

JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES >
Discussion on urban construction land allocation based on element flow
Received date: 2021-09-13
Revised date: 2022-04-07
Online published: 2023-01-28
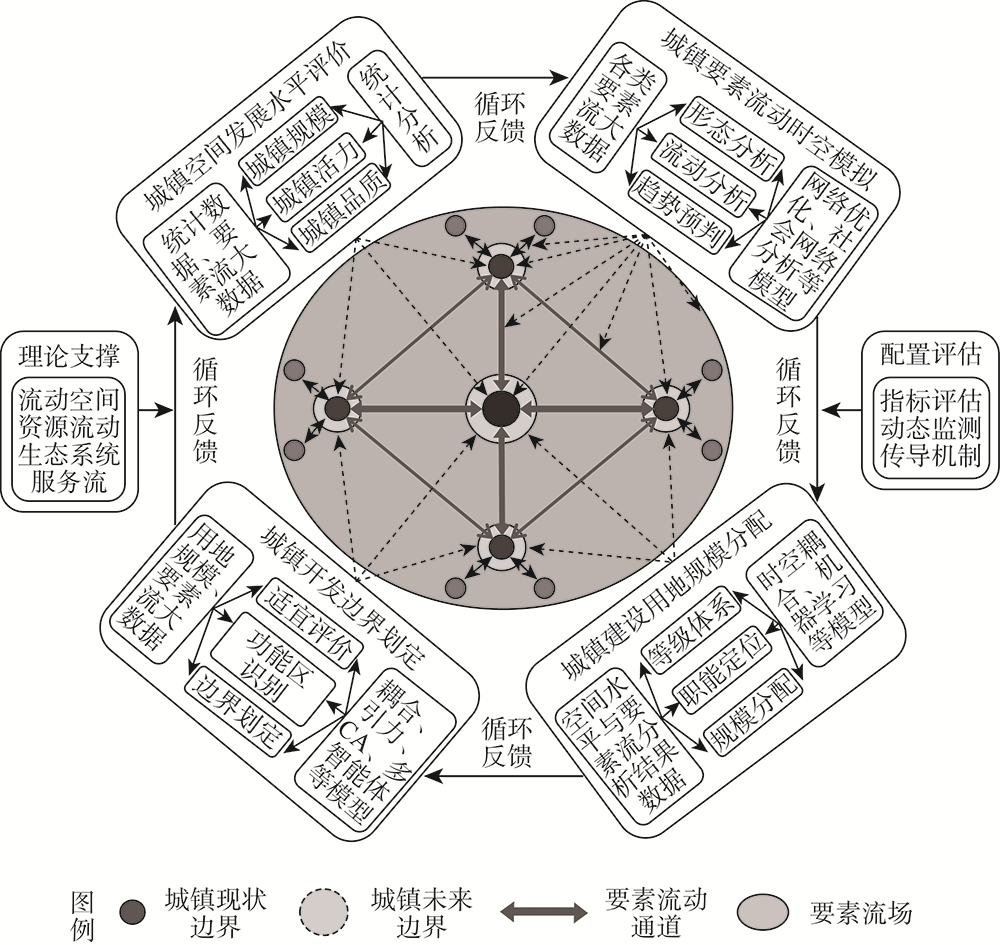
The existing urban construction land allocation mainly follows the guidance of spatial development, which is carried out by using static data and land allocation standards, evaluation and prediction models. There are some phenomena of "regional preference" and "seeking large scale". In the new era of emphasizing the construction of ecological civilization and high-quality development, the implementation of territory spatial planning strategy requires that the allocation method of urban construction land needs to be innovated in time. This project focuses on the inevitable trend that the urban place space will be transformed into the urban flow space under the deep influence of information or intelligent technology in the future, and considers that the spatiotemporal flow and distribution of production, life and ecological elements of different scales will be the key to the scientific allocation of urban construction land. Therefore, the project uses multi-source big data of element flow and multi-disciplinary analysis methods, trying to establish a new method framework from four aspects: evaluation of urban spatial development level, spatio-temporal simulation of urban element flow network and land allocation, identification of urban element functional area and delimitation of development boundary, and dynamic evaluation of urban construction land allocation effect. Firstly, it is found that the evaluation of urban spatial development level needs to comprehensively consider the ability of cities to control, attract and overflow the current regional elements, and construct the evaluation index system from three aspects of spatial development scale, vitality and quality. Secondly, in the process of regional distribution of urban construction land index, we pay attention to using network optimization model and social network analysis method to describe the flow law of regional elements, and find out the cities with different levels and types of combination of "spatial development level and element control" through time-space coupling model. Thirdly, the future expansion direction and boundary shape of cities are determined by the spatiotemporal matching of supply and demand between the flow changes of various internal elements and the functional space layout. It is necessary to identify the functional influence area and flow preference of elements by using models of spatiotemporal coupling, gravity, cellular automata and agent-based system. Finally, the evaluation index of urban construction land allocation effect needs to reflect the requirements and trends of future urban development, such as ecological civilization, high quality, smart governance and integration. These research results can provide reference for the delimitation and implementation of urban development boundary in territory spatial planning.
Key words: element flow; urban construction land; big data; method framework
QIN Xiao , ZHEN Feng . Discussion on urban construction land allocation based on element flow[J]. JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES, 2022 , 37(11) : 2774 -2788 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20221102
| [1] |
黎斌, 贺灿飞, 黄志基, 等. 城镇土地存量规划的国际经验及其启示. 现代城市研究, 2017, (6): 39-46.
[
|
| [2] |
王卉. 存量规划背景下的城市用地兼容性的概念辨析和再思考. 现代城市研究, 2018, (5): 45-54.
[
|
| [3] |
邹兵. 增量规划向存量规划转型: 理论解析与实践应对. 城市规划学刊, 2015, (5): 12-19.
[
|
| [4] |
林坚, 叶子君, 杨红. 存量规划时代城镇低效用地再开发的思考. 中国土地科学, 2019, 33(9): 1-8.
[
|
| [5] |
程迎轩. 省级规划调整完善新增建设用地指标分配研究: 以广东省为例. 国土资源情报, 2017, (3): 17-22, 34.
[
|
| [6] |
陈逸, 陈志刚, 周艳, 等. 江苏省地级市建设用地利用效率的区域差异与优化配置. 经济地理, 2017, 37(6): 171-176, 205.
[
|
| [7] |
陆张维, 吴次芳, 岳文泽. 土地利用总体规划建设用地指标区域动态分配问题研究. 中国土地科学, 2010, 24(8): 59-65.
[
|
| [8] |
丁建中, 金志丰, 陈逸. 基于空间开发潜力评价的泰州市建设用地空间配置研究. 中国土地科学, 2009, 23(5): 30-36.
[
|
| [9] |
刘耀林, 郝弘睿, 谢婉婷, 等. 基于生态系统服务价值的土地利用空间优化. 地理与地理信息科学, 2019, 35(1): 69-74.
[
|
| [10] |
张红伟, 王占岐, 张利国, 等. 我国建设用地指标配置研究进展及展望. 中国国土资源经济, 2021, 34(11): 34-43.
[
|
| [11] |
王颖, 顾朝林, 李晓江. 中外城市增长边界研究进展. 国际城市规划, 2014, 29(4): 1-11.
[
|
| [12] |
黄金碧, 冯长春. 基于DEA模型优化的城镇建设用地需求预测: 以皖江城市带为例. 城市发展研究, 2013, 20(11): 75-80.
[
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
郑伟伟, 柯新利. 基于案例推理的城镇建设用地需求预测: 以重庆市为例. 城市问题, 2018, (8): 79-86.
[
|
| [15] |
谭荣辉, 刘耀林, 刘艳芳, 等. 城市增长边界研究进展: 理论模型、划定方法与实效评价. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39(2): 327-338.
[
|
| [16] |
孟霖, 郭杰, 孙驰, 等. 基于供求关系的城镇建设用地适宜性评价: 以扬州市为例. 资源科学, 2018, 40(1): 11-21.
[
|
| [17] |
龙瀛, 韩昊英, 毛其智. 利用约束性 CA 制定城市增长边界. 地理学报, 2009, 64(8): 999-1008.
[
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
李鑫, 肖长江, 欧名豪, 等. 基于生态位适宜度理念的城镇用地空间优化配置研究. 长江流域资源与环境, 2017, 26(3): 376-383.
[
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
杨鑫, 姜海, 范宇, 等. 基于效率—公平的区际建设用地指标配置方式评价及改进: 以南京市为例. 中国土地科学, 2017, 31(7): 20-27.
[
|
| [27] |
王艺洁, 付万年, 刘志有. 新疆绿洲县域建设用地配置效率及优化措施研究: 以乌鲁木齐县为例. 中国农业资源与区划, 2019, 40(5): 188-194.
[
|
| [28] |
聂雷, 邵子南. 基于资源场势的江苏省建设用地空间配置研究. 河南农业大学学报, 2019, 53(3): 434-440.
[
|
| [29] |
黄琳珊, 陈彦光, 李双成. 京津冀城镇用地空间结构的多分维谱分析. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(1): 50-64.
[
|
| [30] |
刘海龙. 从无序蔓延到精明增长: 美国“城市增长边界”概念述评. 城市问题, 2005, (3): 67-72.
[
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
秦萧, 甄峰. 大数据与小数据据结合: V信息时代城市研究方法探讨. 地理科学, 2017, 37(3): 321-330.
[
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
成升魁, 甄霖. 资源流动研究的理论框架与决策应用. 资源科学, 2007, 29(3): 37-44.
[
|
| [35] |
张新林, 赵媛. 基于空间视角的资源流动内涵与构成要素的再思考. 自然资源学报, 2016, 31(10): 1611-1623.
[
|
| [36] |
王嘉丽, 周伟奇. 生态系统服务流研究进展. 生态学报, 2019, 39(12): 4213-4222.
[
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
秦萧, 甄峰, 李亚奇, 等. 国土空间规划大数据应用方法框架探讨. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(10): 2134-2149.
[
|
| [39] |
王宜强, 赵媛. 资源流动研究现状及其主要研究领域. 资源科学, 2013, 35(1): 89-101.
[
|
| [40] |
姚婧, 何兴元, 陈玮. 生态系统服务流研究方法最新进展. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(1): 335-342.
[
|
| [41] |
李哲睿, 甄峰, 傅行行. 基于企业股权关联的城市网络研究: 以长三角地区为例. 地理科学, 2019, 39(11): 1763-1770.
[
|
| [42] |
甄峰, 王波, 陈映雪. 基于网络社会空间的中国城市网络特征: 以新浪微博为例. 地理学报, 2012, 67(8): 1031-1043.
[
|
| [43] |
王德, 朱查松, 谢栋灿. 上海市居民就业地迁移研究: 基于手机信令数据的分析. 中国人口科学, 2016, (1): 80-89, 127.
[
|
| [44] |
钮心毅, 李晓晗, 刘思涵. 应用手机信令数据的建设用地活动强度监测方法. 地理信息世界, 2021, 28(4): 1-8.
[
|
| [45] |
罗桑扎西, 甄峰. 基于手机数据的城市公共空间活力评价方法研究: 以南京市公园为例. 地理研究, 2019, 38(7): 1594-1608.
[
|
| [46] |
王灿, 王德, 朱玮, 等. 基于消费者行为的商业空间绩效评价体系建构. 城市规划, 2021, 45(3): 33-45.
[
|
| [47] |
冯晓玙, 黄斌斌, 李若男, 等. 生态系统服务流特征及量化方法研究进展. 环境保护科学, 2019, 45(6): 29-38.
[
|
| [48] |
刁星, 程文. 城市空间绩效评价指标体系构建及实践. 规划师, 2015, 31(8): 110-115.
[
|
| [49] |
王新峰, 袁兆宇, 李君, 等. 基于空间绩效的总规实施评估方法探索. 规划师, 2018, 34(6): 112-117.
[
|
| [50] |
任晓娟, 陈晓键, 马泉. 空间经济绩效导向下的城市用地布局优化研究. 城市规划, 2019, 43(7): 50-59.
[
|
| [51] |
龙瀛, 唐婧娴. 城市街道空间品质大规模量化测度研究进展. 城市规划, 2019, 43(6): 107-114.
[
|
| [52] |
阳建强, 朱雨溪, 张倩. 面向空间品质提升的城市更新. 时代建筑, 2021, (4): 12-15.
[
|
| [53] |
秦萧, 甄峰, 朱寿佳, 等. 基于网络口碑度的南京城区餐饮业空间分布格局研究: 以大众点评网为例. 地理科学, 2014, 34(7): 810-817.
[
|
| [54] |
王德, 王灿, 谢栋灿, 等. 基于手机信令数据的上海市不同等级商业中心商圈的比较: 以南京东路、五角场、鞍山路为例. 城市规划学刊, 2015, (3): 50-60.
[
|
| [55] |
李涛, 程遥, 张伊娜, 等. 城市网络研究的理论、方法与实践. 城市规划学刊, 2017, (6): 43-49.
[
|
| [56] |
钮心毅, 刘思涵, 朱艺. 地区间人员流动视角下的中国城镇化空间特征研究. 城市规划学刊, 2021, (1): 82-89.
[
|
| [57] |
李苑君, 吴旗韬, 张玉玲, 等. 中国三大城市群电子商务快递物流网络空间结构及其形成机制研究. 地理科学, 2021, 41(8): 1398-1408.
[
|
| [58] |
温旭丽, 陆燕楠, 向星月. 面向多式联运的货运网络优化模型构建与应用. 物流技术, 2021, 40(1): 67-72, 82.
[
|
| [59] |
杨忠振, 穆雪, 朱晓聪. 交通流变化下的多配送中心—多需求点配送网络优化模型. 交通运输工程学报, 2015, 15(1): 100-107.
[
|
| [60] |
王茂军, 田丽英, 杨雪春. 山东省城镇网络结构与城镇网络角色识别: 基于民国时期土货/洋货流通网络的分析. 地理研究, 2011, 30(9): 1621-1636.
[
|
| [61] |
赵宏波, 魏甲晨, 孙东琪, 等. 大城市内部“生产—生活—生态空间”多尺度耦合协调度: 以郑州市为例. 资源科学, 2021, 43(5): 944-953.
[
|
| [62] |
王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器:原理与展望. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1): 116-134.
[
|
| [63] |
钟炜菁, 王德. 上海市中心城区夜间活力的空间特征研究. 城市规划, 2019, 43(6): 97-106, 114.
[
|
| [64] |
龙瀛, 周垠. 街道活力的量化评价及影响因素分析: 以成都为例. 新建筑, 2016, (1): 52-57.
[
|
| [65] |
席广亮, 甄峰, 沈丽珍, 等. 南京市居民流动性评价及流空间特征研究. 地理科学, 2013, 33(9): 1051-1057.
[
|
| [66] |
钮心毅, 康宁, 李萌. 都市圈视角下的上海城市公共中心体系重构探讨. 城市规划学刊, 2019, (3): 42-49.
[
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
王梓洋, 石培基, 张学斌, 等. 基于多智能体模型的兰州市城镇用地扩展模拟. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(6): 2169-2179.
[
|
| [70] |
刘小平, 黎夏, 艾彬, 等. 基于多智能体的土地利用模拟与规划模型. 地理学报, 2006, 61(10): 1101-1112.
[
|
| [71] |
全泉, 田光进, 沙默泉. 基于多智能体与元胞自动机的上海城市扩展动态模拟. 生态学报, 2011, 31(10): 2875-2887.
[
|
| [72] |
王宏杰. 基于元胞自动机与多智能体模型的城市空间扩展研究. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2016.
[
|
| [73] |
张跃胜, 李思蕊, 李朝鹏. 为城市发展定标:城市高质量发展评价研究综述. 管理学刊, 2021, 34(1): 27-42.
[
|
| [74] |
江宗文, 张军. 生态城市评价指标体系研究综述. 山西建筑, 2016, 42(13): 245-246.
[
|
| [75] |
宫攀, 张令新. 国内外智慧城市评价指标体系对比分析及启示. 规划师, 2018, 34(11): 96-100, 107.
[
|
| [76] |
曾刚, 王丰龙. 长三角区域城市一体化发展能力评价及其提升策略. 改革, 2018, (12): 103-111.
[
|
| [77] |
甄峰, 张姗琪, 秦萧, 等. 从信息化赋能到综合赋能: 智慧国土空间规划思路探索. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(10): 2060-2072.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |