伴随人工智能、物联网、大数据和云计算等新一代智能技术的快速发展及应用,智慧城市建设在改善或解决城市问题、提升城市品质与治理能力进而促进可持续发展目标方面的作用和价值已是全球性共识。2019年,全球已启动或在建的智慧城市达1000多个,其中50%以上分布在城市化快速增长与环境压力巨大的亚洲[1]。截至目前,中国已有国家级智慧城市试点300多个,这些试点城市通过智能基础设施、城市大脑、智慧服务、智慧管理、智慧社区等项目的建设运营,很大程度上提高了城市智慧治理能力与智慧化发展水平。2020年,中央政府提出加快“新基建”建设进度,之后又印发了《数字中国建设整体布局规划》(2023年),标志着智能技术集成应用开始加速驱动生产生活和治理方式变革,全新的数字化、智慧化时代正在到来。
尽管如此,我们也看到当前智慧城市建设高度依赖智能技术,轻视人的需求,缺乏对城市发展规律的把握[2]。近年来国内发生的化工园区爆炸、重大公共卫生事件等突发性公共安全事件,表面上是城市在应急防控方面的不足,实则暴露出城市整体功能韧性的不足,以及城市发展在规划、建设与管理中的短板。在新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情爆发初期,智慧城市未能在感染人群流动监测、时空感染风险预警、精准疫情防控与应急资源调配等方面很好地发挥作用,让智慧城市受到了诸多质疑与指责。究其根本,是对复杂环境下城市人地系统要素及时空耦合过程、规律及变化认识不足。也就是说,现有的智慧城市研究与建设过于关注技术驱动及治理导向,缺少对人地关系动态性、综合性与复杂性等问题的统筹考虑。同时,地理学有关人地系统的成果也未对智慧城市规划建设发挥应有的理论支撑与实践指导作用。
作为人类社会经济活动的主要载体,全球城市预计在2050年将拥有66%的世界人口[13],城市地域人地系统逐渐成为人地关系研究的热点与重点,以及关乎城市和谐与可持续发展的重要理论与实践命题。近些年来,技术创新与人地关系一直是城市地理学关注的重点领域,尤其是强调建立适应信息时代与智慧城市建设需求的人地关系新理论与新方法[14]。主要研究包括:(1)智能技术、流空间与人地关系。智能技术进步不仅促使时空压缩[15],而且改变了各种要素“流”以及人地互动耦合关系,进而重塑信息时代的“人地关系”[2,16]。流空间成为分析技术、居民活动和空间互动耦合的重要框架,学者们对职住空间、迁居行为、企业空间组织等城市人地系统各要素耦合关系与影响机理进行了大量研究[17⇓⇓⇓⇓-22]。同时,从行为地理、时间地理等角度对智能技术作用下的个人行为时空变化、居民流动模式进行了理论研究和实践探索[23⇓-25]。(2)基于复杂适应系统与韧性理论的人地关系。西方学者将人地关系系统视做人类与环境相互作用形成的复杂适应系统[26],并从社会—生态系统可持续性框架等方面对其进行了探索[27,28]。同时,已有学者将城市韧性理论作为分析与调控城市人地关系的基本逻辑框架[29],并衍生出开放互助、创新学习的城市适应性治理体系[30]。(3)基于智能技术及多源数据的人地系统研究。智能技术应用为研究人地系统提供了新的全样本、多尺度、多粒度数据[31,32],大量学者开展多源数据支撑下的人地系统要素识别、评价与耦合分析,包括人类活动模式识别与特征[33⇓-35]、人类活动与城市网络[36⇓-38]、人类活动与城市建成环境[39⇓⇓-42]、人类活动与城市体检[43⇓-45]。这些探索在智慧城市建设、国土空间规划等领域也得到了积极应用[46,47]。(4)智慧城市可持续发展模型与评价。智慧可持续城市更加强调社会、文化、福祉、知识等柔性的智慧指标[48]。国内学者从城市数据采集与共享、城市系统运行问题分析、城市空间模拟仿真与决策评估、城市空间发展规划体系四个层面提出智慧可持续城市空间发展模型[49]。同时,将“流动性”引入到多尺度空间分析并构建城市信息模型[50]。
从上述分析来看,人地系统及其耦合协调发展一直是国内外地理学关注的核心主题,也是中国推进生态文明与新型城镇化建设的迫切需求。受制于数据等多方面因素的限制,当前的研究主要集中在国家、区域、流域等宏观、中观尺度人地关系耦合总体格局及机理的探索,对最为复杂的城市人地系统时空耦合过程与机理还缺乏系统综合的研究。面向未来,如何在生态文明、智慧社会框架下去推进以人为本的城市人地系统建设,是当前新型城镇化发展与国土空间治理中亟待破解的重大战略问题。
因此,本文试图将人地关系理论与分析方法引入到智慧城市研究与实践中,通过探讨智慧城市人地系统相关理论,提出智慧城市人地系统研究亟待突破的重点方向与应用领域,这既是当前城市地理学创新发展的需要,也是开展人地关系视角的智慧城市研究、助力智慧城市规划建设持续发展的迫切需求,为理解智能技术影响下的城市人地关系提供样本与示范,将进一步彰显和加强地理学服务国家战略需求的现实意义。
1 智慧城市人地系统理论框架
1.1 智慧城市人地系统内涵
作为一个复杂的非线性耦合系统,城市人地系统中单个要素的变化可能会导致整个系统要素的巨变,其中技术进步对城市人地系统的影响作用长期受到关注。尽管对智慧城市的概念尚没有统一认识,但已有文献大都强调了传感器、实时监测和数字平台使用[51]、可持续性和高品质生活[52]、高质量人力与社会资本[53],以及智慧治理[54]。可见,智慧城市是信息化发展的高级形态,突出表现为智能技术对其地域系统内部基础设施、资源环境、经济社会以及空间的流动性产生持续深刻的影响。因此,厘清智能技术使用对城市社会经济环境影响及其治理应对,是理解智慧城市目标的关键所在。城市人地系统由地理环境和人类社会两大子系统构成,又进一步分解为生态系统、社会系统、经济系统、土地系统、技术与基础设施系统、公共服务系统与治理系统等,其内部的人口、资源、环境等要素交叉作用,促使人地系统不断发展变化。伴随着智能技术应用、政策创新等方面的影响,对“人”的理解从自然人转向情感关怀、需求满足和智慧化生活,对“地”的认识从地理环境、自然资源条件等转向要素流动、科技创新、网络关系等方面 [2]。因此,认识智慧城市人地系统的内涵,首先要充分认识到智能技术作为城市人地系统的最重要组成和创新驱动力,智能技术应用支撑下的要素流将重塑社会经济活动、公共服务等子系统,改变各类要素流动的结构和范式,进而构建起“虚实融合”“形流融合”的智慧化城市人地系统;其次应当立足于城市居民需求、人地和谐的视角,考虑智能技术作用下城市人地系统内部技术、活动及物质环境等要素的运行状态、互动耦合关系与过程、协同演化趋势与机理,同时强调智能技术集成应用对人类活动方式、地理环境及其耦合关系的影响与调控作用[55]。这一认识有助于打破智慧城市建设中只重视智能技术应用的局限性,推动人本化和地理学系统综合视角的智慧城市发展。
1.2 智慧城市人地系统理论认知
根据上述理解,要超越单纯计算科学视角的局限性,立足人本需求和可持续发展理念,以及智能技术、地理、城乡规划、社会、经济、管理等多学科视角,构建更加全面系统和要素综合的智慧城市人地系统理论认知体系。
(1)流空间与智慧城市空间组织
作为生命有机体,智慧城市运营要依托于智慧管理中心、一体化数据平台、智慧功能区,通过智慧管理、要素流有机组织以保障整个系统的持续运行[57],这也是调控智慧城市人地系统的重要途径。聚焦城市数据治理及功能与业务需求,一方面从智能技术、人类活动与地理环境的时空协调角度,引导各类信息基础设施、信息系统、智慧功能区、要素流的协同建设和时空优化布局,提高智慧城市要素运行效率和质量;另一方面可以利用多源数据对城市各类要素资源的时空配置进行分析评价、仿真模拟与预测,并通过智能技术进行资源配置的调节与优化,以实现提升城市综合承载能力和可持续发展能力的目标。
(2)“人—技术—空间”一体化的智慧城市人地耦合系统
人地耦合关系是人类活动和地理环境在特定地域上相互联系、相互作用而呈现出的状态,是人地系统相互作用过程及其结果的重要表现。传统的人地关系地域系统,主要关注人与自然物质环境等之间的耦合关系。智能技术的快速发展及应用,使得物质环境和空间距离对人类活动的限制下降,并对人地关系地域系统持续产生影响,不断改变着人地系统的互动方式、广度和深度[58,59],使得人地系统耦合关系也从传统的“人”“地”二元耦合转向“人—技术—空间”的三元耦合结构[55,60],还有学者则强调了物理空间、社会空间和信息空间的映射与融合[61]。因此,开展技术、人和地理环境三者耦合关系的研究,既是理解智慧城市人地系统的核心,也是智慧城市规划、基础设施建设与要素协同布局的重要理论基础。
在智慧城市发展框架下,人、智能技术和城市空间要素的耦合关系具有远程交互、虚实关联、时空协同等特点。首先,传统人地系统的地方耦合转向智慧城市 “人—技术—空间”的复杂耦合,在物联网等智能技术的远程控制与联动作用下,实现对信息传输、人类活动以及地理环境、土地系统的远距离联系、流动和反馈[62]。与强调不同地域空间尺度耦合关系的传统人地系统不同,智慧城市人地系统更强调时空耦合性,注重对技术、人与地理环境在不同时间、空间维度上的耦合关系、特征与规律的探索和挖掘。其次,传统人地系统的实体和物质要素耦合转向智慧城市人地系统的虚实耦合协同,主要体现为在线虚拟活动与实体活动、虚拟空间与实体空间之间的互动联系,实体空间要素在虚拟信息系统平台中的映射及其动态信息更新和运行管理,这也是城市信息模型(CIM)以及数字孪生城市建设的关键所在。
(3)智慧城市人地系统韧性
智慧城市人地系统的动态运行、时空耦合和互动作用是理解其韧性状况的重要方面。居民行为活动对城市基础设施、公共服务以及资源环境的慢性压力,反映了各类设施、资源环境的活动承载和韧性水平。同时,灾害等突发事件的不同阶段和发生过程,系统要素的承灾能力、应对能力和恢复能力等,以及人流聚集与地理环境的时空交互和耦合关系会有差异。因此,对智慧城市人地系统的动态适应性变化及风险进行综合监测评估和仿真模拟分析,可为探索大数据、云计算、虚拟现实等智能技术支撑的城市人地系统韧性提升与调控方法提供解决路径及方案。
1.3 智慧城市人地系统概念模型
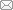
在物联网、大数据、云计算等智能技术的影响下,城市中日益增加的各类线上线下活动,不断重塑社会经济活动、基础设施和公共服务等要素系统。与此同时,智能技术改变了人流、物流、资金流、信息流、技术流、生态流等要素流动的结构和范式,虚拟要素流与各类实体要素流更加融合,促进了网络在线活动和实体活动、虚拟空间和物质空间之间的互动,并持续对智慧城市人类活动系统与地理环境系统之间的调控、反馈和交互机制产生影响作用(图1)。
图1
与传统的城市人地关系相比,智慧城市人地系统中要素交互与联系的时空尺度在不断变化。空间尺度上,基于山水林田湖草要素系统在社区、功能区/组团、城市、区域等多层次空间的组合状况,探索人类活动、要素流动和地理环境互动作用的空间尺度变化,挖掘智能技术支撑下的活动系统和地理环境系统跨尺度协同、远程耦合和反馈作用。时间尺度上,关注智能技术广泛应用所带来的居民活动和城市地理环境互动耦合的时间弹性、灵活性和破碎化,进行智慧城市人地系统全生命周期的监测、管理和动态优化调控。
2 智慧城市人地系统重点研究方向与应用
2.1 人地系统要素时空耦合过程
借助基于智慧城市平台的数据采集分析、指标算法、业务应用与实施保障等建设框架,将多源大数据获取与社会调查、访谈相结合,构建由基础地理信息、资源环境、人口活动、社会经济等若干专题数据库组成的智慧城市人地系统多源数据库。针对不同类型智慧城市,进一步开展城市人地系统关键要素的识别,构建人地系统综合评价指标体系。关键要素的识别是一个演绎和归纳的双向过程。一方面从城市人地系统特征与规律角度演绎出一些预设的关键领域,如能源、资源、环境等底线要素,交通、生产等活力要素,居民生活相关的医疗、教育等民生要素。另一方面通过多源数据模拟分析,归纳出哪些是真正关键的要素;结合要素运行状态监测进行问题诊断、要素关联分析以及功能评价。针对智慧城市人地系统的特殊性,围绕城市居民活动和出行(居住、就业、通勤、消费、休闲娱乐、社交、健康活动等),从点、线、面等维度将城市居民的社会经济活动与城市物质空间关联起来,探索不同空间尺度的居民活动模式、空间需求及满意度、幸福感等内容,深入理解和阐释智慧城市人地系统要素结构、功能及布局模式变化。
城市人地系统耦合度是对要素之间、子系统之间相互关联水平和作用强度的度量。在对智慧城市人地系统要素分析的基础上,从个体与家庭、社区、功能区(组团)、城市尺度展开对人地系统时空耦合过程与规律分析,总结不同耦合类型及其特征,如域内与域外耦合、功能耦合(远程耦合、虚拟耦合)、内容耦合等。基于多维指标构建耦合度分析模型,在多角度、多时空维度下测度、评价城市居民社会经济活动和城市物质环境时空耦合水平(表1)。
表1 智慧城市人地耦合系统:要素、结构与尺度
Table 1
| 层级尺度 | 要素 | 结构 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 节点 | 连接 | 网络 | |||
| 域外耦合 | 区域、国 家和全球 | 经济、贸易、创新、 资本等要素 | 城市、门户与枢纽 | 经济流、商品流、技术流、资金流等 | 区域、国家和全球经济网络、贸易网络、创新网络、资本网络 |
| 域内耦合 | 城市 | 社会经济、基础设施、文化、生态、治理等 要素 | 商业中心、游憩休闲中心、综合服务中心 | 经济流、交通流、能源资源流、生态流等 | 社会经济网络、基础设施网络、生态网络等 |
| 功能区 (组团) | 产业、服务、居住区、休闲、交通等要素 | 功能区/组团中心 | 居住、就业、休闲、出行等活动流 | 功能组团网络 | |
| 社区 | 居住、服务、文化等 要素 | 社区活动中心、社区服务中心 | 社区日常活动—移动 | 社区生活圈网络 | |
| 个体与家庭 | 居民活动、情感、幸 福感等 | 智慧市民、智能家庭 | 阶层流、思想流 | 个体与家庭社会网络 | |
首先,加强城市居民(活动本体)社会经济活动的时空耦合分析与评价。在深入挖掘人对地理环境、城市空间的感知、体验、偏好等情感及时空数据的基础上,进行居民个体及群体流动性和行为活动分析与评价,包括线上活动与线下活动,以及情绪与空间的互动研究。其次,加强城市物质空间(活动环境)要素时空耦合的分析与评价,包括不同地理空间要素的发展质量及存在问题,如不同商业设施间的耦合关系与互动模式。最后,加强城市人地系统要素综合耦合协调度评价与可视化模拟。在居民日常行为活动模式、时空利用与交通出行特征分析基础上,借助流分析、复杂网络分析方法,通过居民行为活动要素和智能技术与城市基础设施布局、绿化设施与生态服务、公共服务供给、社会文化服务、经济发展等要素间的关联与耦合协调度评价研究,探索智慧城市中人与地理环境的时空耦合过程、模式与规律。
2.2 人地系统要素构成及影响机理
在个体与家庭、社区、功能区(组团)、城市等不同时空尺度下,智慧城市人地系统要素构成与耦合状态存在差异。因此,智慧城市人地系统研究,需要针对不同时空尺度构建差异化的时空耦合要素集,并挖掘不同尺度时空耦合的影响因素。按照全面感知系统要素、精准识别要素变化特征、系统认知要素关联、抽象要素互动耦合机理的思路,开展不同类型、不同尺度智慧城市人地系统时空耦合影响机理研究。
个体与家庭尺度,重点挖掘个人属性与家庭结构、个体活动与行为习惯、消费偏好、环境认知等要素对人—人关系、人—地关系及其形成的耦合关系网络结构的影响机理。社区尺度,分析社区功能、社区活动、社区服务、交通与建成环境、治理模式以及智慧社区系统建设等要素,对社区内部居民各类活动与物质环境时空耦合的影响,以及对智慧社区生活圈构建的促进作用。城市功能区(组团)尺度,探索其功能空间分布与规模、功能结构与组合关系等特征,以及相互之间的交通联系、信息、人口、资本、能源资源等要素流动,挖掘功能区内部的人地系统耦合和功能区之间时空交互的影响机理。城市尺度,基于社会经济、人口结构、空间布局与用地形态、基础设施与服务质量、道路交通系统支撑、资源环境承载能力、治理结构等全要素系统,分析其对城市内部人地系统时空耦合的影响机理及动力变化。全球与区域(国家)尺度,重点考虑不同等级城市的等级与节点作用、跨区域和城市的信息、人员、货物、资本、技术以及能源资源要素流动对人地系统时空耦合的影响,并考虑远程连接与信息交互、全球化与本地化互动的影响作用。
2.3 人地系统建模方法与评价
基于智能技术的城市人地系统的感知监测、模拟仿真与预测分析,为城市人地系统复杂关系研究提供了新视角和新方法,有助于厘清智慧城市人地系统的构成要素、组织结构、作用机制及其功能变化,从而开展符合中国国情及新型城镇化发展与智慧城市建设需求的城市人地系统研究。通过构建人地系统耦合协调的智慧城市可持续发展仿真模型,科学评估人地系统要素的时空耦合协调度,建立智慧城市人地系统时空耦合调控模型工具集,为监测和评价智慧城市运行状态、支撑智慧城市发展决策提供重要的科学依据。
(2)构建人地系统时空耦合协调度评价方法,利用多源时空大数据,对城市要素耦合协同状态进行监测与评估,构建城市智慧发展监测评价的技术体系。基于人、地、业等多维度要素的相互作用关系,构建耦合协调度模型,测算城市人地系统要素的耦合协调程度;进而利用手机信令、社交媒体、移动支付等人类活动数据,遥感影像、土地覆盖、POI等基础地理信息数据,空气质量、水污染等环境监测数据,统计年鉴、问卷调查等统计数据,动态监测城市人—地—业各类要素的耦合协调状态,及时发现城市人地系统要素的矛盾与冲突。
(3)建立人地系统时空耦合调控模型工具集,对不同调控政策下人地耦合关系变化、耦合协调度等进行模拟与预测,综合评估调控政策的影响。在智慧城市可持续发展仿真模型的基础上,结合元胞自动机、神经网络、贝叶斯网络、多智能体模型等方法,模拟在不同政策下,城市人地系统发展的情景;进而结合资源承载力评价、发展适宜性评价、耦合协调度模型等方法,分析在每种情境下,资源环境的承载情况、城市发展的适宜性情况和人地系统的耦合协调情况,为智慧城市发展决策提供支撑。
2.4 人地系统综合调控与优化路径
智慧城市人地系统研究需要以国家新型城镇化、高质量发展战略需求为导向,以解决城市可持续发展的实际问题为目标,探索一体化、协同发展的智慧城市空间数据和规划整合系统,重点从要素耦合与配置、空间布局优化、科学决策与协同治理等方面完善“人”与“地”之间相互作用方式、作用强度及其空间调控策略,推动智慧基础设施的整合协同以及城市空间布局的优化,并在此基础上构建具有中国特色的人地系统调控与适应性机制。
在要素耦合与配置方面,需要从贯彻落实生态文明建设战略和保障国土空间格局安全的视角,全面评估区域及城市内部山水林田湖草及土地等资源要素的供需匹配度,充分考虑智能技术影响和支撑下的要素加速流动所带来的未来区域城市网络及城市内部形态和功能结构可能发生的变化。一方面,利用大数据分析技术精准监测和动态调配区域各城市的资源要素,在供需相对平衡的基础上优先保障区域枢纽和潜力城市的配额;另一方面,深度理解智能技术与居民(自然人)、企业(法人)及政府(管理人)社会经济活动相互作用机制,结合智慧城市人地关系耦合模型分析结果,从不同类型“人”的全生命周期需求、日常活动规律及活力变化、流动性特征及模式等方面统筹安排城市内部各功能区的资源要素组合。
在空间布局与优化方面,以全域智慧化的目标来指导城市各功能区的协调与整合,重点推进智慧场景布局与建设。例如,利用智能技术去强化居民的社区感,提升社区的公共服务能力,并通过智慧平台和工程项目来完善居民生活圈功能体系;同时,利用这些技术、平台及空间场所改造项目来增加社区应对突发公共事件的韧性。智慧园区建设以园区产业数字化转型升级为目标,通过感知技术将人、设施、企业、环境等的相关信息全方位互联,科学诊断产业问题,全面分析产业发展链条,智慧化布局产业空间及配套设施,实时支撑园区的运行与管理。更重要的是,智慧城市是一个生命有机体,需要通过“智慧大脑”建设为智慧社区、智慧园区等场景提供决策分析和学习能力,并通过城市信息模型将实体城市的各种要素及功能数字化到虚拟空间,把实体城市中复杂的社会联系、人与信息设施关系、人地关系映射到信息模型来支撑动态模拟分析与预测,搭建一个“数字孪生城市”,进而对实体城市的建设起到实时监测、动态优化的作用。
在科学决策与协同治理方面,需要从智慧城市全要素感知出发,利用大数据与人工智能技术,动态诊断城市问题,综合评估城市发展质量及可能的风险,科学模拟预测城市未来发展趋势,进而精准指导城市领导决策和部门管理服务,实现城市智慧治理。同时,智慧城市是一个复杂的巨系统,要做好技术系统、空间系统、活动系统和决策系统之间,以及各系统内部的交互联动,将各行各业的智慧应用协同起来,实现城市空间的智慧化发展。此外,还需要因地制宜地探索智慧城市数据采集、共享、安全、挖掘应用等方面的政策、标准或技术导则,最大限度地保障公民数据权益,充分发挥数据应用价值。
3 研究展望与讨论
新型智慧城市建设已成为推进中国以人民为中心的新型城镇化与国土空间治理体系建设的重要手段,也是未来城市发展的方向。面向未来的智慧城市理论研究与创新,需要更加深刻地理解智能技术变革对社会经济发展、人类活动以及城市物质环境的影响,将地理学关于人地关系研究的理论与方法引入智慧城市研究,通过对人地系统更全面地感知、监测、评估和预警,探索城市功能空间与人地关系的重构变化,提高对城市人地系统的调控能力。
(1)探索未来智慧城市人地系统理论。首先,探讨智能技术应用下人类行为模式和活动方式变化,尤其是虚拟活动、远程在线活动的快速普及,对生产生活活动复杂性、适应性、时空弹性以及社会经济组织结构的影响效应。其次,研究城市空间的智能化以及未来智慧城市的空间重构。从绝对空间、相对空间、关系空间和情感空间等维度去架构智能空间[68];超越地方的资源禀赋和地理区位,从场所所处的网络关系出发,研究未来智慧城市空间的远程和邻近、虚拟和实体、流动和停滞等不同耦合状态。最后,从虚实活动关联、虚实空间互动以及流动性角度,加强智慧城市人地系统的交互模式、组织形态与耦合机理研究。
(2)创新智慧城市人地系统的分析与研究方法。大数据、云计算、人工智能、虚拟现实等智能技术,为人地关系的分析、监测和模拟方法创新提供了新的手段,可将人地系统理论和城市计算技术进行深度融合,构建智能人地系统研究方法体系,从而分析城市的物质空间和社会空间[69],并进行城市人地系统时空动态、虚实关系的综合评估、仿真模拟和安全预警。
(3)建构可持续的智慧城市人地系统。探索如何通过智慧城市建设,来促进可持续的人地系统构建与优化,一方面研究智能基础设施对各类资源能源以及教育、医疗等公共资源配置的作用,引导高效协同的智慧治理,构建安全、包容、韧性的城市;另一方面,考虑智慧城市建设对不同社会阶层、不同区域、城乡之间的公平性影响,探讨未来的“智慧鸿沟”解决方案以及数字化参与方式、社会包容性、充分就业等问题。
立足于中国新型城镇化发展的阶段性特点以及城市发展的实际情况,对于中国智慧城市人地系统的理论研究,在考虑“人—技术—城市空间”耦合协调基础上,综合生态城市、宜居城市、安全韧性城市、健康城市、可持续城市等理论与实践框架,并结合中国新型基础设施、智慧城市服务在生产生活和政务管理中高度渗透融合的趋势,进一步完善适应中国国情的智慧城市人地系统理论体系。在实践和具体应用场景中,一方面,注重“智慧大脑”的建设,通过“智慧大脑”引导城市经济可持续发展、社会运行效率提升、基础设施创新和城市功能空间转型[70,71];另一方面,加强以城市信息模型(CIM)为基底的数字孪生城市发展,促进数字城市与现实城市的深度融合与交互,并为国土空间的全生命周期规划、建设和管理提供应用支撑。
参考文献
基于地理视角的智慧城市规划与建设的理论思考
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.04.001
[本文引用: 4]

智慧城市建设是推动城镇化发展的重要动力,其建设除了技术支撑之外,还应充分考虑信息技术对城市政府、企业和居民活动及其空间的影响。本文在对国内智慧城市建设现状与问题分析思考的基础上,认为智慧城市的出现是适应当前城市化战略转型、公共服务提升、社区发展和城市问题解决的必然趋势,从多源异构数据整合、信息系统和空间分析平台两个方面梳理智慧城市建设的关键技术,从流动空间以及新的人地关系、时空协调发展等方面提出智慧城市的理论支撑,并进一步明确地理学应对和研究重点。同时,提出基于城市地理研究的智慧城市规划与建设实践的主要方向,包括顶层设计、功能和空间布局、基础设施整合、城乡治理等内容。
Smart city planning and construction based on geographic perspectives: Some theoretical thinking
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.04.001
[本文引用: 4]

The construction of smart cities is an important impetus for promoting the development of urbanization. In addition to the technological support, the construction of smart cities should also consider the impact of information technology on city governments, enterprises, and residents' activities and activity space. Based on the analysis of the general situation and consideration of existing problems of the construction of smart cities in China, the authors conclude that the development of smart cities is an inexorable trend to adapt to the strategic transformation of urbanization, upgrading of public services, community development, and solving urban problems. Innovations in geography and their theoretical support function to smart cities are then discussed with regard to the coupling of multiple heterogeneous data, time-space compression, the new mobility paradigm, space of flows, human-nature relationship under new circumstance, and spatiotemporally coordinated development. Also, the innovation research of geography interact with the different systems of smart cities. Based on the research and application of urban geography, we put forward the key aspects of planning and construction of smart cities, including the top design, the distributing of functional zones and spaces, the integration of infrastructure, and rural-urban governance, among others.
论地理学的研究核心: 人地关系地域系统
Research core of geography: Man-land relationship geographic system
DOI:10.2307/140646 URL [本文引用: 2]
Framing and reframing questions of human-environment interactions
DOI:10.1080/00045608.2012.678035 URL [本文引用: 1]
Illustrating the coupled human-environment system for vulnerability analysis: Three case studies
DOI:10.1073/pnas.1231334100
PMID:12815106
[本文引用: 1]

The vulnerability framework of the Research and Assessment Systems for Sustainability Program explicitly recognizes the coupled human-environment system and accounts for interactions in the coupling affecting the system's responses to hazards and its vulnerability. This paper illustrates the usefulness of the vulnerability framework through three case studies: the tropical southern Yucatán, the arid Yaqui Valley of northwest Mexico, and the pan-Arctic. Together, these examples illustrate the role of external forces in reshaping the systems in question and their vulnerability to environmental hazards, as well as the different capacities of stakeholders, based on their access to social and biophysical capital, to respond to the changes and hazards. The framework proves useful in directing attention to the interacting parts of the coupled system and helps identify gaps in information and understanding relevant to reducing vulnerability in the systems as a whole.
关于地理学的“人—地系统”理论研究
Theoretical studies of man-land system as the core of geographical science
DOI:10.11821/yj2002020001
[本文引用: 1]

In the late 1970s and early 1980s, geographical science entered a new stage, which is characterized by the shift of major attention from the nature dominated environmental changes to the human dominated ones, that is, the interactions between natural process, biological process and human activity. All this shows the changing nature of geography is at the core of dramatic changes within ecosphere, the dynamic man land relationship. Unfortunately, it is the dramatic relationship that has led to the continuing destruction of resources bases as well as ecological and environmental bases upon which human being are dependant. Given the global changes, geographers are obliged to carry out theoretical and empirical studies about sustainable development and environmental protection, from both man land relationship and regional perspectives. The central issues to be concerned are the influences of global change on China and rational approaches for China to realize sustainable development. In recent years, Chinese geographers have contributed a lot to the fields of natural environment, territorial planning and regional development, providing scientific analysis and suggestions essential to China's responses to global change and sustainable development. However, the potential advantages of geography in terms of resolution of these critical issues have not been realized so far. To change such a situation, geographers have to make great efforts to synthetic theories and methodologies, giving full recognition to the theoretical studies of man land territorial system. The issues of sustainable development should remain as major concern by China's geographers in a long time. In fact, the efforts to coordinate the man land relationship aim at the realization of sustainable development. Clearly, the theories of man land territorial system should work as important theoretical bases of sustainable development. Therefore, it is a significant task for geographers to enhance the theoretical studies of man land territorial system. The prior issues regarding man land territorial system are as follows: 1) studies on regional differences from systematic perspective; 2) a deeper understanding of the characteristics of man land territorial system; and 3) studies on the approaches for comprehensive integration. Furthermore, the development of methodologies with comprehensive and systematic perspectives, territorial and dimensional perspectives as well as model building and simulation applicable to practice deserves more efforts.
人地关系研究范型: 地域系统实证
A paradigm of the research on man-earth relationship: Positive study of territorial system
中国人地关系研究的新进展与展望
Recent progress of studies on man-land relationship and its prospects in China
人文地理学科学化的总体目标与实现路径
The major objectives and implementation methods for human geography toward the tendency of physical science
DOI:10.11821/xb201112001
[本文引用: 1]

The development of contemporary human geography shows a diverse tendency. Physical science should be the base of human geography, and the tendency of physical science will be the unavoidable choice and unique way for future development of human geography in China. According to the disciplinary property of human geography and the need of Chinese economic social development, the tendency of physical science should not be a passive target but an initiative pursuit. There are two elementary goals. One is building a relatively complete theory system of regional spatial structure. It is necessary to discover new regional spatial structure patterns, construct evolution model of the central place system and find the internal logical relationship among different structure patterns from the perspective of typology and phylogeny. The other is constructing relatively complete methods of spatial analysis. The region can be divided into homogeneous region and functional region, and furthermore be decomposed into three fundamental elements: point, line, and area. The theoretical framework of spatial analysis for human geography in this article is constructed by the technologies to explore and express the spatial coupling inter- and intra-elements. Expanding the accessibility analysis technology, integration of economic models and spatial analysis technologies, construction of the comprehensive system of spatial-temporal spectrum spatial analysis, and discovery of new spatial analysis technologies based on the extension of space concepts, should be the significant fields of spatial analysis for human geography in the future. To achieve these goals, we should establish scientific thinking patterns, integrate resource and environment basis, improve the long period analysis of historical process from the perspective of phylogeny and fully use modern technology such as mathematical model and GIS technology.
人地系统可持续过程、格局的前沿探索
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408003
[本文引用: 1]

本文结合笔者近年来在人文地理学前沿问题探讨的综述,阐释了人—地系统相互作用时空分异规律是现代地理学最高层级的科学难题、也是决定未来地理学前途的关键问题的认识,提出了截至目前开展人地系统综合研究所采用的“过程归纳、区域比较、定性分析、逻辑判断”等4个实用方法,并围绕着区域均衡、资源环境承载能力、地域功能、空间结构等4个前沿领域,讨论了影响区域发展格局变化的驱动力、自然圈对人类活动圈层的作用、综合地理区划原理和方法、以及“生活—生产—生态”空间结构变化规律等研究的学术思想,探讨了“未来地球”框架下区域可持续发展研究的意义和重要命题,认为“自然科学和社会科学交叉”、“基础研究和决策应用贯通”的复杂性科学基础理论体系和综合研究集成方法体系建设,将深刻影响着人地系统过程和格局的研究进展。
Frontier approach of the sustainable process and pattern of human-environment system
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408003
[本文引用: 1]

In combination with the author's review of frontier issues in human geography in recent years, this paper clarifies that uncovering the spatiotemporal difference rules of human-environment system interaction in the geographic pattern is the highest-level scientific puzzle in modern geography, and is the understanding of key issues which could decide the prospect of future geography. Four practical methods including "process induction, regional comparison, qualitative analysis, logical judgment" until now for integrated human-environment system researches are proposed. Aiming at four frontier fields including regional equilibrium, resources and environment carrying capacity, territorial function, and spatial structure, academic ideas including the driving forces of regional development pattern changes, the impact carrier of natural sphere on human activity sphere, the rules and methods for integrated geographic zoning, and the changing laws of "living-production-ecology" spatial structure, are discussed. Finally, this paper discusses the significance and key issues of regional sustainable development in the framework of "Future Earth", and presents that the integrated method system and basic theoretical system of comprehensive research in complexity science based on "integration of both natural and social sciences" and "interpenetration of both basic researches and decision-making application", will profoundly influence research progress of the process and framework of human-environment system.
中国人地关系综合评价的理论模型与实证
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201906001
[本文引用: 2]

人地关系是地理学研究的经典问题,也是中国人文—经济地理学在国际地理学研究中具有突出贡献的命题。人地关系在动态演变过程中不断出现新的时代内涵,如何科学表征中国现代人地关系的状态,是精准认知现代人地关系进而寻求协调人地矛盾路径的基础。基于人地关系地域系统理论,在梳理中国现代人地关系时代特征的基础上,构建人地关系综合评价的理论框架,从人类活动的施压强度、核心资源要素的承压能力、生态环境系统的约束力度以及人—地系统的开放程度4个层面选取表征指标,秉承分级评价、逐级修正的思想,以县级单元为基础对全国层面的人地关系状态进行综合评价。结果发现:中国的人类活动强度具有明显的东西分异性及依托核心城市群布局的特征,而核心资源要素的综合支撑能力空间布局较为分散,且土地、水、核心能矿资源以及人类活动强度四者之间的空间错配度较高,在一定程度上增加了区域人地关系的紧张状态。生态环境系统的约束紧密区多集中在胡焕庸线两侧及青藏高原西南部,全国层面上人—地系统的开放程度不高,开放程度较高的区域主要集中在中国经济发达地区。综合评价结果显示,全国大约85.56%的区域人地关系状态以宽松为主,但是局部地区尤其是东南沿海地区人地矛盾突出,西部地区人地关系相对宽松,但人地系统演进的等级也相对较低。
Comprehensive evaluation on China's man-land relationship: theoretical model and empirical study
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201906001
[本文引用: 2]

Relationship is a classic concern of geographical research, which is also a research field where China's human and economic geography has made notable contributions to international geographical research. The connotation of man-land relationship changes constantly during its dynamic evolution process. Therefore, a scientific evaluation on the status of modern man-land relationship in China is the basis for an accurate understanding of it with which paths of coordinating conflicts between man and land can be sought. Based on the territorial system theory of man-land relationship and a review of the new characteristics of modern man-land relationship in China, this study constructs a theoretical framework to make a comprehensive evaluation on man-land relations using the following four indicators: intensity of human activities, carrying capacity of core resources, ecological and environmental constraints, and openness of man-land system. Counties are taken as the basic spatial units in the evaluation. The following results are found: there are apparent differences between eastern and western China in terms of intensity of human activities and the distribution pattern of it follows the layout of core urban agglomerations; the carrying capacities of core resources take on a relatively dispersed spatial distribution; there is a high level of spatial mismatch between land, water, core energy resources, and the intensity of human activities, which intensifies the tension of regional man-land relationship; areas with strong ecological and environmental constrains are concentrated on both sides of the Heihe-Tengchong Line (also known as the Hu Huanyong Line) and in the southwestern part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; overall, the level of openness of China's man-land system is not high, with relatively open areas mainly concentrated in economically developed regions. The evaluation results show that about 86% of the regions in China are faced an unstrained man-land relationship, but noticeable man-land conflicts are found in some areas, particularly in southeastern coastal areas. In the western region of China, man-land relationship is relatively unstrained though the level of man-land system evolution is low.
社会信息化与人地关系:香山科学会议第169次学术讨论会观点摘要
Social informatization and man-land relationship:Summary of the opinions of the 169th Academic Symposium of Xiangshan Science Conference
人地系统远程耦合的研究进展与展望
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.02.012
[本文引用: 1]

在越发紧密关联的全球化世界中,如何实现可持续发展日益需要跨系统思维和超区域政策。这首先要求致力于可持续发展研究的学科要提升自身对跨区域资源环境问题的洞察力,因此就有必要推动地理学传统研究框架的适应性创新和变革。远程耦合作为聚焦于“远距离人类与自然耦合系统之间社会经济与环境相互作用”的理论框架,有极大的潜力和优势来促进这一理论创新进程。为了缩小国内外在远程耦合领域的研究差距,论文基于文献研究和笔者对远程耦合框架的理解,从远程耦合的理论建构、经验证据、重点研究领域和研究方法4个方面介绍了该理论框架及其应用进展,并提出3个方面的展望来激发新的研究。综述表明,由于远距离人类活动不断增长以及大尺度自然过程与人类活动的相互作用,在远程连接、全球化和城市化维度上均存在大量远程耦合的经验证据;目前学术界对远程耦合框架的应用主要集中于生态系统服务、远程耦合的社会经济和环境影响及土地变化科学3个方面;同时得益于理论操作化的进展,目前开展远程耦合研究已具备较好的方法支持。基于此,论文认为,为应对新兴的现实科学命题,基于远程耦合框架的地理学研究应当在人地关系网络系统的理论创新、远程耦合动力机制和远程耦合的调控工具集3个方面实现突破。
Research progress and prospect of telecoupling of human-earth system
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.02.012
[本文引用: 1]

Achieving sustainable development in an increasingly interconnected globalized world requires cross-system thinking and more integrated regional policy. First, it requires disciplines devoted to sustainable development research to improve their insights into trans-regional resource and environmental issues. Accordingly, it is necessary to promote the adaptive innovation and transformation of the traditional research framework of geography. Telecoupling, as a theoretical framework focusing on socioeconomic and environmental interactions among coupled human and natural systems over distances, has great potential and advantages to facilitate the process of theoretical innovation. In order to narrow the gap between Chinese and international research in the field of telecoupling, we introduce the telecoupling framework and its application progress from theoretical construction, empirical evidence, key research areas, and research methods based on literature review, document analysis, and our own understanding of telecoupling, and further give some suggests. The review shows that there is a large amount of empirical evidence of telecoupling in the dimensions of teleconnection, globalization, and urbanization due to the continuous growth of long-distance human activities and their interaction with large-scale natural processes. Currently, the application of the telecoupling framework in academia mainly focuses on three aspects: ecosystem services, the socioeconomic and environmental impacts of telecoupling, and land change science. Due to the progress in operationalizing the theories, current telecoupling research has been well supported methodologically. We further argue that geographical research based on the telecoupling framework should make breakthroughs in the theoretical innovation of Human-Earth relationship network system, telecoupling mechanism, and telecoupling regulatory tool sets, so that scientific research can keep up with the latest trends and solve the emerging real world problems.
A typology of relationships between telecommunications and transportation
DOI:10.1016/0191-2607(90)90060-J URL [本文引用: 1]
Telecommunications and the City: Electronic Space
网站信息流对现实人流替代函数的计算与应用: 以中国互联网络发展状况统计报告为例
The calculation and application on replacement effect of website information flow to real human flow: The case of statistic report of internet development in China
集聚经济、政策激励与中国计算机制造业空间格局: 基于贸易数据的实证研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.10.001
[本文引用: 1]

利用中国海关贸易库数据,对计算机上游和下游出口源地的空间格局演变进行对比分析,以面板数据方法揭示产业集聚和政策激励的作用。研究发现:① 计算机上游出口集中在长三角和珠三角,下游出口集中于长三角和成渝,上游出口格局更分散;② 从动态看,上游出口从珠三角逐步向内陆扩散呈现集聚-分散-集聚的过程,内陆地区承载大部分出口增长;下游出口增长态势更为明显,最初集中分布在长三角和珠三角,2010年以后内陆地区增长迅速,成渝成为继长三角后最为重要的集聚区;③ 研究时段集聚经济对计算机上下游制造业的推动作用降低,政策激励的影响显著增加;④ 沿海和内陆计算机制造业发展模式不同,前者的兴起主要是市场化条件下的集聚经济,后者则受到集聚经济和政策激励的共同影响;⑤ 由于产业特征的差异,集聚经济对计算机上游的影响高于下游。在计算机制造业的发展中,要素成本增加造成的集聚不经济和地方政府的政策激励使得集聚效应逐步让位于政策支持。不同区域不同阶段产业对政策的敏感程度并不相同,政策制定应顺应产业演变规律。
Agglomeration economy, incentive policy and the spatial pattern of Chinese computer manufacturing industry: A case study based on export data
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.10.001
[本文引用: 1]

The coast areas of China took the lead in developing and exporting computer products based on comparative advantages. However, with the rising of wage, land price and environmental standards, as well as strong incentives of local governments, a large number of enterprises started to relocate to the inland areas of China. Thus, the spatial pattern of Chinese computer manufacturing had changed dramatically. On the base of export data compiled by the Chinese Customs Trade Statistics, this article investigated the spatial patterns of upstream and downstream computer industry during 2004 to 2013. Based on panel data method this research revealed the role of agglomeration economy and incentive policy in affecting the pattern of computer exportation. The results indicate that: 1) The exportation of upstream computer industry is concentrated in the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta while the downstream industry is concentrated in the Yangtze River Delta and Chengdu-Chongqing region. The distribution of the upstream industry is more dispersed. 2) From a dynamic perspective, the exportation of upstream computer industry shows agglomeration-scattered-agglomeration feature as it decreased in the Pearl River Delta while increased in inland areas. Exportation of downstream computer industry is initially concentrated in the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta. After 2010, the downstream industry grew rapidly and Chengdu-Chongqing region became the second biggest (after the Yangtze River Delta) export areas in 2013. 3) The influence of agglomeration on both upstream and downstream computer manufacturing was reduced while the impact of policy increased significantly. 4) The developing routines of computer manufacturing in the coastal and inland regions are different. The rise of the former is mainly stimulated by agglomeration under the background of marketization, and the latter is influenced by both agglomeration and policy. 5) Due to the difference of industrial characteristics, the impact of agglomeration on the upstream industry is more than the downstream. This article suggests that with the increasing of cost, agglomeration is gradually becoming not economical. Policy development should be consistent with the evolution of agglomeration economy to realize expected economic performance.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 1]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the New Era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 1]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
信息革命下的社会经济空间集聚与分散
Agglomeration and dispersion of social economic space under the information revolution
The internet, mobile phone and space-time constraints
DOI:10.1016/j.geoforum.2007.11.005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Influence of information technology on social spatial behaviors of urban residents: Case of Nanjing city in China
DOI:10.1007/s11769-008-0316-x URL [本文引用: 1]
中国时空间行为研究进展
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.09.006
[本文引用: 1]

自时间地理学和活动分析法引入中国以来的近20年间,时空间行为研究已经成为中国城市地理学的重要领域。中国时空间行为研究关注城市空间重构的描述与解释,试图从行为角度解释中国城市社会转型,强调转型期中国城市空间与居民个体行为之间的互动关系,重视日常生活、生活质量、社会公正、低碳社会、智慧城市等热点问题,探索在城市交通、旅游和城市规划等领域中的实践应用。中国时空间行为研究已经形成了以解读城市转型为目标、以规划应用为导向的鲜明特点,为理解中国城市制度与空间转型背景下人类行为模式的复杂性和多样性提供了一个全新的视角。但是,中国时空间行为研究依然面临着理论发展滞后、实践应用需要突破等挑战。本文是对时空行为研究近年来发展的综述性文章,从数据采集与分析方法演进、实证研究与规划应用进展等方面回顾了近20年来中国城市时空间行为研究的最新进展,致力于推动不同学科领域之间的交流和时空间行为研究自身的发展。
Progress in space-time behavior research in China
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.09.006
[本文引用: 1]

As a unique perspective for understanding the complex relationships between human activities and urban environments in space and time, the space-time behavior approach has become an influential methodology in China's urban geography since 1990s. Aiming at promoting communications and exchanges among urban geographers in different contexts, this article provides a critical review of space-time behavior research in China. Ever since time geography and activity-based model were introduced to China's urban geography, space-time behavior research in China has benefited from the fruitful theoretical and methodological progress made in Western geographical research. On one hand, GPS and mobile phone tracking technologies have been integrated into activity-diary surveys to collect more accurate and real-time activity-travel information. On the other hand, advanced statistical models and geocomputational and 3D geovisualization methods have been adopted in more recent empirical literature in China. Yet, while Chinese urban geographers have made more methodological progress in data collection and analytic tools thanks to the development of GPS and GIS technology, theoretical development still lags behind. However, space-time behavior research in China, with planning-oriented characteristics, offers a unique framework for understanding urban transformation in China. It has become a new perspective for understanding the complexity and diversity of human behavior patterns in the transitional cities in China. In other words, space-time behavior research tries to describe and interpret urban spatial structures and spatial reconstructing in urban China from the perspective of individuals' behaviors. The impacts of danwei-based urban spatial organization and its disappearance, as well as the impacts of suburbanization on individuals' daily activities, have been studied carefully. Especially, this approach emphazes how spatial restructuring impact individuals' daily life experiences, which in turn are related to the issues such as life quality, social equity and environmental sustainability. Urban geographers in China have begun to apply the space-time activity approach to the socio-spatial issues in the cities by focusing on daily-activity experiences of low SES (socioeconomic status) populations. And the development of the low-carbon city movement in China has prompted the application of the space-time behavior approach in understanding the impacts of land use characteristics on travel-related carbon- dioxide emissions through individuals' travel decisions. At the same time, planning practices based on the space-time behavior approach is carried out in urban transportation, tourism, and urban planning. The space-time behavior approach has become a very useful human-oriented approach to land use and transportation planning in China. The article concludes by discussing key theoretical and practical challenges for future development of space-time activity research in China.
Operationalizing the social-ecological systems framework to assess sustainability
DOI:10.1073/pnas.1414640112
PMID:25918372
[本文引用: 1]

Environmental governance is more effective when the scales of ecological processes are well matched with the human institutions charged with managing human-environment interactions. The social-ecological systems (SESs) framework provides guidance on how to assess the social and ecological dimensions that contribute to sustainable resource use and management, but rarely if ever has been operationalized for multiple localities in a spatially explicit, quantitative manner. Here, we use the case of small-scale fisheries in Baja California Sur, Mexico, to identify distinct SES regions and test key aspects of coupled SESs theory. Regions that exhibit greater potential for social-ecological sustainability in one dimension do not necessarily exhibit it in others, highlighting the importance of integrative, coupled system analyses when implementing spatial planning and other ecosystem-based strategies.
Social-ecological system framework: Initial changes and continuing challenges
Defining urban resilience: A review
DOI:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.11.011 URL [本文引用: 1]
Adaptive governance of social-ecological systems
未来城市研究范式探讨: 数据驱动亦或人本驱动
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.004
[本文引用: 1]

回顾传统城市研究范式,指出其“重宏观社会经济发展研究、而轻微观居民个体需求分析”这一问题,在此基础上,综述了城市研究领域的大数据热潮,进而抛出“数据亦或人本驱动?”的争论;从大数据自身的缺陷、智慧社会的到来及未来城市发展维度3个方面分析未来城市研究数据和人本之间的关系,提出应遵循“人本驱动、数据支撑”的研究范式,扩展了“人本驱动”的内涵。最后,从城市居民生活(生活圈打造、社会网络构建、满足生命周期需求)、企业生产(人才流动网络构建、产业链打造、营销模式转变)、政府管治(数据共享与融合、社会服务供应、公众参与机制创新)3个方面提出了未来城市研究的新框架。
The discussion of urban research in the future: Data driven or human-oriented driven
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.004
[本文引用: 1]

Technological innovation is constantly changing the process of urban development, and the emergence of big data has attracted great attention of urban researchers. Some people believe that data will become the main driving force of future urban research. However, the development stage of human society and the historical transformation of urban research indicate the humanistic trend of future urban development. So, are future urban studies data driven or human-oriented driven? What is the relationship between them and the direction of future urban research? Firstly, this article reviews the traditional urban research and points out the limitations of methodological and data usage, which paid more attention on social-economic development instead of individuals’ needs. Secondly, it summarizes the big data booming in urban research field, and then put forward the argument of “data driven or human-oriented driven?”. Thirdly, the relationship between data and human-oriented in future urban research is analyzed from 3 aspects: the limitations of big data, the arrival of smart society and the trend of future urban development. Fourthly, the research paradigm of “human-oriented driven and data supported” is proposed. Finally, it also builds a new framework of future urban research from three aspects of residents' life, enterprise production and government governance.
A tale of one city: Using cellular network data for urban planning
DOI:10.1109/MPRV.2011.44 URL [本文引用: 1]
利用公交刷卡数据分析北京职住关系和通勤出行
Identifying commuting pattern of Beijing using bus smart card data
DOI:10.11821/xb201210005
[本文引用: 1]

This paper combines the one-week bus smart card data (SCD) and one-day household travel survey as well as the parcel-level land use map for identifying jobs-housing places and commuting trips in the Beijing Metropolitan Area with an area of 16,410 square kilometers. The identification result is aggregated in the bus stop and traffic analysis zone (TAZ) levels, respectively. In particular, commuting trips with commuting time and distance attached from three typical residence communities and those to five typical business zones are mapped and compared with each other to analyze commuting patterns of Beijing. The identified commuting trips are compared with those in the household travel survey in terms of commuting time and distance, indicating that our results are coincident with the survey significantly. Our approach is proved to have its potential in identifying more solid identification result based on rules extracted from existing surveys or censuses.
中国城市间人口流动空间格局的网络分析: 以国庆—中秋长假和腾讯迁徙数据为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020171231
[本文引用: 1]

“腾讯迁徙”大数据基于位置服务,实时、动态、完整、系统地描述了用户日常出行活动的轨迹。通过采集“腾讯迁徙”数据平台中2017年国庆-中秋长假期间国内299个城市之间的逐日人口流动数据,分“出行期、旅途期、返程期”3个时间段,利用复杂网络分析方法,从人口流动集散层级、集散网络体系的分层集聚、人口流动空间格局、网络空间特征等角度分析各时间段城市间的人口流动特征与空间格局。结果表明,腾讯迁徙大数据直观地揭示了国庆-中秋期间中国各地级城市间人口的迁移规律,3个时段人口的净流入均呈现十字形骨架支撑的菱形分布,人流集散中心主要集中在京津冀、长三角、珠三角和成渝四大城市群,与城市等级有较强的一致性。人口流动集散体系呈明显的分层集聚,城市行政级别的高低与人口流动影响力存在一定的正相关关系,大部分城市人口流动处于“相对平衡”状态。人口流动空间格局呈现出明显的核心-边缘结构,大理-鹤岗一线是人口流动强度空间分布的显著分界线,以此线为界,城市网络呈现东密西疏的分布特征和东部并联、西部串联的网络关联特征。人口流动网络总体表现出“小世界”网络特征,局部具有较明显的“社区”结构特征,聚为2个国家级、2个区域级和3个地区级社区。
Research on spatial pattern of population mobility among cities: A case study of "Tencent Migration" big data in "National Day-Mid-Autumn Festival" vacation
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020171231
[本文引用: 1]

Population migration, social check-in, vehicle navigation, and other spatial behavior big data have become vital carriers characterizing users' spatial behavior. The big data used in this paper were collected from the locations provided by hundreds of millions intelligent mobile phone users through Location Based Service (LBS) Tencent Migration data platform, and were displayed by means of real-time heat map which indicates user’s moving trajectory in China. "Tencent Migration" big data can real-timely, dynamically, completely and systematically record population flow routes using LBS device. Through gathering residents daily mobility among 299 cities in China during the period of "National Day-Mid-Autumn Festival" (NDMAF) vacation (from September 30 to October 8) in 2017 in "Tencent Migration" and defining three periods with "travel period, journey period, return period", this paper is designed to analyze and explore the characteristics and spatial patterns of daily flow mobility cities from the perspective of population daily mobility distribution levels, flow distribution layers network aggregation, spatial patterns and characteristics of the complex structure of the flow network. Results show that "Tencent migration" big data clearly discovers the temporal-spatial pattern of population mobility in China during the period of NDMAF. The net inflow of population showed a diamond-shaped pattern with cross frame support in each period, with the four nodes of Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Xi’an. Main mobility assembling centers are distributed in the urban agglomerations of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta and Chengdu-Chongqing, and those centers have strong coherence with those urban hierarchies. There is a positive correlation between the level of urban administration and the influence of population flow. Most cities are in a state of "relative equilibrium" in the population flow, and clear hierarchical structure and level distinction can be identified. Spatial patterns of population mobility present obvious core-periphery structures. The Dali-Hegang line exhibits a significant network of spatial differences in terms of boundary divisions. In this context, the spatial distribution of urban network could be summarized as "dense in the East and sparse in the West", and the core linkages of urban network could be characterized as "parallel in the East and series in the West". The whole network exhibits a typical "small world" network characteristic, which shows that China's urban population flow network has high connectivity and accessibility during the period of NDMAF. The network has a distinct "community" structure in the local area, including 2 national communities, 2 regional communities and 3 local-level communities.
Urban gravity: A model for inter-city telecommunication flows
基于网络社会空间的中国城市网络研究: 以新浪微博为例
DOI:10.11821/xb201208003
[本文引用: 1]

信息技术影响下的城市区域空间结构变化得到了国内外学者的关注。本文以新浪微博为例, 从网络社会空间的角度入手, 对中国城市网络发展特征进行了研究。研究表明:微博社会空间视角下的中国城市网络存在着明显的等级关系与层级区分, 城市的网络连接度与城市等级表现出了相对一致性。根据城市网络层级与网络联系强度, 东部、中部、西部3 大区域板块的网络联系差异明显, 东部地区内部的联系, 以及东部与中部地区和西部地区的联系几乎构成当前网络体系中的全部。城市网络呈现出分层集聚现象, 具体表现为“三大四小”发展格局, 即京津冀区域、珠三角区域、长三角区域、成渝地区、海西地区、武汉地区、东北地区。高等级城市在整个城市网络中处于绝对支配地位, 北京以突出的优势成为全国性的网络联系中心, 而上海、广州、深圳则成为全国性的网络联系副中心。
China's city network characteristics based on social network space: An empirical analysis of Sina micro-blog
DOI:10.11821/xb201208003
[本文引用: 1]

The change of urban regional spatial structure influenced by information technology has become a hotspot of research at home and abroad. This study tries to analyze China's city network characteristics from the social network space perspective by using Sina microblog as an example. The result shows that China's city network based on the micro-blog social space has a clear hierarchical structure and level distinction. Firstly, the result shows the existence of regional characteristics, performance as a visible regional development pattern which contains "Three Main-regions and Four Sub-regions" according to the analysis of the level distinction in the city network and the connection rate between cities. Specifically speaking, the three main regions contain the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region represented by Beijing, Pearl River Delta region represented by Guangzhou and Shenzhen, and the Yangtze River Delta region represented by Shanghai, Hangzhou and Nanjing. The four sub-regions contain Chengdu-Chongqing region, west coast of the Taiwan Straits region represented by Fuzhou and Xiamen, Wuhan region represented by Wuhan and Changsha, Northeast China represented by Shenyang, Harbin and Changchun. Secondly, the result shows there is a significant difference of the network links among Eastern, Central and Western China. Links within Eastern China and the links between Eastern, Central and Western China constitute almost all of the current network systems. It is also found that the high-level cities have an absolute dominance in the city network pattern, and that Beijing is the contact center in China's city network, with an overwhelming advantage. Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen are the sub-contact centers in the China's city nework.
基于多源大数据的武汉市区域空间格局研究
Study on regional spatial structure of Wuhan based on multiple online data
Exploring place through user-generated content: Using Flickr tags to describe city cores
基于手机数据识别上海中心城的城市空间结构
Understanding urban spatial structure of Shanghai central city based on mobile phone data
手机信令数据在城市建成环境评价中的应用: 以上海市宝山区为例
The application of cell phone signaling data in the assessment of urban built environment: A case study of Baoshan district in Shanghai
基于多维数据的特大城市建设用地类型识别
Classifying development-land type of the megacity through the lens of multisource data
Lessons in urban monitoring taken from sustainable and livable cities to better address the smart cities initiative
DOI:10.1016/j.techfore.2014.01.012 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于多源大数据的城市体征诊断指数构建与计算: 以上海市为例
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

基于多源大数据,构建了整合城市活动-移动系统、城市人口系统、城市运行系统、城市环境系统4个系统的城市体征诊断指数体系。该指数体系分解为底力、动力、压力、活力4个维度,具有4个层次和12个时空间尺度。底力指数表征土地、人口等空间单元基本属性,用以把握区域总体特征;动力指数通过企业发展状况、环境质量等反映了空间单元的发展状态;压力指数用以监测城市系统运行状况,起到风险评判与预警的作用;活力指数以活动和流的时空特征进行活动动态展现,反映空间单元的真实活力。最后以2016年4月6日为例,计算和展示了上海各街道的综合和各维度体征诊断指数,说明了体征诊断指数的可应用性和指数计算结果的稳健性。城市体征诊断指数可以辅助于城市网格化管理、压力预警等治理需求。
Construction and calculation of diagnostic index of urban signs based on multi-source big data: Case of Shanghai
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

Urban signs characterize the state of development and operation of a city, including construction conditions of built environment,driving force of urban economic and social development, operational status of facilities and urban activities of individuals in the city, etc. The diagnosis of urban signs equals to the health examination of urban development and operation, by which sticking points are recognized. A set of reliable and practical urban diagnostic indices is required not only to comprehensively reflect correlative sub urban systems that are static or dynamic, but also illustrate the status of urban system through quantitative methods and geo-visualization. Using traditional data and big data from different sources, this paper constructs a system of diagnostic index of urban signs based upon the integration of urban activity-travel system, urban population system, urban operation system, and urban environment system. The diagnostic index system is decomposed into 4 dimensions including fundamental force, driving force, pressure and vitality. The fundamental force index is used to describe basic attributes of land use and population; the driving force index reflects the state of development of spatial units through development of enterprises and quality of the environment; the pressure index is used to monitor the running status of the urban system, and as such, it plays a role in risk-evaluation and risk-warning; the vitality index reflects the real vitality of the spatial units by demonstrating the dynamic characteristics of the activity system and flows in time and space. 12 spatio-temporal scales are acquired through intersection of 4 levels of the spatial units(municipal Shanghai, district, Jiedao, census tract)and 3 levels of temporal scales(annual,daily and real time levels). The index weight is determined by fuzzy hierarchy analysis. Taking April 6, 2016 as an example, we calculate both comprehensive and dimensional diagnostic index of urban signs of Jiedaos (subdistrict that is sub-divided into several residential communities or neighbourhoods) in Shanghai and elaborate on how the diagnostic index of urban signs corresponds to actual state and facilitates detection of urban problems. Results show that comprehensive diagnostic index varies slightly while considerable variations emerge in diagnostic index of each dimension. Fundamental force index, driving force index and vitality index decline gradually from inner city to suburbs. On the contrary, pressure index increases from inner city to suburbs. Through visual and real-time analysis and evaluation, the diagnostic index of urban signs has huge potential for implementation in urban grid management, pressure warning and other needs of urban governance.
北京西城区城市区域体检关键技术研究与实践
Key techniques in urban physical examination evaluation for Beijing Xicheng district
智慧城市中的大数据
Big data in smart city
从信息化赋能到综合赋能: 智慧国土空间规划思路探索
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20191004
[本文引用: 1]

党的十九大报告明确的“智慧社会”建设目标,对当前国土空间规划工作的开展提出了新的要求。如今,以互联网、大数据、云计算等为主的信息化技术赋能是当前国土空间规划智慧化的主要动力与发展重点,而如何理解并推进智慧社会发展则是智慧编制与实施国土空间规划的重要基础。人地关系和地域生命有机体理论是智慧社会下国土空间规划与治理的理论与方法基础,需要从信息化赋能向包含技术赋能与创新赋能的综合赋能理念转变,探讨智慧国土空间规划的总体思路,进而构建以生态文明为基础、以人为本为核心、技术集成应用和制度创新为支撑的智慧国土空间规划框架(EPTI),并探讨规划编制的智慧化以及规划实施的智慧化。
From informational empowerment to comprehensive empowerment: Exploring the ideas of smart territorial spatial planning
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20191004
[本文引用: 1]

The Communist Party of China's 19th National Congress Report has clearly set the goal of "smart society" and put forward new requirements for the current development of territorial spatial planning. Nowadays, the empowerment of information technology based on the Internet, big data, cloud computing, etc. is the main driving force and development focus of the current practices of smart territorial spatial planning. How to understand and promote the development of smart society is the foundation of the compilation and implementation of smart territorial spatial planning. This paper emphasizes the importance of human-land relationship and the theory of urban life organism to the planning and governance of territory in a smart society. It points out that the overall conceptualization of smart territorial spatial planning should be transformed from informational empowerment to comprehensive empowerment, which includes technological empowerment and innovative empowerment. The paper constructs a smart territorial spatial planning framework-EPTI-based on the ideas of ecological civilization, people-oriented, technology integration application and institutional innovation, and discusses the paths toward smart compilation and implementation of territorial spatial planning.
Comparative analysis of standardized indicators for smart sustainable cities: What indicators and standards to use and when?
DOI:10.1016/j.cities.2019.01.029 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于智慧城市的可持续城市空间发展模型总体架构
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.04.004
[本文引用: 2]

在智慧城市建设上升为国家战略的大背景下,以城市人口、经济、资源、环境等历史数据分析为基础的传统城市空间发展模型面临着数据来源与研究框架的革新。本文首先阐述了智慧城市与可持续发展理念产生的时代背景、概念内涵、相互关系,进而在梳理国内外可持续发展视角下的城市模型相关研究基础上,认为智慧城市建设为城市模型研究提供了更为精细、实时、全面的数据来源,拓宽了城市模型研究的时空尺度,并在城市系统运行模拟与仿真方面提供新的技术手段。本文从城市数据监测采集与互联共享、城市系统运行问题梳理与综合分析、城市空间发展模拟仿真与决策评估、城市空间发展规划体系4个层面尝试构建基于智慧城市的可持续城市空间发展模型总体架构,对于丰富城市可持续发展研究理论框架,指导智慧城市空间规划与建设实践具有重要意义。
The overall architecture of sustainable urban spatial development model based on the construction of smart cities
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.04.004
[本文引用: 2]

Under the background that smart city construction has become a national development strategy, traditional urban spatial development models based on the analyses of historical data of population, economy, resource, and environment need to incorporate new sources of data and innovative research framework. This article first discusses the background and connotation of, and relationship between smart city and sustainable development, and then summarizes the Chinese and international research on sustainable urban spatial development models. It concludes that smart city construction provides finer, comprehensive, and real-time data and broadens the spatial and temporal scales of models for urban system modeling, as well as offers new technical means for the simulation of urban system operation. Based on the above, this article presents the overall architecture of an sustainable urban spatial development model based on the construction of smart cities. The model contains four parts that: (1) monitor, collect, and share urban data; (2) decipher and analyze urban operation problems; (3) simulate urban spatial sustainable development and evaluate the related policies and decisions; and (4) design the urban spatial development planning system based on the construction of smart cities. It is important for enriching the theoretical framework of urban sustainable development and guiding the spatial planning and construction practices of smart cities that aim at sustainable development for the ultimate goal.
改革开放40年来中国城乡规划知识网络演进
Evolution of knowledge network of urban-rural planning in China in four decades since the opening up in 1978
Identifying the results of smart city development: Findings from systematic literature review
DOI:10.1016/j.cities.2019.102397 URL [本文引用: 1]
What are the differences between sustainable and smart cities?
DOI:10.1016/j.cities.2016.09.009 URL [本文引用: 1]
Defining the role of the smart-city manager: An analysis of responsibilities and skills
Smart governance as key to multi-jurisdictional smart city initiatives: The case of the eCityGov Alliance
DOI:10.1177/0539018416629230
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Quite a number of smart-city initiatives from around the world have been analyzed and documented, and a growing body of academic knowledge is evolving around the phenomenon of the smart city. Smart-city government is seen as an important driver for developing a smart urban environment. The eCityGov Alliance in the Pacific Northwest of the USA represents a special case of a successful smart-city collaboration between nine neighboring municipalities, which combined forces to provide smart services to citizens and businesses that no single municipality could have provided alone. Developing and maintaining a collaborative governance model appears as the most important key success factor in such multi-jurisdictional smart-city undertakings. This study investigates the governance model of the eCityGov Alliance and its opportunities, and potential pitfalls. It concludes that the eCityGov Alliance can serve as a role model for such multi-jurisdictional smart-city initiatives.
“人—技术—空间”一体的智慧城市规划框架
An integrated "human-technology-space" framework of smart city planning
“人地关系地域系统”是综合研究地理格局形成与演变规律的理论基石
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
[本文引用: 1]

同近年国外人文地理学呈现人文化趋势相比,中国人文与经济地理学秉承吴传钧先生关于人文与经济地理学是研究自然圈与人文圈相互作用下、人类活动分布格局形成和演变规律的一门交叉学科的定位,形成了以不同空间尺度的地域、重要的生产生活领域、以及典型的地域空间类型的可持续发展时空规律作为研究指向的中国人文与经济地理学主流学派。吴先生提出的“人地关系地域系统”理论不仅为人文与经济地理学,而且是为整个地理学的综合研究提供了重要的理论基石。地域功能性、系统结构化、时空变异有序过程、以及人地系统效应的差异性及可调控性,是该理论的精髓,这与“未来地球”研究计划的前沿思想完全契合。近10年来,以城镇化科学模式、主体功能区划、一带一路路线图、京津冀城市群、农村空心化和精准扶贫、东北振兴与资源型城市转型、行政区划优化等为研究对象,发展了人文与经济地理重要的可持续过程、地域功能形成和综合地理格局有序化规律、城市群形成演化机理及其资源环境效应、问题地区可持续生命周期与振兴路径、地缘政治地缘经济和区域间相互作用关系、人文界线对可持续发展的影响等理论方法。人文与经济地理学科建设取得重要进展,应用成果对近年来中国生态文明建设和可持续发展产生了重要影响。中国人文与经济地理学在全球范围内发展态势最佳、总体水平领先,以此告慰吴传钧先生,并以此纪念吴传钧先生百年诞辰。
"Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction": Atheoretical cornerstone for comprehensive research on formation and evolution of the geographical pattern
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
[本文引用: 1]

Compared with the increasingly obvious humanistic tendency in foreign human geography, China's human and economic geography still follows Academician Wu Chuanjun's theory, with human and economic geography as an interdisciplinary subject which is the study of the formation and evolution of the distribution pattern of human activities under the interaction of natural circle and human circle. And China's mainstream school on human and economic geography has been formed with studies on spatio-temporal rule of sustainable development on territories with different space scales, territories with important production and living, and territories with typical geospatial patterns as the main research points. "Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction", developed by Academician Wu Chuanjun, is the important theoretical foundation not only for human and economic geography, but also for the comprehensive research on geography. The essence of the theory, which includes territorial functional, system structured, orderly process for spatio-temporal variation, and the difference and controllability of human-environment interaction system effect, is entirely harmonious with the forefront of thought of the "Future Earth" studies program. In recent decade, with scientific mode of urbanization, major function oriented zoning, road map for the Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, rural hollowing and targeted poverty alleviation, revitalization of Northeast China and transformation of resource-based cities, and administrative area optimization as the main research objects, theoretical methods have been developed in the aspects of important sustainable process of human and economic geography, territorial function formation and ordering rules for comprehensive geographical pattern, formation and evolution mechanism of urban agglomeration and its resources and environmental effects, sustainable life cycle and the revitalization of the path for problem areas, the interaction between geopolitics, geo-economy and regions, and effect of cultural boundaries on sustainable development. China's human and economic geography has made great progress in discipline development, and the application results have produced profound influences on the ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in recent years. With decades of hard work, China's human and economic geography has reached a world-class advanced level, so as to console the soul and spirit of Wu Chuanjun on the occasion of commemoration of the centenary of his birth.
基于可持续发展目标的智慧城市空间组织和规划思考
The spatial organization and planning of smart cities based on the sustainable development goals
21世纪人地关系研究前瞻
Prospects of studies on man-land relationship in the 21st century
DOI:10.11821/yj2002010002
[本文引用: 1]

Man-land relationship includes human dependent upon nature and human activity to nature. Contents of man-land relationship are changed with development of human society. Man-land relationship research is the basis for development of modern geography. Various schools of geography such as determinism, possibilism, cultural landscape and human ecology are focusing studies on man-land relationship. The earth system science should carry out interdisciplinary studies between natural and human sciences, to reveal interaction between man and nature as well as the corresponding countermeasures. Developments of information techniques and knowledge economy bring about new opportunities and challenges for human society. Characteristics of man-land relationship in information era differ from those in industrial era. The way and intensity of interaction between human activities and nature will be obviously different. The understanding to nature will be systematically deepened, and ideas of time and space are changing in information era. Knowledge and techniques are becoming main driving forces for social and economic development. Owing to the entirety of the earth, the complexity, protracted nature and potentiality of the interactions among various spheres of the earth, many global environmental issues, such as climate warming, ozonosphere depletion, environmental pollution, etc., are becoming the foci of the countries and public concern throughout the world. The realities impel us to learn lessons and experience accompanied with the traditional development models and to explore new development models for human society. Man-land relationship research covers extensive domains. The hotspots of both global environmental change and sustainable development are closely related to man-land relationship. Global environmental changes have been arisen from slow accumulation process of human impact, and sustainable development is a new development model, which has been obtained by self-examination to development course and model of the human society.The main frontiers of man-land relationship research include the following issues: global environmental change and its regional response, regional sustainable development and mechanism regulation of man-land relationship, studies on social ecological and environmental ethics, etc.
现代人地关系与人地系统科学
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

人地关系地域系统理论系统提出30 a来,对促进地理学综合研究、学科建设和服务国家重大战略决策发挥了重要的科学支撑与导向作用。深入解析了人地关系地域系统理论的科学内涵及时代价值,诠释了现代人地系统的类型与环境,提出了“人地圈”与人地系统科学研究的主要内容和前沿领域。初步研究表明:① 现代人地系统具有复杂性、地域性和动态性特征,人?地交互作用过程、格局及其综合效应正在发生深刻变化,地球表层人地系统成为现代地学综合研究的核心内容和重要主题。② 科学认知和有效协调人地关系,亟需深入探究人地系统耦合格局与机理,探明人地关系地域系统类型、结构及其动力机制。依据城乡关系将人地关系地域类型划分为城市地域系统、城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统。乡村地域系统可细分为农业系统、村庄系统、乡域系统、城镇系统等子系统,分别对应于作土关系、人居关系、居业关系、产城关系。③ 现代人类活动强烈地作用于地球表层人地系统,形成了人地系统耦合与交互作用的地表圈层——“人地圈”,其实质是现代人类活动与地表环境相互联系、耦合渗透而形成的自然–经济–技术综合体或人地协同体。④ 人地系统科学或人地科学是研究人地系统耦合机理、演变过程及其复杂交互效应的新型交叉学科。它是现代地理科学与地球系统科学的深度交叉和聚焦,以现代人地圈系统为对象,致力于探究人类活动改造和影响地表环境系统的状态,以及人地系统交互作用与耦合规律、人地协同体形成机理与演化过程。人地系统耦合与可持续发展是人地系统科学的研究核心。传承创新人地关系地域系统理论和发展人地系统科学,更能凸显地球表层人类的主体性、人地协同的过程性和可持续发展的战略性,为人地系统协调与可持续发展决策提供科学指导。
Modern human-earth relationship and human-earth system science
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

In the past 30 years, the theory of human-earth areal system has played an important support and guidance role in promoting the comprehensive research, disciplinary development and serving national strategic decision of geography. This study analyzes the scientific connotation and era value of human-earth areal system, explores the types and environment of modern human-earth system, and puts forward 'human-earth sphere' and the main contents and frontier fields of human-earth system science. The results show that: 1) The modern human-earth system is characterized by complexity, regionalism and dynamicity. The processes, pattern and comprehensive effect of human-earth interaction are undergoing profound changes, and the human-earth system on the surface of the earth has become the critical content and important theme of modern geosciences. 2) To scientifically understand and effectively coordinate the human-earth relationship, it is urgent to explore the coupling pattern and mechanism of human-earth relationship and to analyze the type, structure and dynamic mechanism of human-earth areal system. Based on the urban-rural relationship, the human-earth areal system can be divided into urban regional system, urban-rural integration system and rural regional system. Furthermore, the rural regional system is subdivided into agricultural system, village system, rural system and township system. 3) Modern human activities strongly affect the human-earth system on the surface of the earth, forming a new surface with the coupling and interaction between human and earth. In essence, it is a natural-economic-technological synthesis or human-earth coordination. They are also the main contents of deepening the researches on the coupling of human-earth system and supporting decision-making for coordinated development of human-earth system. 4) Human-earth system science or human-earth science is a new interdisciplinary subject which studies the coupling mechanism, evolution process and complex interaction effect of man earth system. It is the deep intersection and focus of modern geographic science and earth system science. Taking the modern human-earth sphere system as the research object, it is committed to exploring the state of human activities transforming and affecting the surface environment system, the interaction and coupling law of human-earth system, the formation mechanism and evolution process of human-earth coordination.Human-earth system coupling and sustainable development is the core of human-earth system science. Inheriting and innovating the theory of human-earth areal system and developing the human-earth system science will highlight the subjectivity of human on the earth surface, the process of human-earth coordination and the strategy of sustainable development, thus providing scientific guidance for the coordination of human-earth system and sustainable development decision-making.
基于人地耦合系统的国土空间重塑
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20191003
[本文引用: 1]

地理系统主要研究地球表层人与环境相互作用的机理,强调人地关系、自然和人文要素的综合,即人地耦合系统。地理系统在国土空间中的应用主要由地理决策、地理模拟、地理工程所组成,并且相互作用构成了地理治理。国土空间是自然与人类所共同实践的物质载体,人类被自然所塑造的程度并不亚于自身塑造自然的程度,以人地耦合系统为核心的地理系统理论成为国土空间规划与整治修复的理论基础。基于人地耦合系统的国土空间重塑最终以地理治理的形式反映在人类作用于自然环境的各种活动中。经过改革开放40年的发展,中国国土空间已基本形成了较为稳定的格局,形成了经济区、贫困区、小城镇为主的三种形态空间。中国的城镇化发展与发达国家有所不同,是城市化、城镇化、乡村化“三化耦合”并存的状态。必须重视泛第三极、环中国南海、东北亚—北极等以“一带一路”全球空间为基础的战略区域研究。基于人地耦合系统理论与国土空间价值均衡理论,国土空间重塑的基础科学问题是人地耦合系统演化机理与驱动机制。国土空间规划可以划分为三种类型:发展型规划、控制型规划和修复型规划。国土空间的保护与治理包括以土地利用为核心的国土空间全域整治,以生态文明为核心的国土空间系统修复,以社会和谐为核心的国土空间综合治理。人地耦合系统最终的发展目标是形成人类与自然相互作用的命运共同体。
Geogovernance of national land use based on coupled human and natural systems
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20191003 URL [本文引用: 1]
面向智慧城市的GIS框架
GIS framework for smart cities
From teleconnection to telecoupling: Taking stock of an emerging framework in land system science
DOI:10.1080/1747423X.2015.1096423 URL [本文引用: 1]
Smart cities: Concepts, architectures, research opportunities
Defining urban resilience: A review
DOI:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.11.011 URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1016/j.cities.2016.05.011 URL [本文引用: 1]
城镇化与生态环境耦合动态模拟模型研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.01.010
[本文引用: 1]

按照地理学科发展趋势,对城镇化与生态环境耦合的研究将由定量描述转入动态模拟。目前,城镇化与生态环境耦合动态模拟模型呈现多元化。论文系统梳理了其中4类常见的动态模拟模型,包括城镇化与生态环境耦合系统动力学模型、基于人工智能算法的城镇化与生态环境耦合动态模拟模型、基于土地利用变化的城镇化与生态环境耦合动态模拟模型以及基于多模型集成的城镇化与生态环境耦合复合模型。主要结论如下:系统动力学模型被广泛应用于城市复杂系统、城市转型和可持续发展以及城镇化与生态环境单要素耦合的动态模拟之中,但存在空间解释不足以及忽视系统自适应性等问题;人工智能算法(ANN和BN)在自学习、自组织、自适应系统或不确定性系统模拟中具有显著优势,并被应用于城市扩张、环境变化、资源需求以及生态脆弱性的识别之中,但应用面相对狭窄且限制条件偏多;土地利用变化模型(CLUE/CLUE-S、CA和MAS)局限于从土地城镇化视角模拟城镇化与生态环境耦合;基于多模型集成的复合模型实现了各模型之间的优势互补,已成为城镇化与生态环境耦合动态模拟模型的发展趋势。今后,应从技术和理论2个层面实现城镇化与生态环境耦合动态模拟模型的进一步发展,并加强对微观过程的模拟。
Progress in dynamic simulation modeling of urbanization and ecological environment coupling
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.01.010
[本文引用: 1]

The development trend of geographical science indicates that the research on urbanization and ecological environment coupling will move from quantitative description to dynamic simulation. At present, the dynamic simulation models of urbanization and ecological environment coupling are diverse. This article reviewed and summarized four common types of models, including system dynamics model, artificial intelligence algorithm, land use change model, and composite model. The main conclusions are as follows: 1) System dynamics models are widely used in the dynamic simulation of urban complex nonlinear systems, urban transition and sustainable development, and urbanization and ecological environment elements coupling. However, spatial interpretation is insufficient and system adaptability is ignored. 2) Artificial intelligence algorithm has significant advantages in simulating self-learning, self-organizing, and adaptive systems, as well as uncertain systems. It is applied to identify urban expansion, environmental change, resource demand, and ecological vulnerability, but the application range is narrow. 3) Land use change models are limited to the simulation of urbanization and ecological environment coupling under the condition of land transfer to urban use. 4) To achieve complementarities between the various models, it has become a trend to develop composite models based on multi-model integration. In the future, we should develop dynamic simulation models from both the technical and theoretical aspects, and strengthen the simulation of microscopic processes.
特大城市群地区城镇化与生态环境交互耦合效应解析的理论框架及技术路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201604001
[本文引用: 1]

特大城市群地区是国家经济发展的战略核心区和国家新型城镇化的主体区,担当着世界经济重心转移承载地的历史重任,但在发展过程中面临着日益严重的资源与生态环境的胁迫压力。开展特大城市群地区城镇化与生态环境交互耦合效应的研究,是未来10 年地球系统科学研究的前沿领域和高优先研究主题。本文系统解析了特大城市群地区城镇化与生态环境交互耦合效应的基本理论框架。首先从理论上分析了特大城市群系统各自然要素和人文要素交互作用的非线性耦合关系及耦合特征,科学辨识近远程主控要素作用下城市群系统内外部各要素相互作用的胁迫强度、近远程耦合机理与规律,总结特大城市群地区城镇化与生态环境交互耦合圈理论,进一步构建多要素—多尺度—多情景—多模块—多智能体集成的时空耦合动力学模型,研发特大城市群地区可持续发展优化智能调控决策支持系统;其次从方法上将特大城市群地区视为一个开放的复杂巨系统,在建立同一标准化共享数据库的基础上,采用多要素—多目标—多模型—多情景环境下的城镇化与生态环境交互耦合集成技术方法、大数据支持下的城镇化与生态环境交互耦合技术方法,构建多尺度—多技术—多智能体集成的城镇化与生态环境交互耦合技术框架,按照分析时空演变特征—寻求主控要素—辨识耦合关系—揭示胁迫机制—发现耦合规律—筛选调控变量—求解临界阈值—进行调控试验—完成情景模拟—提出优化方案—完成情景模拟—提出优化方案—实现国家目标这样一条技术路径,提出解决问题的整体优化方案。本文旨在为特大城市群地区由问题集中区转为可持续发展区提供理论指导和方法支撑。
Theoretical analysis of interactive coupled effects between urbanization and eco-environment in mega-urban agglomerations
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201604001
[本文引用: 1]

Mega- urban agglomerations in China play a vital role in both national economic development strategies and national new-type urbanization, and undertake important historical responsibility with the world economic center transfer to China. However, they suffer a series of increasingly serious eco- environmental problems in the process of development. Thus,studies on the interactive coupled effects between urbanization and eco-environment in megaurban agglomerations are the frontier areas and high priority tasks in the earth system science for the future ten years. This paper analyses the basic theory frame of the interactive coupled effects between urbanization and eco- environment in mega- urban agglomerations systematically. In theoretical aspect, based on the nonlinear relationship and coupling characteristics of the natural and human elements in mega- urban agglomerations system, we could estimate the interactive coercing intensity, nearcoupling and telecoupling mechanism ofthe inside and outside mega-urban agglomerations system after scientific identification of the key elements, and then form the basic interactive coupling theory. Moreover, we could build a spatio- temporal coupling dynamic model, which is integrated with multi- elements, multiscales,multi-scenarios, multi-modules and multi-agents. The model will be used to develop the intelligent decision support system for urban agglomeration sustainable development. In methodology aspect, the mega- urban agglomeration is regarded as an open complex giantsystem. We should establish the standardized shared database for exploring the interactive coupled effects between urbanization and eco- environment. Then using new technology for analyzing big data and the integration methods incorporating of multi- elements, multi- scales,multi- targets, multi- agents, multi- scenarios and multi- modules, we can build a methodology framework to analyze the complex interaction coupling between urbanization and ecoenvironment. The technical route is to analyze spatiotemporal evolution characteristics, identifythe key elements, interpret coupling relationship, reveal the mechanism of coercing effect, find the general rules, filtrate the control variables, solve the critical thresholds, conduct regulation experiments, simulate different scenarios, propose an optimized schemes, and achieve national goals. Furthermore, we could put forward the overall optimization scheme. In general, this research could provide theoretical guidance and method support for the transformation and sustainable development in mega-urban agglomerations.
Understanding the new human dynamics in smart spaces and places: Toward a splatial framework
DOI:10.1080/24694452.2019.1631145 URL [本文引用: 1]
Being smarter about space: Drawing lessons from spatial science
DOI:10.1080/24694452.2019.1674630
[本文引用: 1]

Smart technology-in its many facets-is often critiqued within geography in ways that parallel the critiques of quantitative geography in the 1960s and GIScience in the 1990s. In this way, both the development of "smart" technology itself and its criticisms are the latest chapter in a long-standing disciplinary debate around quantification and technology. We reevaluate this history and argue that quantitative methodology and its theoretical critiques are not as incompatible as often claimed. To illustrate how we might address this apparent tension between theory and quantitative methods, we review how both approaches conceptualize one of geography's core concepts-space-and highlight opportunities for symbiosis. Although smart technologies can further orthodox positivist approaches, we argue that the actual practice is more nuanced and not necessarily absolute or totalizing. For example, recent computational work builds on critical geographic theories to analyze and visualize topological and relational spaces, relevant to topics such as gentrification and segregation. The result is not a geography in which smart technology and algorithms remove the need for human input but rather a rejoinder in line with the recent resurgence of a critical quantitative geography. In short, the result is a geography where social theory and the human intellect play a key role in guiding computational approaches to analyze the largest, most versatile, most and relevant data sets on social space that we have ever had. Key Words: geocomputation, GIScience,smart technology, space, spatial science.
2022年城市数字化转型发展热点回眸
Research of hot topics on urban digital transformation development in 2022