

JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES >
Safety evaluation and classification of cross-border oil and gas transportation pipelines in China
Received date: 2023-07-17
Revised date: 2023-10-23
Online published: 2024-03-12
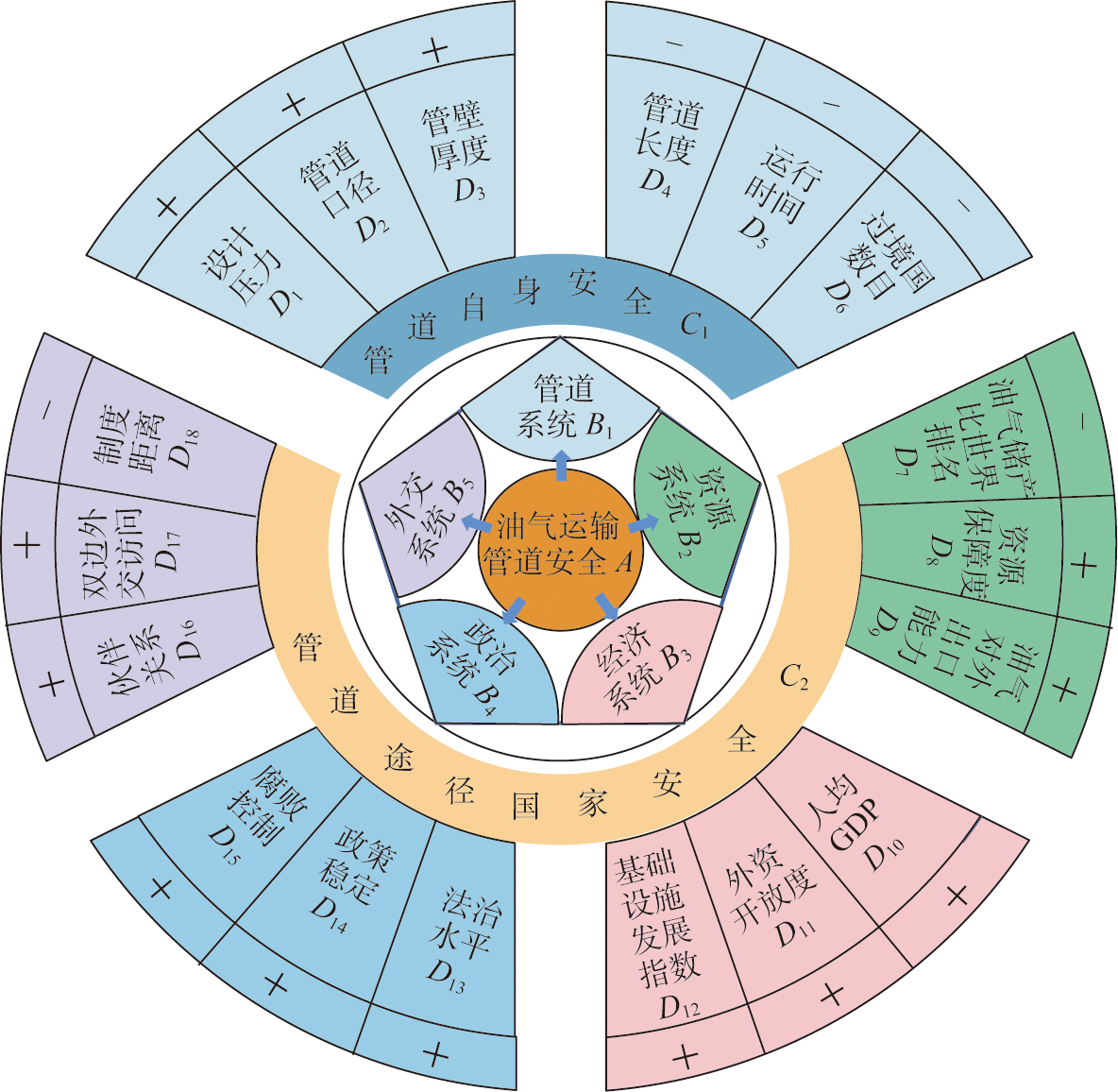
Energy interconnection is an important part of the Belt and Road Initiative, and ensuring the safety of energy transportation pipelines is of great significance in promoting the high-quality development of the Belt and Road Initiative. This paper takes China's cross-border oil and gas transport pipelines as the research object, and constructs an oil and gas transport pipeline safety evaluation index system covering five dimensions of pipeline, resources, economy, politics and diplomacy from two aspects of pipeline safety and pipeline routing involving national security. Based on the entropy-catastrophe progression method, the safety of China's cross-border oil and gas transport pipelines in 2020 is evaluated and classified into categories. The results show that: (1) The catastrophe level values of crude oil transportation pipelines are ranked as China-Kazakhstan crude oil pipeline>China-Russia crude oil pipeline>China-Myanmar crude oil pipeline; the catastrophe level values of natural gas transportation pipelines are ranked as China-Central Asia natural gas pipeline line C>China-Central Asia natural gas pipeline lines A and B>east route of China-Russia natural gas pipeline>China-Myanmar natural gas pipeline; and the pipelines have their respective advantages and disadvantages under the sub-dimensions. (2) According to the system clustering method, the pipelines are divided into two types: high security type and low security type. The high safety pipelines are in good condition at present, but there are still safety hazards; resource scarcity, political instability, and economic weakness have become unfavourable factors affecting the safety evaluation of low safety pipelines.
LI Yi , ZHAO Yuan , XIA Si-you . Safety evaluation and classification of cross-border oil and gas transportation pipelines in China[J]. JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES, 2024 , 39(3) : 547 -563 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20240304
表1 中国跨境油气运输管道基本情况表Table 1 Basic situation of cross-border oil and gas transport pipelines in China |
| 通道 | 管道组成 | 管道途经国家 | 投用时间/年 | 运输能力 | 资源地(含潜在) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 西北 | 中哈原油管道 | 哈萨克斯坦 | 2006 | 2000×104 t/a | 哈萨克斯坦(里海地区) |
| 中国—中亚天然气管道A线、B线 | 土库曼斯坦、乌兹别克斯坦、哈萨克斯坦 | 2010 | 300×108 m3/a | 土库曼斯坦、乌兹别克斯坦、哈萨克斯坦(里海地区) | |
| 中国—中亚天然气管道C线 | 2014 | 250×108 m3/a | |||
| 中国—中亚天然气管道D线 | 土库曼斯坦、乌兹别克斯坦、塔吉克斯坦、吉尔吉斯斯坦 | 规划 | 300×108 m3/a | ||
| 东北 | 中俄原油管道 | 俄罗斯 | 2011 | 3000×104 t/a | 俄罗斯 |
| 中俄东线天然气管道 | 2019 | 380×108 m3/a | |||
| 西南 | 中缅原油管道 | 缅甸 | 2017 | 2200×104 t/a | 中东地区(非洲地区) |
| 中缅天然气管道 | 2013 | 120×108 m3/a | 缅甸 |
图3 中国跨境油气运输管道安全性突变级数法结构Fig. 3 Structure of catastrophe series method for safety of cross-border oil and gas import transportation pipelines in China |
表2 常见突变模型的势函数和归一化公式Table 2 Common potential function and normalization foumula of catastrophe models |
| 突变模型 | 控制变量 | 势函数 | 归一化公式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 折迭突变 | 1 | ||
| 尖点突变 | 2 | ; | |
| 燕尾突变 | 3 | ; ; | |
| 蝴蝶突变 | 4 | ; ; ; |
| [1] |
杨宇, 夏四友, 钱肖颖. 能源转型的地缘政治研究. 地理学报, 2022, 77(8): 2050-2066.
[
|
| [2] |
杨宇, 于宏源, 鲁刚, 等. 世界能源百年变局与国家能源安全. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(11): 2803-2820.
[
|
| [3] |
BP. Statistical Review of World Energy data. https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/sustainability/reporting-centre-and-archive.html, 2022-06-28.
|
| [4] |
杨宇, 何则. 中国海外油气依存的现状、地缘风险与应对策略. 资源科学, 2020, 42(8): 1614-1629.
[
|
| [5] |
杨足膺, 赵媛, 周昊, 等. 中石化江苏成品油一次配送空间格局与优化. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(11): 2770-2782.
[
|
| [6] |
夏四友, 郝丽莎, 唐文敏, 等. 复杂网络视角下世界石油流动的竞合态势演变及对中国石油合作的启示. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(11): 2655-2673.
[
|
| [7] |
杨宇, 夏四友, 金之钧. 能源转型重塑地缘政治的逻辑与研究展望. 地理学报, 2023, 78(9): 2299-2315.
[
|
| [8] |
鄢继尧, 赵媛, 崔盼盼, 等. 石油安全视角下中国原油进口贸易时空格局演化分析. 经济地理, 2020, 40(11): 112-120.
[
|
| [9] |
李志斐. 南海非传统安全问题的现状与应对机制分析. 太平洋学报, 2020, 28(4): 69-80.
[
|
| [10] |
高天航, 吕靖. 海上通道关键节点安全保障效率及应急效率评价研究. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2017, 17(6): 27-32.
[
|
| [11] |
李振福, 颜章龙. 基于盲数理论的我国海上战略通道安全风险评价. 武汉理工大学学报: 交通科学与工程版, 2014, 38(1): 16-20.
[
|
| [12] |
赵旭, 高建宾, 林玮. 基于投影寻踪的海上能源运输通道安全评价. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2011, 11(6): 30-37.
[
|
| [13] |
苗雨莹, 赵旭, 何晨甲. “一带一路”背景下我国原油海运节点安全度评价. 中国水运(下半月), 2021, 21(8): 25-26, 30.
[
|
| [14] |
韩梦瑶, 熊焦, 刘卫东. 中国跨境能源贸易及隐含能源流动对比: 以“一带一路”能源合作为例. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(11): 2674-2686.
[
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
潘家华. 油气管道的风险分析. 油气储运, 1995, 14(3): 11-15.
[
|
| [19] |
王辉, 纪翔, 洪亮. 基于优化贝叶斯网络的油气管道失效风险安全评价. 化工安全与环境, 2023, 36(1): 35-40.
[
|
| [20] |
黄亮亮, 姚安林, 鲜涛, 等. 考虑脆弱性的油气管道风险评估方法研究. 中国安全科学学报, 2014, 24(7): 93-99.
[
|
| [21] |
李师瑶, 侯磊, 熊毅, 等. 油气管道本质安全影响因素分析及启示. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2017, 13(11): 79-84.
[
|
| [22] |
谢明华, 杨明珠. “一带一路”油气通道建设的地缘政治和安全风险. 探索, 2016, 32(2): 63-69.
[
|
| [23] |
梁萌, 徐建山, 安雨康, 等. 论石油通道权. 国际石油经济, 2020, 28(4): 1-16, 102.
[
|
| [24] |
王劲松, 陈默, 熊中浩, 等. 跨国油气管道社会安全风险浅议. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2014, 10(s2): 83-86.
[
|
| [25] |
代启福. 中国跨国油气管道边境地区的民族关系与边疆安全研究: 以中缅油气管道为例. 世界民族, 2019, 41(6): 39-50.
[
|
| [26] |
戴永红, 秦永红. 中缅油气管道建设运营的地缘政治经济分析. 南亚研究季刊, 2015, 31(1): 16-22, 117.
[
|
| [27] |
王礼茂, 李红强. 中国与周边国家在油气领域的竞争与合作及其地缘政治影响. 资源科学, 2009, 31(10): 1633-1639.
[
|
| [28] |
解晓燕, 刘咏梅. 中国周边跨境油气管道布局及联动效应研究. 长江大学学报: 社科版, 2014, 37(6): 83-87.
[
|
| [29] |
陆如泉. 对当前全球能源管道安全形势的观察与思考. 国家安全研究, 2022, 36(6): 72-87, 166.
[
|
| [30] |
王勇辉. “21世纪海上丝绸之路”东南亚战略支点国家的构建. 世界经济与政治论坛, 2016, 36(3): 61-73.
[
|
| [31] |
李鹤林, 吉玲康, 田伟. 高钢级钢管和高压输送: 我国油气输送管道的重大技术进步. 中国工程科学, 2010, 12(5): 84-90.
[
|
| [32] |
汪玲玲, 赵媛. 中国石油进口运输通道安全态势分析及对策研究. 世界地理研究, 2014, 23(3): 33-43.
[
|
| [33] |
王强, 陈俊华. 基于供给安全的我国石油进口来源地风险评价. 世界地理研究, 2014, 23(1): 37-44.
[
|
| [34] |
张中元. 人类命运共同体理念对双边外交关系的影响. 世界经济与政治, 2021, 35(12): 24-53, 156.
[
|
| [35] |
中华人民共和国外交部政策规划司. 中国外交. 北京: 世界知识出版社, 2019.
[ Department of Policy Planning Ministry of Foreign Affairs People's Republic of China. China's Foreign Affairs. Beijing: World Affairs Press, 2019.]
|
| [36] |
刘京星, 黄健柏, 刘天琦. 中国与“一带一路”国家钢铁产能合作影响因素研究: 基于多维动态距离的新视角. 经济地理, 2018, 38(10): 99-110.
[
|
| [37] |
赵宏波, 马延吉, 苗长虹. 基于熵值—突变级数法的国家战略经济区环境承载力综合评价及障碍因子: 以长吉图开发开放先导区为例. 地理科学, 2015, 35(12): 1525-1532.
[
|
| [38] |
邹亚锋, 李亚静, 袁志鸿. 西部省会城市新型城镇化水平综合测度研究. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(6): 1612-1621.
[
|
| [39] |
牛剑平, 杨春利, 白永平. 中国农村经济发展水平的区域差异分析. 经济地理, 2010, 30(3): 479-483.
[
|
| [40] |
崔守军, 杨宇. 俄罗斯与乌克兰冲突的地缘政治渊源与地缘战略逻辑. 地理研究, 2022, 41(8): 2065-2075.
[
|
| [41] |
陆如泉, 李晨成, 段一夫. 中缅油气合作: 新形势新挑战新思维. 国际石油经济, 2015, 23(6): 63-67, 111.
[
|
| [42] |
陈晓鹏, 成升魁, 吴良. 中亚主要能源出口国地缘政治风险的度量与评价. 资源科学, 2018, 40(4): 773-783.
[
|
| [43] |
曾向红. “无声的协调”: 大国在中亚的互动模式新探. 世界经济与政治, 2022, 36(10): 42-70, 165-166.
[
|
| [44] |
刘承良, 王杰, 杜德斌. 中美能源权力的空间领域与均势区演化. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(11): 2596-2612.
[
|
| [45] |
胡志丁, 张喆, 赵路平. 地缘环境研究的理念及议程与路径. 地理学报, 2023, 78(1): 198-213.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |