环境保护税额 | 元/kg | 6.27 | ||
| 氟化物排环境保护税额 | 元/kg | 5.74 | ||
| 固碳 | 碳交易价格 | 元/t | 58 | 全国碳排放权交易市场 |
| 释氧 | 氧气价格 | 元/t | 1200 | 中国森林资源核算研究项目组 |
| 防风固沙 | 生态认购价 | 元/hm2 | 7312 | 中国森林资源核算研究项目组 |
| 农田防护 | 农作物价格 | 元/kg | 4.36 | 中国农业信息网 |
| 公益性文化 | 人林共生时间 | h/d | 2 | 国家统计局 |
| 区域文化综合指数 | — | — | 森林文化综合指数标准为0~2 [21] | |
| 流量现值 | 折现率 | % | 5 | 资本资产定价模型[24] |
注:价值量参数每个区域的情况略有差别,可参考国家公布的相关指导文件并结合当地实际情况填写。
(3)主表的内容及编制要求
表10 森林资源实体资产表
Table 10
| 编制单位 年 月 日 单位:hm2、m3、元等 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 资产项目 | 期初余额 | 本期变动 | 期末余额 | ||||
| 行次 | 实物量 | 价值量 | 实物量 | 价值量 | 实物量 | 价值量 | |
| 林地资产 | 1 | ||||||
| …… | … | ||||||
| 林木资产 | … | ||||||
| …… | … | ||||||
| 合计 | … | ||||||
(4)总表的内容及编制要求
表11 森林资源资产负债表
Table 11
| 编制单位:湖北省林业局 201*年 12 月 31 日 单位:万hm2、万m3、亿元等 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 资产项目 | 期初余额 | 期末余额 | 负债和净 权益项目 | 期初余额 | 期末余额 | ||||||||
| 实物 | 价值 | 实物 | 价值 | 实物 | 价值 | 实物 | 价值 | ||||||
| 一、资产 | 1 | 二、负债 | 27 | ||||||||||
| (一)林地 资产 | 2 | (一)应付 生态恢复 | 28 | 1.44 | 3.25 | 0.47 | 1.82 | ||||||
| 1.乔木林地 | 3 | 589.85 | 1342.48 | 606.67 | 1868.17 | (二)应付 生态维护 | 29 | — | 33.02 | — | 65.77 | ||
| 2.竹林地 | 5 | 16.94 | 54.54 | 17.92 | 77.36 | (三)应付 灾害防治 | 30 | 29.27 | 0.66 | 39.35 | 3.08 | ||
| 3.疏林地 | 6 | 2.82 | 3.33 | 3.2 | 4.95 | (四)应付 超载补偿 | 31 | 2.93 | 6.52 | 0.44 | 3.02 | ||
| 4.灌木林地 | 4 | 160.99 | 123.25 | 162.55 | 166.05 | 负债合计 | 32 | 33.64 | 43.45 | 40.26 | 73.69 | ||
| 5.未成林造地 | 9 | 62.65 | 81.47 | 68.47 | 116.16 | 三、净权益 | 33 | ||||||
| 6.迹地 | 8 | 16.03 | 19.13 | 16.64 | 25.45 | (一)林地 净权益 | 34 | ||||||
| 7.苗圃地 | 7 | 0.57 | 7.18 | 0.64 | 10.82 | 1.国有林地 | 35 | 66.41 | 121.89 | 66.86 | 173.24 | ||
| 林地资产合计 | 10 | 849.85 | 1631.38 | 876.09 | 2268.96 | 2.集体林地 | 36 | 803.44 | 1509.49 | 809.23 | 2095.72 | ||
| (二)林木资产 | 11 | 3.其他林地 | 37 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| 1.用材林 | 12 | 13546.94 | 553.09 | 17729.04 | 954.39 | 林地净权益 合计 | 38 | 869.85 | 1631.38 | 876.09 | 2268.96 | ||
| 2.防护林 | 13 | 12974.64 | 562.45 | 16074.06 | 931.34 | (二)林木 净权益 | 39 | ||||||
| 3.特种用途林 | 14 | 2004.44 | 69.98 | 2451.08 | 119.27 | 1.国有林木 | 40 | 5484.02 | 273.31 | 5501.65 | 380.51 | ||
| 4.能源林 | 15 | 214.07 | 38.19 | 225.93 | 128.67 | 2.集体林木 | 41 | 5324.45 | 265.35 | 5467.32 | 378.14 | ||
| 5.经济林 | 16 | 26.86 | 149.67 | 27.8 | 292.98 | 3.个人林木 | 42 | 20516.22 | 1022.43 | 28610.94 | 1978.83 | ||
| 6.其他林木 | 17 | 2557.74 | 105.13 | 3072 | 166.01 | 4.其他林木 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 7.竹林 | 18 | — | 82.58 | — | 144.82 | 林木净权益 合计 | 44 | 31324.69 | 1561.09 | 39579.91 | 2737.48 | ||
| 林木资产 合计 | 19 | 31324.69 | 1561.09 | 39579.91 | 2737.48 | (三)生态产 品权益a | 45 | — | 1137.61 | — | 2031.93 | ||
| (三)生态 产品 | 20 | 生态产品 权益b | 46 | — | 2004.18 | — | 2943.73 | ||||||
| 1.供给产品a | 21 | — | 508.71 | — | 666.17 | 减:应补偿权益 | 47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 2.调节服务 产品b | 22 | — | 649.02 | — | 869.68 | 1.应补偿 林地权益 | 48 | 33.64 | 43.45 | 40.26 | 73.69 | ||
| 3.文化服务 产品a | 23 | — | 628.90 | — | 1365.76 | 2.应补偿 林木权益 | 49 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 文化服务 产品b | 24 | — | 1355.16 | — | 2074.05 | 应补偿 权益合计 | 50 | 33.64 | 43.45 | 40.26 | 73.69 | ||
| 生态产品 合计 | 25 | — | 3141.79 | — | 4975.66 | 净权益 合计 | 51 | — | 6290.81 | — | 9908.41 | ||
| 资产合计 | 26 | — | 6334.26 | — | 9982.10 | 负债和净 权益合计 | 52 | — | 6334.26 | — | 9982.10 | ||
注:a代表经济价值,b代表公益价值。
表12 森林资源资产及权益变动表
Table 12
| 编制单位:湖北省林业局 | 201*年12月31日 | 单位:万hm2、万m3、亿元等 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变动项目 | 本期增加 | 本期减少 | 本期净变动 | |||||
| 实物量 | 价值量 | 实物量 | 价值量 | 实物量 | 价值量 | |||
| 一、资产 | ||||||||
| (一)林地资产变动 | 57.16 | 931.32 | 30.92 | 293.74 | 26.24 | 637.58 | ||
| (二)林木资产变动 | 11551.87 | 1881.92 | 3296.65 | 705.53 | 8255.22 | 1176.39 | ||
| (三)生态产品经济价值变动 | — | 894.32 | — | 0 | — | 894.32 | ||
| 生态产品公益价值变动 | — | 939.55 | — | 0 | — | 939.55 | ||
| 资产变动合计 | — | 4647.11 | — | 999.27 | — | 3647.84 | ||
| 二、负债变动项目 | ||||||||
| (一)应付生态恢复 | 0 | 0 | 0.97 | 1.43 | -0.97 | -1.43 | ||
| (二)应付生态维护 | — | 32.75 | — | 0 | 0 | 32.75 | ||
| (三)应付灾害防治 | 10.08 | 2.42 | 0 | 0 | 10.08 | 2.42 | ||
| (四)应付超载补偿 | 0 | 0 | 2.49 | 3.50 | -2.49 | -3.50 | ||
| 负债变动合计 | 10.08 | 35.17 | 3.46 | 4.93 | 6.62 | 30.24 | ||
| 三、净权益变动合计 | ||||||||
| (一)林地资产权益 | 6.24 | 637.58 | 0 | 0 | 6.24 | 637.58 | ||
| (二)林木资产权益 | 8255.22 | 1176.39 | 0 | 0 | 8255.22 | 1176.39 | ||
| (三)生态产品经济权益 | — | 894.32 | — | 0 | — | 894.32 | ||
| 生态产品公益权益 | — | 939.55 | — | 0 | — | 939.55 | ||
| 净权益变动合计 | — | 3647.84 | — | 0 | — | 3647.84 | ||
4 森林资源资产负债表的应用
4.1 森林资源资产负债表及变动表编制
根据《中国林业统计年鉴》、森林资源连续清查与二类调查等数据资料,并结合本文的报表编制思路,编制湖北省201*年森林资源资产负债表及变动表,其中期初与期末跨度为五年,并根据农产品生产价格指数中的林业产品价格指数,将期初数值调整为期末年度的价格水平。
4.2 森林资源资产负债表及变动情况分析
由表11、表12可知,201*年湖北省资源森林覆盖率为39.61%,资产负债率为0.74%,均处于合理区间,表明湖北省森林资源管理工作进行较好。同时与期初相比五年间湖北省森林资产实物量与价值量都呈现出双增长趋势,林地实物量增加26.24万hm2,增长3.09%,林地资产价值增加637.58亿元,增长39.08%;林木资产实物量增加了8255.22万m3,增长26.35%,林木资产价值增加1176.39亿元,增长38.90%;生态产品经济性价值增加894.31亿元,增长78.61%;生态产品公益性价值增加939.55亿元,增长46.88%。取得这些成绩的主要原因在于,一是近些年湖北省大力推进多项造林绿化工程,林地面积稳中有增,其中未成林造地面积增长了9.29%,乔木林地增长了2.85%,二者贡献了林地资产86.28%的增长额;二是各级林业部门近年连续制定多项林业保护与发展政策,各种类林木均有显著增长;三是不断完善森林生态建设与维护,以及对生态美学、森林文化遗产等进行广泛宣传,生态产品价值中公益性价值增长最为突出,其增长量占生态产品价值总增长量的51.23%。
负债方面,应付生态恢复与应付超载补偿较期初有所下降,即在更新采伐与火烧迹地、退耕还林、违规占用补偿林地等方面,湖北省取得一定成效;但总体上看,近五年湖北省森林资源负债仍处于上升状态,其中应付生态维护方面缺口较大,同时也为管理当局敲醒了警钟,仍需加大生态资金投入力度,促进森林生态系统的快速恢复。
5 结论与讨论
本文分别从理论与实践两个角度对现有森林资源负债表的编制情况进行梳理,并在此基础上秉承“内容全、质量高、便操作”的原则,构建了“底表+辅表+主表+总表”的报表体系。与现有研究相比,本文完善了森林资源资产核算的内容,尤其是对生态产品的经济性与公益性价值进行单独核算,既避免了林地与林木分属不同账户可能存在的重复核算问题,也规避了不计算森林资源生态产品价值引起的低估资产的风险。同时,从代际公平的角度对森林资源负债内涵进行界定,保证了报表内容的完整性;最后,以服务各级政府森林资源资产管理受托责任的目的,与中国现有的四级行政区结合起来,对报表的编制主体与报送周期进行了明确陈述,详细设计了一系列表格,并以湖北省为例进行省级森林资源资产负债表的编制,有利于进一步增强报表制度的可操作性与连续性。
但本文仍存在以下不足:关键的核算难点问题仍然存在,对生态产品价值的计量只是提供了计算公式,但因篇幅问题,未能对分布式测算方法[1]展开详细研究;其次只是为森林资源资产负债表的编制贡献了一种思路,但在实际运用中可能存在的执行难、推行难等问题,文中也未提及;最后,受到基础性数据的限制,本文的应用性研究只编制了省级森林资源资产负债表,缺少对市级、县级报表的报表展示。因此后续研究需继续对关键核算难点进行探索,尝试用更全面的方法对森林资源资产负债表各项目进行核算;加大调研走访力度,理清报表制度推行过程中的真正阻碍因素,同时加强对基础性数据的搜寻与整理,探索建立森林资源资产数据库,促进森林资源资产负债表编制制度的顺利推行,服务于国家经济社会发展战略的需要。
参考文献
A basic framework for the compilation of a forest resource balance sheet
DOI:10.18402/resci.2018.05.06
[本文引用: 4]

It is a major institutional innovation to compile balance sheets of natural resources in ecological civilization construction. Forest resources are an important part of natural resources. Strengthening forest resource supervision and management in each government level is needed. At the same time, this work will assist related forestry and natural resource management institutes carry out assessment of natural resource assets. This paper is based on a review of forest resource accounting at home and abroad, and on the preparation of relevant literature on natural resource balance sheets. Through learning from the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting 2012, edited by the UN and other international institutions, and previous research results on natural resource balance sheets we put forward forest resource assets and liabilities. These two concepts have strong relationships with the three-level accounting framework, based on forest resource management requirements which should be combined by forest resource entities accounting, forest resource accounting with operational rights, and forest resource accounting use rights. We investigated and discussed forms and formulas of the balance sheet of forest resources. We provide a deeper analysis of the balance sheet accounting framework for forest resource assets and propose forms of forest resource inventory and change tables and forest resource balance sheets. Combined with levels of forest resource entities, forest resource with operational rights and forest resources with use rights, we built an accounting framework in three levels of a forest resource balance sheet.
Issues regarding the compilation of the natural resource balance sheet
DOI:10.18402/resci.2017.09.01
[本文引用: 3]

Exploring the compilation of a natural resource balance sheet (NRBS)and its practical application is of great importance to promoting the construction of an ecological civilization. As a new concept there are no precedents for this framework. At present,the investigation of operationally compiling NRBS is in its initial stage of exploration. So,the compilation of NBRS should be brought into the establishment of the related technical norms and standards. Here,we summarize NRBS research and combine our NRBS compiling practice with the example of the Huzhou Pattern and Chengde Pattern. In this framework,from foundation to application and from theory to practice,we discuss what NRBS is and how to compile one. We also describe several other aspects of the NRBS,such as the conceptual framework,technological pathways,principles,reporting system and table patterns. We found that the NRBS is an accounting,statistical and management statement of natural resources. The balance sheet may reflect synthetic characteristics of natural resource assets. The basic principle and possible pathways for compiling NRBSs involves six principles and three aspects:physical and monetary terms,quantity and quality terms,stock and flow terms,category and integration terms,scientific and practical terms. The balance-sheet of natural resources involves at least the following balance-sheet,one summary sheet,four classification sheets and two extension sheets or six primary sheets. We hope to promote and perfect the NRBS system through investigation and practical application across many regions.
湖州/安吉: 全国首张市/县自然资源资产负债表编制
First report of the national natural resources balance sheet for Huzhou city and Anji county
自然资源资产负债表研究现状、评述与改进方向
Rsearch status, literature review and improvement direction of the natural resource balance sheet
我国森林资源资产平衡表的编制工作研究
以国际规范与实践为视角
The research on preparing the balance sheets of Chinese forest resource assets: From the perspective of international standards and practices
自然资源资产负债表中的负债问题研究
Research on the liabilities of natural resources in the balance sheet of natural resources
扩展的自然资源核算: 以自然资源资产负债表为重点
Comprehensive accounting of natural resources: Focusing on the balance sheet of natural resources
自然资源资产负债的界定及其核算思路
DOI:10.18402/resci.2018.05.02
[本文引用: 2]

自然资源资产负债表是十八届三中全会为生态文明建设与社会经济可持续发展提出的全新概念。因此,探索各种自然资源资产负债表编制的框架与方法、界定并核算自然资源资产负债对于编制自然资源资产负债表具有极其重要的意义。本研究首先从自然资源资产负债的经济学本质出发,结合自然资源资产负债产生的前提、途径以及界定依据,阐述自然资源资产负债的基本内涵;在此基础上,从可再生资源数量变化、不可再生资源数量变化和自然资源质量变化三个方面对因自然资源“过度”消耗而产生的自然资源资产负债进行界定;最后,以森林资源、水资源、矿产资源和土地资源为研究对象,从资源可持续利用阈值和国家政策红线两个方面提出了自然资源资产负债核算的基本思路,以期为自然资源资产负债表中的负债界定及其核算提供借鉴。
The definition and accounting approaches towards natural resource liabilities
DOI:10.18402/resci.2018.05.02
[本文引用: 2]

Natural resource asset balance sheets(NRABs)were proposed in 2013 for ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in China. Defining and accounting natural resource liabilities are most important in compiling natural resource asset balance sheets. In this study we illumined the basic connotation of natural resource assets and liabilities via economic properties, preconditions of liabilities, and routes of induced liabilities by natural resource overuse. On this basis we defined categories of natural resource liabilities for quantitatively and qualitatively changes in renewable resources and non-renewable resources caused by excessive consumption. Finally, we proposed methods for natural resource liabilities accounting of land resources, water resources, forest resources and mineral resources. Hopefully this study provides suggestions for compiling natural resource assets balancing sheets. Our research results showed that natural resource liabilities are special liabilities, which should have basic characteristics of liabilities and generated in the process of resource utilization; the sustainability of natural resource utilization is an important basis for defining natural resource liabilities. The change in the quantity and quality of natural resources was the root cause of generating natural resource liabilities, so we proposed that natural resource liabilities of renewable resources was the difference between the amount of resource exploitation and renewables. Natural resource liabilities of non-renewable resources is the difference in resource consumption between the actual exploitation-utilization ratio and the standard exploitation-utilization ratio, and building a qualitative transfer matrix of natural resources accounting for natural resource liabilities arising from changes in the quality of natural resources according to existing national quality classification systems.
自然资源资产负债表编制研究: 以林木资源为例
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.20170178
[本文引用: 1]

自然资源资产负债表是促进资源和经济可持续发展的有效工具,然而,在其编制过程中所涉及的基本理论问题,学术界并未达成共识。论文认为:1)自然资源资产具有两种形式,一种是客观存在的自然资源,另一种是进入经济体系、参与经济过程的自然资源,只有后者才具有相应的自然资源负债;2)自然资源负债是经济主体对自然资源的过度消耗而导致的一种现时义务,其中,过度消耗可以通过设定负债临界值的方法予以确认;3)不同自然资源的负债临界值确认方法不同,以林木资源为例,其负债临界值应为兼顾林木可持续发展以及非经济效益的最大可开采量,将超过最大可开采量的消耗量确认为自然资源负债;4)与自然资源资产相对应,自然资源资产负债表的表式也具有两种形式,并且两者之间存在勾稽关系。
Study on the preparation of natural resources balance sheet: A case study of forest resources
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.20170178
[本文引用: 1]

Natural resources balance sheet is an effective tool to promote the sustainable development of resources and economy. Nevertheless, academics have not reached a consensus on the basic theoretical issues involved in its preparation process, such as definitions of natural resources balance sheet elements, measurements of natural resources liabilities, basic forms of natural resources balance sheet. This study tries to discuss the preparation of natural resources balance sheet beginning with these basic theoretical problems. This study draws the following conclusions: 1) There are two basic purposes of natural resources balance sheet. One is to reflect the status and changes of natural resources assets, the other is to reflect the resources and environment costs of economic development and set up lifelong accountability system for ecological and environmental damages. Corresponding to the two purposes of natural resources balance sheet, there are two sorts of natural resources assets, that one is objective natural resources assets and the other is implicit natural resources assets that have come into economic system and participated in economic process. Only the latter type has corresponding natural resources liabilities. 2) Natural resources liability is a kind of current obligation which is caused by excessive depletion of natural resources. The excessive depletion of natural resources can be identified by setting a threshold of liability that the natural resources depletion exceeding the threshold can be considered as excessive depletion. 3) The thresholds of different natural resources are set by different methods. For instance, the set of the liability threshold of forest resources should consider the sustainable development and non-economic benefits such as ecological and social values. A natural resources liability of forests is thus defined as the consumption amount that exceeds the threshold of liability. 4) Accordingly, there are two kinds of natural resources balance sheet. One is natural resources assets account in natural, and the other is natural resources balance sheet in the usual sense. There is multi-relationship between the two kinds of forms.
基于复式记账的自然资源资产负债表平衡关系研究
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20180846
[本文引用: 2]

自然资源资产负债表的平衡关系研究是编制自然资源资产负债表和开展自然资源核算的理论基础。由于对自然资源产权关系和价值活动认识的不一致,对于自然资源资产负债表平衡关系的认识存在不同,也导致了自然资源资产负债表编制工作长期陷入争议状态。对于《环境经济核算体系2012:中心框架》(System of Environmental-Economic Accounting 2012,SEEA 2012)的“期初+增加-减少=期末(期初-减少=期末-增加)”四柱平衡基本认识一致,但对于“资产=权益”、自然资源负债的确认等是否列入编制自然资源负债表的框架存在较多争议。自然资源相关研究的学者较多认为应基于SEEA 2012的“期初+增加-减少=期末(期初-减少=期末-增加)”四柱平衡编制自然资源资产负债表,并分别编制自然资源资产表、负债表,报表基于统计调查结果列示,因此严格意义上也无法称之为自然资源资产负债表,准确说应该称之为自然资源统计报表;会计学界相关研究的学者较多认为应基于“资产=负债+权益”编制自然资源资产负债表,采用会计学复式记账进行核算,但由于对自然资源属性认识存在差异,部分学者提出的“资产-负债=净资产”的概念理解也不统一,没有学者据此设计自然资源复式记账的过程核算体系。论文基于资源科学和会计学理论的交叉研究成果,以资源产权属性和价值属性为基础,构建了自然资源资产负债表的框架体系,明确自然资源资产负债表采用复式记账,对自然资源资产负债表的静态平衡关系和动态平衡关系进行了研究。基于复式记账的自然资源资产负债表静态平衡关系总体表示为“资产=权益”,这是借贷记账的理论基础;动态平衡关系表示为:“期初+增加-减少=期末(期初-减少=期末-增加)”、“入-出=余”,这是进行自然资源资产核算的理论基础。论文进一步分析了基于复式记账的自然资源核算体系恒等式及自然资源资产负债表的框架。
Research on equilibrium relation of natural resources balance sheet based on double-entry bookkeeping
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20180846
[本文引用: 2]

The equilibrium relationship of natural resources balance sheet is the theoretical basis for compiling natural resources balance sheet and developing natural resources accounting. Because of the disagreement between the awareness of natural resources property and value, there are different understandings of balance relationship of natural resource balance sheet, which leads to the long-term dispute on the compilation of balance sheet of natural resources. The basic understanding of SEEA-2012’s “beginning + increase - decrease = end” is consistent. However, there is much controversy over the framework of the natural resources balance sheet. The researchers of natural resource believe that the natural resource balance sheet should be compiled based on the “early period + increase - decrease = end of term” of SEEA-2012, but this report cannot reflect natural resource liabilities, so it cannot be called the balance sheet of natural resources in strict sense and should be called the statistical report of natural resources. Many scholars in the accounting field believe that the balance sheet of natural resources should be compiled based on “assets = liabilities + rights and interests” and use complex accounts. However, because of the lack of understanding of natural resources, the concept of “asset liability = net assets” proposed by some scholars is also lack of practical significance. It is also impossible to design such an accounting system with double-entry bookkeeping. In this paper, based on the cross research of resource science and accounting theory, the framework of natural resource balance sheet is constructed with the property and value attributes of resources. The equilibrium relationship of the balance sheet is clarified, and the static balance relationship and dynamic balance relationship of natural resource balance sheet are studied. The static balance relationship of the natural resources balance sheet based on the double-entry accounting is generally expressed as “assets = equity”, which is the theoretical basis of debit and credit accounting; the dynamic balance relationship is expressed as “beginning + increase - decrease = end of period (beginning - decrease = end - increase)” and “income - output = surplus”, which is the theoretical basis for the period accounting. The paper further analyzes the equations of natural resources accounting system and the framework of natural resources balance sheet based on double-entry accounting.
森林资源资产负债表核算系统研究
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190610
[本文引用: 4]

森林资源是重要的自然资源,编制森林资源资产负债表,将森林资源管理纳入生态文明绩效评价考核体系,对实现可持续发展和保障生态安全具有重要意义。本文在分析森林资源核算研究进展的基础上,将森林资源资产负债表定位于服务各级政府森林资源资产管理的信息系统,借鉴会计理论与方法,结合中国森林资源管理的特点,构建了森林资源资产负债表核算系统。核算系统主要包括:森林资源资产负债表核算要素的界定和确认标准,森林资源资产、森林资源负债、森林资源净权益的核算账户设置,森林资源资产负债表、森林资源资产变动表、森林资源权益变动表的表式,以资源调查数据和资源变动数据为基础的动态核算流程,以及复式记账的核算方法。通过核算系统,实现以年度为核算周期编制森林资源资产负债表。
Study on the accounting system of forest resources balance sheet
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190610 URL [本文引用: 4]
Natural resources accounting and the natural resources balance sheet
Investigation and preparation of natural resources balance sheet is an important measurement for perfecting natural resources management system and promoting development in China. Natural resources accounting is regarded as an important method of sustainable development and the basis of natural resources balance sheet. Here,we briefly described the link and differences between RA and EA and reviewed international research progress of natural resources accounting from theoretical and practical aspects,natural resources accounting progress from resource accounting,environmental pollution and comprehensive accounting aspects in China. We described the evolution of the SEEA system in detail and compared the major Environment-Economic accounting systems from the aspect of accounting content,accounting scope and accounting methods and through this comparison of different Environment-Economic accounting systems,pointed out the virtue we need to learn from natural resources accounting during the establishment of natural resources balance sheet. On this basis,we analyzed the difficulty when preparing natural resources balance sheet and its relationship with SEEA which the system of Environment-Economic accounting serves as an important theoretical basis and data sources for the preparation of the natural resources balance sheet. We hope to promote and perfect system of natural resources balance sheet through investigation and practical application.
关于自然资源核算的研究进展与争议问题
Research progress and controversial issues of natural resources accounting
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.20150366
[本文引用: 1]

An exploration on the compilation of natural resources asset debt sheet was proposed in the third plenary session of the 18th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China to audit the retired leading cadres. China's natural resources balance sheet and its related criterion are designed to audit all natural resources asset and promote the construction of ecological civilization, whilst the natural resources accounting is the fundamental work of resources auditing. This article aims to analyze the consensus and dispute during natural resources accounting in three aspects, including the classification of accounting projects, theoretical methods and their practical applications. We found that the researches about resources accounting were started a little bit earlier in developed countries, where many achievements had been obtained in both theoretical methods and practical applications. China's researches, however, still focused on theoretical method, though some accounting methods used in empirical study were basically derived from the existed achievements of developed countries, and lacked innovation. At present, many countries follow the principles of first physical quantity then value, first stock then flow, first class then general analysis when conducting natural resources accounting. However, there is no unified classification of the core projects of accounting widely accepted by all countries, and many disputes still exist in the selections of valuation approaches. In practice the System of Integrated Environment and Economic Accounting (SEEA), which was proposed by the UN, has been accepted by a wide range of authorities, and then many countries began to explore their own resources accounting system in accordance with the SEEA. The authors propose some essential issues in making the natural resources balance sheet of China based on research progresses and existing disputes at home and abroad, such as determining accounting project, selecting valuation approach, the steps of natural resources accounting, and the connection between the accounting and the debt sheet. Some thoughts and methods for solving the above issues are put forward in the article, that is, selecting controllable or property right clear natural resources as accounting project; taking economic, ecological and social values into account when choosing valuation approach; placing priority to the regional natural resources accounting system of single resource; and designing specific natural resource accounting standards. Considering the resources and environmental accounting in the system of national economic accounting,constructing natural resources accounting system is of crucial importance to the compilation of natural resources balance sheet, and plays an important role in the construction of ecological civilization.
自然资源资产负债表编制设计及应用Ⅰ: 设计
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20171361
[本文引用: 1]

十八届三中全会提出“探索编制自然资源资产负债表,对领导干部进行自然资源资产离任审计”,这是我国在生态文明制度建设中的一项重大改革。自然资源资产负债表是表明一定期间内自然资源的存量以及存量变化情况的报表,论文在研究自然资源资产负债表概念内涵的基础上,分析自然资源资产负债表实物量和价值量核算方法,提出两者之间的换算表,最后研究自然资源资产负债表编制样式,提出设计方案,为自然资源资产负债表应用研究提供基础。
Design and application of natural resources balance sheet Ⅰ: Design
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20171361 URL [本文引用: 1]
自然资源资产辨析和负债、权益账户设置与界定研究: 基于复式记账的自然资源资产负债表框架
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20180845
[本文引用: 2]

资源环境问题成为经济社会发展的约束性问题,成立自然资源部,探索编制自然资源资产负债表是加强自然资源统筹管理的重要举措。自然资源核算和自然资源资产负债表的编制是自然资源统筹管理的基础工作,目前国外较多自然资源核算成果建立在SEEA 2012的基础上。编制自然资源资产负债表首先由中国提出来并开展研究,但综合来看,在基础理论研究和实践方法上还处于研究初级阶段,需要进一步加强理论基础和科学方法研究。论文基于会计理论的复式记账核算理论,研究了自然资源负债和权益的生产论和自然资源循环理论基础,提出了基于资源环境承载力、相关资源功能规划、生态红线基础上的自然资源负债和权益界定标准,以及在此界定标准上设计自然资源资产负债表及其相关平衡核算。自然资源资产是指能够给人类带来直接或间接福利的自然要素总和,它不仅包括直接参与经济社会系统循环的物质和环境要素,也包括参与生态循环间接为人类带来生态服务价值的自然要素;基于自然资源资产分析,论文将自然资源资产的权益分为自然资源的生态权益和自然资源的经济权益,这样的分类也有其生态文明的伦理基础;自然资源负债的产生是由于资源过度损耗、环境污染和生态破坏,既有人为因素,也有自然因素,是经济社会为了补偿生态系统的可持续性而需要付出的经济代价。通过以上资产、负债、权益的界定,为我们设计自然资源资产负债表提供了逻辑基础。论文研究旨在设计合理的基于复式记账的自然资源过程核算,以及资源资产负债表编制账户体系设计和平衡关系理论,以期为自然资源核算和资产负债表的编制提供科学的理论基础,构建科学合理的自然资源核算理论和编制科学的自然资源资产负债表。
Analysis of natural resource assets and establishment and definition of liability and equity accounts: Based on framework of natural resources balance sheet with double-entry bookkeeping
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20180845 URL [本文引用: 2]
中国自然保护地生态资产核算框架研究
Study on ecological assets accounting framework of nature reserve in China
自然资源资产负债表编制研究
以云南省景东县森林资源资产为例
Research on the compilation of balance sheet of natural resources: A case study of the forest resources assets of Jingdong county in Yunnan province
森林文化价值评估指标体系和方法研究
Forest cultural value evaluation index system and methodology
国有林场森林资源资产负债表核算系统研究: 以福建省将乐国有林场为例
Accounting system of forest resources balance sheet in national forest farm: Based on a forest farm in Fujian province
自然资源资产负债表编制中生态损益核算
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200401
[本文引用: 1]

生态损益核算是自然资源资产负债表的重要部分,是对自然资源分类核算的扩展和补充。本文梳理生态损益核算的总体思路,系统总结生态损益核算技术,以围场县为例进行实证,遵循先实物后价值的核算原则,选择森林、草地、湿地生态系统,按不同的生态服务指标进行实物量和价值量的核算,并在已有的核算基础上计算各类型生态系统的实物量参数和价值量参数,以便根据面积统计数据进行快速简洁的核算比较。研究发现:围场县2015年生态系统服务功能价值量总值为338.99亿,与2013年相比增加了0.04%。生态系统服务功能价值量从大到小依次为草地、森林、湿地,核算期间森林和草地生态系统价值量分别下降0.06%和0.22%,湿地生态系统价值量增加4.47%。研究成果有助于全面理解和量化自然资源数量变化和质量变化带来的生态效应,并为自然资源资产负债表中的负债核算提供数据基础。
Ecological profit and loss accounting in the preparation of natural resources balance sheet
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200401
[本文引用: 1]

Ecological profit and loss accounting is an important part of the natural resources balance sheet and it is an extension and supplement to the classification of natural resources. This study combs the general idea of ecological profit and loss accounting, systematically summarizes the ecological profit and loss accounting technology, and takes the Weichang county as an example. Following the principle of accounting for values after the physical quantity, the forest, grassland and wetland ecosystems are selected, the service indicator carries out the accounting of the physical quantity and the value quantity, and calculates the physical quantity parameter and the value quantity parameter of each type of ecosystem based on the existing accounting, so as to make a quick and simple accounting comparison based on the area statistics. The study found that, in 2015, the total value of the ecosystem service function value of Weichang county was 33.899 billion, an increase of 0.04% compared with 2013. The value of ecosystem services functioned from grassland to forest and wetland. The values of forest and grassland ecosystems decreased by 0.06% and 0.22%, respectively, and the value of wetland ecosystem increased by 4.47%. The results contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the ecological effects brought by the changes in the quantity and quality of natural resources, and provide a data base for liability accounting in natural resource balance sheets.
基于资本资产定价模型的森林资源资产评估基准折现率测算
DOI:10.18402/resci.2019.03.14
[本文引用: 1]

折现率是森林资源资产评估中对评估结果有重大影响的参数,也是最难以确定的参数。本文引入资本资产定价模型,在定量计算无风险收益率、市场风险溢价和营林行业市场风险系数的基础上,对森林资源资产评估中的基准折现率进行了测算。结果显示,以2016年12月31日为评估基准日,森林资源资产评估中的无风险收益率为1.84%;市场风险溢价为2.88%,市场风险系数为0.92,风险收益率为2.65%;基准折现率为4.50%。根据评估基准日基准折现率测算结果,结合已有研究成果,建议森林资源资产评估中基准折现率的取值为5.0%,其中无风险收益率为2.0%、风险收益率为3.0%,风险收益率中经营风险、财务风险和行业风险取值均为1.0%。但不同经营类型、目标和特点的森林资源资产评估,应以基准折现率为参考设定评估实务中采用的具体折现率。
Benchmark discount rate calculation for forest resource asset valuation via capital asset pricing model
DOI:10.18402/resci.2019.03.14
[本文引用: 1]

Discount rate has a significant impact on the assessed value of forest resource asset and is a parameter whose value is most difficult to determine. Applying a capital asset pricing model, and based on quantitative calculation of risk-free rate of return, market risk premium, and market risk coefficient of forestry industry, this study empirically calculated the benchmark discount rate for forest resource asset valuation. The result shows that, taking 31 December 2016 as the base date of valuation, the final benchmark discount rate for forest resource asset valuation was 4.50%, among which, risk-free return rate was 1.84%, market risk premium was 2.88%, market risk coefficient was 0.92, and risk return rate was 2.65%. According to the calculation result of benchmark discount rate on the valuation date combined with existing research results, this article suggests that, without considering valuation date, the general value of the benchmark discount rate for forest resource asset valuation is 5.0%, among which, risk-free return rate is 2.0%, risk return rate is 3.0%, and the value of operating risk, financial risk, and industry risk in the risk return rate is 1.0% respectively. However, specific discount rates used in practical forest resource asset valuation with different types of businesses and operation objectives and characteristics could be different, and the setting of specific discount rates in practice should take the general discount rate as the reference.