

JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES >
Progress towards the research on the doughnut-shaped framework as a novel roadmap for sustainable development assessment
Received date: 2023-06-19
Revised date: 2023-09-20
Online published: 2024-01-24
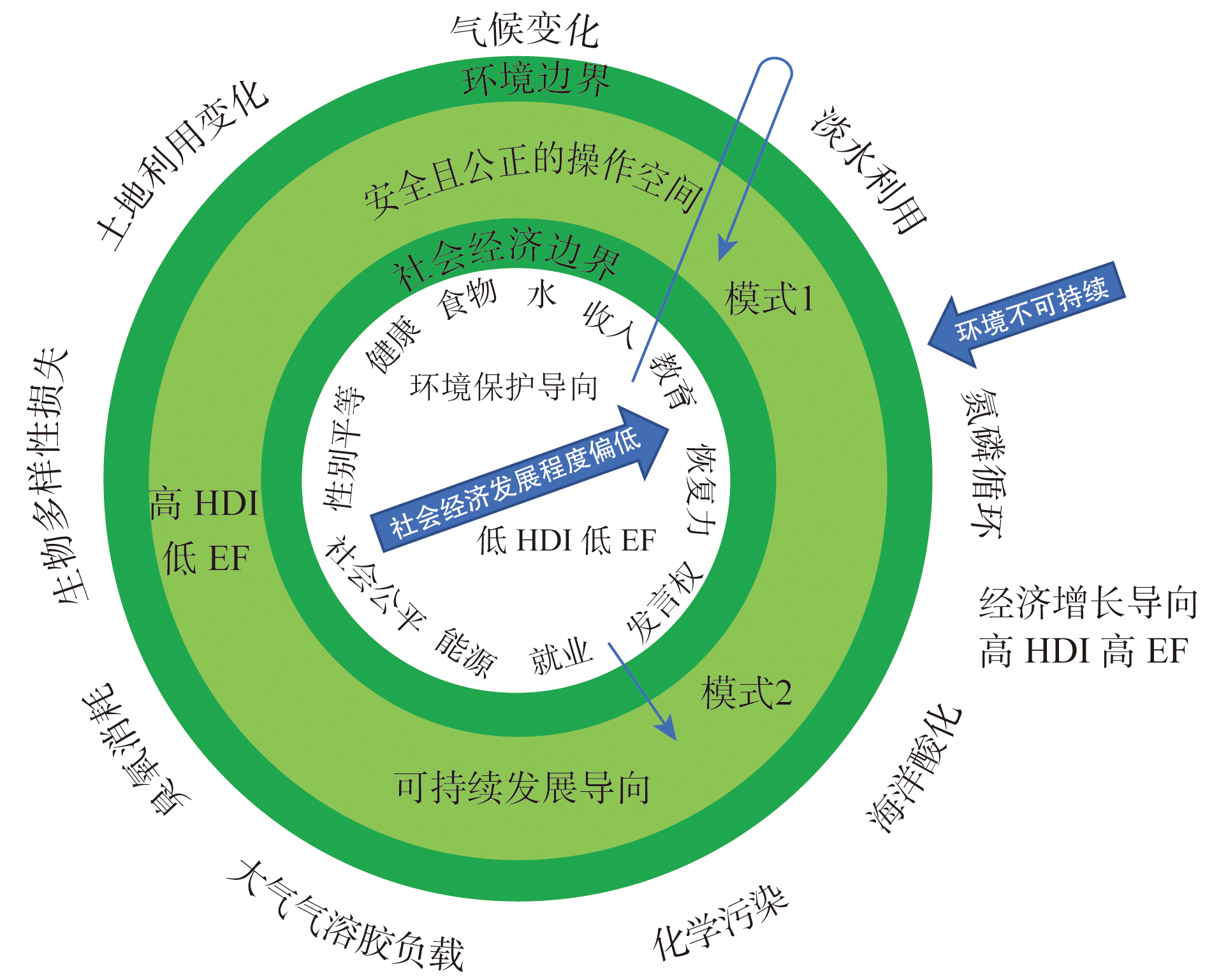
Sustainable development is a hot topic of universal concern and heated discussion among all humanity. As an extension of the planetary boundaries framework to the socio-economic field, the doughnut-shaped framework provides new ideas for sustainable development assessment across the globe. This paper provides a systematic review and in-depth analysis of the concept, theoretical basis, localization expansion, existing problems, and improvement directions of the doughnut-shaped framework. The research has shown that the doughnut-shaped framework organically integrates environmental boundaries and basic socio-economic needs, thereby incorporating environmental sustainability and socio-economic development into the same analytical framework. This framework is based on the theory of steady-state economy, emphasizing the need for both a certain amount of man-made capital to meet human's socio-economic needs and a constant amount of natural capital to maintain environmental sustainability. The localization expansion applications of the doughnut-shaped framework mainly focus on the evaluations of environmental sustainability and socio-economic development respectively, lacking in-depth explanation of internal interaction mechanisms. In order to enhance the scientific understanding of the transmission mechanisms between environmental boundaries and socio-economic boundaries, it is urgent to strengthen research on the interactions between environmental boundaries, ecosystem services, and socio-economic boundaries based on ecosystem units. The guiding value of the doughnut-shaped framework for global and regional sustainable development needs to be further enhanced. Due to its high compatibility with China's development philosophy of balancing ecological protection red line and socio-economic bottom line, the doughnut-shaped framework has great potential for application in the field of sustainable development in China.
CHEN Xian-peng , FANG Kai . Progress towards the research on the doughnut-shaped framework as a novel roadmap for sustainable development assessment[J]. JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES, 2024 , 39(2) : 307 -318 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20240205
表1 甜甜圈框架的本地化探索Table 1 Localization explorations of the doughnut-shaped framework |
| 尺度 | 文献 | 环境边界及其确定方法 | 社会经济边界及其确定方法 | 两类边界间的交互机制 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 国家 | Cole等[25] | 碳:国家目标 臭氧:国际目标 水、土地:国家资源极限 磷、氮、生物多样性、海洋捕捞、PM10:局地阈值 | 能源、水、卫生设备、住房、教育、医疗、就业、收入、家庭用品、食物安全、社会安全:基本需求的100%满足 | 简要描述两者的联系 |
| Hickel[26] | 碳、物质足迹:行星边界的人均配额 | 预期寿命、教育:边界未定 收入:20000 $/cap(PPP) | 通过构造可持续发展指数建立两者的联系 | |
| O'Neill等[27] | 碳、磷、氮、蓝水、eHANPP、生态足迹、物质足迹:行星边界的人均配额 | 生活满意度、健康的预期寿命、营养、卫生设备、收入、能源、教育、社会支持、民主质量、平等、就业:主观判定 | 认为两者间存在供给系统,讨论了两者间的相关性 | |
| 方恺等[28] | 水、土地、碳、氮、磷:行星边界的人均配额 | SDG1-SDG 12、SDG 16、SDG 17:基于SDSN指标板确定 | 基于空间计量分析两者间的关联 | |
| 省域 | Cole等[29] | 碳:国家目标的分配 臭氧:局地数据整合 水、土地:省域资源极限 磷、生物多样性、海洋捕捞、PM10:局地阈值 | 能源、水、卫生设备、住房、教育、医疗、发言权、就业、收入、家庭用品、食物安全、社会安全:基本需求的100%满足 | 未探讨 |
| Han等[30] | 碳、水、土地、氮、磷:行星边界的人均配额 | 参考O'Neill等[27] | 基于耦合协调度模型探讨了环境可持续性与社会经济发展状态之间的关系 | |
| 邵庆龙等[31] | 未探讨 | 幸福感、发言权、社会参与、健康、性别平等:统计经验 收入、社会公正:国际标准 工作机会、教育、能耗、水资源:国家规划文件规定 | 未探讨 | |
| 城市 | Dearing等[32] | 空气质量、沉积物调节、水质、土壤稳定性、沉积物质量:系统行为观测 | 食物安全、收入、水、卫生设备、医疗、教育、就业:基本需求的100%满足 | 未探讨 |
| Hoornweg等[33] | GHG、生物多样性、水、土地、氮、污染、地质风险:全球边界均值 | 青年机会、经济、能源、机动性和连通性、制度、基本服务、治安与公共安全:全球目标均值 | 未探讨 | |
| 流域 | Dearing等[32] | 空气质量、水资源调节、沉积物调节、水质、土壤稳定性:系统行为观测 | 食物安全、收入、水、医疗、教育、能源、就业:基本需求的100%满足 | 未探讨 |
| 苏彦瑜等[34] | 碳、水、耕地:本地目标 碳、臭氧:全球边界均值 化肥、PM10、生物多样性、水质、土壤稳定性、沉积物调节、化学污染:系统行为观测 | 无贫困、健康、教育、性别平等、清洁用水与卫生设备、能源安全、可持续的城市、产业创新:统计报告、公报等文件的数据 | 基于Pearson相关系数分析社会发展状况和生态系统变量的关系 | |
| 企业 | Bjørn等[35] | 以气候变化为主:2 ℃温控目标 | 未探讨 | 未探讨 |
注:eHANPP为隐含的净初级生产力的人类占用,SDG为可持续发展目标,SDSN为可持续发展解决方案网络,GHG为温室气体。 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
张军泽, 王帅, 赵文武, 等. 可持续发展目标关系研究进展. 生态学报, 2019, 39(22): 8327-8337.
[
|
| [10] |
王红帅, 董战峰. 联合国可持续发展目标的评估与落实研究最新进展: 目标关系的视角. 中国环境管理, 2020, 12(6): 88-94.
[
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
陈先鹏, 方恺, 彭建, 等. 资源环境承载力评估新视角: 行星边界框架的源起、发展与展望. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(3): 513-531.
[
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
诸大建. 用国际可持续发展研究的新成果和通用语言解读生态文明. 中国环境管理, 2019, 11(3): 5-12.
[
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
方恺, 许安琪, 何坚坚, 等. “一带一路”沿线国家可持续发展综合评估及分区管控. 科学通报, 2021, 66(19): 2441-2454.
[
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
邵庆龙, 李默, 康鹏, 等. 可持续发展评估的新方法: “甜甜圈”理论的中国案例分析. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(2): 334-347.
[
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
苏彦瑜, 李燕, 董旭辉. 湖北梁子湖流域社会生态系统可持续发展的“安全公正空间”. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(12): 4206-4214.
[
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
张军泽, 王帅, 赵文武, 等. 地球界限概念框架及其研究进展. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(4): 465-476.
[
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
侯鹏, 王桥, 申文明, 等. 生态系统综合评估研究进展: 内涵、框架与挑战. 地理研究, 2015, 34(10): 1809-1823.
[
|
| [45] |
戴尔阜, 王晓莉, 朱建佳, 等. 生态系统服务权衡: 方法、模型与研究框架. 地理研究, 2016, 35(6): 1005-1016.
[
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
[
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
方恺, 许安琪, 何坚坚, 等. 可持续发展目标实现进程中的环境效应分析: 以“一带一路”沿线国家为例. 浙江大学学报: 人文社会科学版, 2022, 52(3): 100-119.
[
|
| [54] |
李扬, 汤清. 中国人地关系及人地关系地域系统研究方法述评. 地理研究, 2018, 37(8): 1655-1670.
[
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
史园莉, 高吉喜, 张文国, 等. 生态保护红线监管台账关键技术研究与应用. 生态学报, 2022, 42(21): 8892-8901.
[
|
| [57] |
方利, 姚敏, 于忠伟, 等. “三区三线”统筹划定中永久基本农田布局优化方法与实证. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(16): 42-50.
[
|
| [58] |
秦萧, 甄峰. 基于要素流动的城镇建设用地配置方法框架探讨. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(11): 2774-2788.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |