

JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES >
Key issues in natural resource management under carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality targets
Received date: 2021-09-09
Revised date: 2022-01-05
Online published: 2022-07-28
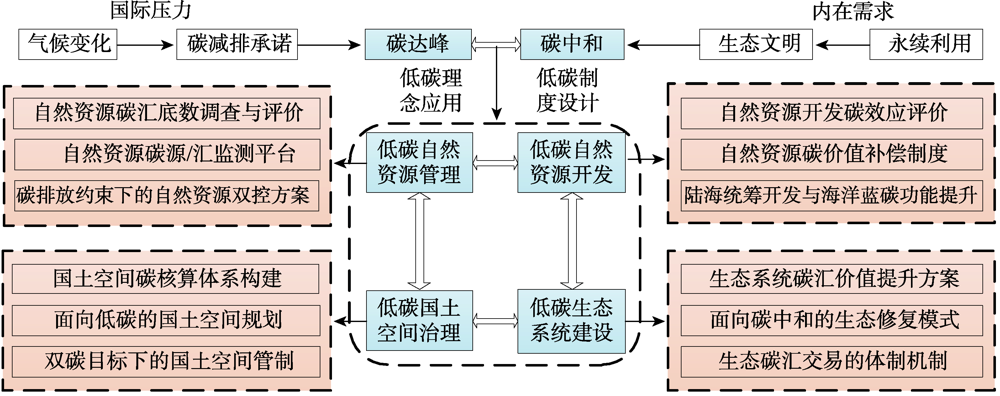
The targets of carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality will certainly promote the systematic revolution of China's economy and society. Natural resources are crucial materials and space carrier for human activities. Low-carbon-based innovation of natural resource management system and territorial space governance pattern is of great significance for enhancing ecosystem carbon sinks and resources supporting capacity, improving resource utilization efficiency, and promoting long-term low-carbon transition of the whole society. Focusing on natural resource management under the target of carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality, nine scholars put forward key strategies for the innovation of natural resource management, which mainly include resource coupling management, territorial space optimization and land control, fine farmland management, land use carbon metabolism regulation, ecological carbon sink system and sustainable forests management. This provides a vital guidance for the establishment of low-carbon natural resource management system based on multi-level perspectives of "resource elements-territorial space-ecosystem", which helps to comprehensively improve carbon sink/emission reduction function within the field of natural resources. Generally, the researchers suggested that the systematic response framework of natural resource management under the targets of carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality should be established. The future top-level design should be strengthened to establish a multi-level collaborative management system of natural resources based on element-space-system. Carbon cycle monitoring network and carbon accounting standards system related to natural resources and territorial space with Chinese characteristics should be regulated. Resources coupling management, elaborative spatial management and land structure optimization should be strengthened to explore different territorial space control schemes. The management of resource circulation within nature-economy-society system should be improved to establish a net-framework for carbon metabolism and its regional nexus and realize regional coordinated carbon emission reduction based on resource optimization management. The carbon sink function of natural resources and territorial space should be stressed, which should be incorporated into the carbon trading and ecological compensation system. The regional horizontal carbon compensation system should be established based on carbon neutrality evaluation of territorial space to promote the coordinated emission reduction and development among different regions.
ZHAO Rong-qin , HUANG Xian-jin , YUN Wen-ju , WU Ke-ning , CHEN Yin-rong , WANG Shao-jian , LU He-li , FANG Kai , LI Yu . Key issues in natural resource management under carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality targets[J]. JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES, 2022 , 37(5) : 1123 -1136 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20220502
:感谢研究生罗慧丽在论文文献整理和校对等方面的帮助。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
DE LA PEÑA L,
|
| [6] |
沈镭, 钟帅, 胡纾寒. 新时代中国自然资源研究的机遇与挑战. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(8): 1773-1788.
[
|
| [7] |
郝庆, 封志明, 赵丹丹, 等. 自然资源治理的若干新问题与研究新趋势. 经济地理, 2019, 39(6): 1-6.
[
|
| [8] |
严金明, 王晓莉, 夏方舟. 重塑自然资源管理新格局: 定位、价值导向与战略选择. 中国土地科学, 2018, 32(4): 1-7.
[
|
| [9] |
岳文泽, 吴桐, 王田雨, 等. 面向国土空间规划的“双评价”: 挑战与应对. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(10): 2299-2310.
[
|
| [10] |
郝庆, 邓玲, 封志明. 面向国土空间规划的“双评价”: 抗解问题与有限理性. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(3): 541-551.
[
|
| [11] |
郝庆, 邓玲, 封志明. 国土空间规划中的承载力反思: 概念、理论与实践. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(10): 2073-2086.
[
|
| [12] |
甄峰, 张姗琪, 秦萧, 等. 从信息化赋能到综合赋能: 智慧国土空间规划思路探索. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(10): 2060-2072.
[
|
| [13] |
陈明星, 梁龙武, 王振波, 等. 美丽中国与国土空间规划关系的地理学思考. 地理学报, 2019, 74(12): 2467-2481.
[
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
孙赫, 梁红梅, 常学礼, 等. 中国土地利用碳排放及其空间关联. 经济地理, 2015, 35(3): 154-162.
[
|
| [18] |
夏楚瑜. 基于土地利用视角的多尺度城市碳代谢及“减排”情景模拟研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019.
[
|
| [19] |
杜金霜, 付晶莹, 郝蒙蒙. 基于生态网络效用的昭通市“三生空间”碳代谢分析. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(5): 1208-1223.
[
|
| [20] |
张利国, 王占岐, 李冰清. 湖北省土地整治项目碳效应核算及其分析. 自然资源学报, 2018, 33(11): 2006-2019.
[
|
| [21] |
方恺, 沈万斌, 董德明. 能源足迹核算的改进与预测: 以吉林省为例. 地理研究, 2011, 30(10): 1835-1846.
[
|
| [22] |
秦华鹏, 袁辉洲. 城市水系统与碳排放. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.
[
|
| [23] |
刘江宜, 窦世权, 肖建忠, 等. 基于全生命周期的矿产资源开发环境影响评估: 以贵州松桃锰矿整装勘查区为例. 资源与产业, 2019, 21(4): 36-43.
[
|
| [24] |
谢高地, 李士美, 肖玉, 等. 碳汇价值的形成和评价. 自然资源学报, 2011, 26(1): 1-10.
[
|
| [25] |
赵荣钦, 刘英, 马林, 等. 基于碳收支核算的河南省县域空间横向碳补偿研究. 自然资源学报, 2016, 31(10): 1675-1687.
[
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
赵荣钦. 提升管理效能促进“双碳”目标实现. 中国自然资源报, 2021-07-14(3).
[
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
赵荣钦, 李志萍, 韩宇平, 等. 区域“水-土-能-碳”耦合作用机制分析. 地理学报, 2016, 71(9): 1613-1628.
[
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
徐晓晔, 黄贤金. 基于碳排放峰值的长江经济带人口承载力研究. 现代城市研究, 2016, 30(5): 33-38.
[
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
谢高地, 肖玉. 农田生态系统服务及其价值的研究进展. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(6): 645-651.
[
|
| [36] |
袁凯华, 张苗, 甘臣林, 等. 基于碳减排目标的省域碳生态补偿研究. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(1): 21-29.
[
|
| [37] |
赵荣钦, 黄贤金, 徐慧, 等. 城市系统碳循环与碳管理研究进展. 自然资源学报, 2009, 24(10): 1847-1859.
[
|
| [38] |
董锁成, 陶澍, 李飞, 等. 气候变化对区域发展的影响. 秦大河主编. 中国气候与环境演变:2012国家气候变化科学评估报告. 北京: 气象出版社, 2012.
[
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
李飞, 董锁成, 李宇, 等. 中国东部沿海地区农业污染风险地域分异研究. 资源科学, 2014, 36(4): 801-808.
[
|
| [42] |
IPCC. 2021: Summary for policymakers. Edited by VALÉRIE M D. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |