全域土地综合整治源于“千村示范、万村整治”工程,通过调整全域地类结构与布局优化农村生产、生活、生态空间,促进乡村空间重构、产业重整、环境重生[1]。当前全域土地综合整治普遍开展了生态修复,促进生态价值增长。但生态价值增长并非必然转换为经济收益增长,因此需要通过多样化的模式和路径将生态价值转化为经济价值,推动生态产品价值实现[2]。只是全域土地综合整治以生产物质产品、提供生态服务与生态衍生权利交易等途径发掘生态产品价值实现潜力,特别是增加建设用地发展旅游、商业、教育等产业,很可能制约生态修复增加生态价值[3]。因此对不同整治目标的权衡会导致全域土地综合整治用地需求的差异,甚至潜在的用地冲突[4,5]。那么当全域土地综合整治在生态价值增长目标与生态产品价值实现目标之间做出权衡时,需要针对性地优化土地利用结构与布局,并弄清其规律。
依托土地利用优化,全域土地综合整治通过“人口—土地—产业”等要素整合,优化调整乡村空间[4]。土地利用优化作为全域土地综合整治的主要工具,指在土地利用变化的基础上,通过调整土地利用结构和布局,以适应经济、社会和环境可持续发展的需要[6]。土地利用结构优化中,线性规划[7]、模糊数学[8]、神经网络算法[9]、多目标规划[10]等被广泛使用。土地利用结构优化通过优化配置各种地类的数量实现了土地利用中的经济利益—生态系统服务平衡、城市土地生态适宜化利用、碳排放总量控制、生态优先、生态—经济协调发展等方面的目标[7⇓⇓⇓-11]。土地利用布局优化通过运用GIS技术实现了土地资源配置从数量优化向空间优化的深化。土地利用布局优化中,元胞自动机[12]、多智能体模型[13]、CLUE-S模型[14,15]、FLUS模型[16]、GeoSOS-FLUS模型[17]等为代表的空间模拟工具被广泛使用。模拟工具在多情景土地利用格局优化[10,14,18]、城市增长边界划定[16]、三生空间功能格局优化[19]、轨道交通影响分析[20]等土地利用布局优化领域进行了运用。因此运用现有的工具,也可以实现基于生态价值与生态产品价值实现潜力权衡的全域土地综合整治用地优化。
全域土地综合整治应该均衡配置生产、生活、生态空间。生态空间通过提供生态产品或生态系统服务保障了生产空间与生活空间效用的发挥,而生产和生活空间则承载了生态空间发挥功能所需的生产过程和配套公共服务[21]。全域土地综合整治中生产、生活、生态空间的功能互补、有效融合可以实现增加生态价值与促进生态产品价值。只是全域土地综合整治中将生态产品价值通过市场化或非市场化手段转换为经济收益这一过程能否实现,不仅需要国土空间的优化,也受制于市场需求、基础设施配套、体制机制要求等条件。因此本文用生态产品价值实现潜力来表征全域土地综合整治建设项目实施后可能实现的生态产品价值大小。以海南省儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点项目区为研究区(起步区国家级试点项目区简称“试点项目区”,下同),根据儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点实施方案》中的儋州市全域土地综合整治试点项目区主要建设项目,探究如何基于不同整治目标合理安排各地类的数量与位置来完成整治建设项目。一方面,试点项目区全域土地综合整治中推进滨海湿地生态系统修复和退塘还林还湿,期望增加生态价值。另一方面,试点项目区又得增加建设用地来发展旅游、商业、教育等产业,促进生态产品价值实现。那么在有限的土地面积约束下,全域土地综合整治用地的结构与布局调整就面临着增加生态价值与促进生态产品价值实现之间的权衡。为此,本文多目标全域土地综合整治用地布局优化通过设置生态价值与生态产品价值实现潜力之间不同的优先序来描述这种权衡关系,分为两种整治情景:一种是生态价值优先于生态产品价值实现潜力,全域土地综合整治建设项目实施中首先确保生态价值最大化(生态价值优先);另一种是生态产品价值实现潜力优先于生态价值,全域土地综合整治建设项目实施中首先确保生态产品价值实现潜力最大化(生态产品价值实现潜力优先)。通过观察两种情景下全域土地综合整治用地优化结果,揭示不同整治情景下全域土地综合整治中湿地、耕地、园地、商业服务业用地等布局的差异,以及生产、生活、生态空间演化特征。
1 研究方法与数据来源
1.1 研究区概况
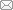
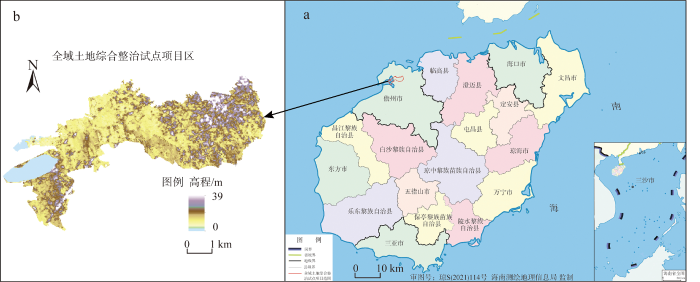
本文研究区为儋州市天角潭—北门江—新英湾全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点项目区(图1)。试点项目区位于儋州市中北部地区,包括黄江村、长村、五里村、七里村、黄玉村、攀步村、新地村、兰田村等八个行政村,土地面积为30.98 km2。2019年末整治前试点项目区土地利用结构如图2所示:水田、旱地、园地、林地与草地分别占总面积的33.60%、9.73%、0.01%、26.29%;商业服务业用地、住宅用地、工矿用地、水域及水利设施用地、公共服务及特殊用地、交通运输用地占总面积的0.04%、4.44%、5.22%、14.79%、0.77%、1.52%;红树林地、滩涂湿地、其他土地占总面积的1.12%、2.27%、0.19%。试点项目区土地集中连片,地势平坦,大部分坡度小于6%,局部坡度在25%~90%之间,补充耕地资源潜力大,可以通过农用地整理提高耕地质量和数量。试点范围内村庄存在零星建设用地和150 hm2已经废弃多时的新英盐场,可以通过建设用地整理改善人居环境。试点项目区生态本底较好,田、林、水、湿地要素齐备,生物资源丰富,但受当地盐场建设和坑塘养殖的破坏,试点项目区红树林地的面积萎缩严重,可以通过生态保护修复提升湿地资源质量。
图1
图1
研究区区位图
注:本图基于海南测绘地理信息局标准地图服务系统下载的标准地图制作,底图无修改。
Fig. 1
Location of the research area
图2
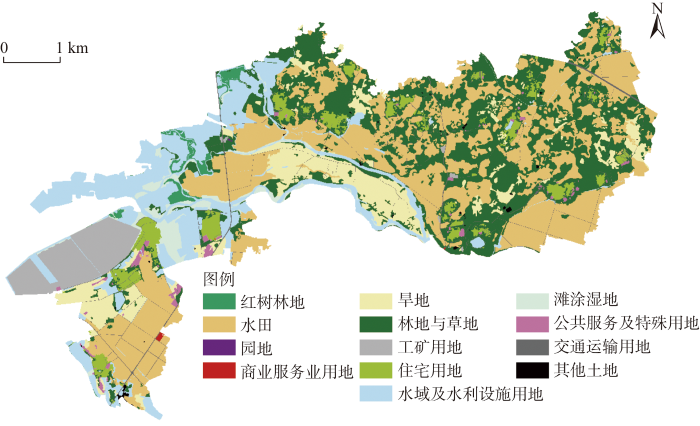
根据《儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点实施方案》,试点项目区通过实施农用地整理项目垦造耕地项目可新增耕地114.30 hm2;旱地改水田项目规模126.65 hm2。通过建设用地复垦项目拆旧总面积123.76 hm2,预计复垦为水田2.10 hm2,复垦为林地与园地121.67 hm2。通过生态保护修复项目拟退塘还林(还滩)面积共计296.13 hm2,通过养殖塘平整和生境改造,修复红树林268.33 hm2。通过产业布局和引入,配套建设5个产业项目,建设总规模为41.43 hm2。试点项目区全域土地综合整治建设项目布局见图3。
图3
图3
试点项目区全域土地综合整治建设项目布局
Fig. 3
Construction project layout of comprehensive land consolidation in the pilot project zone
1.2 数据来源
数据说明见表1。首先基于2016年试点项目区土地变更调查成果数据库以及试点项目区三调成果数据库(2019年),统一矢量数据的范围以及地理与投影坐标系,并转换为10 m×10 m的栅格数据,生成试点项目区2016年和2019年的土地利用现状栅格数据。其次将其余矢量数据基于试点项目区三调成果数据库(2019年)进行配准并转换为统一格式的栅格数据。再次基于ASTER GDEM V3提取试点项目区DEM数据,并生成试点项目区的坡度、坡向数据;基于OpenStreetMap开源地图,提取2019年儋州市交通路网数据,并通过欧氏距离计算不同地类到乡镇中心、等级公路的距离;基于中国长时间序列逐年人造夜间灯光数据集提取2019年儋州市的夜间灯光数据,综合上述成果作为试点项目区土地利用驱动因子。最后采用空间配准和镶嵌的操作将生态红线内土地提取为土地利用的限制转换面。
表1 数据说明
Table 1
| 数据类型 | 数据来源 | 数据说明 | 数据用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土地利用数据 | 2016年试点项目区土地变更调查成果数据库 | 比例尺1∶1万 | 基础数据 |
| 试点项目区三调成果数据库(2019年) | 比例尺1∶1万 | 基础数据 | |
| 统计数据 | 儋州市统计年鉴 | 2020年 | 相关统计数据 |
| 海南统计年鉴 | 2015—2019年 | 相关统计数据 | |
| 规划数据 | 《儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点区域发展策划》文本 | 文本 | 约束条件参考 |
| 《儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点区域发展策划》规划图 | 图件 | 空间布局参考 | |
| 《儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点实施方案》文本 | 文本 | 约束条件参考 | |
| 儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点项目区生态红线 | 矢量图 | 限制转化区域 | |
| DEM数据 | ASTER GDEM V3版(2019年) | 30 m高程数据 | 自然地形驱动因子 |
| 夜间灯光数据 | 中国长时间序列逐年人造夜间灯光数据集(2019年) | 1 km×1 km | 社会经济驱动因子 |
| 交通图 | OpenStreetMap开源地图(2019年) | 比例尺1∶1万 | 交通区位驱动因子 |
1.3 研究方法
1.3.1 生态价值评估
全域土地综合整治后的生态价值评估核算期为一年。多数生态价值的评估为静态评估[22,23],因此本文生态价值评估对象为全域土地综合整治后形成了稳定生态系统服务功能的生态系统。采用由谢高地等[24]改进过的当量因子法估算全域土地综合整治主要建设项目的生态价值。谢高地等[24]在Costanza等[25]和谢高地等[26]的研究基础上,更新了中国的单位面积价值当量表。1个标准单位的生态系统服务价值当量因子为研究区1公顷平均产量的农田每年自然粮食产量的经济价值(即农田食物生产的经济价值)。多数研究中1个生态服务价值当量因子的经济价值量等于研究区当年平均粮食单产市场价值的1/7[26,27]。一般基于稻米、小麦和玉米三大主要粮食估算1个生态服务价值当量因子的经济价值量。但儋州市本地基本不生产小麦和玉米,因此基于稻谷来计算1个生态服务价值当量因子的经济价值量。根据国家粮食海南交易中心的平台成交价格结果,2019年海南省稻米的成交价格为2.3~3元/kg之间,本文取中位数为2.65元/kg。根据《儋州市统计年鉴2020年》,2019年儋州市粮食总产量为135191 t,粮食播种面积为352799亩(1亩≈667 m2)。根据《海南统计年鉴》,2015—2019年海南省复种指数为179.1%、171.3%、161.5%、162.4%、158.7%。本文取算数平均值为166.6%。最终计算得到儋州市1个生态服务价值当量因子的经济价值量为3625元/(hm2·年)。
将《儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点实施方案》中安排的主要建设项目进行整理后(表2),估算主要建设项目地类改变后的生态价值。该实施方案中的地类标准为第三次全国国土调查土地分类标准,因此对第三次全国国土调查土地分类标准与谢高地等[24]成果中的生态价值地类进行归类匹配,以满足生态价值计算的需要。基于中国单位面积生态服务价值当量表[24]以及儋州市1个生态服务价值当量因子的经济价值量,以儋州市各地类单位面积价值当量表征其单位面积生态价值,即生态价值系数。考虑到儋州市当地植被以阔叶林和灌草丛为主,因此以阔叶林与灌草丛生态价值系数的平均值来估算园地的生态价值系数。考虑到篇幅限制,并未列出试点项目区有关地类生态价值系数的详细计算过程。
表2 儋州市全域土地综合整治试点项目区主要建设项目
Table 2
| 类型 | 主要建设项目 | 最终地类 | 对应生态价值地类 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 农用地整理 | 农用地整理实施“旱改水” | 水田 | 水田 |
| 农用地整理实施耕地开垦 | 水田 | 水田 | |
| 建设用地整理 | 宅基地复垦为水田 | 水田 | 水田 |
| 盐场建设用地整理为红树林 | 红树林地 | 湿地 | |
| 矿山复垦为园地 | 果园或其他园地 | 阔叶林与灌草丛平均值 | |
| 产业引入与生态保护修复 | 建设热带花卉苗木产业园 | 其他园地 | 阔叶林与灌草丛平均值 |
| 发展高效果林发展区 | 果园 | 阔叶林与灌草丛平均值 | |
| 建设红树林生态旅游体验区项目 | 红树林地 | 湿地 | |
| 建设儒学耕读书院、儒学养生庄园、儿童萌宠庄园和田园文创庄园 | 商业服务业设施用地 | — | |
| 建设历史文化与乡村民俗商业街 | 商业服务业设施用地 | — |
结合建设项目实施后形成的各最终地类面积,求出建设项目实施后获得的生态价值总量,计算公式如下:
式中:V为全域土地综合整治建设项目实施后获得的生态价值总量(万元/年);Aj为第j种全域土地综合整治建设项目最终地类面积(hm2);Tj为第j种地类的全部生态系统服务功能的单位面积生态价值 [元/(hm2·年)]。
1.3.2 生态产品价值实现潜力评估
基于儋州市全域土地综合整治试点项目区主要建设项目,确定了试点项目区的生态产品价值实现方式。将全域土地综合整治生态产品价值实现潜力分为生态产品转换为物质产品、生态产品转换为生态服务和生态产品转换为生态衍生权利三类(表3)。
表3 儋州市全域土地综合整治生态产品价值实现潜力
Table 3
| 潜力内容 | 生态产品价值实现方式 | 产出结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 转换为物质产品 | 开发水田发展生态农业 | 粮食、水产 |
| 建设热带花卉苗木产业园 | 热带兰花卉 | |
| 发展高效果林发展区培育特色果蔬产业 | 蜜柚、冬季瓜菜、精品果蔬、烟草、菠萝、槟榔、胡椒等高附加值林果产品 | |
| 依托沿海红树林湿地发展红树林特色产业 | 红树林果实、树皮、渔业产品 | |
| 转换为生态服务 | 建设红树林生态旅游体验区项目 | 生态旅游服务 |
| 建设儒学耕读书院、儒学养生庄园、儿童萌宠庄园和田园文创庄园 | 文化教育服务 | |
| 建设历史文化与乡村民俗商业街 | 商业经营服务 | |
| 通过海洋生态保护修复项目修复红树林湿地 | 灾害防护价值 | |
| 转换为生态衍生权利 | 红树林固碳结果参与碳排放交易 | 碳排放权 |
| 红树林水体净化结果参与交易 | 排污权 |
全域土地综合整治生态产品价值实现潜力计算公式如下:
式中:P为全域土地综合整治建设项目实施后的生态产品价值实现潜力(万元/年);Si为第i种生态产品价值实现方式涉及的地类面积(hm2);Ui为第i种生态产品价值实现方式中单位土地面积的生态产品价值实现潜力 [元/(hm2·年)],即生态产品价值实现潜力系数。
试点项目区生态产品价值实现潜力评估涉及的地类主要有水田、湿地、园地、商业服务业用地。按照不同地类生态产品价值实现中各方式单位面积潜在收益,涉及新增水田粮食收益潜力、种植花卉园地的热带兰花卉收益潜力、果蔬林果种植用途土地的果蔬林果产品收益潜力、红树林果实收益潜力、红树林渔业增产收益潜力、红树林生态旅游体验区的旅游服务门票生态补偿收益潜力、儒学耕读书院/儒学养生庄园/儿童萌宠庄园和田园文创庄园的生态补偿收益潜力、商业经营设施用地的生态补偿收益潜力、红树林灾害防护价值生态补偿收益潜力、红树林固碳价值转换为碳排放权交易收入潜力、红树林净化价值转换为排污权交易收入潜力,最终确定各地类生态产品价值实现潜力系数(表4)。
表4 试点项目区有关地类生态价值系数及生态产品价值实现潜力系数
Table 4
| 系数 | 红树林地 | 水田 | 园地 | 商业服务业用地 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花卉苗木用途 | 果蔬林果用途 | 生态旅游服务用途 | 文化教育服务用途 | 商业经营服务用途 | ||||
| 生态价值系数 | 188572.80 | 14101.60 | 77285.20 | 77285.20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 生态产品价值实现潜力系数 | 40740.00 | 7500.00 | 57975.00 | 53280.00 | 62355.00 | 81033.00 | 79215.00 | |
1.3.3 多目标规划模型
多目标规划模型(Multi-objective Programming,MOP)用于全域土地综合整治用地结构优化分析。MOP模型包含目标函数与约束条件,实现在主观或客观条件下,规划某个或多个目标达到最值的决策。本文设置生态价值优先以及生态产品价值实现潜力优先两种整治情景和约束条件。
(1)整治情景设定
基于生态价值增长目标与生态产品价值实现目标之间的权衡,全域土地综合整治用地设定两种整治情景。① 生态价值优先整治情景:全域土地综合整治以试点项目区生态价值总量最大化为优先目标,扩张生态价值量较高的土地面积,修复与维持当地的生态环境。② 生态产品价值实现潜力优先整治情景:全域土地综合整治,在保护生态环境的前提下,合理利用自然资源,提高生态产品的转换效率和实现潜力,以生态产品价值的实现潜力最大化为优先目标,适量扩张有利于生态产品价值实现的地类。基于式(1),生态价值优先情景下,建设项目实施后优先获得最大生态价值总量的公式如下,式中变量内涵与式(1)一致:
基于式(2),生态产品价值实现潜力优先情景下,建设项目实施后优先获得最大生态产品价值实现潜力的公式如下,式中变量内涵与式(2)一致:
(2)约束条件设定
MOP模型约束条件见表5,具体解释如下。
表5 试点项目区全域土地综合整治用地结构优化约束条件
Table 5
| 约束类型 | 约束因素 | 约束表达式 |
|---|---|---|
| 整治目标约束 | 土地总面积S | X1+X2+X3+X4+Z1+Z2+Z3+Z4+Z5+B1+B2+B3+B4=S |
| 红树林地X1、水田X2、园地X3、商业服务业用地X4 | X1≥现状用地面积、X2≥现状用地面积、X3≥现状用地面积、X4≥现状用地面积 | |
| 旱地面积Z1 | 0.8×现状用地面积Z1≤现状用地面积 | |
| 林地与草地Z2 | 0.7×现状用地面积≤Z2≤现状用地面积 | |
| 工矿用地Z3 | Z3≤10 hm2 | |
| 住宅用地Z4 | 0.7×现状用地面积≤Z4≤现状用地面积 | |
| 水域及水利设施用地Z5 | 0.65×现状用地面积≤Z5≤现状用地面积 | |
| 滩涂湿地B1、公共服务及特殊用地B2、交通运输用地B3、其他土地B4 | B1=现状用地面积、B2=现状用地面积、B3=现状用地面积、B4=现状用地面积 | |
| 用途转换约束 | 土地增减平衡 | X1-现状红树林地面积+X2-现状水田面积+X3-现状园地面积+X4-现状商业服务业用地面积=现状旱地面积-Z1+现状林地与草地面积-Z2+现状工矿用地面积-Z3+现状住宅用地面积-Z4+现状水域及水利设施用地面积-Z5 |
| 全域土地整治地类转换总面积 | X1-现状红树林地面积+X2-现状水田面积+X3-现状园地面积+X4-现状商业服务业用地面积=500 hm2 | |
| 花卉苗木用途与果蔬林果用途转换总面积 | X3=X31+X32 | |
| 生态旅游服务用途、文化教育服务用途、商业经营服务用途转换总面积 | X4=X41+X42+X43 | |
| 用地保护约束 | 耕地保护 | X2+Z1≥1.05×(现状水田面积+现状旱地面积) |
| 红树林保护1 | X1-现状红树林地面积≥现状工矿用地面积-Z3+0.5×(现状水域及水利设施用地面积-Z5) | |
| 红树林保护2 | X1-现状红树林地面积≥X2-现状水田面积+X3-现状园地面积 | |
| 用地配套约束 | 园地与水田配套 | X3-现状园地≥(X2-现状水田)×0.25 |
| 园地、商业服务业用地与水田配套 | X3-现状园地+X4-现状商业服务业用地≥X2-现状水田面积 | |
| 商业服务业用地与住宅用地、林地与草地配套 | X4-现状商业服务业用地≥现状住宅用地面积-Z4+0.2×(现状林地与草地面积-Z2) | |
| 花卉苗木用途与林地与草地、水域及水利设施用地配套 | X31≥0.1×(现状林地与草地面积-Z2)+0.1×(现状水域及水利设施用地面积-Z5) | |
| 果蔬林果用途与花卉苗木用途配套 | X32≥X31×2 | |
| 生态旅游服务用途与红树林地配套 | X41≥(X1-现状红树林地)×0.1 | |
| 文化教育服务用途与商业经营服务用途配套 | X42≥X43×0.5 | |
| 商业经营服务用途与生态旅游服务用途配套 | X43≥X41×1.5 |
注:(1)变量X、Z、B为优化后地类面积(hm2),其中X为优化后面积增加地类,Z为优化后面积减少地类,B为优化后面积不变地类。(2)X31与X32分别为花卉苗木用途与果蔬林果用途用地面积(hm2),X41、X42、X43分别为生态旅游服务用途、文化教育服务用途、商业经营服务用途用地面积(hm2)。
① 整治目标约束
旱地、林地与草地、住宅用地、水域及水利设施用地优化后将出现面积的减少,但这四种地类必须保留适当的面积来维持其功能,因此按照现状用地面积的比例根据设置下限。试点项目区内工矿用地约为160 hm2,其中占地150 hm2的新英废弃盐场,在蓝色海湾红树林修复任务中明确将工矿用地整治为红树林湿地,因此设置优化后工矿用地不大于10 hm2。除此之外,滩涂湿地、公共服务及特殊用地、交通运输用地以及其他土地的空间分布与用途转换受土地管理政策、自然地形限制,因此将其数量设置为土地利用现状值,不再改变。
② 用途转换约束
根据《儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点实施方案》,土地综合整治中新增的红树林地、水田、园地、商业服务业用地总规模约为500 hm2。试点项目区现状园地面积仅为0.37 hm2,因此优化为花卉苗木用途和果蔬林果用途的园地面积之和为优化后园地面积。同理,商业服务业用地现状面积仅为1.37 hm2,因此优化为生态旅游服务用途、文化教育服务用途、商业经营服务用途的商业服务业用地面积之和为优化后商业服务用地面积。
③ 用地保护约束
《海南省人民政府办公厅关于开展全域土地综合整治试点的意见》中要求新增耕地面积原则上不少于原有耕地面积的5%,因此设置约束表达式“X2+Z1≥1.05×(现状水田面积+现状旱地面积)”,要求优化后耕地面积不少于现状耕地面积的1.05倍。试点项目要全面落实蓝色海湾红树林修复任务,规划中明确将工矿用地整治为红树林湿地,因此设置“X1-现状红树林地面积≥现状工矿用地面积-Z3+0.5×(现状水域及水利设施用地面积-Z5)”,要求新增红树林面积需不少于工矿用地减少面积和水域及水利设施用地减少面积的一半之和。此外,设置“X1-现状红树林地面积≥X2-现状水田面积+X3-现状园地面积”,期望红树林地新增面积不少于新增水田和园地面积之和。
④ 用地配套约束
全域土地综合整治要满足不同类型的建设项目用地需要。根据试点项目区的相关建设方案,在园地、商业服务业用地以及相对应的花卉苗木用途、果蔬林果用途、生态旅游服务用途、文化教育服务用途、商业经营服务用途等用地面积之间建立一定比例的配套关系。
1.3.4 GeoSOS-FLUS模型
元胞自动机、多智能体模型等经典空间模拟工具存在着难以确定合适的空间分辨率和地类转换规则等不足。黎夏等[17]、Liu等[28]改进了FLUS模型,建立了GeoSOS-FLUS模型用于模拟和预测人类活动与自然影响下的土地利用变化。本文中GeoSOS-FLUS模型步骤和处理如下:(1)将2016年试点项目区土地变更调查成果数据库地类转换为三调地类,从而匹配2019年试点项目区三调成果数据库,用于模型精度验证。(2)选择高程、坡度、坡向等作为自然地形驱动因子。选择与乡镇中心距离、高等级公路距离等交通区位因子和人造夜间灯光数据作为社会经济因子。运用神经网络进行适宜性分析,逐栅格计算试点项目区内各地类出现概率。(3)因生态红线内实施特殊保护,因此提取生态保护区域图层作为限制转换面予以保护。(4)叠加生态保护区域图层,结合不同情景设置基础系数以及地类间转换矩阵,再对2019年土地利用现状分别进行生态价值优先整治情景和生态产品价值实现潜力优先整治情景的模拟优化。(5)因“蓝色海湾”工程,试点项目区西南部原新英盐场作为废弃工矿用地必须恢复为红树林地,但大面积集中的工矿用地会显著影响适宜性分析结果,因此在进行适宜性分析前,先将原新英盐场所属工矿用地转换为红树林地。
2 结果分析
2.1 全域土地综合整治用地结构优化结果
全域土地综合整治建设项目实施后的最终地类面积若导致了该地类面积的增加,那么优化后的该地类面积为现状地类面积与全域土地综合整治建设项目最终地类面积之和。基于Lingo 18平台,在整治目标、用途转换、用地保护、用地配套四类约束下,求取生态价值优先和生态产品价值实现潜力优先两种整治情景下的全域土地综合整治用地结构优化结果(表6)。
表6 试点项目区全域土地综合整治用地结构优化
Table 6
| 变量 | 变量名称 | 2019年现状 | 整治情景1(生态价值优先) | 整治情景2(生态产品价值实现潜力优先) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 红树林地/hm2 | 34.86 | 250.51 | 220.17 | ||||
| X2 | 水田/hm2 | 1040.90 | 1169.05 | 1145.62 | ||||
| X3 | 园地/hm2 | 花卉苗木用途/hm2 | 0.31 | — | 87.80 | 29.27 | 80.90 | 26.97 |
| 果蔬林果用途/hm2 | — | 58.53 | 53.93 | |||||
| X4 | 商业服务业用地/hm2 | 生态旅游服务用途/hm2 | 1.37 | — | 70.08 | 21.56 | 130.75 | 40.23 |
| 文化教育服务用途/hm2 | — | 16.17 | 30.17 | |||||
| 商业经营服务用途/hm2 | — | 32.35 | 60.35 | |||||
| Z1 | 旱地/hm2 | 301.40 | 262.87 | 263.79 | ||||
| Z2 | 林地与草地/hm2 | 814.42 | 570.09 | 570.09 | ||||
| Z3 | 工矿用地/hm2 | 161.52 | 10.00 | 10.00 | ||||
| Z4 | 住宅用地/hm2 | 137.35 | 120.08 | 96.15 | ||||
| Z5 | 水域及水利设施用地/hm2 | 458.27 | 409.92 | 432.93 | ||||
| B1 | 滩涂湿地/hm2 | 70.39 | 70.39 | 70.39 | ||||
| B2 | 公共服务及特殊用地/hm2 | 23.69 | 23.69 | 23.69 | ||||
| B3 | 交通运输用地/hm2 | 47.18 | 47.18 | 47.18 | ||||
| B4 | 其他土地/hm2 | 5.98 | 5.98 | 5.98 | ||||
| V | 建设项目实施后获得的生态价值总量/(万元/年) | — | 4923.34 | 4264.99 | ||||
| P | 建设项目实施后的生态产品价值实现潜力/(万元/年) | — | 1966.05 | 2238.67 | ||||
生态价值优先整治情景下,试点项目区红树林地、水田、园地、商业服务业用地比现状均有较大幅度的增加,而旱地、林地与草地、工矿用地、住宅用地、水域及水利设施用地比现状均有较大幅度的减少。生态产品价值实现潜力优先整治情景下,试点项目区红树林地、水田、园地增加规模比生态价值优先整治情景有所降低,而商业服务业用地规模则明显增加。生态价值整治优先情景下,建设项目实施后获得的生态价值总量为4923.34万元/年,比生态产品价值实现潜力优先整治情景增加了15.44%。生态产品价值实现潜力优先整治情景下,全域土地综合整治建设项目实施后的生态产品价值实现潜力为2238.67万元/年,比生态价值优先整治情景增加了13.87%。
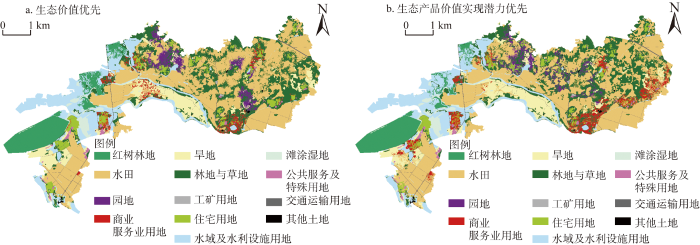
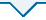
2.2 全域土地综合整治用地布局优化结果
GeoSOS-FLUS模型经过训练与模拟,OA指数为0.936,Kappa指数为0.918,模型精度满足后续分析要求。因此以2019年土地利用现状数据库为基础数据,对试点项目区全域土地综合整治用地进行布局优化。试点项目区生态价值优先布局优化模拟与生态产品价值实现潜力优先布局优化模拟见图4。
图4
图4
儋州市试点项目区全域土地综合整治用地布局优化
Fig. 4
Land use layout optimization of comprehensive land consolidation in Danzhou city
采用Fragstats 4.2软件对试点项目区2019年土地利用现状及两种整治情景的下的土地利用景观格局进行景观指数计算,得出试点项目区土地利用整体景观指数(表7)。两种整治情景与现状比较,景观分离度指数无明显变化,均表现出较高的景观分离程度;生态产品价值实现潜力优先情景的香浓多样性指数高于生态价值优先情景,两种整治情景的香浓多样性指数均高于现状,表明两种整治情景下各地类的分布比现状更加均衡;生态价值优先情景的聚合度指数高于生态产品价值实现潜力优先情景,两种整治情景的聚合度指数均低于现状,表明两种整治情景下各地类的分布更加破碎。
表7 试点项目区土地利用整体景观指数
Table 7
| 景观指数 | 土地利用现状 | 生态价值优先情景 | 生态产品价值实现潜力优先情景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 景观分离度指数 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| 香浓多样性指数 | 1.77 | 1.87 | 1.89 |
| 聚合度指数 | 90.30 | 86.28 | 85.14 |
对各地类聚合度指数进一步分析(表8),分析不同景观类型内部斑块的聚合程度,并结合各地类的空间分布解释两种情景下地类间的相互转换。生态价值优先情景相比现状,红树林地和园地的聚合度指数有所提高,其余地类的聚合度指数均有不同幅度的减少。而生态产品价值实现潜力优先情景相比现状及生态价值优先情景,红树林地的聚合度指数高于现状但低于生态价值优先情景,商业服务业用地与水域及水利设施用地的聚合度指数高于生态价值优先情景但低于现状,工矿用地的聚合度指数与生态价值优先情景相同但低于现状,其余地类的聚合度指数均低于土地利用现状及生态价值优先情景。
表8 试点项目区主要地类的景观聚合度指数
Table 8
| 地类 | 土地利用现状 | 生态价值优先情景 | 生态产品价值实现潜力优先情景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 红树林地 | 86.25 | 94.94 | 94.87 |
| 水田 | 93.71 | 91.91 | 91.05 |
| 园地 | 69.39 | 75.18 | 63.14 |
| 商业服务业用地 | 90.16 | 58.93 | 66.31 |
| 旱地 | 91.76 | 88.36 | 87.77 |
| 林地与草地 | 88.38 | 78.92 | 78.40 |
| 工矿用地 | 98.58 | 87.42 | 87.42 |
| 住宅用地 | 87.34 | 82.85 | 76.81 |
| 水域及水利设施用地 | 91.69 | 90.09 | 90.64 |
生态价值优先整治情景下,红树林地聚合度指数为94.94,与现状相比集聚程度有较大提高,景观分布高度集中,主要分布在西部水域及沿海的原工矿用地,面积上较现状有显著扩张,新增红树林地主要由水域及水利设施用地以及西南部的工矿用地转换而来。水田聚合度指数为91.91,与现状相比集聚程度有所降低,景观分布高度集中,分布范围仍主要位于试点项目区的东部、中部和西南部,面积较现状有所扩张,新增水田主要由分布在东部、北部的林地和旱地转换而来。园地聚合度指数为75.18,与现状相比集聚程度有所提高,景观分布较为离散,分布范围主要集中在试点项目区的东部和北部,面积上较现状有显著扩张,新增园地主要由林地与草地、旱地以及少量住宅用地转换而来。商业服务业用地聚合度指数为58.93,与现状相比集聚程度有较大降低,景观分布高度破碎,主要分布在中部交通线路及居民点附近,面积较现状有显著扩张,新增商业服务业用地主要由住宅用地、林地与草地和旱地转换而来。旱地聚合度指数为88.36,与现状相比集聚程度有所下降,景观分布较为集中,中部地区旱地缩减面积主要转换为商业服务业用地,东部及北部地区旱地缩减面积则主要转换为水田与园地。林地与草地聚合度指数为78.92,与现状相比集聚程度有较大降低,景观分布较为离散,东部及北部林地与草地缩减面积主要转换为水田、园地和商业服务业用地。工矿用地聚合度指数为87.42,与现状相比集聚程度有较大降低,景观分布较为集中,西南部集中连片的工矿用地转换为红树林地,面积较现状有显著缩减。住宅用地聚合度指数为82.85,与现状相比集聚程度有所降低,景观分布较为集中,东部、北部住宅用地缩减面积主要转换为商业服务业用地和林地与草地。水域及水利设施用地聚合度指数为90.09,与现状相比集聚程度有所下降,景观分布高度集中,缩减面积主要转换为红树林地。
生态产品价值实现潜力优先整治情景下,红树林地聚合度指数为94.87,与生态价值优先整治情景相比集聚程度有所降低,面积有所缩减,但景观分布状况及扩张来源基本一致。水田聚合度指数为91.05,与生态价值优先整治情景相比集聚程度有所降低,面积有所缩减,景观分布高度集中,新增面积主要由北部林地与草地及旱地转换而来。园地聚合度指数为63.14,与生态价值优先整治情景相比集聚程度有所降低,面积有所缩减,景观分布较为破碎,新增面积主要由北部、中部的林地与草地、旱地及少量住宅用地转换而来,形态上更加破碎。商业服务业用地聚合度指数为66.31,与生态价值优先整治情景相比集聚程度有较大提高,面积有显著扩张,景观分布较为破碎,新增面积主要由林地与草地、旱地及住宅用地转换而来,并在东部、中部与西部沿交通线路和居民点扩张。旱地聚合度指数为87.77,与生态价值优先整治情景相比集聚程度有所降低,面积略有扩张,景观分布较为集中,中部的旱地得到更多保留而东部与北部的旱地则更多转换为园地及商业服务业用地。林地与草地聚合度指数为78.40,与生态价值优先整治情景相比集聚程度略有下降,面积保持不变,景观分布较为离散,北部的林地与草地得到更多保留,而东部的林地与草地更多转换为商业服务业用地。工矿用地聚合度指数为87.42,与生态价值优先整治情景相比面积和集聚程度均无变化且景观分布状况一致。住宅用地聚合度指数为76.81,与生态价值优先整治情景相比集聚程度有所降低,面积有所缩减,景观分布较为离散,东部和西部的住宅用地更多转换为商业服务业用地。水域及水利设施用地聚合度指数为90.64,与生态价值优先整治情景相比集聚程度有所提高,面积有所扩张。
两种整治情景的用地布局与《儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点实施方案》中的全域土地综合整治建设项目布局(图3)相似与差异并存。两种整治情景下,红树林的布局位置与建设项目布局图大致相同,但其布局规模则小于建设项目布局中的规模。其主要原因是在多目标规划当中限制了全域土地综合整治中新增地类的总规模。此外,本文突出了全域土地综合整治中生态产品价值实现目标,因此需要优先布局足够数量的生态产品价值实现潜力系数较大的地类。两种整治情景下,旱地改水田项目规模都要小于建设项目布局中的规模,且布局位置与建设项目布局图存在差异。其主要原因是以当量因子法估算的生态价值中,水田由于水资源的消耗,生态价值要低于旱地,而建设项目布局中“旱改水”的规模一般较大,但以生态价值优先甚至生态价值次优的整治则需要限制旱地向水田的转换。两种整治情景下,新增产业项目(商业服务业用地)的布局规模均大于建设项目布局图,不同之处在于生态产品价值实现潜力优先整治情景下,新增产业项目布局范围同建设项目布局图中的规划较为接近,东、中、西部均有分布,而生态价值优先情景下,新增产业项目布局范围主要集中在中部。其主要原因是产业项目在实现生态产品价值转换当中发挥着重要作用,因而本文更加突出了产业项目与各用地类型之间的布局配套,这也使得产业项目的规模扩大。
3 结论与讨论
3.1 结论
全域土地综合整治在增加生态价值与提高生态产品价值实现潜力之间的权衡,将导致差异化的用地需求。本文以儋州市全域土地综合整治试点项目区为研究区,通过集成MOP与GeoSOS-FLUS模型,分析了生态价值优先和生态产品价值实现潜力优先两种整治情景下,全域土地综合整治用地优化结果。研究结论如下:(1)生态价值和生态产品价值实现潜力优先序的不同,会导致差异化的全域土地综合整治用地优化结果。(2)全域土地综合整治用地结构优化中,生态价值优先整治情景下,与现状相比,试点项目区红树林地和水田规模明显增加。生态产品价值实现潜力优先整治情景下,与生态价值优先整治情景相比,试点项目区红树林地和水田增加规模有所变小但仍大于现状,而商业服务业用地规模明显增加。(3)全域土地综合整治用地布局优化中,两种整治情景与现状比较,整体景观均表现出较高的景观分离程度,分布比现状更加均衡且破碎。(4)两种整治情景的用地布局与《儋州市全域土地综合整治起步区国家级试点实施方案》中的全域土地综合整治建设项目布局相似与差异并存。
3.2 讨论
本文提供了重要政策启示:(1)全域土地综合整治应统筹配置各用地类型以辅助增加生态价值与提高生态产品价值实现潜力。本文发现不论是增加生态价值还是提高生态产品价值实现潜力,都需要不同地类的保障,但实现不同目标会导致不同地类的此消彼长。因此全域土地综合整治应按照“区域—功能—项目”有针对性地配置满足生产、生活、生态各类需求的土地,利用生态空间保障生产空间与生活空间效用的发挥,利用生产空间与生活空间提供生态空间中生态产品价值实现所需的生产和交换功能。(2)全域土地综合整治应耦合社会经济要素优化用地布局。本文发现不同情景下的全域土地综合整治,在差别化的空间安排了各类整治建设项目来增加生态价值与促进生态产品价值实现。这些整治建设项目统筹“山水林田湖草沙”生命共同体系统治理,但其项目布局仍受经济水平、交通条件、文化习俗等社会经济要素的制约。因此全域土地综合整治应实现土地要素与社会经济要素协同治理,基于特定的整治目标,厘清用地布局与社会—经济系统相互影响,追求经济、社会、生态三者的协同最优。(3)全域土地综合整治应合理确定“旱改水”规模。本文发现两种整治情景下的“旱改水”规模要小于实施方案中的建设项目“旱改水”规模,其主要原因是水田需要消耗大量的水资源从而损害生态价值。因此全域土地综合整治中“旱改水”要从土地适宜性出发,提前做好水资源调查,宜水则水,宜旱则旱。
参考文献
面向乡村振兴的全域土地综合整治创新: 公共价值创造与实现
DOI:10.18402/resci.2022.07.01
[本文引用: 1]

全域土地综合整治近年来迅速发展,已成为推动乡村振兴战略实施的重要工具,但作为一项崭新而重大的土地制度供给,从理论到实践都有很大的探索空间。本文根据公共价值创造理论,认为由政府推动的乡村振兴成果具有公共产品属性,乡村振兴的过程就是公共价值创造和实现的过程。全域土地综合整治作为乡村振兴的重要手段,本质上就是通过土地制度创新促进乡村振兴中公共价值的创造和实现。为此,本文首先总结了中外土地整治实践经验,分析了全域土地综合整治的公共价值取向,以此为基础,深入探讨了全域土地综合整治的公共价值创造和实现问题,其中公共价值的创造需要推进理念创新、方法创新和科技创新,公共价值的实现需要推进产权创新、组织创新和监管创新。
Comprehensive land improvement innovation for rural revitalization: Public value creation and realization
DOI:10.18402/resci.2022.07.01
[本文引用: 1]

Region-wide comprehensive land improvement has expanded greatly in recent years and has become a critical tool for promoting the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy. However, as a brand-new and substantial systematic land institution provision, it presents a big room for exploration both in theory and in practice. From the perspective of public value creation, this article argued that the achievements of the government-promoted rural revitalization have the attributes of public goods, and the rural revitalization is a process of creating and realizing public values. As an important means of rural revitalization, region-wide comprehensive land improvement is essential for promoting the creation and realization of public values in rural revitalization through land institution innovation. Therefore, this article first summarized the practical experiences of land regulation in China and internationally, and analyzed the public value orientation of region-wide comprehensive land improvement. On this basis, this article further discussed the creation of public value and the realization of region-wide comprehensive land improvement. Of all the related issues, the creation of public value calls for conceptual innovation, methodological innovation, and science-technological innovation; and the realization of public value needs to realize property rights innovation, organizational innovation, and regulatory innovation.
生态产品价值实现的内涵、目标与模式
The connotation, goal and mode of realizing the value of ecological products
国土空间生态修复布局研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.11.011
[本文引用: 1]

实施国土空间生态修复是新时期生态文明建设的重要途径。国土空间生态保护与修复的布局影响着保护实施力度、工程修复成效以及社会资源分配,是科学开展生态修复工作的前置条件和基础环节。论文在辨析生态修复相关概念关联的基础上,从区域识别和时序判别2个层面出发,结合文献计量学分析整理了国际生态修复布局研究现状,梳理了景观“格局—过程—服务—可持续”理论范式在国土空间生态修复布局研究中的应用。论文提出了支撑可持续发展的生态保护修复目标构建、以社会满意度为导向的生态修复时空需求权衡、面向多重成本的生态修复成本科学评估、在生态刚性约束背景下的基于自然解决方案、恢复力思想下生态保护和人工修复决策阈值、基于时空模拟的生态保护与修复工程选址决策6项重要研究趋向,从而架构了耦合社会—生态目标的国土空间生态修复布局研究路径,以期为国土空间生态修复相关研究和实践提供参考。
Research progress on the arrangement of territorial ecological restoration
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.11.011
[本文引用: 1]

The implementation of ecological restoration of territorial space is an important way to construct ecological civilization in the new era. The arrangement of ecological protection and restoration is the precondition and basic link for scientifically carrying out ecological restoration, which affects the protection implementation, the effectiveness of engineering restoration, and the allocation of social resources. Based on the analyses of the relationship of the concepts related to ecological restoration, and from the perspectives of region identification and temporal sequence identification, this study used bibliographic analysis to examine the current research status of the ecological restoration arrangement internationally, and reviewed the application of the theoretical paradigm of landscape "pattern-process-service-sustainability" in the study of the arrangement of terrestrial ecological restoration. This article identified six important research trends, including the construction of ecological protection and restoration goals that support sustainable development, the balance of spatial and temporal needs for ecological restoration based on social satisfaction, opportunity cost-oriented ecological restoration cost evaluation, natural solutions based on ecological rigid constraints, decision-making threshold of ecological protection and artificial restoration under the concept of resilience, and location decisions for ecological protection and restoration projects based on spatial and temporal simulation, to construct a terrestrial ecological restoration arrangement research system coupled with social-ecological goals. It may provide a reference for the research and practice of ecological restoration of territorial space.
乡村重构视角下全域土地综合整治的机制解析与案例研究
Mechanism analysis and case study of comprehensive land consolidation from the perspective of rural restructuring
改革开放以来我国国土整治历程回顾与新构想
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200106
[本文引用: 1]

改革开放40多年,国土整治随着资源、生态环境领域政治意愿和体制的变迁而变化,经历兴起、搁浅、整合的过程。在梳理改革开放40余年国土整治领域重要政策文件基础上,总结了国土整治历程中的发展经验、主要问题以及新趋势,并提出了新时代国土整治新构想。新时代国土整治目标将牢牢结合生态文明战略,以期实现空间、资源、生态环境优化,打造以人为本高品质国土空间。新时代国土整治是通过“承载力”“适宜性”评价机制,结合综合研判、归因分析划分“国土整治”功能分区开展重大工程,多措并举处置国土开发利用过程中“负外部性”问题,修复国土功能,以实现空间结构优化调整、资源高效利用、生态保护修复、灾害污染治理,以期提升国土空间承载力、适宜性、美丽度、安全性,提升国土可持续发展能力的综合治理活动。
The new conception and review of territory consolidation based on the past years of reform and opening-up
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200106
[本文引用: 1]

In the past 40 years of reform and opening-up, territory consolidation has changed with the political will and institutional changes in the fields of resources and ecological environment, and has undergone a process of rise, collapse and integration. On the basis of the important policies in the field of territory consolidation in the past 40 years of reform and opening-up, this paper summarizes the development experience, the main problems and the new trend of territory consolidation in the new era, and then puts forward a new conception of territory consolidation. The goal of territory consolidation of the new era will be firmly integrated with the ecological civilization strategy to optimize territorry space, resources and ecology and to create a people-oriented and high-quality territorry space. Territory consolidation in the new era will depend on carrying capacity and suitability evaluation mechanism, combining comprehensive research and attribution analysis to divide "territory consolidation" functional zones and carry out major projects. Territory consolidation will deal with "negative externalities" in the process of territory space development and utilization to restore land functions by various measures, so as to optimize territory space,improve resource utilization efficiency, protect important ecosystem, restore damaged ecosystem, prevent disaster and control pollution. It will enhance carrying capacity, suitability, beauty, security and the sustainability of territory space.
Improving ecosystem services supply provides insights for sustainable landscape planning: A case study in Beijing, China
Optimization of land use structure to balance economic benefits and ecosystem services under uncertainties: A case study in Wuhan, China
Multi-objective urban land use optimization using spatial data: A systematic review
基于改进粒子群算法的低碳型土地利用结构优化: 以重庆市为例
Optimization of low-carbon land use structure based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm: A case study in Chongqing Municipality
DOI:10.1111/ejs.1994.45.issue-3 URL [本文引用: 2]
耦合MOP与GeoSOS-FLUS模型的县级土地利用结构与布局复合优化
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190604
[本文引用: 3]

在自然资源整合不断加强,土地利用结构日趋复杂的形势下,采用单一土地利用结构优化方式难以有效满足区域土地利用合理规划的需求。综合考虑生态文明、乡村振兴、城乡融合等土地可持续利用目标,构建土地利用结构优化与布局优化的集成体系,对提升规划适用性具有积极作用。选取常州市金坛区为研究区,以经济效益与生态效益为优化目标,设置自然演变、经济优先和生态优先三种发展情景,在通过MOP(多目标规划)模型进行土地利用结构优化的基础上,利用GeoSOS-FLUS模型实现土地利用布局优化。结果表明:通过集成MOP和GeoSOS-FLUS模型,采用”结构+约束+布局+准则“研究模式探索县域单元下的土地利用结构布局优化,对调整土地利用结构,优化土地利用空间布局有一定帮助。从案例分析结果看,城镇工矿用地数量在自然演变和经济效益优先情景下分别增加了39%和95%;林地在生态效益优先情景下增加了40%;农村居民点在三种情景下分别减少33%、66%和66%。在三种发展情景下,空间格局都将面临城镇空间与生态空间两级分化的现象,后期区域发展中应加强城乡土地利用与生态保护协调发展,促进空间布局均衡化。
Coupled MOP and GeoSOS-FLUS models research on optimization of land use structure and layout in Jintan district
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190604
[本文引用: 3]

Faced with the background of natural resources integration and the more complex land use structure, it is difficult to effectively meet the demand for rational land use planning with a single land use structure optimization method. Considering the objectives of sustainable utilization of land use, ecological civilization, rural development, and urban-rural integration, we constructed an integrated system for land use structure and layout optimization, which will play a positive role in improving the applicability of planning. This study first sets three scenarios of natural evolution, economic priority, and ecological priority, and then uses the MOP model (multi-objective planning model) to calculate the optimal land use structure under different scenarios. Finally, it can carry on land use layout optimization based on the GeoSOS-FLUS model in 2030, Jintan district, Jiangsu province, China. Results show that, by integrating the MOP and GeoSOS-FLUS models and adopting the "Structure + Constraint + Layout + Criterion" approach to optimize the land use structure and layout in the county, it is conducive to optimize the quantitative land use structure and improve the land use spatial distribution; from the results of the case analysis, the area of industrial and mining land in cities and towns has increased by 39% and 95% under the natural evolution and economic efficiency priority scenarios; the forest land has increased by 40% under the eco-efficiency priority scenario; rural settlements decreased by 33%, 66% and 66%, respectively in the three scenarios. Under the three development scenarios, the spatial pattern will face the two-level differentiation of urban space and ecological space. In the later period of regional development, it is necessary to strengthen the coordinated development of urban and rural land use and ecological protection, and promote a balanced spatial distribution.
基于生态—经济权衡的京津冀城市群土地利用优化配置
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.01.003
[本文引用: 1]

探索生态保护与经济发展的权衡关系,并利用该权衡关系协调土地利用优化配置是解决城市群经济与生态协调发展难题的重要途径,已成为目前的一个研究热点。论文针对京津冀城市群生态友好型协同发展的需求,设置生态系统服务价值最大化和经济价值最大化2种优化目标,每种目标下再设置“生态保护”“统筹兼顾”“粮食安全”和“经济发展”4种土地利用情景,采用CLUE-S模型模拟2025年京津冀城市群在不同情景下的土地利用空间配置格局,及其生态系统服务价值、经济价值在不同目标的各种情景下的变化。研究结果表明:相比2015年,2025年在不同目标不同情景下,各类土地利用面积的数量变化和空间格局均有较大不同,且生态目标和经济目标下不同情景的土地利用配置不同。生态系统服务价值在生态目标生态保护情景下最大,为14423.58亿元;而经济价值则在经济目标经济发展情景下最大,为96771.49亿元。从土地利用变化的空间分布上来看,生态用地中林地与草地的增加多出现在坝上高原和燕山与太行山山地,水体的增加则主要分布在东部沿海地区。研究认为,生态效益与经济效益间存在权衡关系,基于生态-经济权衡的土地利用优化研究结果对未来京津冀城市群生态实践工作有较大的参考价值。
Optimal allocation of land use types in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration based on ecological and economic benefits trade-offs
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.01.003
[本文引用: 1]

In order to achieve harmonious ecological and economic development in urban agglomerations, it is important to explore the trade-offs between environmental protection and economic development, and use this knowledge to optimize land use allocation. This study aimed to simulate land use changes in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration with different goals and under different scenarios in 2025 to identify the optimal land use allocation strategies based on the trade-offs between ecological and economic benefits. In order to meet the land use demands for environment-friendly development in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, we developed two optimization goals—ecosystem services value maximization and economic value maximization, and four land use scenarios—environmental protection, balanced development, food security, and economic development focus. A CLUE-S model was built to simulate and predict the optimal land use allocation strategy. The results show that the optimal land use allocations with the ecosystem services maximization goal were very different comparing to that with the economic value maximization goal. The ecosystem services value is estimated to be approximately 1442.36 billion Yuan with the ecosystem services maximization goal and under the environmental protection scenarios, more than that with the economic value maximization goal and under the same scenario. Spatially, the increase of ecologically beneficial land-use types, including forest land and grassland, is more often seen in the Bashang Plateau, Yanshan Mountains, and Taihang Mountains. The increase of water areas often occurs in coastal regions in the east. There are significant trade-offs between ecosystem services value maximization and economic value maximization. The results of this trade-off analysis can provide a basis for future ecological projects in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration.
A cellular automata model for urban land-use simulation
DOI:10.1068/b31110
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper presents an urban land-use simulation model using cellular automata (CA). In the model urban growth is regarded as the result of a global process underpinned by local actions and land-use change as the joint action of three different effects: attribute, heterogeneity, and gravity. The attribute and heterogeneity effects are regarded as different aspects of a local driving force for change constituted by changing accessibility and other attributes resulting from the interaction of land use and transport at the neighborhood level. The gravity effect is a universal resistance to change as a result of inertia and agglomeration of compatible land uses in the vicinity. To ensure that local actions would lead to global behavior, a multipass, in addition to a single-pass, land-use-allocation algorithm is designed to mimic land-use changes. With metropolitan Melbourne in Australia as a case study, the performance of the model in replicating land-use changes is compared with that of an alternative model developed by using only a distance function. The results of the comparison show that the proposed CA model outperforms the alternative model with only a distance function, confirming the importance of incorporating local attributes in modeling land-use changes.
多智能体区域土地利用优化配置模型及其应用
A model for regional land use optimization allocation based on multi-agent system and its application
DOI:10.11821/xb201107010
[本文引用: 1]

Land use optimization allocation is one of the important aspects of sustainable regional land use. However, the current prevalent land use optimization allocation model, which is used for directing a sustainable land use system, needs to be improved, because the current models ignore the collaborative optimization of land uses in terms of quantitative structure, spatial pattern, and benefit. The objective of this paper is to establish a new model to solve the shortcomings, i.e., the RLUOA (Regional Land Use Optimization Allocation) model, which aims to achieve regional sustainable land use. The model is established through a multi-agent system, which defines respectively the decision making rules of the related agents including the central government of the region, the branches of the government that implements the downstream orders, and the land users practically using the land. The RLUOA model was applied to the simulation of land use optimization allocation in Changsha, a typical city located in central China. The simulation result shows that the model can reasonably allocate the land into different spatial units under the constraint of multi-objective, and achieve the collaborative optimization of land use in terms of quantitative structure, spatial pattern, and benefit. The resulted optimal land allocation meets the requirements of building economically feasible, socially acceptable, and environment-friendly land use pattern, and improves obviously the overall economic, ecological and social benefits of the land use in the region. Consequently, the model can provide auxiliary support and scientific references for the decision making associated with sustainable regional land use and for the general land use planning design.
基于CLUE-S模型的区域土地利用布局优化
The regional land use layout optimization based on the CLUE-S model
基于CLUE-S模型的黑河中游土地利用情景模拟研究: 以张掖市甘州区为例
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.2013.02.015
[本文引用: 1]

由于传统的土地利用空间统计分析问题中存在固有的空间自相关效应,进而影响到不同土地利用类型空间分布概率模拟的精度.研究在CLUE-S模型中传统的二值Logistics回归的基础之上引入了空间自相关因子形成Autologistic回归模型,并将其用于区域土地利用情景模拟.结果表明:(1)考虑了土地利用类型空间自相关性的Autologistic回归模型在模拟土地利用空间格局时能更好地反映真实土地利用分布格局.耕地、林地、草地、水域及未利用地的空间格局拟合优度ROC值分别从0.914、0.820、0.697、0.635和0.798提高到0.924、0.892、0.766、0.716和0.835;(2)基于Autologistic回归分析的建模对CLUE-S模型的模拟精度有一定的提高.Autologistic回归分析下模拟结果的Kappa指数0.935 4大于Logistic回归模拟结果0.888 0;(3)通过模拟2020年研究区5种情景方案下土地利用格局,表明在不同情景方案下的土地利用/覆被格局存在显著的空间差异:①自然增长情景方案下,耕地的增加对于保障粮食安全有重要意义,而建设用地的扩张则会促进研究区经济建设的快速发展,但林地和草地转化为未利用地会加剧土地的退化和生态环境的恶化;②在3种水资源约束情景方案下,水资源对干旱区土地利用/覆被变化的制约非常明显,提高水资源利用率是改善干旱区生态环境的一个重要措施;③土地结构优化情景方案下土地利用比较全面地考虑到了流域粮食安全、生态保护以及经济发展等需要,具有较强的合理性;④经济发展情景方案下建设用地快速扩张,大量侵占周边耕地和草地,粮食安全会受到较大的威胁;⑤生态保护情景方案下林地、草地和水域等生态保护用地面积呈显著扩张,区域生态环境质量明显改善.
Land use change scenarios simulation in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin based on CLUE-S model: A case of Ganzhou district of Zhangye city
Delineating multi-scenario urban growth boundaries with a CA: Based FLUS model and morphological method
DOI:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.04.016 URL [本文引用: 2]
地理模拟优化系统GeoSOS软件构建与应用
The implementation and application of geographical simulation and optimization systems (GeoSOS)
基于生态系统服务价值的东北农牧交错区土地利用格局优化与评价
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220710
[本文引用: 1]

为完善土地规划评估指标、挖掘东北农牧交错区生态建设潜力,在明晰2001—2018年东北农牧交错区生态系统服务价值(ESV)时空特征的基础上,分别以供给服务、调节服务和支持服务三种生态功能为优先发展目标,结合CLUE-S模型提出了三种土地利用格局规划方案。结果显示:(1)2001—2018年研究区ESV总量增长9.69%,其中调节、支持和供给服务功能年均占比分别为67.25%、21.88%和6.74%;(2)三种规划方案对区域ESV提升明显,其中支持服务优先情景下ESV总量提升5.84%,高于供给服务(2.66%)和调节服务(5.19%)优先情景;(3)不同土地利用类型的环境适应性不同,研究区西北部、西南部和东部部分地区更适宜造林和退耕,ESV总量和支持服务价值的提升潜力较大,而北部和东南部地区更适宜开垦农田,供给和调节服务价值提升潜力较大。不同生态系统服务间的权衡与协同是保障区域生态与经济稳定可持续发展的关键。充分考虑政策与环境适应性等因素,对东北农牧交错区土地利用格局进行优化,将为当地规划提供理论基础和实践参考。
Land use pattern optimization and evaluation based on ESV of agro-pastoral ecotone in Northeast China
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220710
[本文引用: 1]

To improve the evaluation indicators in land planning and tap the potential of ecological construction in agro-pastoral ecotone of Northeast China, the spatiotemporal characteristics of ecosystem service value (ESV) in the region from 2001 to 2018 were interpreted, and three land use options (i.e., prioritized provisioning service, regulating service, and supporting service) were simulated using the multi-objective programming model and CLUE-S model. The results show that: (1) The total ESV increased by 9.69% from 2001 to 2018, with provisioning service, regulating service, and supporting service accounting for 67.25%, 21.88% and 6.74%, respectively. (2) The total ESV increased by 5.84% in the scenario of prioritized supporting service, which was higher than that of prioritized provisioning service (2.66%) and of prioritized regulating service (5.19%). (3) The environmental adaptability of different land use types is different, i.e., in northwestern, southwestern and eastern parts of the study area with more suitability for afforestation and conversion of farmland, the total ESV and supporting service have great potential to improve, while northern and southeastern parts are more suitable for farmland reclamation, which facilitates the improvements of prioritized provisioning service and regulating service. The synergy among different ecosystem services is important in ensuring the security and sustainable development of regional ecology and economy. Aiming to improve ESV with full consideration of policy and environmental adaptability, the land use optimization can provide theoretical basis and practical guidance for the land planning in agro-pastoral ecotone of Northeast China.
黑土保护与粮食安全背景下齐齐哈尔市国土空间优化调控路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202207007
[本文引用: 1]

市域国土空间规划是空间规划体系构建的关键一环,基于黑土资源的特殊性和重要性,东北黑土区的市域国土空间规划需统筹考虑黑土保护与粮食安全双重目标。本文以黑龙江省齐齐哈尔市为例,建立了融合格网尺度与行政区尺度的黑土区国土空间功能评价指标体系,分析了市域“生产—生活—生态”(“三生”)用地的时空演变特征,诊断了其耦合协调状况,并以区域发展的多元性、社会需求的多样性为导向,提出了齐齐哈尔市黑土保护与粮食安全战略背景下国土空间优化调控路径。研究结果表明,2010—2018年齐齐哈尔市生产空间与生活空间均有一定程度的增长,“三生”功能轻度失调和勉强协调地区占比有所增加。国土空间格局冲突表现为“三生”功能协同性弱,冲突强度地域差异明显,对黑土资源的可持续性开发利用存在一定风险。本文以多尺度下“三生”功能冲突诊断结果为约束,建立了“三生”空间格局优化配置模型。研究认为,东北黑土区市域国土空间功能提升要在国家粮食安全保障能力基础上,坚持以黑土保护利用为导向,统筹“人—水—地”资源要素的组合与匹配,依托现有工业基础和产业优势,分别从引导优势功能区发展、加强重点城镇建设、提高黑土资源利用效率,协调城乡国土空间利用水平等路径来具体实施。
Optimal regulation of spatial planning in the context of black soil preservation and food security in Qiqihar
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202207007
[本文引用: 1]

In China, the national spatial planning system is built largely upon prefectural plans, a critical part of which in many prefecture-level cities would be agricultural planning. When we develop such plans for the black soil regions in Northeast China, much effort is needed to guarantee both the black soil conservation and food security, given the rarity and importance of the black soil to agricultural use. In this research, we took Qiqihar as a case to establish an evaluation index system of land space function in the black soil areas that integrated grid-scale and administrative regional-scale. We analyzed the spatio-temporal evolution features of the production-living-ecological space (PLES) in the study area and evaluated their coupling coordination. Based on this analysis, we put forward an optimal strategy for spatial planning regulation to meet the requirement of the diversified regional development and social demands in Qiqihar in the context of prioritizing black soil preservation and food security. The main conclusions can be drawn as follows: regarding the production-life-ecology function, the mildly imbalanced and barely coordinated areas increased from 2010 to 2018, when the production and living space grew to a certain extent. The low coordination of PLES, the regionally varied conflict between different functional spaces, and the potential risks of unsustainable development of black soil resources jointly constituted the conflict arising from its spatial planning. Eventually, we constructed a configuration model for optimizing spatial planning under the constraint of conflict between PLES on multiple scales. It is our suggestion that the enhancement of functional spatial planning at the prefecture level should drive the priority on which the national food security is based, by which the black soil preservation is oriented, and on which the allocation of "human-water-land" resources depends. To achieve such enhancement with the advantages of our prosperous industry, we should wisely channel the advantages of particular regions toward better development, promote the accelerated development of the critical cities and towns, improve the utilization efficiency of black soil resources, and encourage effective land use of towns in harmony with that of counties.
顾及轨道交通影响的浙中城市群土地利用多情景模拟与分析
DOI:10.12082/dqxxkx.2020.190305
[本文引用: 1]

土地利用变化受到地形地貌、自然环境、城市规划和经济发展等的影响,预测其未来情景对政策调整具有重要的参考意义。元胞自动机模型是模拟和预测不同规划政策下土地利用变化的常用方法。本文基于GlobeLand30数据集,利用浙中城市群2000—2010年土地利用变化校准FLUS模型,并模拟2010年土地利用格局,其总体精度、Kappa系数和图形优化(FOM)分别为89.74%、82.69%和29.86%。采用马尔可夫链预测2030年各类型土地总量,利用FLUS预测一般条件下(常规情景)和城市轨道交通规划站点影响下(轨交情景)浙中城市群未来土地格局。结果表明,在5 km范围内城市轨道交通站点对建设用地增长影响较大,在该区域轨交情景比常规情景面积增加45.25 km <sup>2</sup>、且主要发生在城市边缘区。建设用地扩张主要通过侵占优质农田实现,轨交情景5 km范围内农田转化为建设用地比常规情景增加33.34 km <sup>2</sup>,建设用地扩张强度高于常规情景,其中最低扩张强度以上占比高于常规情景3.70%。景观指数表明,2种情景中林地、草地和水域格局具有较高相似性。本研究表明,综合使用FLUS、遥感、GIS等技术方法,能够准确模拟和预测不同规划条件下未来土地利用格局,并为规划和政策调整提供高可信空间数据。
Simulating land use patterns of the Mid-Zhejiang Urban Agglomeration considering the effects of urban rail transit
全域土地综合整治中生态产品价值实现的逻辑分析
Logical analysis on the realization of ecological product value in comprehensive land consolidation
经济差异化增长下生态系统服务价值的时空演变特征: 以珠江—西江经济带为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220709
[本文引用: 1]

为了应对经济增长与生态保护双重压力,使用生物量与植被覆盖度修正后的当量因子法测度珠江—西江经济带的生态系统服务价值(ESV);基于STIRPAT模型构建地理加权回归模型,实证研究人文因素对ESV影响的空间异质性,并着重将经济增长因子的回归系数以表格形式展示。结论认为:(1)珠江—西江经济带的ESV在研究年份截面中呈现先下降、后上升、再下降的变动趋势;(2)人均GDP对地均ESV在研究区域东部表现为持续负向影响、中部和北部地区表现为由负转正的影响态势、西北部和西南部的回归结果不显著。基于上述结论,针对避免东部地区ESV进一步下降、鼓励中部和北部经济追赶,以及提高西北和西南部对经济与生态环境协调发展问题的重视方面提出政策建议。
Spatio-temporal dynamic characteristics of the ecosystem service values under differential economic growth: A case study of the Pearl River-West River Economic Belt
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220709 URL [本文引用: 1]
Trade-offs across value-domains in ecosystem services assessment
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.03.003 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于单位面积价值当量因子的生态系统服务价值化方法改进
Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.08.001
[本文引用: 4]

Ecosystem service value is the base of decision-making for ecological protection, ecological regionalization and ecological compensation, and it appears the dynamic spatio-temporal changes which are closely connected with the variations of ecological structure and function. However, it is still lack of a universal and integrated dynamic evaluation method for ecosystem service value in China. Based on literature survey, expert knowledge, statistical data and remote sensing data, using model simulations and GIS spatial analysis method, this paper modified and developed the method for evaluating the value equivalent factor in unit area, and proposed an integrated method for dynamic evaluation on Chinese terrestrial ecosystem service value. This method can realize the comprehensive and dynamic assessment of ecosystem service value for 11 service types of 14 different types of terrestrial ecosystem at monthly and provincial scales in China. The preliminary application indicated that the total ecosystem service value was 38.1×10<sup>12</sup> yuan in 2010, in which the value from forest ecosystem was the highest, accounting for about 46%, followed by water body and grassland. Among different ecosystem service types, the contribution from regulation function was the highest, especially the values from hydrological regulation and atmospheric regulation which accounted for about 39.3% and 18.0% of total service value, respectively. Moreover, ecosystem service value presented apparent spatio-temporal patterns in China. Spatially, the ecosystem service value decreased from southeast to northwest and the highest value appeared in southeastern and southwestern regions. Temporally, the ecosystem service value for most of the ecosystems attained the peak in July and reached the trough during December and January except desert, barren and glacier ecosystem. Generally, although this established method still needs to be developed and optimized, it is the first to provide a relatively comprehensive approach for the spatio-temporal dynamic evaluation of ecosystem service value in China, which will be helpful to the scientific decision-making on natural capital rating and ecological compensation.
The value of the world's ecosystem services and natural capital
DOI:10.1038/387253a0 [本文引用: 1]
一个基于专家知识的生态系统服务价值化方法
Expert knowledge based valuation method of ecosystem services in China
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.2008.05.019
[本文引用: 2]

Valuation of global ecosystem services by R Costanza(1997)has attracted attention of the Chinese ecological researchers over the years. And many Chinese scientists have been using the methods to valuate the ecosystem services for forest, grassland and farmland ecosystems. However, it has been turned out that there are several shortcomings in direct adaptation of the methods, for instance, some ecosystem services have been insufficiently valuated or even ignored via using Costanza’s method. To fill this gap, we have, on the basis of Costanza’s method, developed a new method or 'unit value’ based method for assessment of ecosystem services. Expert interviews with structured questionnaire were contacted in 2002 and 2007 respectively, and altogether 700 Chinese ecologists were involved in the interviews for testing the method. It has been found that the values of ecosystem services from expert knowledge based unit value method and biomass based method are comparative. Therefore, expert knowledge based assessment of ecosystem services could be used as a method for assessing ecosystem services with known land use areas, and a good result could be generated within a short period of time. However, for scientifically sound and concrete results, the spatial disparity of ecosystem services should be taken into account.
基于生态系统服务价值评估的东江流域生态补偿研究
Ecological compensation of Dongjiang River Basin based on evaluation of ecosystem service value
A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects
DOI:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.09.019 URL [本文引用: 1]