

生态资产质量评估方法与进展
|
赵钰(1995- ),女,山东德州人,博士研究生,主要从事生态资产评估研究。E-mail: yuzhao_st@rcees.ac.cn |
收稿日期: 2024-08-26
修回日期: 2024-11-13
网络出版日期: 2025-06-20
基金资助
第二次青藏高原综合科学考察研究(2019QZKK0308)
Review of ecosystem asset quality assessment methods and progress
Received date: 2024-08-26
Revised date: 2024-11-13
Online published: 2025-06-20
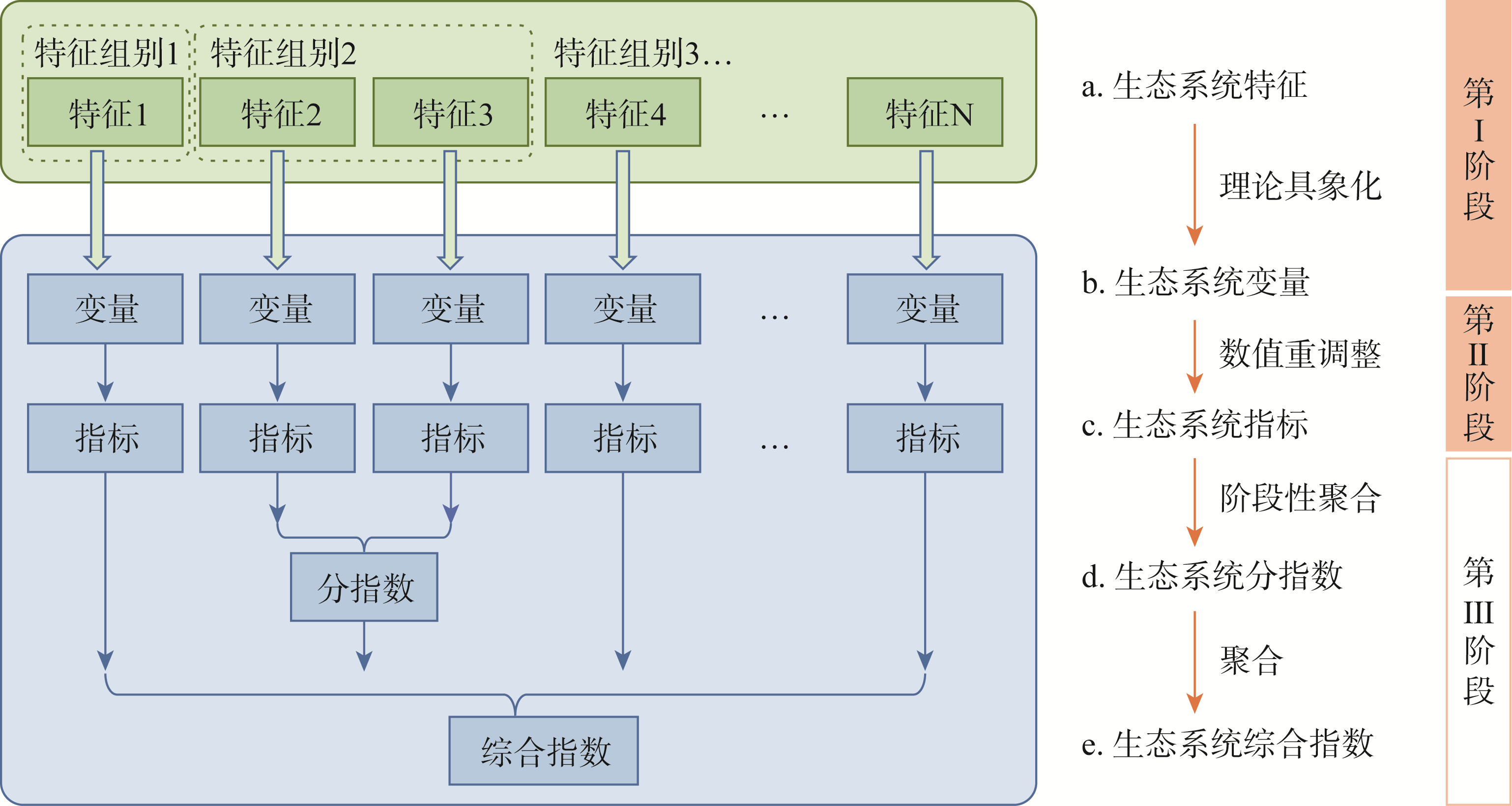
生态资产是为人类提供生态产品和服务、形成生态效益和生态系统生产总值的基础,是支撑人类社会经济发展的重要自然资源资产,包括森林、草地等自然生态系统,农田、城镇绿地等以自然生态过程为基础的人工生态系统,以及野生动植物资源等。生态资产质量是生态系统结构与功能特征的综合体现,反映了生态资产持续提供生态产品和服务的能力。评估生态资产质量是生态资产评估与核算中最复杂的部分之一。生态资产质量评估作为生态系统核算与评估的新视角,强调了生态系统的自然属性和社会经济属性,对于生态系统价值化、生态资产管理及生态产品价值实现等具有重要的推动意义。本文系统梳理和归纳了生态资产质量的概念、评估方法和指标,综述了国内外生态资产质量及相关评估案例与实践,揭示了当前研究中仍存在指标体系待完善、综合评估方法待改进等问题并提出对策建议,以期为未来的生态资产质量研究提供参考,推动全球生态系统评估与核算及其在生态环境保护政策制定中的应用。
赵钰 , 应凌霄 , 张观石 , 欧阳志云 . 生态资产质量评估方法与进展[J]. 自然资源学报, 2025 , 40(7) : 1719 -1742 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20250701
Ecosystem assets, as an important part of the natural resource assets to support human socio-economic development, are the basis for the provision of ecosystem products and services to humans, and consequently for the generation of ecological benefits and gross ecosystem product, including natural ecosystems such as forests and grasslands, artificial ecosystems based on natural ecological processes such as farmland and urban green space, as well as wildlife resources. Ecosystem asset quality is the synthesis of structural and functional characteristics of ecosystems, reflecting the capacity to provide ecosystem services sustainably. Assessing the ecosystem asset quality is one of the most complex parts in ecosystem asset accounting. As a new perspective of ecosystem accounting, ecosystem asset quality emphasizes both natural and socio-economic attributes of ecosystems, which is highly significant in promoting ecosystem valorization, ecosystem asset management and the realization of the value of ecosystem products. In this review, we systematically summarize the concepts, assessment methods and indicators of ecosystem asset quality, and also provide an overview of global relevant cases. Issues, such as the improvement of the indicator system and the comprehensive assessment, and suggestions for the assessment of ecosystem asset quality are proposed to establish a framework for future research, and to promote global ecosystem assessment and accounting with its application in ecological and environmental protection policymaking.

| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
高吉喜, 范小杉. 生态资产概念、特点与研究趋向. 环境科学研究, 2007, 20(5): 137-143.
[
|
| [12] |
TEEB. Frequently asked questions about NCA, 2012, 2024-02-20.
|
| [13] |
欧阳志云, 郑华, 谢高地, 等. 生态资产、生态补偿及生态文明科技贡献核算理论与技术. 生态学报, 2016, 36(22): 7136-7139.
[
|
| [14] |
于贵瑞, 杨萌. 自然生态价值、生态资产管理及价值实现的生态经济学基础研究: 科学概念、基础理论及实现途径. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(5): 1153-1165.
[
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
GB/T 42340-2023. 生态系统评估生态系统格局与质量评价方法. 中华人民共和国国家市场监督管理总局, 中华人民共和国国家标准化管理委员会, 2023.
[GB/T 42340-2023. Ecosystem assessment: Methods for ecosystem pattern and quality assessment. State Administration for Market Regulation & Standardization Administration of P.R.C., 2023.]
|
| [17] |
GB/T 43677-2024. 生态系统评估陆地生态资产核算技术指南. 中华人民共和国国家市场监督管理总局, 中华人民共和国国家标准化管理委员会, 2024.
[GB/T 43677-2024. Ecosystem assessment: Technical guideline for terrestrial ecosystem asset accounting. State Administration for Market Regulation & Standardization Administration of P.R.C. 2024.]
|
| [18] |
United Nations, European Union, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, et al. System of Environmental-Economic Accounting: Ecosystem Accounting (SEEA EA). White Cover. 2021, https://seea.un.org/ecosystem-accounting.
|
| [19] |
于贵瑞, 王永生, 杨萌. 生态系统质量及其状态演变的生态学理论和评估方法之探索. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(4): 865-877.
[
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
钱爱民, 张新民. 资产质量: 概念界定与特征构建. 财经问题研究, 2009, (12): 99-104.
[
|
| [22] |
张新民, 钱爱民, 陈德球. 上市公司财务状况质量: 理论框架与评价体系. 管理世界, 2019, 35(7): 152-166, 204.
[
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
陈展, 林波, 尚鹤, 等. 适应白洋淀湿地健康评价的IBI方法. 生态学报, 2012, 32(21): 6619-6627.
[
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
马克明, 孔红梅, 关文彬, 等. 生态系统健康评价: 方法与方向. 生态学报, 2001, 21(12): 2106-2116.
[
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
欧阳志云, 靳乐山, 甄林, 等. 面向生态补偿的生态系统生产总值(GEP)和生态资产核算. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.
[
|
| [52] |
谢高地. 生态资产评价: 存量、质量与价值. 环境保护, 2017, 45(11): 18-22.
[
|
| [53] |
张慧龙, 杨秀春, 杨东, 等. 2000—2020年内蒙古草地植被覆盖度时空变化及趋势预测. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 1-13.
[
|
| [54] |
湖泊(水库)富营养化评价方法及分级技术规定. 中华人民共和国: 中国环境监测总站, 2001.
[Technical regulations on eutrophication evaluation methods and grading for lakes (reservoirs). The People's Republic of China: China National Environmental Monitoring Centre, 2001.]
|
| [55] |
GB/T 28407-2012. 农用地质量分等规程. 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局、中华人民共和国国家标准化管理委员会, 2012.
[GB/T 28407-2012. Regulation for gradation on agriculture land quality. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine & Standardization Administration of P.R.C., 2012.]
|
| [56] |
宋昌素, 肖燚, 博文静, 等. 生态资产评价方法研究: 以青海省为例. 生态学报, 2019, 39(1): 9-23.
[
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
董天, 张路, 肖燚, 等. 鄂尔多斯市生态资产和生态系统生产总值评估. 生态学报, 2019, 39(9): 3062-3074.
[
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
甘依霖, 罗静, 朱媛媛, 等. 城市空间生态资产评估及其人地关系内涵: 以武汉市府河湿地为例. 自然资源学报, 2023, 38(7): 1756-1770.
[
|
| [61] |
宗乐丽, 陈孜, 张明, 等. 长江中下游地区流域生态资产价值评估: 以新安江流域为例. 中国地质, 2024, 51(4): 1252-1265.
[
|
| [62] |
张会儒, 雷相东, 张春雨, 等. 森林质量评价及精准提升理论与技术研究. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(5): 1-18.
[
|
| [63] |
冯继广, 王景升, 姚帅臣, 等. 基于因子分析的森林资源质量综合评价. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2017, 37(1): 27-32, 42.
[
|
| [64] |
刘海轩, 李锋, 马远, 等. 基于景观多样性的北京市域森林质量综合评价. 中国园林, 2022, 38(10): 14-19.
[
|
| [65] |
丁文成, 宋大利, 周卫. 我国耕地质量主控因素及提升策略. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2024, 30(8): 1580-1594.
[
|
| [66] |
武岩, 刘宏金, 迟文峰, 等. 基于层次分析—客观赋权法的耕地质量等级评价方法研究与实证. 中国土壤与肥料, 2024, (4): 17-25.
[
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
United Nations, European Union, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, et al. System of Environmental Economic Accounting 2012: Experimental Ecosystem Accounting, 2014.
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
SEEA. Ecosystem accounting for the Netherlands, 2016, https://seea.un.org/news/ecosystem-accounting-netherlands, 2024-01-25.
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
Office for National Statistics. Habitat extent and condition, natural capital, UK: 2022.
|
| [77] |
The White House. National strategy to develop statistics for environmental-economic decisions. A U.S. system of natural capital accounting and associated environmental-economic statistics. Office of Science and Technology Policy, Office of Management and Budget, Department of Commerce. U.S., 2023.
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
SEEA. Natural capital accounting and valuation of ecosystem services project, 2017, https://seea.un.org/home/Natural-Capital-Accounting-Project, 2024-01-20.
|
| [84] |
IBGE. Ecosystem accounts for Brazil: Report of the NCAVES project. Brazil, 2021.
|
| [85] |
South African National Biodiversity Institute & Statistics South Africa. Ecosystem accounts for South Africa: Report of the NCAVES project. SANBI, Pretoria, 2021.
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
European Union. INCA platform: About INCA, 2015, https://ecosystem-accounts.jrc.ec.europa.eu/about-inca, 2024-01-07.
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
董贵华, 何立环, 刘海江, 等. 生态系统管理中生态环境评价的关键问题. 中国环境监测, 2013, 29(2): 41-45.
[
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
牛丽楠, 邵全琴, 宁佳, 等. 黄土高原生态恢复程度及恢复潜力评估. 自然资源学报, 2023, 38(3): 779-794.
[
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
European Union. Water framework directive. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European parliament and of the council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy, 2014, https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2000/60/oj, 2024-03-15.
|
| [107] |
European Union. Marine strategy framework directive. Directive 2008/56/EC of the European parliament and of the council of 17 june 2008 establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy, 2017, https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/56/oj, 2024-03-15.
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
European Union. The birds directive. Directive 2009/147/EC of the European parliament and of the council of 30 November 2009 on the conservation of wild birds, 2009, https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32009L0147, 2024-03-15.
|
| [111] |
European Union. The habitats directive. Council directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora, 2013, https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A31992L0043, 2024-03-15.
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
European Commission. Proposal for a regulation of the European parliament and of the council amending regulation (EU) No 691/2011 as regards introducing new environmental economic accounts modules, 2022, https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52022PC0329, 2024-05-06.
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
于贵瑞, 王永生, 杨萌. 提升生态系统质量和稳定性的生态学原理及技术途径之探讨. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(1): 1-10.
[
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
李梦桃, 周忠学. 基于多维评价模型的都市农业多功能发展模式探究. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(9): 1275-1284.
[
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
高宇婷, 高甲荣, 顾岚, 等. 北京市汤河生态健康评价指标相关性分析. 中国水土保持科学, 2014, 12(3): 119-124.
[
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
| [126] |
董贵华, 王业耀, 于洋, 等. “十三五” 以来我国生态质量状况时空变化分析. 中国环境监测, 2023, 39(1): 1-9.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |