

人海关系视角下公海保护区海洋地缘环境系统解析
|
彭飞(1986- ),男,山西阳泉人,博士,教授,研究方向为海洋经济与政治地理。E-mail: pfly324@163.com |
收稿日期: 2023-04-03
修回日期: 2023-08-15
网络出版日期: 2023-11-06
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42271253)
教育部基地人文社会科学重大项目(22JJD790032)
Analysis of marine geo-setting system in high seas protected areas from the perspective of human-ocean relationship
Received date: 2023-04-03
Revised date: 2023-08-15
Online published: 2023-11-06
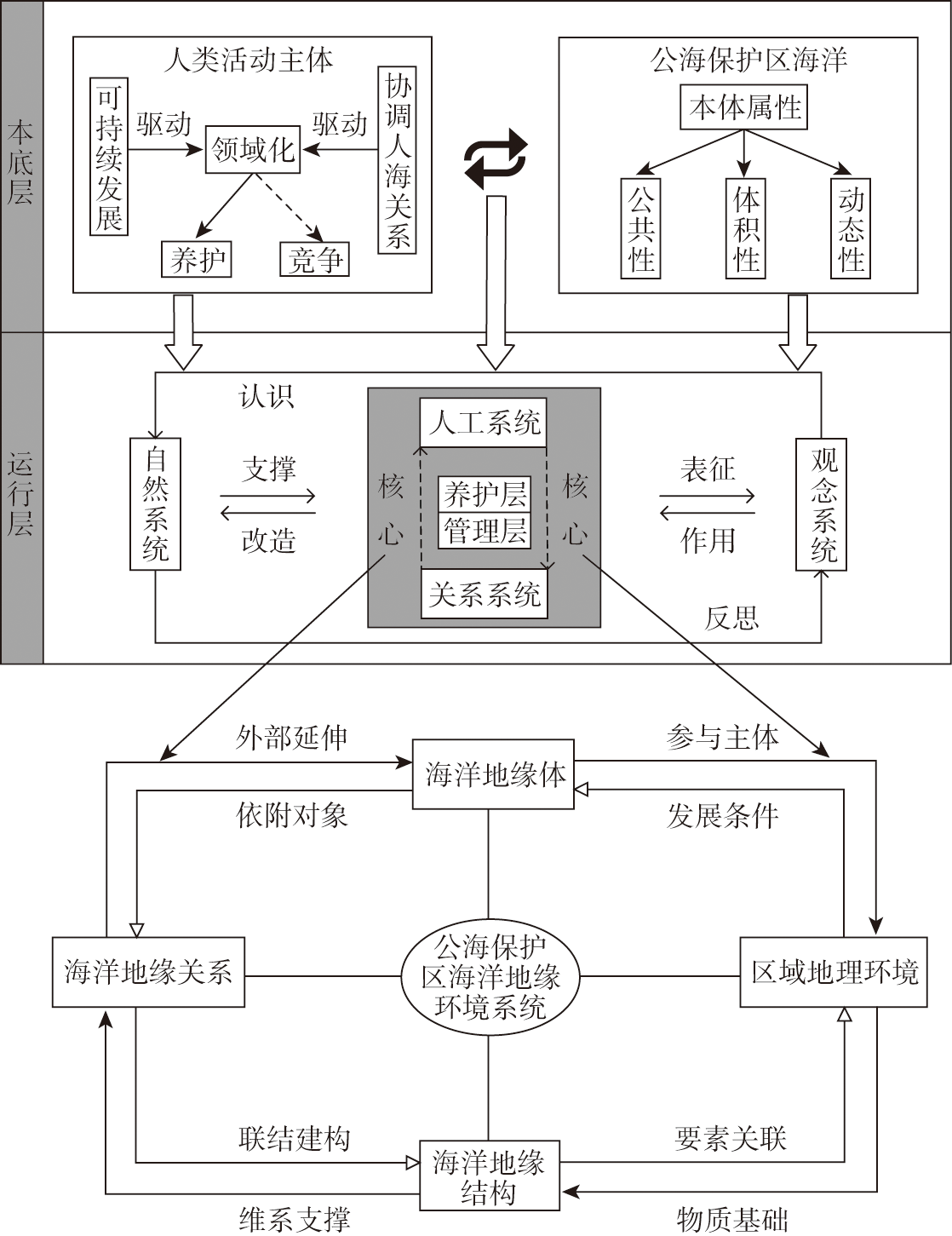
随着人类对海洋资源的争夺空间逐步由“领地化”海洋向公海领域拓展,公海海洋资源的可持续发展面临多重威胁,公海保护区的划定成为当前全球海洋治理的重要议题。基于人海互动关系,对BBNJ协定下的公海保护区地缘环境系统展开研究,提出具有地理特色的公海保护区解析思路与方法。首先,解构公海保护区人海关系为本底层与运行层,分别探讨本底层中人类领域化行为、海洋本体属性以及运行层中人海互动过程的三大环节、四大系统,引出人海互动核心公海保护区海洋地缘环境系统;其次,对公海保护区海洋地缘环境系统展开系统解析,并提出公海保护区海洋地缘环境系统演变机制;最后,结合当前时代背景,对中国下一步介入公海保护区工作提出政策建议。
彭飞 , 王浩然 , 刘春涛 . 人海关系视角下公海保护区海洋地缘环境系统解析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2023 , 38(11) : 2704 -2721 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20231102
With the continuous improvement of human production innovation, the ontological cognition of ocean as a resource has gradually expanded from 'territorial' ocean to the field of high seas. The sustainable development of marine resources in the high seas is facing multiple threats. The delineation of protected areas on the high seas has become an important issue of global marine governance. From the perspective of human-ocean relationship, this paper studies the geo-setting system of high seas protected areas under the BBNJ, and puts forward the analytical thoughts and methods of high seas protected areas with geographical characteristics that China needs at present. First of all, this study deconstructs the human-ocean relationship in the high seas protected areas into the bottom layer and the operation layer. It reveals the human domain behavior of repair, maintenance and potential competition in the bottom layer, as well as the attributes of public, volumetric and dynamic ocean ontology. We simulate the human-ocean interaction process in the high seas protected areas in the operation layer, deconstruct the three links in the interaction process: foundation and support of human-ocean interaction, core of human-ocean interaction, premise and reflection of human-ocean interaction, and cover four subsystems: natural system, artificial system, relational system, and conceptual system. This leads to the marine geo-setting system of the high-seas protected areas, which is the core of human-ocean interaction. Secondly, this paper analyzes the marine geo-setting system of the high seas protected areas. According to the multiple interactions between human territorialization behavior and marine ontological attributes of the high seas protected areas, the paper summarizes the characteristics of the marine geo-setting system of the high seas protected areas into four aspects: subject diversity, spatial limitation, complex sensitivity and pattern variability and proposes that the marine environment is the supporting force; rules and institutions are the driving force; marine geo-relationships and geo-structure are the powering force; marine technology is the guarantee capability of evolution mechanism. Finally, according to the contents discussed in this study, combined with the current situation and the actual needs of China's participation in global marine governance, the policy suggestions for China's involvement in the demarcation of high seas protected areas are put forward.

表1 公海保护区人海互动过程解析Table 1 Analysis of human-ocean interaction process in high seas protected areas |
| 系统构成 | 基本要素 | 所属部分 | 互动环节 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然系统 | 生态系统、生物种群、生境、生物多样性、生物栖息地 | 利用对象/依托 | 基础 | |
| 人工系统 | 养护层 | 生态数据、养护措施、运营维护机制、划区标准 | 物质、能量交换 | 核心 |
| 管理层 | 划区管理、法理依据、职权范围、冲突协调机制 | |||
| 关系系统 | 保护活动的交流与合作、规则制定的协商、利益分配机制 | 主体间关系 | ||
| 观念系统 | 海洋保护政策、海洋战略、缔约国意见与立场 | 理念 | 前提与反思 |
表2 公海保护区地缘体中的国际组织及机构Table 2 International organizations and institutions in high seas protected areas |
| 组织类别 | 组织名称 | 组织介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| 政治性组织 | 欧盟(EU) | 欧洲政治、经济共同体 |
| 七十七国集团(G77) | 发展中国家组成的政府间国际组织 | |
| 非政治性组织 | 国际民用航空组织(ICAO) | 为促进全世界民用航空安全、有序的发展而成立的联合国专门机构 |
| 国际海洋考察理事会(ICES) | 协调促进海洋科学考察的国际组织 | |
| 国际海事组织(IMO) | 负责海上航行安全和防止船舶造成海洋污染的联合国专门机构 | |
| 国际海底管理局(ISA) | 管理国际海底区域及其资源的联合国分支机构 | |
| 国际捕鲸委员会(IWC) | 国际捕鲸管制机构 | |
| 政府间海洋学委员会(IOC) | 促进各国开展海洋科学调查研究和合作活动的联合国教科文组织下属机构 | |
| 国际自然保护联盟(IUCN) | 世界上规模最大、历史最悠久的全球性非营利环保机构 | |
| 联合国粮食及农业组织(FAO) | 联合国各成员国间讨论粮食和农业问题的国际组织 |
注:表中所列均为全球性国际组织。此外,公海保护区还涉及较多区域性国际组织,此处不再罗列。 |
| [1] |
李加林, 沈满洪, 马仁锋, 等. 海洋生态文明建设背景下的海洋资源经济与海洋战略. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(4): 829-849.
[
|
| [2] |
方瑞安, 张磊. “公地悲剧”理论视角下的全球海洋环境治理. 中国海商法研究, 2020, 31(4): 38-44.
[
|
| [3] |
刘美, 管建强. 从区域实践到普遍参与: BBNJ协定下公海治理的条约困境. 中国海商法研究, 2021, 32(2): 102-112.
[
|
| [4] |
秦奇, 成升魁, 李飞, 等. 1992年以来国内外地缘政治比较研究: 基于地理学视角的分析. 地理科学进展, 2017, 36(12): 1475-1488.
[
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
韩增林, 彭飞, 张耀光, 等. 海洋地缘政治研究进展与中国海洋地缘环境研究探索. 地理科学, 2015, 35(2): 129-136.
[
|
| [7] |
彭飞, 韩增林. 东海问题的周边地缘环境解析. 世界地理研究, 2014, 23(2): 35-42.
[
|
| [8] |
胡浩, 葛岳静, 胡志丁. 南海问题的大周边地缘环境. 世界地理研究, 2012, 21(3): 36-44.
[
|
| [9] |
张耀光. 从人地关系地域系统到人海关系地域系统: 吴传钧院士对中国海洋地理学的贡献. 地理科学, 2008, 28(1): 6-9.
[
|
| [10] |
薛桂芳. “海洋命运共同体”理念: 从共识性话语到制度性安排: 以BBNJ协定的磋商为契机. 法学杂志, 2021, 42(9): 53-66.
[
|
| [11] |
江河, 胡梦达. 全球海洋治理与BBNJ协定: 现实困境、法理建构与中国路径. 中国地质大学学报: 社会科学版, 2020, 20(3): 47-60.
[
|
| [12] |
李洁. BBNJ全球治理下区域性海洋机制的功用与动向. 中国海商法研究, 2021, 32(4): 80-87.
[
|
| [13] |
王婷婷, 章晶晶. BBNJ协定中的“适当顾及”及我国之应对方案. 中国海洋大学学报: 社会科学版, 2023, (2): 97-107.
[
|
| [14] |
邢望望. 公海保护区法律概念界定. 武大国际法评论, 2019, 3(2): 48-68.
[
|
| [15] |
缪晓靓. 自由与保护的冲突: 公海保护区制度探析. 江南社会学院学报, 2019, 21(1): 75-80.
[
|
| [16] |
杨显滨. 北极公海保护区的治理模式与体系构造. 学术界, 2022, (11): 130-143.
[
|
| [17] |
王勇, 孟令浩. 论BBNJ协定中公海保护区宜采取全球管理模式. 太平洋学报, 2019, 27(5): 1-15.
[
|
| [18] |
马学广, 朱开磊, 白佳玉, 等. 多尺度海洋空间规划法律问题论纲. 中华海洋法学评论, 2021, 17(2): 56-109.
[
|
| [19] |
郭建科, 董梦如, 郑苗壮, 等. 海洋命运共同体视域下国际海洋资源战略价值评估理论与方法. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(4): 985-998.
[
|
| [20] |
于宏源. 全球海洋治理视阈下生物保护区管理的重叠到协同效应分析. 云梦学刊, 2021, 42(6): 12-25.
[
|
| [21] |
刘桂春. 人海关系与人海关系地域系统理论研究. 大连: 辽宁师范大学, 2007.
[
|
| [22] |
韩增林, 刘桂春. 人海关系地域系统探讨. 地理科学, 2007, 27(6): 761-767.
[
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
刘玄宇, 刘云刚. 海洋本体论及其视角下的南海海洋国土治理研究. 地理学报, 2022, 77(9): 2374-2388.
[
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
刘云刚, 王丰龙. 政治地理学中的领域概念辨析. 人文地理, 2019, 34(1): 14-19.
[
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
刘玄宇, 刘云刚. 中国南海海洋国土开发与管控研究展望. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(9): 2205-2218.
[
|
| [36] |
桂静. 公海保护区的国际法基本原则辨析. 江南社会学院学报, 2014, 16(4): 17-22.
[
|
| [37] |
朱超. 公共产品、外部性与气候变化. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2011.
[
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
刘惠荣, 马玉婷. 实现BBNJ划区管理工具制度中的海洋生态连通性: 以“适当顾及”沿海国权益为路径. 中国海洋大学学报: 社会科学版, 2021, (1): 12-20.
[
|
| [45] |
刘天宝, 杨芳芳, 韩增林, 等. 人海关系地域系统视角下海洋本体的解构与研究重点. 地理科学, 2019, 39(8): 1321-1329.
[
|
| [46] |
胡伟, 胡志丁, 葛岳静. 中国地缘环境研究进展与思考. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(4): 477-488.
[
|
| [47] |
葛全胜, 江东, 陆锋, 等. 地缘环境系统模拟研究探讨. 地理学报, 2017, 72(3): 371-381.
[
|
| [48] |
彭飞, 富宁宁, 张琦琦, 等. 海洋地缘环境系统构建及其脆弱性解析. 世界地理研究, 2019, 28(2): 133-140.
[
|
| [49] |
赵融. 公海保护区与沿海国外大陆架主权权利的冲突与协调. 哈尔滨工业大学学报: 社会科学版, 2021, 23(1): 17-23.
[
|
| [50] |
韩炳浩. 国家管辖外海洋保护区与“区域”冲突问题研究. 法制与经济, 2018, (1): 174-176.
[
|
| [51] |
吴宁铂, 王勤. 南极海洋保护区的设立及阻碍因素评析. 中华海洋法学评论, 2021, 17(3): 77-107.
[
|
| [52] |
姜秀敏, 陈坚. BBNJ协定谈判的焦点与中国的路径选择. 中国海洋大学学报: 社会科学版, 2021, (3): 1-12.
[
|
| [53] |
孙才志, 王泽宇, 李博, 等. 中国海洋经济可持续发展基础理论与实证研究. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022: 3-8.
[
|
| [54] |
何志鹏, 王艺曌. BBNJ国际立法的困境与中国定位. 哈尔滨工业大学学报: 社会科学版, 2021, 23(1): 10-16.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |