

JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES >
Optimization of network structural resilience of territory development zones based on propagation simulation
Received date: 2020-06-22
Request revised date: 2020-11-06
Online published: 2021-11-28
Copyright
Propagation simulation is an important way to recognize the resilience of network structure from a dynamic perspective. Exploring the relationship between the difference in network structure and the state of network propagation is of great significance to the improvement of network structure resilience and the optimization of territory development space. This paper constructs four typical urban network models: nearest neighbor network, small world network, scale-free network and random network. Using complex network theory and SIS virus propagation model, MATLAB and Gephi are used to simulate infectious diseases, and the four types of networks are analyzed. The variation characteristics of infection quantity and infection time under the difference of network shape, node scale and degree value, and the influence mechanism are discussed. The results showed that: (1) From the perspective of overall characteristics, the difference in network structure affects the strength of network propagation. The heterogeneity value distribution, highly local clustering, and short path length of irregular network will expand the scale of infection and shorten the time of infection. (2) From the perspective of decomposition characteristics, scale is not the core factor affecting network communication. High degree of urban network with power law distribution is the risk of regional and urban suppression of negative transmission. (3) From the perspective of spatio-temporal characteristics, heterogeneous network and regular network have the dual characteristics of robustness and fragility. The advantages of heterogeneous network in peacetime and the advantages of regular network in epidemic time should be fully developed through network switching. Based on this, the resilience optimization strategy of land development space network structure is proposed from the regional and urban levels.

LIN Ying-zi , PENG Chong , WANG Bao-qiang . Optimization of network structural resilience of territory development zones based on propagation simulation[J]. JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES, 2021 , 36(9) : 2193 -2204 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20210903
表1 四类网络模型Table 1 Four types of urban network models |
| 网络类型 | 最近邻网络 | 随机网络 | WS小世界网络 | BA无标度网络 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 网络算法机制 | 节点以确定的规则进行连边所形成的网络 | 节点以随机方式进行连边所形成的网络。该模型可以通过两种不同的方法构建,一是具有固定节点和边数,即给定节点数N和边数n,节点产生连线的概率相同;二是具有固定节点和连边概率,即给定节点数N,并以给定的概率p1进行连边 | 介于规则网络和随机网络之间的网络,其算法机制是在最近邻网络上对其进行断边,再以概率p2随机重连网络中的所有边 | 算法机制是包括初始网络、节点增长和择优连接三个过程。首先构建一个节点数为N0的全连接网络,然后引入新节点与网络中的N1个节点相连(N1≤N0),接着新节点以概率p3优先与度值较大的节点连接 |
| 备注 | 选择规则网络中的最近邻网络,是指网络中的节点仅与最近的K个邻居节点连接 | 采用前者进行随机网络构建 | 采用WS小世界模型并给定p2参数值为0.15 | 模型具有动态增长性和择优连接性的特点,网络中多数节点的度值较小,少数节点的度值很大,网络连接异质不均 |
表3 网络结构的平疫切换模型Table 3 A switching model of network structure for normal time and epidemic time |
| 网络类型 | 非规则网络 | 非规则网络与规则网络之间的平疫切换 | 规则网络 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 模式图 | 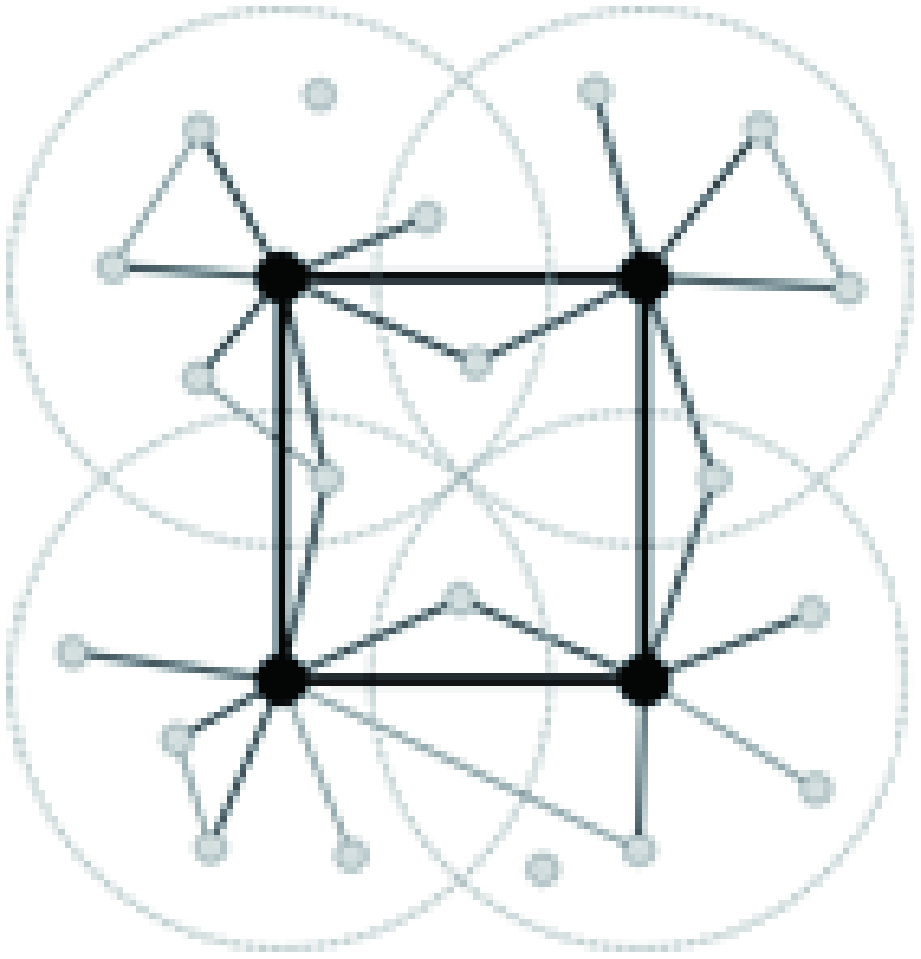 | 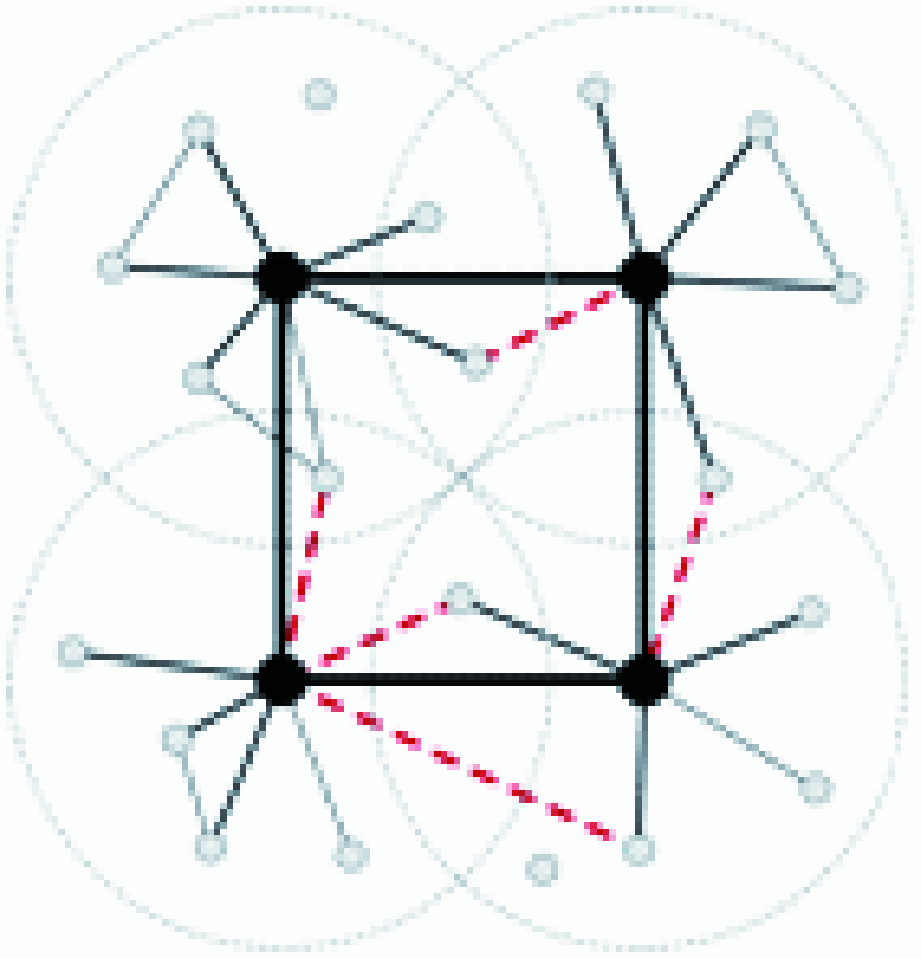 | 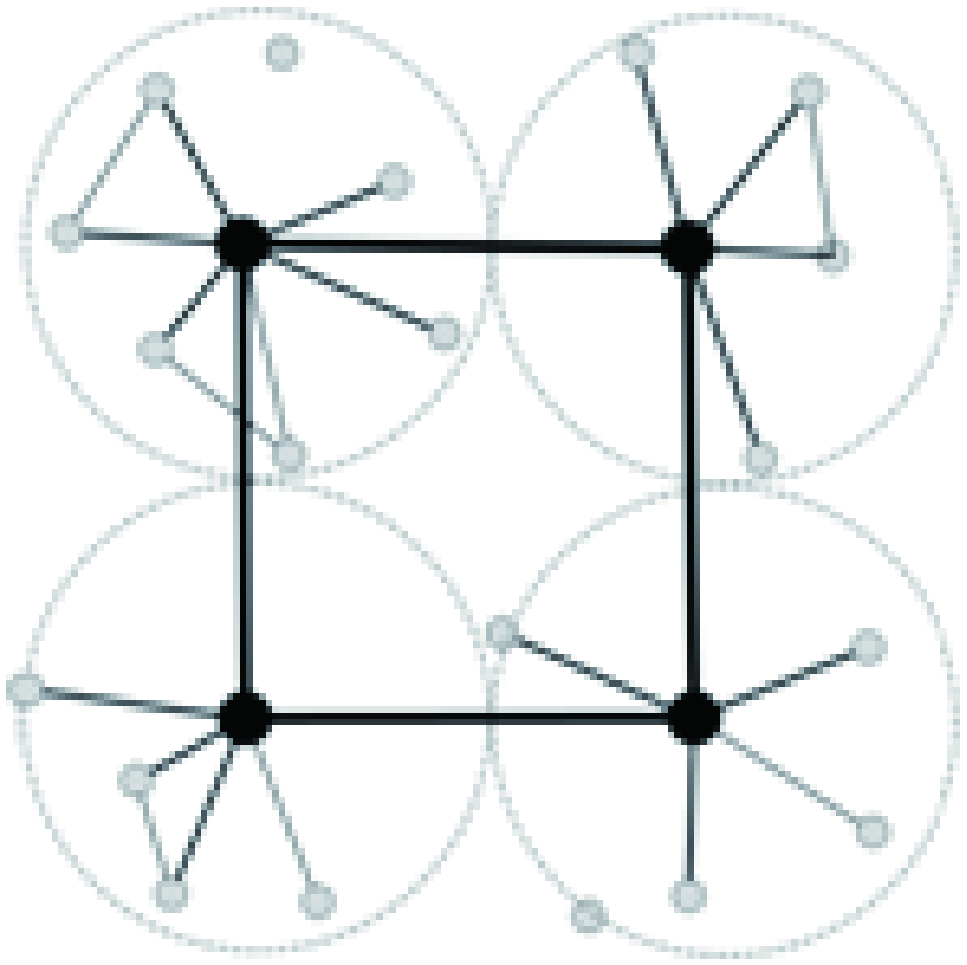 |
| 结构特征 | 偏好依附、路径随机所形成的活动范围交叉,网络结构异质多元 | 切断/重连随机化的跨层级、跨区域联系 | 层级嵌套、路径锁定所形成的活动范围分区,网络结构簇状有序 |
| [1] |
刘涛, 陈忠, 陈晓荣. 复杂网络理论及其应用研究概述. 系统工程, 2005, 23(6):1-7.
[
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
周涛, 柏文洁, 汪秉宏, 等. 复杂网络研究概述. 物理, 2005, 34(1):31-36.
[
|
| [5] |
刘建香. 复杂网络及其在国内研究进展的综述. 系统科学学报, 2009, 17(4):31-37.
[
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
李仙德. 基于上市公司网络的长三角城市网络空间结构研究. 地理科学进展, 2014, 33(12):1587-1600.
[
|
| [9] |
甄峰, 王波, 陈映雪. 基于网络社会空间的中国城市网络特征: 以新浪微博为例. 地理学报, 2012, 67(8):1031-1043.
[
|
| [10] |
朱杰. 多源数据融合的市县国土空间规划人口城镇化模式: 以扬州市为例. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(10):2087-2102.
[
|
| [11] |
杜超, 王姣娥, 刘斌全, 等. 城市道路与公共交通网络中心性对住宅租赁价格的影响研究: 以北京市为例. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(12):1831-1842.
[
|
| [12] |
顾秋实, 张海平, 陈旻, 等. 基于手机信令数据的南京市旅游客源地网络层级结构及区域分异研究. 地理科学, 2019, 39(11):1739-1748.
[
|
| [13] |
丁亮, 钮心毅, 宋小冬. 基于个体移动轨迹的多中心城市引力模型验证. 地理学报, 2020, 75(2):268-285.
[
|
| [14] |
黄勇, 李林, 万丹. 基于复杂网络分析法的养老设施空间配置规划优化: 以重庆市主城四区为例. 西部人居环境学刊, 2017, 32(5):52-58.
[
|
| [15] |
崔喆, 沈丽珍, 刘子慎, 等. 基于公司行业结构的哈尔滨跨区域联系网络分析. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(7):1672-1685.
[
|
| [16] |
蔡宁, 吴结兵, 殷鸣. 产业集群复杂网络的结构与功能分析. 经济地理, 2006, 26(3):378-382.
[
|
| [17] |
赵渺希, 黎智枫, 钟烨, 等. 中国城市群多中心网络的拓扑结构. 地理科学进展, 2016, 35(3):376-388.
[
|
| [18] |
吴康, 方创琳, 赵渺希. 中国城市网络的空间组织及其复杂性结构特征. 地理研究, 2015, 34(4):711-728.
[
|
| [19] |
冷炳荣, 杨永春, 李英杰, 等. 中国城市经济网络结构空间特征及其复杂性分析. 地理学报, 2011, 66(2):199-211.
[
|
| [20] |
彭翀, 陈思宇, 王宝强. 中断模拟下城市群网络结构韧性研究: 以长江中游城市群客运网络为例. 经济地理, 2019, 39(8):68-76.
[
|
| [21] |
孟祥芳, 汪波. 基于弹性相关因素分析的集群可持续发展研究. 科学学与科学技术管理, 2014, 35(8):49-56.
[
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
周艳, 李妍羲, 江荣贵, 等. 交通拥堵与预警信息交互传播动力学分析. 地球信息科学学报, 2017, 19(10):1279-1286.
[
|
| [26] |
李婵婵, 蒋国平, 宋玉蓉. 动态小世界社团网络上的病毒传播研究. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2014, 11(3):33-39.
[
|
| [27] |
阮中远. 复杂网络上的流行病传播. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2020, 50(1):98-117.
[
|
| [28] |
王伟, 舒盼盼, 唐明, 等. 网络传播动力学模拟方法评述. 电子科技大学学报, 2016, 45(2):288-294.
[
|
| [29] |
彭翀, 林樱子, 顾朝林. 长江中游城市网络结构韧性评估及其优化策略. 地理研究, 2018, 37(6):1193-1207.
[
|
| [30] |
李萍. 复杂网络中若干模型上的传播特性研究. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2013.
[
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
贾俊波. MATLAB在网络传染病模拟中的应用. 数字技术与应用, 2016, (2):107-108.
[
|
| [33] |
魏冶, 修春亮. 城市网络韧性的概念与分析框架探析. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39(3):488-502.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |