生态型地区是以生态保护、提供生态产品为主体功能的地区。由于更严格的生态环境保护管控,容易陷入发展动力缺失、低水平循环、村镇衰败的困境,城乡融合发展面临更大的挑战[17]。国内学者对生态型地区城乡融合发展的研究主要关注两个方面:一是生态型地区城乡融合水平的评价和影响因素研究。通过构建经济、社会、文化、空间、生态等多维评价指标体系,分析影响城乡融合水平的关键因素,一般认为自然约束力、行政干预力是生态型地区城乡融合的关键影响因素[18⇓⇓⇓-22]。二是生态型地区城乡融合的路径研究。生态型地区要通过特色资源导向的城乡产业分工、区域产业协作推动城乡经济融合[18];通过乡土文化复兴、生态保护和生态价值发掘带动乡村旅游和生态产业发展[23⇓-25],构建生态地区“多点集聚”的村镇体系[26,27];通过产业整合、景观重构手段建设特色小镇等城乡融合载体[28],探索城乡绿色产业融合用地保障生态产业项目落地[29],并通过要素资源合理配置补齐乡村人、地、业等发展短板[30,31]。但是,现有研究往往陷入一般地区城乡融合的套路,缺乏对生态型地区深层次的资源特色和动力逻辑认知,忽视了生态资源价值转化和城乡融合之间的关系,难以解决生态型地区城乡融合的可持续动力和路径问题;同时,现有研究更多基于生态地区本身,缺乏生态地区和周边城市群区域统筹的视角。
本文以粤北生态发展区为例,以生态产品价值实现的视角切入,探究生态产品价值实现和城乡融合之间的逻辑关系,从区域统筹的视野研究生态型地区城乡融合路径,丰富中国特定地域的城乡融合研究体系,有利于弥补现有研究在动力逻辑和空间视野上的不足,为生态型地区建立可持续的城乡融合路径提供参考。研究创新点体现在建构了生态产品价值实现促进城乡融合的逻辑框架,并从生态型地区与周边城市群区域统筹的视野建立生态型地区特色的城乡融合路径。
1 城乡融合发展与生态产品价值实现
1.1 城乡融合发展
城乡融合发展是通过各类空间要素及体制机制来协调新型城镇化和乡村振兴,促进城乡发展机会的公平化、发展水平的均值化和发展价值的特色化,路径主要包括城乡价值增值、空间融合及要素对流:一是促进城乡价值增值,挖掘区域和城乡各自资源禀赋和价值,促进村镇地区采取生态与地方文化的传承保护、现代农业与乡村旅游开发等地方特色发展模式,延长产业发展链条,提升城乡特色空间价值[32,33];二是促进城乡空间融合,依托产业链条优化城镇和乡村的专业化分工,重塑区域城、镇、村职能体系,凸显都市圈、村镇体系对于乡村的支撑和引领作用,构建城乡空间共同体[34,35];三是促进城乡要素对流,基于城乡空间职能体系,创建城乡融合体制机制,促进城乡各类生产要素的配置和流动,形成“城乡互促、功能互补”的双向流动格局,消除城乡生产、生活质量差别,保留、强化城乡特色差异,逐渐形成城乡等值融合格局[36,37]。
1.2 生态产品价值实现
1.3 生态产品价值实现促进城乡融合的理论框架
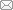
生态产品价值实现将重构生态型地区城乡融合的动力逻辑。由于城乡和区域之间资源禀赋差异带来的价值空间差异,加上城市居民的生态产品消费需求日益增长,生态型地区可以依托生态资源优势融入区域循环分工格局,为城市化地区提供特色生态产品,建构“价值链—供应链—要素链”组合的城乡融合路径(图1),以城乡生态经济的融合共生促进城乡融合发展。
图1
图1
生态产品价值实现促进城乡融合的理论框架
Fig. 1
The theoretical framework of realizing the value of ecological products to promote urban-rural integration
一是以生态产品价值链提供城乡融合动力。价值链包括生态产品研发、设计、生产、消费、服务等链条,是生态产品价值实现的动力形式。生态型地区依托生态资源比较优势提供生态产品,延长生态产品价值链条,释放经济、生态、社会文化等复合价值,推动生态价值增值,有利于建立高附加值的生态产业体系,不断缩小城乡发展水平差距,从而为城乡融合发展提供新动力。
二是以生态产品供应链提供城乡融合载体。供应链是区域和城乡围绕生态产品价值链进行分工而形成的供给链条,是生态产品价值实现的空间载体。城乡区域内各级城市、村镇结合资源禀赋和比较优势,分别提供生态产品研发设计、生产、消费等功能空间,形成跨区域和城乡垂直分工的生态产品供给空间体系,有利于促进城乡功能互补和要素流动,塑造城乡互补共生的地域综合体,从而为城乡融合提供新的载体空间。
综上,生态产品价值实现是生态型地区城乡融合的新动力,通过构建“价值链—供应链—要素链”组合的城乡融合路径,延长生态产品价值链,基于价值链的空间分工重构供应链,围绕供应链优化要素链的配置流动,通过要素链不断反馈强化供应链和价值链,“三链”之间形成互动反馈的关系,循环推动生态价值增值、城乡空间融合和要素对流,不断提升城乡融合发展水平。
2 案例区概况与研究方法
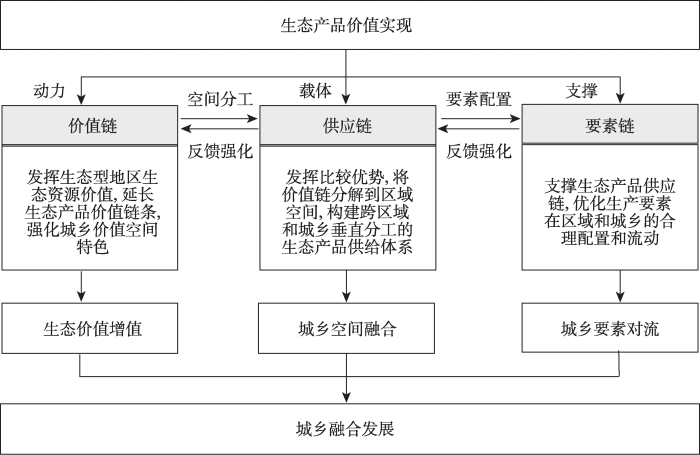
粤北生态发展区位于广东省北部山区,地处南岭山系和北江、东江、西江的上游源头,是中国亚热带森林植被景观和生物多样性保护的重点地区、全省重要的生态屏障,包括韶关市、河源市、梅州市、清远市、云浮市、肇庆市6个地级市,总面积约5.82万km2,占全省面积的32%(图2),经济发展水平滞后。根据广东省区域发展战略,粤北生态发展区以生态保护和发展生态产业为主,是以生态产品价值实现促进城乡融合发展的典型地区。
图2
图2
粤北生态发展区范围
注:本图基于广东省自然资源厅标准地图服务子系统下载的审图号为粤S(2019)029号的标准地图制作,底图无修改,下同。
Fig. 2
Scope of Northern Guangdong Ecological Area
结合在粤北开展的国土空间规划编制项目和相关科研课题,采取了多种研究方法:一是数据分析法,收集粤北各市县2010年和2020年统计年鉴、五普和六普人口数据、碳排放权交易数据、典型生态产品网络销售大数据等,通过横向和纵向量化比较分析,寻找生态产品价值实现促进城乡融合发展的特征问题。二是实地调研法,先后对粤北6个地市及13个典型县区进行了多轮调研,收集生态产品价值链、供应链、要素链建设的实践案例和政策文件,通过案例提炼、文本分析等方法,分析生态产品价值实现推动城乡融合发展的做法和成效;三是深度访谈法,采访了粤北市县政府部门、乡镇行政管理人员和村干部12名,粤北生态旅游、农旅开发等企业管理人员8名,广东省农业龙头企业协会等相关行业协会人员5名,共获得有效样本25份(分别编号S1~S25),重点访谈生态产品价值实现、生态产品供应链分工和要素流动方面的问题与建议,形成了约37000字的文本记录,通过文本分析法提炼核心观点,支撑城乡融合路径的优化。
3 粤北生态发展区生态产品价值实现促进城乡融合的困境
3.1 生态产品价值链短,城乡融合发展动力不足
粤北生态发展区亚热带自然资源富集。根据广东省第三次国土调查数据,粤北生态发展区拥有全省约85%的山林资源、50%的水资源,是广东省固碳释氧、水源涵养等重要生态源地;根据《广东省统计年鉴(2022年)》和《广东省农村统计年鉴(2022年)》,2021年粤北生态发展区生产了广东省约20%(771万t)的蔬菜、30%(548万t)的水果,拥有约80个国家地理标志产品,约占全省数量的52%,是广东省重要的蔬菜、水果供应基地;根据携程网统计,2021年国庆期间粤北生态发展区接待的游客约80%来自粤港澳大湾区,是粤港澳大湾区重要的文旅服务基地。
但是,根据粤北生态发展区调研访谈,并对比相似地理和资源禀赋的浙江西部地区,发现粤北生态发展区的生态产品价值链短,生态产品价值不高(表1)。粤北的生态物质产品以原材料或粗加工为主,缺少精加工和生态品牌,如大米、鸡等特色农产品售价明显低于浙江西部地区;生态旅游、文化消费等生态文化产品的知名度和附加值偏低,多元生态和文化优势整合不足,缺乏农文旅融合、康养服务等深度体验产品;生态调节产品目前仅限于碳排放权交易,如2017年以来粤北韶关市完成碳普惠交易额3100万元,交易额和交易种类都有限,对比浙江丽水市“生态贷”“两山贷”等生态金融产品差距较大。粤北生态发展区生态产品价值实现程度较低,乡村生态资源价值增值不足,尚未形成高附加值的生态产业体系,乡村经济发展和收入水平难以提升,城乡融合发展动力不足。
表1 粤北生态发展区和浙江西部地区典型生态产品对比
Table 1
| 生态产品类型 | 生态产品名称 | 粤北生态发展区平均价格 | 浙江西部地区平均价格 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 生态物质产品① | 大米 | 约5元/kg | 约20元/kg |
| 鸡 | 约20元/kg | 约28元/kg | |
| 雪梨 | 约5元/kg | 约8元/kg | |
| 生态文化产品② | 民宿 | 约200元/间 | 约240元/间 |
| 生态调节产品③ | 碳排放权交易、绿色金融等 | 2017年以来韶关市完成碳普惠交易额3100万元 | 截至2021年底,浙江丽水市发放“生态贷”“两山贷”约250亿元 |
注:① 生态物质产品选取粤北和浙西共同的热门产品大米、鸡、雪梨,分别抓取淘宝网2021年两地这几类农产品搜索热度前50的产品平均价格。② 民宿数据来源于2021年国庆期间两地携程网搜索热度排前50的民宿平均价格。③ 韶关市碳普惠交易额数据来自韶关市人民政府网站(
3.2 生态产品供应链不健全,区域和城乡缺乏分工联系
近年来粤北地区逐步加大发展生态产业,提供各类生态产品,但尚未形成区域和城乡统筹的供应链。一是城乡之间缺乏分工合作。生态产品供应以乡村地区零散开发的生态农业基地、生态旅游度假区等为主,附加值较低,生态产品标准认证、品牌运营、人才培训、加工物流等产业链支撑不足;而县城、中心城市主要以提供旅游服务配套、农产品粗加工等为主,尚未深度参与到生态产品的供应链中,尚未形成城乡一体化的生态产业体系。二是生态产品供应链缺乏区域统筹。粤北生态产业发展缺乏研发、融资和交易等环节支撑,但粤港澳大湾区尚未整合进生态产品供应链中,大湾区丰富的科教、技术、资金等对供应链的支撑作用不足。“我们茶园有3000多亩(1亩≈667 m2),茶叶生产、加工、展示销售基本在园内,这些年县里不断加大扶持力度,但仍面临着产品研发、销售渠道、物流、人才等短板,希望全市能统筹资源,借助珠三角资源,统一做好研发、销售、物流、人才培训等平台”(S3,清远英德市某红茶企业管理者,男)。
3.3 生产要素对流不足,区域和城乡差距不断拉大
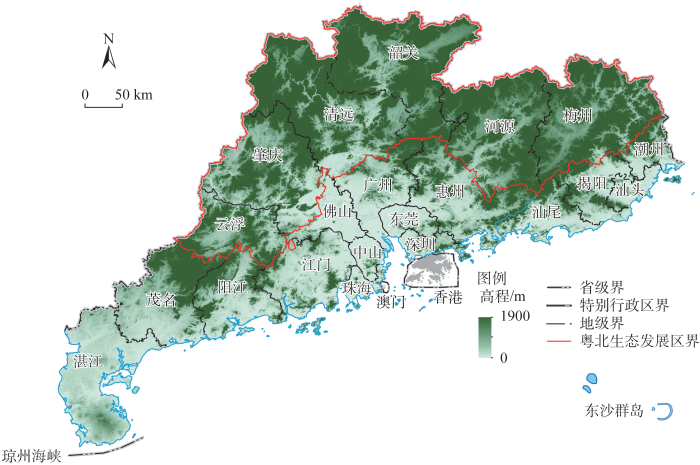
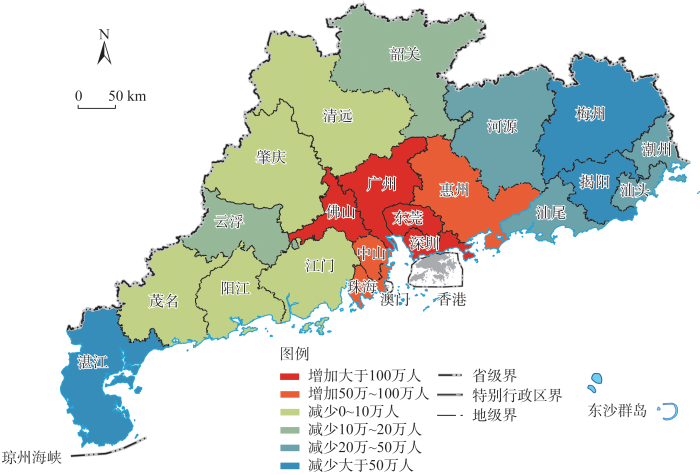
由于粤北生态发展区和粤港澳大湾区之间、城市与乡村之间发展水平的巨大差距,生产要素从乡村地区加速向粤港澳大湾区和城市地区流动。乡村地区生产要素不断流失,难以支撑生态产品价值实现,经济发展和收入水平难以提升,进一步加剧村镇的老弱化、空废化、污损化和贫困化现象,陷入要素流出和村镇衰败彼此加强的恶性循环中,区域和城乡差距不断拉大。一是人口不断向粤港澳大湾区和粤北中心城市流动。2010—2020年粤北地区15~59岁常住人口减少了141万人,主要流向东莞、佛山等制造业发达城市(图3);2010—2020年粤北地区乡村常住人口减少150万人,粤北6个地级市市区城镇人口增加了112万人,乡村地区青壮年人口的流失造成生态产品供给缺乏生产和服务型人才的支撑。二是城乡土地要素流动不足。伴随着粤北乡村人口的流失,大量乡村土地被废弃和抛荒,土地利用效率日益低下,如2010—2020年粤北紫金县人均村庄建设用地由106 m2增长到249 m2;但跨区域和城乡的土地要素流转交易机制仍不完善,在乡村低效用地摸查管理、交易平台和流转形式上仍有制度短板,且尚未覆盖到林地、湿地等全要素自然资源,大量的乡村低效闲置土地难以盘活,生态产品供给的土地要素支撑不足。三是资金和技术要素难以流向乡村地区。近年来广东省不断加大对粤北地区的对口帮扶,包括产业转移、财政转移支付、技术帮扶等,但帮扶领域以产业园区共建、基础设施建设为主,对乡村地区生态产业发展的资金和技术帮扶不足,缺乏相关的专项基金、政策性金融工具等;粤港澳大湾区生态产业相关的院校、科研机构对粤北地区的科研和技术帮扶不足,生态产品供给缺乏资金和技术支撑。
图3
图3
2010—2020年广东省各地市15~59岁常住人口变化情况
Fig. 3
Change of permanent resident population aged 15-59 in various cities of Guangdong province from 2010 to 2020
4 基于生态产品价值实现的粤北生态发展区城乡融合路径
4.1 构建全链条的生态产品价值链
表2 粤北生态发展区生态产品清单示例
Table 2
| 生态产品一级类 | 生态产品二级类 | 典型产品示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 生态物质产品 | 水果 | 三华李、鹰嘴桃、荔枝、龙眼、水晶梨、金柚等 |
| 蔬菜 | 麻竹笋、桑芽、石韭、苦菜、小葱头、黑皮冬瓜等 | |
| 林木 | 速生苗、木材等 | |
| 禽畜 | 走地鸡、土猪、麻鸭等 | |
| 茶叶 | 英红九号 | |
| 生态调节产品 | — | 碳排放权、取水权、排污权等 |
| 生态文化产品 | 自然观光 | 韶关丹霞山景区、梅州雁南飞茶田、清远连州地下河等 |
| 乡村游览 | 清远连樟样板区、河源畲族村、韶关平甫“国家森林”村等 | |
| 历史体验 | 云浮六祖故里、清远南山摩崖石刻、梅州千佛塔等 |
图4
4.1.1 打造粤北品牌标准,提升生态物质产品价值链
根据与粤北地区政府部门及相关企业的调研访谈,粤北生态发展区的蔬菜、水果、禽畜等生态物质产品种类丰富、品质优良,但目前主要以生产、粗加工为主,价值链的最大短板是前端的研发、品牌和标准不足。“我们镇做麻竹笋已经有很多年的历史了,但每年收的笋80%都用于批发、晒干和粗加工,赚的是血汗钱,基本没有自己的研发和品牌,主要是代工,也没有标准,竹笋原材料与产品品质不稳定,但做品牌和标准需要大量的投入,光靠我们镇里、县里的力量不够;而国内麻竹笋做的最好的镇主要就是做品牌、做标准,他们制定了《竹笋栽培技术规程》等标准,打造中国竹笋之乡品牌,举办竹文化节、设计统一logo,单位产值是我们的5倍”(S5,清远市某镇政府官员,男)。
针对生态物质产品,应当以提升粤北品牌标准为价值实现路径,重点加强研发投入和粤北区域品牌、标准建设,建立“研发—品牌—标准—生产—精加工—展销—流通”的价值链。一是支持大湾区的农科院等科研机构与粤北乡镇、企业合作设立科研基地,加强特色生态产品研发;二是以粤北县域为单元统筹创建区域公用品牌,县级政府要统筹品牌创建工作,以绿色生态和地域文化为特色,创建三华李、英红茶叶、西牛麻竹笋等一批粤北区域公用品牌;三是结合品牌制定绿色标准,包括生产、采摘、分拣、销售等全过程绿色标准,并利用5G、3S技术推广智慧农业,实现全过程标准化、可监管、可追溯,提高生态产品的知名度和附加值。
4.1.2 推动资产化交易,构建生态调节产品价值链
粤北生态发展区丰富的森林、水等自然资源的生态价值较高,根据水资源公报、森林调查数据和生态服务价值当量估算,粤北的取水权和碳排放权年交易潜力约为45亿元,约占粤北各市财政收入总和的8%,转化潜力较大,但由于缺乏覆盖各类自然资源的价值评估和交易机制,生态调节产品价值转化交易量较小。
针对生态调节产品,应当建立资产化交易为主的价值实现路径,构建“调查—确权—生态保护修复—价值评估—资产交易—资本增值”的价值链。在对山水林田湖草等各类自然资源进行调查、确权登记、生态保护修复的基础上,重点加强产业链后端环节的补链强链,实现资源到资产、资本的价值转化。一是建立生态产品价值评价体系,开展粤北地区森林碳汇、取水权等各类生态调节产品的价值评估和权益登记,实现生态资源的资产化;二是建立生态资产交易平台,结合广州碳交所等平台纳入粤北生态产品交易体系,制定生态产品定价、税费调节机制,实现生态资源的资本化;三是设立生态资产抵押、融资、证券化等金融产品,提供资本增值服务。
4.1.3 推动农文旅融合开发,完善生态文化产品价值链
粤北生态发展区自然山水和文化资源丰富,但由于产品策划、农文旅融合发展不足,缺乏有区域影响力、体现地域特色的生态文化产品。“我们茶园主要还是茶叶生产和销售为主,受到运输和人工成本上涨的影响,利润越来越小,应该早点做整体产品策划,预留好土地建设茶文化博物馆、七彩茶园,走向农文旅融合的景观化茶园,现在想做这些但没有地了”(S8,清远市某茶园经营者,男)。
针对生态文化产品,应当大力推动农文旅融合开发,建立“产品策划—融资—设计—生产—文旅融合—康养服务”的价值链,重点弥补价值链两端的短板。一是加强产品策划,发掘粤北自然风光、岭南风情、客家文化、红茶文化多元要素融合优势,提供自然观光、乡村游览、历史体验等生态文化产品,打造一批山区乡村、景观茶园、农业公园、峰林小镇等农文旅融合的生态文化产品;二是延伸服务链条,加强文旅融合、康养服务功能注入,联合大湾区的文化、医院、康养机构,充分利用红茶、温泉等地方特色资源发展绿色康养服务。“我们这里的旅游度假区大部分都是简单的自然观光度假,产品比较单一,很多经营状况不太好;最近有个项目联合省国企和医疗机构,以国际营地教育为品牌,融合红色文化、温泉康养等功能,形成文教、康养、度假一体化模式,做得比较成功,但这样的案例还比较少”(S10,梅州市文化旅游部门官员,男)。
4.2 构建区域和城乡垂直分工的生态产品供应链
围绕生态产品价值链,建立粤北和粤港澳大湾区协同分工的供应链。适应粤北乡村人口向大湾区中心城市、市县城区流动的特征,建立“大湾区中心城市—粤北市县城区—粤北村镇”三级空间分工体系,发挥各级城市和村镇的比较优势,形成跨区域和城乡垂直分工的生态产品供应链(图5),建立城乡优势互补、合作共生的生态产业体系,基于产业合作形成城乡互补共生的城镇村职能体系,促进城乡空间融合,有力支撑城乡高质量融合发展。
图5
图5
跨区域和城乡垂直分工的生态产品供给空间体系
Fig. 5
The spatial system of ecological product supply with cross-regional and urban-rural vertical division of labor
4.2.1 大湾区中心城市:头部引领,打造生态产品总部经济中心
发挥广州、深圳等大湾区中心城市人才、资金和信息集聚优势,打造生态产品总部经济中心,统筹生态产品供应链组织和资源配置功能,聚焦生态产品总部办公、研发、融资和交易等价值链头部环节,整体提升生态产品价值链,引领带动全省生态产品价值转化。“广东的生态产品价值转化要注重发挥湾区中心城市的带动作用,例如在生态农产品开发方面,目前缺少一个头部性的农业总部科研基地,建议在广州建设服务全省的农业总部科研基地,集聚农业科研、总部办公、创业孵化、融资、展贸交流等功能,链接好科研机构、金融机构、农业企业和创业者,形成产学研对接平台”(S11,广东省农业龙头企业协会官员,女)。湾区生态产品总部经济中心要依托大湾区中心城市的高等学校和科研机构,建设生态产品研发中心和产学研对接平台,加强对粤北生态产品企业的科技帮扶;建设生态产品企业总部基地和融资中心,提供创业投资、绿色金融、生态抵押等服务;建设生态产品交易中心,提供碳排放权、取水权、耕地指标、林地指标等市场化交易平台。
4.2.2 粤北市县城区:分类引导,打造地域性的生态产品专业服务中心
要发挥粤北城市市区和县城作为城镇化核心载体、人口集聚与公共服务优势,依托当地的资源禀赋和产业基础,建设一批生态产品专业服务中心,提供差异化、特色化的生态产品专业服务功能,如生态产品标准认证中心、人才培训中心、加工物流中心、展贸服务中心、文旅服务中心等。目前,粤北部分市县在生态产品专业化服务上初步取得成效,如:英德市建设英德红茶标准认证中心,建立以标准化为核心的工业化模式,制定了《英德高香红茶》《英德红茶冲泡与品鉴标准》等;龙川县打造大湾区“油瓶子”,制定了《龙川山茶油》的行业标准;新兴县依托“六祖故里”历史文化资源全力打造禅宗生态旅游圣地,打造“禅都”文化品牌;南雄利用特色银杏资源打造“银杏染秋”旅游品牌。要进一步推广经验和整合资源,形成一批生态文化特色服务县,构建一批粤北生态产品标准和区域公用品牌,提升生态产品价值。
4.2.3 粤北村镇:乡村性建构,建设复合化生态产品社区
粤北村镇地区在提供生态产品上取得了一定的成效,如清远市九龙镇开发峰林观光、蔬果种植、农业旅游为一体的“峰林晓镇”,梅州市叶塘镇利用地热资源开发山、水、泉、居于一体的旅游区,河源市热水镇打造了兴隆客家民俗文化村IP等。但大多面临功能单一、特色不足、缺乏可持续性的问题。“我们的村落凭借优越的交通环境和独特的文化,推进新农村建设,绿化美化乡村环境,着力发展民俗文化旅游业,成为远近闻名的网红打卡点。但一年也就那么一阵时间,外地游客一阵新鲜劲过了就不会来了,村里的年轻人也都走了,说到底这里还是只能看,吃的、玩的、住的都不多,没有真正能让人留下来的地方”(S15,河源市热水镇某村村主任,男)。
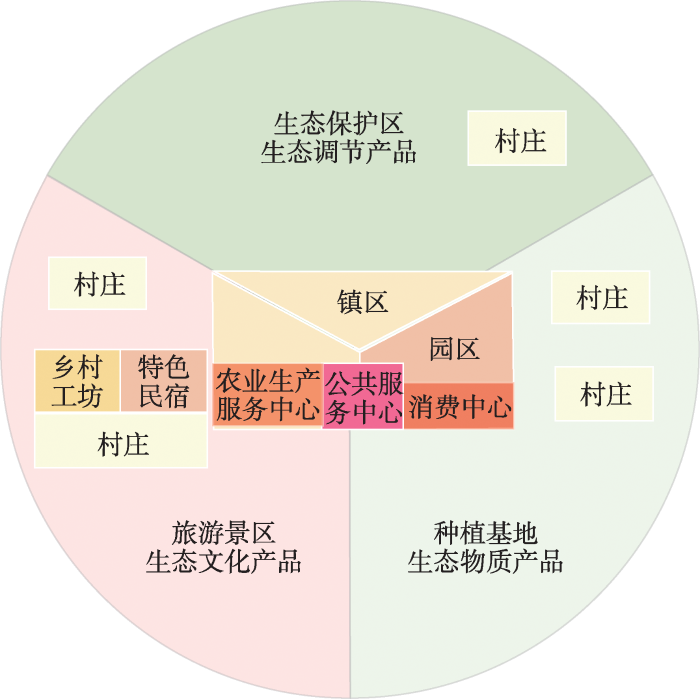
要解决乡村发展可持续的问题,应当以乡村性建构为核心,建设复合化生态产品社区(图6),它是以自然和文化同源的村镇单元为对象,以提供乡土自然文化生态产品为目标,兼具生态、生产、消费、文化、人居等多元功能于一体的村镇社区场景;要推动村镇由垂直分工走向水平整合,将生态产品社区作为共同体进行整体规划设计运营,丰富社区功能,划分生态保护区、文化旅游区、种植基地、公共服务和消费区、农产品加工园、村庄建设区等功能分区,缩小村镇与城市的生产、生活差距,吸引人才回流。突出特色化分类发展,建设一批农业型、文化型、旅游型、生态型等生态产品社区。农业型社区要营造农业景观化、美学化的乡村意向,文化型社区打造特色鲜明的文化IP,旅游型社区要整合特色旅游资源推动农旅融合发展,生态型社区应加强生态景观保护和自然体验功能开发。
图6
图6
村镇生态产品社区示意图
Fig. 6
Sketch map of ecological product communities in villages and towns
4.3 建立生产要素城乡对流的要素链
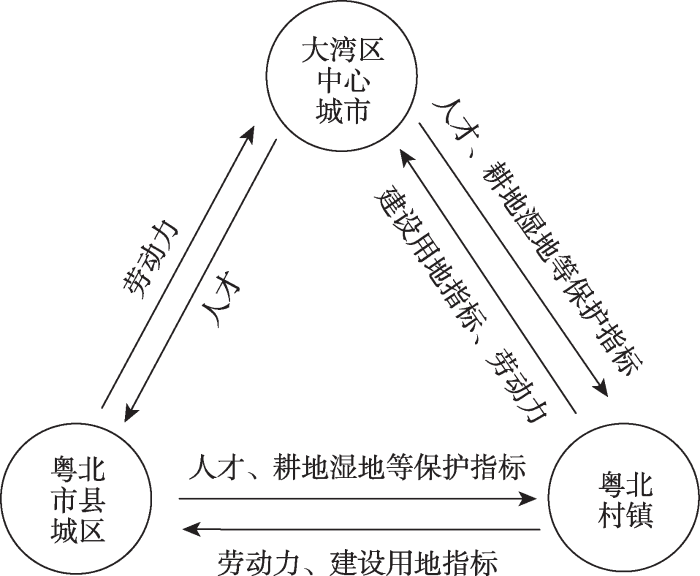
为支撑生态产品供应链,在尊重要素市场化配置的前提下,通过适当的政策引导,优化人口、土地等生产要素的配置和流动(图7),促进要素向大湾区中心城市和粤北市县城区集聚。同时,提升村镇地区的生态魅力和价值潜力,吸引生产要素下乡,提升生态产品供给能力,通过要素对流进一步反馈强化生态产品价值链和供应链,促进城乡多层次、多领域、全方位的渗透融合。
图7
图7
粤港澳大湾区和粤北地区生产要素流动示意图
Fig. 7
Flow diagram of production factors of Northern Guangdong Ecological Area and Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
4.3.1 推动人才对流,在粤北市县建设生态产业人才培训基地
在乡村地区劳动力向粤港澳大湾区和粤北市县城区集聚的背景下,要积极推动生态产业人才下乡,支撑粤北市县生态产品专业服务中心、村镇生态产品社区的建设。“去年省里开展驻镇帮镇扶村,组建驻镇帮扶工作队,切实起到了很大的效果,我们最缺的还是现代农业、生态旅游方面的技术人才,建议省里高校和本地企业联合成立人才培训基地,同时要有激励机制把人留下来”(S18,河源市农业农村部门官员,男)。建立省域统筹生态产业人才培训机制,推动大湾区中心城市的高等学校和科研机构在粤北市县建设生态产业人才培训基地,加强村镇劳动力、返乡人员技能培训;建立大湾区生态产业人才向粤北流动激励机制,建立健全人才下乡激励机制,探索编岗适度分离等方式,强化人才下乡设施保障,推动大学生回乡创业、科研院所智力下乡。
4.3.2 完善区域和城乡土地指标对流交易机制
围绕生态产品供应链和人才流动趋势,建立区域和城乡土地指标对流交易机制,促进建设用地指标向大湾区中心城市和粤北市县城区流动,耕地、湿地、林地等保护指标向粤北村镇地区流动,形成跨区域、全要素的对流格局。一是完善升级跨区域土地指标交易机制。广东省自2013年起已经实施耕地储备指标、拆旧复垦指标跨市县交易,应将土地指标交易范围扩大到建设用地指标、林地保护指标、湿地保护指标等全要素自然资源,建设跨区域土地指标交易平台,全面摸查粤北“低小散”建设用地和抛荒低效耕地、林地等非建设用地,通过整治修复增加耕地、林地、湿地等生态产品承载空间,推动建设用地指标和自然资源保护指标对流交易,实现空间资源的优化配置;探索“飞地”模式,支持粤北市县将腾挪出的建设用地指标,在大湾区中心城市建立创新型“飞地”,实现合作开发和利益共享。二是建立市县全域土地要素整治流转机制。以全域土地综合整治为抓手,实施适度的迁村并居、退宅还耕、空心村整治等工程,增加生态空间,腾挪出的建设用地指标保障生态农业、生态旅游配套设施,或者转移到市县城区。
5 结论与讨论
城乡融合是关乎中国式现代化建设的重大问题,而生态型地区城乡融合发展面临更大的挑战。本文基于生态型地区内部资源特色和外部区域视角重新建构城乡融合的动力逻辑,创新性地提出了生态产品价值实现促进城乡融合的理论框架,建立了生态型地区“价值链—供应链—要素链”组合、相互反馈强化的城乡融合路径,提供了适用于生态型地区、可持续的城乡融合发展路径理论,对开展特定地域城乡融合研究具有理论指导意义。
本文以粤北生态发展区为实证研究对象,提出了基于生态产品价值实现的城乡融合路径:一是构建全链条的生态产品价值链,针对生态物质产品、生态调节产品、生态文化产品分别采取打造品牌标准、推动资产化交易、推动农文旅融合开发的价值实现路径,提升生态产品价值;二是构建跨区域和城乡垂直分工的生态产品供应链,建立“大湾区中心城市—粤北市县城区—粤北村镇”三级空间分工体系,促进城乡空间融合;三是建立生产要素流转交易的要素链,围绕生态产品供应链优化人口、土地等生产要素的配置,促进城乡要素对流。研究提出的路径对生态型地区推动生态产品价值转化、城乡融合发展、城乡空间体系优化和要素配置具有重要应用价值,对经济欠发达山区、城市群周边生态地区城乡融合发展也具有参考价值。
参考文献
新时代城乡融合发展: 现状、问题与对策
Integration of urban and rural development in the New Era: Present situation, problems and countermeasures
城乡融合背景下乡村转型与可持续发展路径探析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912010
[本文引用: 1]

探究乡村转型发展规律对于系统认识乡村发展阶段、研判乡村发展趋势、明确乡村可持续路径、促进乡村转型与振兴具有重要意义。首先基于马斯洛需求层次理论、产业结构演变理论、区域空间结构理论等演绎乡村转型发展阶段,然后结合典型乡村发展历程分析进行实证检验,进而探讨对于新时期乡村可持续发展的启示。研究结果:① 乡村转型发展在理论上可分为4个阶段,一是生产力均匀分布下以实现温饱需求为目标的土地整治促增产阶段,二是城乡联系增强下以改善生活水平为目标的农业结构调整促增收阶段,三是区域联系增强下以提升生活质量为目标的产业结构调整促致富阶段,四是城乡互动融合下以城乡等值为目标的公服设施建设促均等阶段。② 典型发达乡村的发展历程在一定程度上印证了乡村转型发展阶段特征。③ 因资源基础、区位条件、市场规模、发展主动性等因素的差异,乡村实际发展过程可能存在阶段的跃迁或并行的现象。根据发展过程中不同主体发挥作用的变化,每个阶段又可细分为初始阶段、过渡阶段和成熟阶段。④ 基于乡村转型发展规律分析,城乡融合背景下不同类型地区乡村可持续发展路径可分为土地整治集聚路径、特色产业发展路径、产业平台集散路径和社区功能集约路径等4类。
Approaches to rural transformation and sustainable development in the context of urban-rural integration
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912010
[本文引用: 1]

Exploring the evolution rules of rural transformation is significant for systematically understanding stages of rural development, judging trends of rural development, determining paths of rural sustainable development and promoting rural vitalization. Based on Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, industrial structure evolution theory, and regional spatial structure theory, this paper deduced the evolutionary stages of rural transformation. The evolutionary stages were verified by analysis of the development process of typical villages. Further, this paper explored the implication for rural sustainable development in the new era. The results showed that: (1) Evolutionary process of rural transformation included four stages. The first was the cropland-engineering stage, aiming at realizing the need for food and clothing under the uniform distribution of productivity. The second was the agricultural structure adjustment stage, aiming at increasing income under the intensifying urban-rural relationship status. The third was the industrial restructuring, aiming at improving the quality of life under the strengthening of regional linkages. The fourth was the stage of promoting the equalization of public service facilities with the goal of urban-rural equivalence under the urban-rural integration. (2) The development course of typical developed villages confirmed the evolution rules of rural transformation to some extent. (3) In practice, the evolutionary process of rural development presented skip or parallel phenomena because of regional differentiation of resources, location, market size, and willingness. According to the changes of the roles of different groups in development course, each stage could be subdivided into initial stage, transition stage, and maturation stage. (4) Based on the analysis of evolutionary rules of rural transformation, the paths of rural sustainable development in different types of region included land consolidation and agglomeration path, specialty industrial development path, industrial platform for collection and distribution path, and community function intensification path in the context of urban-rural integration.
城乡融合发展试验区存在问题及应对策略
Problems and strategies of urban-rural integration pilot zone
从城乡一体化到城乡融合: 新型城乡关系的思考
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.10.006
[本文引用: 1]

新型城镇化和乡村振兴战略的深入实施,推动城乡关系进入了一个融合发展的新阶段。采用Citespace1.0软件分析及文献归纳方法,识别了城乡关系研究热点,梳理了城乡关系研究在理论探索、影响因素、测度与评价、空间组织及推进策略等方面的研究进展。在此基础上,重点对面向城乡融合发展的新型城乡关系研究进行了总结,从理论基础与总体思路、多源数据与方法集成等方面提出了基于要素流动的城乡融合分析框架,指出了城乡融合研究的重点是基于多源数据的城乡关系测度与评价,城乡要素流动的特征、格局与效应,城乡要素融合发展的流动机制,城乡融合发展调控策略等。
From town-country integration to urban-rural integration: New thinking on the relationship between urban and rural areas
城乡融合与乡村振兴: 理论探讨、机理阐释与实现路径
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201811001
[本文引用: 1]

缩小城乡差距,促进城乡均衡发展,实现城乡居民生活质量等值,是乡村振兴和城乡融合发展的重要目标。通过基础理论的分析,探讨了城乡融合与乡村振兴科学内涵,剖析了城乡融合与乡村振兴的相互关系,构建了城乡空间均衡模型和定义城乡等值线,提出了中国城乡融合与乡村振兴实现途径及需要深入研究的方向。结果表明:① 城乡融合发展是基于空间布局优化和制度供给创新的经济、社会、环境全面融合发展,“乡村振兴五边形”和“人—地—钱—业”是乡村振兴的核心内涵;城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相互支撑,城乡融合和乡村振兴的过程是城乡空间动态均衡的过程。② 城乡发展的空间均衡模型可以较好地阐释促进城乡融合发展、实施乡村振兴的关键问题,通过城乡要素的重新优化配置和人口的流动,城乡人均综合发展效益逐渐趋于相等;城乡等值线可以进一步解释城乡发展空间均衡的动态过程与传导机理。③ 从政策制度构建、“点轴”渐进扩散、分区分类推进、典型发展模式提炼等方面探讨乡村振兴的科学路径,可以为中国乡村振兴战略实施提供理论参考。
Urban-rural integration and rural revitalization: Theory, mechanism and implementation
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201811001
[本文引用: 1]

Rural revitalization and urban-rural integration aim at narrowing the gap between urban and rural areas, promoting balanced development and realizing the equivalent life quality between urban and rural residents. Spatial equilibrium and its quantitative expression provide a new perspective to explain the pattern, process and mechanism of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. Through the analysis of basic theory, this study discusses the scientific content and interaction between urban-rural integration and rural revitalization, sets up the urban-rural spatial equilibrium model, defines the urban-rural development isolines, works out the way to implement the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China, and addresses the potential for further research. The results show that: (1) Theory of regional system of man-land relationship and theory of spatial structure are the important theoretical basis for urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. The urban-rural integrated development depends on the all-round development of economy, society and environment with optimized spatial layout and innovative system, and rural revitalization mainly refers to the "pentagon of rural revitalization" and "people-land-capital-industry"; Urban-rural integration and rural revitalization strategy support each other, and the process of urban rural integration and rural revitalization is a dynamic equilibrium process between urban and rural areas. (2) The key issues of implementing rural revitalization and urban-rural integration can be illustrated through the urban-rural spatial equilibrium model, and the overall per capita benefits in rural areas gradually tend to be the same as that in cities by the re-optimization of urban-rural factors and population mobility; the dynamic process and mechanism of urban-rural integration spatial equilibrium is further interpreted via the urban-rural development isolines. (3) Exploring the implementation path of scientific rural revitalization strategy can achieve the goal of urban-rural integration and urban-rural spatial equilibrium development. The scientific path of rural revitalization is discussed from the perspectives of policy system construction, "pole-axis" spatial progressive diffusion, sub-area classification and typical development pattern, and it can provide theoretical reference for the strategy implementation of China's rural revitalization.
等值化理念下中国城乡融合多维审视及影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190572
[本文引用: 1]

基于等值化理念采用全局主成分分析(GPCA)和空间自相关分析等方法,测度并审视中国城乡多维融合发展;选取空间计量模型探索推进城乡融合的体制机制。研究发现:① 中国城乡融合发展趋势向好且推进有序。社会和经济融合始终分列第一和第二主导位次,生态环境融合水平亦稳步提升。② 城乡融合热点和冷点区基本分列于“胡焕庸线”东南和西北两侧。人口融合沿东中西递减;空间融合形成“北上广”为主的“核心-边缘”区;东部沿海是经济融合扩散互溢区,而生态环境和经济融合存在空间“错位”;社会融合高值簇集中在中部。③ 破解人才瓶颈、夯实“三权分置”、健全财政体制并创新金融服务、调整产业结构和推动三产融合,打好人、地、钱、业组合拳同时规范政府行为、完善社会服务体系、构建小农户与现代农业有机衔接机制等均利于推进城乡融合。
Review of urban-rural multi-dimensional integration and influencing factors in China based on the concept of equivalence
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190572
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the urban-rural equivalence, the Global Principal Component Analysis (GPCA) method is used to measure the China's urban-rural multi-dimensional integration levels, and the Global and Local Moran Index, Local Getis-Ord Gi * Index are performed to reveal the spatial distribution of urban-rural multi-dimensional integration levels in China during 2000-2016. And finally, the spatial econometric model is introduced to explore the influencing factors of urban-rural integration development from the aspects of labors, land, capitals and industries. Research findings are as follows: (1) the trend of urban-rural integration development in China is well and orderly, but has regional heterogeneity. The agglomeration effect is obvious in Eastern China, and the social and economic coordination level has always occupied the first and the second places. (2) China's urban-rural multi-dimensional integration levels often show spatial autocorrelation. The HH values of urban-rural integration overall level are concentrated in Central China and Eastern China, while the LL values are gathered in Western China. The hot and cold spots are located to the southeast and northwest of Heihe-Tengchong Line, respectively. Also the high values of economic integration have always corresponded to those of ecological and environmental integration. Population integration level decreases from Eastern to Western China. Spatial integration level presents the "core-edge" structure such as Beijing, Shanghai and Guangdong. Spatial spillover effect of the economic integration development is obvious in the coastal region of China, while the development of ecological environment integration and economic integration has spatial dislocation. And the clusters of social integration high values are in Central China. (3) The ways of the urban-rural multi-dimensional integration are as follows: Firstly, we should improve the quality of rural labor forces and promote the interaction between urban and rural residents. Secondly, we should stimulate the multi-function of rural land and control the disorderly urban expansion. Thirdly, we should take financial expenditures in a reasonable range and provide a perfect financial support in urban and rural areas. Finally, industrial restructuring is also needed. And moreover, regulating the behavior of the local governments will be benefit to the urban-rural multi-dimensional integration and good governance in China.
大都市城乡融合区空间演进及内在关联性测度: 基于武汉市夜间灯光数据
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

大都市城乡融合区时空演变及其内在空间关联性研究对避免城市低效蔓延式发展、实现空间结构协同和精明增长有重大意义。论文以武汉市城乡融合区为研究对象,基于NPP/VIIRS夜间灯光强度表征都市要素配置及运行效率和效益,利用引力模型测度2016—2018年各城乡融合区空间关联强度,分析各城乡融合区空间联系势能时空演变趋势和社会经济区位度变化。研究结果表明:① 武汉市城乡融合区面积在2016—2018年间扩大了28.10%,小斑块区域逐渐整合,区域发展连续性增强,总体向西北方向扩展最为显著;② 武汉市城乡融合区之间的空间联系网络结构整体上趋向“多中心”分布,这一过程源于各城乡融合区的经济发展水平、城镇化发展规模和交通通达性变化,东湖新技术开发区、中法武汉生态示范城、武汉临空经济区等在此过程中是各城乡融合区的区域发展引擎;③ 武汉市城乡融合区空间联系强度整体上逐年上升,空间联系整体格局从武洪区和江夏区的“大小中心”结构过渡到江夏区—武洪区—蔡汉区—江黄区—江硚东区的“外围圈层式”结构,但洪山区和江夏区作为武汉市城乡融合区中心区域,未能形成多方向空间辐射力和吸引力,对其他地区的带动明显不足;④ 各城乡融合区社会经济区位度变化显示,现行武汉市都市发展区规划实施成效在北部、西部和东北部城乡融合区较为显著。
Spatial change and correlations of desakota regions in a metropolitan area using NPP/VIIRS nighttime light data: A case study of Wuhan city
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

Research on the spatial-temporal change and intrinsic spatial correlation of metropolitan urban-rural integration zones can help cities to avoid inefficient sprawling development and achieve spatial structure coordination and smart growth. Taking the desakota region in Wuhan City as the case, we used the National Polar-Orbiting Partnership / Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (NPP/VIIRS) nighttime light data to assess urban factor allocation and operational efficiency and effectiveness. This study then detected the spatial correlation intensity, spatial-temporal change of spatial connection potential, and the change of socioeconomic location index of the urban-rural integration areas during 2016-2018 using the gravity model. The results show that: 1) The desakota regions in Wuhan City have expanded by 28.10%, and sprawl most significantly to the northwest during 2016-2018. This process is characterized by the integration of small plaques and the enhancement of regional development continuity. 2) The spatial connection network structure among desakota regions in Wuhan tends to be polycentric, which originates from the changes of economic development levels, urbanization development scale, and traffic accessibility. Wuhan East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Sino-French Wuhan Ecological Demonstration City, Wuhan Airport Economic Zone and so on are the engine of regional development in a decentralized process. 3) The spatial correlation pattern of urban-rural integration areas in Wuhan has been transformed from the "large and small cores" structure consisted of Wuhong District and Jiangxia District to the "peripheral circle" structure composed of Jiangxia-Wuhong-Caihan-Jianghuang-Jiangqiaodong. The spatial connection intensities of desakoda regions have increased year by year, but Wuhong and Jiangxia Districts, as the core areas of Wuhan urban-rural integration area, failed to develop multi-directional spatial radiation and attractiveness, which led to insufficient positive effects to other areas. 4) The changes of socioeconomic location index of each urban-rural integration area show that the impact of existing Wuhan urban planning is more significant in the northern, western, and northeastern parts of urban-rural integration area.
大都市区城乡融合系统耦合协调度时空演化及其影响因素: 以环首都地区为例
Spatiotemporal evolution of coupling coordination degree of urban-rural integration system in metropolitan area and its influencing factors: Taking the capital region as an example
长江三角洲城乡融合发展评价与空间格局演化
Evaluation and spatial pattern evolution of urban and rural integrated development in the Yangtze River Delta
论乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 1]

构建现代乡村治理体系成为推动城乡融合发展和乡村振兴的重要内容。破解乡村空间利用过程中出现的发展空间受限、权属关系不明和组织体系不畅等系统性问题,成为乡村空间治理的首要任务。本文从乡村空间“物质—权属—组织”综合治理的视角出发,尝试解析乡村空间治理在推动乡村空间重构、权属关系重塑和组织体系重建中的作用机制,并进一步探讨乡村空间治理优化城乡格局、改善城乡互动关系、推动城乡融合发展的可行路径。结论如下:物质空间治理可作为乡村空间结构和功能优化的重要手段,空间权属治理有助于保障乡村空间不同参与主体的发展权利,空间组织治理可提升乡村空间的组织效率;乡村空间治理导向的“人口—土地—产业”转型过程为“深化空间治理—活化乡村空间—优化人地关系—改善城乡格局”的分析思路创造条件;乡村空间治理推动城乡发展格局不断演化,城乡互动关系改善成为推动城乡融合发展和破解乡村发展困境的重要依据。最后,本文构建了乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展互动分析框架,并探讨了乡村空间治理与国土空间规划的内在关系及研究趋势。
Rural spatial governance and urban-rural integration development
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 1]

The construction of the modern rural governance system becomes an important part in promoting the urban-rural integration development and rural vitalization. Solving systemic problems such as limited development space, unclear ownership relationship and inefficient organization in the process of using rural space has become the primary task of rural spatial governance. Based on the breakthrough of the comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space, this paper attempts to analyze the mechanism of rural space governance in promoting rural space restructuring, ownership reshaping and organizational system reconstruction, and further explores the feasible path of rural space governance to optimize the urban-rural pattern, improve the urban-rural interaction, and promote the urban-rural integration development. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Physical space governance facilitates the optimization of rural spatial structure, the space ownership governance safeguards the development rights of different stakeholders, and the space organization governance enhances rural organizational capabilities. The comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space helps to impel the restructuring of rural space, the reshaping of ownership relations and the reconstructing of organizational system, to achieve the goals of the modern rural space governance system with clear rural space ownership. (2) The "population-land-industry" transformation path guided by rural space governance creates conditions for the analysis of "deepening space governance-activating rural space-optimizing human-land relationship-improving the urban-rural pattern". (3) Rural space governance promotes the continuous evolution of urban-rural development, and the improvement of urban-rural interaction becomes an important basis for upgrading urban-rural integration development and solving the dilemma of rural development. Finally, this paper constructs an analytical framework and feasible path for the interaction between rural space governance and the urban-rural integration development, and explores the internal relationship and research trends of rural space governance and territory spatial planning.
迈向城乡融合: 新型城镇化与乡村振兴结合研究的关键与趋势
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.04.004
[本文引用: 1]

新型城镇化和乡村振兴两大国家战略有机结合并进行城乡共治是实现城乡融合的关键。通过分析新型城镇化和乡村振兴研究文献,认为新型城镇化与乡村振兴战略结合应聚焦两大战略的共生效应,科学评价城乡耦合程度,明确城乡融合的时空格局,提炼两大战略的耦合机制。要实现城乡融合,需要深入探究新型城镇化和乡村振兴战略的结合点和时空差异,以问题为导向进行学科交叉,从空间、经济、社会3方面入手,厘清城乡在行政管理、土地、户籍和社会保障制度间的关系,倡导多维制度联动改革,从国家、省域、城市、县域、乡镇到社区,通过多尺度整合,重构城乡融合的理论,激发以社区为核心的基层治理活力,进而创新中国城乡共治的模式。
Towards rural-urban integration: Key issues and trends on linking new-type urbanization to rural revitalization
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.04.004
[本文引用: 1]

It is the key to achieving the aim of rural-urban integration that combine the two national strategies of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization, and carry out collaborative governance of urban and rural areas. By analyzing the progresses of the studies on the new-type urbanization and rural revitalization, it is pointed out that the coupling of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization strategy should clarify the symbiosis effect of two strategies, and scientifically evaluate the coupling degree of urban and rural areas, then discover the spatio-temporal pattern of rural-urban integration. In order to realize rural-urban integration, it is necessary to explore the combination and spatio-temporal differences of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization strategies. According to conducting interdisciplinary methods to study the relations among the urban and rural administrative management system, the land system, the household registration system as well as the social security system, this article advocates multidimensional system reform from three perspectives of space, economy and society. Reconstructing the theory of rural-urban integration will be based on a whole analysis from the national, provincial, city to community scales. Community-centered governance is significant for rural-urban integration.
我国城乡融合发展演化过程及福州实践
China's urban-rural integration evolution and Fuzhou practice
新时代省域尺度城乡融合发展路径思考: 基于江苏实践案例分析
Thoughts on an integrated urban-rural development path on provincial scale in the New Era: A case study on Jiangsu province
生态资本化: 城乡融合的第三次循环
Eco-capitalization: The third circulation of urban-rural integration
基于乡村经济韧性的传统农区城乡融合发展路径研究: 以河北省典型县域为例
Path of urban-rural integrated development in traditional agricultural zones based on rural economic resilience: The study of typical counties of Hebei province
西咸城乡融合发展试验区融合发展路径与策略
Development path and strategy of Xi'an-Xianyang Urban-Rural Integration Pilot Area
生态系统服务权衡与协同视角下的重点生态功能区保护特征
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202205016
[本文引用: 1]

重点生态功能区提供着源源不断的生态系统服务,在保障国家生态安全和社会可持续发展方面,有着不可或缺的基础作用。但是,以生态系统服务权衡与协同关系为视角,进而探讨分析重点生态功能区保护特征的研究案例相对较少。本文以秦巴重点生态功能区为评估分析区域,选择自然地理条件相似度极高的秦巴山区为参照单元,以生态系统供给服务与调节服务为核心内容,在定量分析2000—2019年期间的生态空间变化特征基础上,分析评估生态系统服务权衡与协同关系。结果表明:秦巴山区生态状况逐渐变好,重点生态功能区划定之后,生态系统趋于稳定;重点生态功能区服务能力呈逐渐增强的趋势,平均净初级生产力、土壤保持总量和水源涵养总量比重点生态功能区外分别高出了25.95 gC/m<sup>2</sup>、5.81亿t和24.95亿m<sup>3</sup>;土壤保持服务和生态系统供给服务的协同关系与生态状况改善呈正相关;由于受到降水的影响,2010年之后的水源涵养服务与生态系统供给服务的协同关系变差。总体来看,秦巴重点生态功能区的划定带动了区域生态空间“量的增长”和生态系统服务“质的提升”,但生态系统服务之间关系的“协调性”仍然不足,甚至从“协同”转为“权衡”关系,这要求未来国家需要制定更有针对性的生态系统保护管理决策,提高生态系统总体效益,支撑区域生态系统服务的可持续供给。
The protection characteristics of key ecological functional zones from the perspective of ecosystem service trade-off and synergy
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202205016
[本文引用: 1]

Key ecological functional zones provide continuous ecosystem services and play an indispensable role in ensuring national ecological security and social sustainable development. From the perspective of ecosystem service trade-off and synergy, this paper discusses and analyzes the protection characteristics of key ecological functional areas. The data includes multi-source datasets such as ecosystem types, meteorological data, elevation data and soil data from 2000 to 2019. Methods of the dynamic degree of ecological spatial change, ecosystem service model and partial correlation coefficient were used for evaluation and analysis. This research selects the Qinling-Daba (Qinba) Mountains region with high similarity of natural and geographical conditions as the reference unit, takes ecosystem supply services and regulation services as the core content, and analyzes the trade-off and synergy relationship of ecosystem services based on the quantitative analysis of the characteristics of ecological spatial changes from 2000 to 2019. The results showed that the ecological status of the study area gradually improved, and the ecosystem tended to be stable after the delimitation of key ecological functional zones. The service capacity of key ecological functional zones is gradually increasing, and the average net primary productivity, total soil conservation and total water conservation are higher than those outside the key ecological functional zones by 25.95 gC/m2, 5.81×108 t and 24.95×108 m3, respectively. The synergy between soil conservation services and ecosystem supply services was positively correlated with the improvement of ecological status. Due to the impact of precipitation, the synergistic relationship between water conservation services and ecosystem supply services after 2010 became worse. Overall, the designation of key ecological functional areas in the Qinba Mountains has driven the "quantitative growth" of regional ecological space and the "qualitative improvement" of ecosystem services. However, the "synergy" of the relationship between ecosystem services is not obvious, and even changed to "trade-off", which requires the country to make more targeted ecosystem protection and management decisions in the future, and improve the overall benefits of ecosystem and support the sustainable supply of regional ecosystem services.
大别山连片特困地区城乡融合水平时空差异及障碍因素分析
Temporal and spatial differences of urban-rural integration level in Dabie Mountain Contiguous Destitute Area and obstacles analysis
淮河生态经济带城乡融合发展水平时空演变研究
Research on the spatio-temporal evolution of the development level of urban-rural integration in the Huaihe Eco-economic Belt
环渤海地区农业地域功能演进及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910005
[本文引用: 1]

农业地域功能是农业地理学的重点理论问题之一,也是关乎粮食安全和区域农业可持续发展的重要实践课题。以环渤海地区为例,通过构建评价体系开展农业地域功能划分及其演进分析,利用空间计量模型诊断农业地域多功能形成的影响因素。结果表明:① 环渤海地区生态保育功能的空间集中度较高,农产品供给、就业与社会保障、文化传承与休闲功能则较低,4种功能空间格局具有显著规律性。② 农产品供给功能显著增强,主要分布区域向平原农区聚集;就业与社会保障高值区从内陆向沿海转移;山地丘陵生态保育功能有所增强;市辖区及周边的文化传承和休闲功能较显著。③ 农产品供给功能主导型县域集中于冀中南平原、鲁西北冲击平原、胶莱平原和辽河平原西部;社会保障主导型集中在燕山山麓平原、滨海平原、胶东半岛以及黄河三角洲;生态保育主导型集中在冀北坝上高原、燕山山地地区,以及辽西、辽东山地丘陵区和京津冀都市圈周边;文化传承与休闲功能集中于京津冀、辽中南和济南都市圈及周边;综合型位于鲁西南黄淮平原与鲁中南丘陵地区。④ 自然因素对农产品供给、就业与社会保障和生态保育功能的形成均具有显著影响;社会经济因素对4种功能的作用则具有较大差异。
Spatio-temporal differentiation of agricultural regional function and its impact factors in the Bohai Rim Region of China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910005
[本文引用: 1]

The agricultural regional function is an important scientific problem in agricultural geography research, and it is also the important practical issue related to the national food security and sustainable development of regional agriculture. Taking the Bohai Rim region of China as an example, this paper identified the agricultural regional function as four types including agricultural products supplying function (APF), labor employment and social security function (LEF), ecological conservation function (ECF), and cultural heritage and recreational function (CRF) and their spatial pattern and evolution process were explored. The study also identified the agricultural regional type and the impact factors affecting the four functions using cluster analysis method and spatial econometric model. The results indicate that: Firstly, the degrees of spatial concentration of the APF, LEF and CRF were low, while that of the ECF was high. The spatial distributions of the four functions presented obvious regularity. Secondly, the APF enhanced largely, its center of gravity was further concentrated in plain agricultural areas. The high value areas of the LEF shifted from inland to coastal areas. The ECF of hilly areas further highlighted. Advantage areas of the CRF were concentrating in the municipal districts and their surrounding counties. Thirdly, the leading counties of the APF were distributed in central and southern plains of Hebei province, the impact plain of northwest Shandong, the Jiaolai plain and the west of Liaohe plain. The leading counties of LEF were distributed in piedmont plain of Yanshan and coastal plain of Hebei province, Jiaodong Peninsula and the Yellow River Delta region. The leading counties of the ECF were distributed in Bashang plateau, mountainous region of Yanshan, hilly area of eastern and western Liaoning province, and the surrounding areas of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. The leading counties of the CRF were distributed in the surrounding areas of central-south Liaoning urban agglomerations, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan region and Jinan metropolitan area. Comprehensive counties were distributed in the Huang-Huai plain and hilly areas of central-south of Shandong province. Fourthly, natural factors possessed a significant impact on the formation of the three functions including APF, LEF and ECF, while social and economic factors on the impact of the four functions were quite different. The study reveals the regularity and influence mechanism of the evolution of agricultural regional function, which can provide theoretical basis for scientific guidance of regional division of labor, strengthening of leading function, highlighting regional value and promoting regional coordinated development.
黄河流域旱塬区农户生计脆弱性及影响因素
Livelihood vulnerability and its influencing factors of farmers in dryland area of Yellow River Basin
基于主体功能区划的湖南省乡村转型发展评价
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.010
[本文引用: 1]

乡村转型是实现乡村可持续发展的重要路径,确立与主体功能定位相协调的乡村转型路径与政策,是促进区域城乡融合发展、实现乡村振兴的重要举措。本文以湖南省为例,围绕人口、土地、产业等乡村转型发展3类要素,构建乡村转型度评价指标体系,并计算各县(市、区)2006-2011年和2011-2016年2个阶段的乡村转型度,并基于主体功能区划方案分析各类主体功能区乡村转型发展差异及驱动机制。研究结果显示:受自然条件、区位因素、经济基础、政策环境等因素的影响,各主体功能区乡村转型特征存在差异;重点开发区乡村转型主要是城镇带动型,城镇辐射力、市场推动力以及农户决策力作用突出,乡村转型度高、乡村转型速度快;农产品主产区乡村转型主要是现代农业推动型,资源支撑力、政策推动力以及文化根植力起主导作用,乡村转型度较高、乡村转型速度较快;重点生态功能区乡村转型主要是政府推动型,受地形条件、经济基础以及资源环境约束,乡村转型度较低、转型速度较慢。各类主体功能区2011-2016年的乡村转型度相比于2006-2011年均有所提升。湖南省主体功能区规划方案在一定程度上体现了乡村发展的差异性,但其主体功能区政策在乡村转型发展过程中的引导作用有待进一步加强。
Evaluation of rural transformation development in Hunan province based on major function oriented zoning
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.010
[本文引用: 1]

Rural transformation is an important way to achieve sustainable development of rural areas. The establishment of rural transformation path and policy in line with major function-oriented zoning is an important measure to promote the integration of urban and rural development and achieve rural revitalization. Taking Hunan Province, an agricultural region in central China, as an example and based on major function oriented zoning, this study constructed an evaluation index system of rural transformation degree around the core elements including population, land, and industry. We calculated the rural transformation degree of each county during 2006-2011 and 2011-2016, and analyzed the spatial differences and driving mechanisms of rural transformation development in various major function oriented zoning. The results show that the characteristics of rural transformation in different major function oriented zones varied because of factors such as natural condition, location, economic foundation, and policy environment. Rural transformation in prioritized development zones was mainly driven by cities and towns. The role of urban influences, market drivers, and farmers' decision-making power was outstanding. The degree of rural transformation was high and the speed was fast. Rural transformation in main agricultural zones was mainly driven by modern agriculture. Resource support, policy impetus, and cultural embeddedness played a leading role. The degree of rural transformation was relatively high, and the speed was relatively fast. Rural transformation in key ecological function zones was mainly driven by the government. Due to the constraints of topography, economic basis, and resources and the environment, the degree of rural transformation was relatively low, and the speed was relatively slow. The rural transformation degree of all major function orientedzones during 2011 to 2016 was improved compared with that during 2006 to 2011. The major function oriented zoning scheme of Hunan Province reflects the difference of rural development to some extent, but the guiding role of major function-oriented zoning policy in the process of rural transformation development needs to be strengthened.
基于县域尺度乡村地域多功能空间分异特征及类型划分: 以湖南省为例
Multifunctional spatial characteristics of rural areas and their type identification based on county scale: A case of Hunan province
民族地区乡村振兴的“摩梭家园”模式研究: 以文化生态保护与城乡融合发展为中心
Rural revitalization in ethnic regions about the research of "Mosuo Home" pattern: In the case of cultural ecology protection and integration development of urban and rural areas as the center
乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的研究框架与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180454
[本文引用: 1]

中国特色社会主义进入新时代,城乡发展不平衡、乡村发展不充分等问题日益突出,实施乡村振兴战略是解决人民日益增长的美好生活需要和不平衡不充分的发展之间矛盾的必然要求。发展乡村旅游能够有力地契合和服务新时代国家发展战略,促进农业提质增效、农民增收致富、农村繁荣稳定,加快统筹城乡融合发展步伐,是实现乡村振兴的重要途径。系统梳理国内外乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的相关研究成果,针对内容深度相对薄弱、功能拓展比较泛化、时代特征不够显著等问题,把握新时代乡村旅游发展的新特点、新使命、新要求,充分考虑中国是一个发展中的经济大国、人口大国、农业大国的基本国情,构建了融合地理学、旅游学、经济学、社会学、管理学等相关学科理论的新时代中国乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的研究框架,归纳了乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的五个重点研究内容,即乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的学理和逻辑机理研究、乡村旅游引导乡村经济振兴的路径研究、乡村旅游引导乡村生态宜居的路径研究、乡村旅游引导乡村治理体系重构的路径研究、乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的政策体系研究。五个重点研究内容包括理论层面、实践层面和保障层面,在相互联系、相互影响、相互作用中共同促进城乡融合发展,实现乡村振兴的科学、持续、健康发展。掌握和运用科学的方法论,汲取科学方法论的智慧和营养,构建多方法综合集成的方法体系,确保数据采集的真实性和数据处理的科学性,是新时代乡村旅游引导乡村振兴研究的关键。
The research framework and prospect of rural revitalization led by rural tourism
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180454
[本文引用: 1]

Socialism with Chinese characteristics has entered the new era. Problems such as unbalanced development between urban and rural and inadequate development in rural areas have become increasingly prominent. The implementation of the rural revitalization strategy is an inevitable requirement for resolving the contradictions between unbalanced and inadequate development and the people's ever-growing needs for a better life. With the rapid advancement of new industrialization and new urbanization, China's rural tourism has entered the era of big tourism instead of small and medium tourism. The development of rural tourism can effectively pursue the development strategy of the country in the new era, promote agricultural quality and efficiency, increase farmers' income, make the countryside prosperous and stable, and speed up the development of urban-rural integration. Therefore, it is an important way to realizing rural revitalization. This paper has reviewed the related research on rural revitalization led by rural tourism at home and abroad. In addition, it has grasped the new characteristics, new missions and new requirements of rural tourism development in the new era. Considering the basic situation of China as a developing economic power, and a large agricultural country with a large population, this paper has constructed a research framework of rural revitalization led by rural tourism in China in the new era, which integrates theories of geography, tourism, economics, sociology, management and other related disciplines. It has summarized the five key research contents of rural revitalization led by rural tourism, which contains study on theory and logic mechanism of rural revitalization led by rural tourism, study on the path of rural economy revitalization led by rural tourism, study on the path of rural ecological livability led by rural tourism, study on the path of reconstruction of rural governance system led by rural tourism and study on the policy system of rural revitalization led by rural tourism. The five key research contents cover the theoretical, practical and safeguard aspects, promote the development of urban-rural integration through interconnection, mutual influence and interaction, and ultimately realize the scientific, sustained, and healthy development of the rural revitalization strategy. In the new era, the key of rural revitalization led by rural tourism is to master and apply scientific methodology, to learn the wisdom and nutrition of scientific methodology, to construct a method system for multi-method comprehensive integration, and to ensure the authenticity of data collection and the scientificalness of data processing.
新时代背景下生态小镇的城乡融合模式探究:以广德县卢村乡为例
A study on the urban-rural integration model of ecological small towns in the New Era: A case study of Lucun township, Guangde county
特色小镇的定位与功能再认识: 城乡融合发展的重要载体
Reconsideration on the positioning and function of characteristic towns: An important carrier for the integrated development of urban and rural areas
新型城镇化背景下特色旅游小镇建设的双轮驱动机制研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.004
[本文引用: 1]

新型城镇化背景下,特色旅游小镇作为城乡融合和乡村振兴的重要载体,承担着产业发展、文化传承、社区管理、空间整合和生态优化等多种功能。针对当前特色旅游小镇产城不融合、特色不鲜明等发展现状,论文以产业整合与景观重构为视角,探讨特色旅游小镇建设的双轮驱动机制,研究结果显示:① 以产业整合实现特色旅游小镇建设的转型升级。在挖掘产业共性与识别产业特色的基础上,运用整合手段实现产业互融,激发出产业整合极强的人口集聚、产业集聚、消费集聚、服务集聚、空间集聚以及生态集聚等效应,促进特色旅游小镇的经济建设、社会建设和生态建设。② 以景观重构实现特色旅游小镇建设的基因传承。通过识别景观基因、提取景观节点、组合景观廊道、构建景观形态的重构路径,描绘出特色旅游小镇文化景观的建设蓝图,以凸显特色旅游小镇的文化基因。③ 将产业整合与景观重构有机结合,形成特色旅游小镇建设的双轮驱动器。在识别景观基因与确定形象定位的前提下开展产业整合,同时利用整合成果提取出景观节点,组成旅游通道,进而整合社会空间功能,形成和谐的景观形态,为特色旅游小镇提供一条产业化与特色化高度融合的建设路径。
Two-wheel driven construction of characteristic tourist towns under the background of new urbanization
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.004
[本文引用: 1]

Under the background of new urbanization, characteristic tourist towns, as an important carrier of rural-urban integration and rural revitalization, undertake multiple functions such as industrial development, cultural heritage preservation, community management, spatial integration, and ecological optimization. Currently, characteristic tourist towns face problems such as the lack of integration of industrial and urban activities, and the lack of distinctive characteristics. Therefore, from the perspective of industrial integration and landscape reconstruction, a two-wheel driven mechanism for the construction of characteristic tourist towns is discussed. The research results show that: 1) With regard to realizing the transformation and upgrading of characteristic tourist towns development through industrial integration: on the basis of recognizing shared features of industries and identifying their unique characteristics, industrial integration can be realized through the use of integration methods. In this way, the strong effects of industrial integration on population, industrial, consumption, service, spatial, and ecological agglomerations are stimulated to promote the economic, social, and ecological construction of characteristic tourist towns. 2) With regard to realizing genetic inheritance in characteristic tourist towns development through landscape reconstruction: through identifying landscape genes, extracting landscape nodes, combining landscape corridors, and constructing landscape forms, the blueprint for the construction of cultural landscape of characteristic tourist towns can be drawn. This path highlights the cultural genes of characteristic tourist towns. 3) Combining industrial integration and landscape reconstruction to form a two-wheel driven mechanism for the construction of characteristic tourist towns: Under the premise of identifying landscape genes and determining the identity of characteristic tourist towns, industrial integration can be carried out. At the same time, the integration results can be used to extract landscape nodes to form tourism channels. Thus, the social space functions are integrated and a harmonious landscape form is formed. It provides a highly integrated development path of industrialization and specialization for characteristic tourist towns.
生态涵养地区城乡产业用地功能融合利用的思考: 以北京市为例
Reflections on the functional integration and utilization of urban and rural industrial land in ecological conservation areas: Taking Beijing as an example
主体功能视角下皖南旅游区乡村多功能演化特征与影响机制
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.05.009
[本文引用: 1]

以皖南旅游区为研究对象,通过构建主体功能县域旅游地乡村多功能研究框架及其指标体系,采用多指标综合评价、热点分析、地理探测器等方法,对比分析不同主体功能区乡村多功能差异特征、影响因素、类型模式,并提出提升路径。结果发现:① 2006—2017年,不同功能结构在各类主体功能区差异明显,旅游休闲功能比重不断增长,农业生产和生态服务功能比重不断下降。② 乡村多功能由重点开发区向重点生态功能区和农产品主产区梯级递减且差距不断扩大,不同主体功能区乡村多功能扩散收敛和功能强度格局基本吻合。③ 重点开发区乡村多功能演化为城镇带动型,主要受城镇辐射、产业结构、人口集聚的影响;农产品主产区乡村多功能演化为农业现代型,主要受自然条件、政策调控、技术应用的影响;重点生态功能区乡村多功能演化为旅游发展型,主要受旅游发展、生态资源、市场需求的影响。④ 基于乡村多功能测度结果,识别7类极化发展型和4类主导发展型县域,并从主体功能区城乡融合角度建议提升路径。
Evolution characteristics and mechanism of rural multifunctionality in South Anhui Tourism Area based on major function-oriented zones
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.05.009
[本文引用: 1]

Taking the tourism area of southern Anhui Province as the research object, adopting multi-index comprehensive evaluation, hot spot analysis, the geographic detector model comparative analyzes the differences in features and influencing factors of rural multifunctional evolution in different main functional areas by constructing a multi-functional research framework for countryside of the tourist destination on a county scale and its indicator system. Then, the multi-functional pattern of rural areas is identified and the promotion path is proposed. The results showed that: 1) From 2006 to 2017, different functional structures have obvious differences in various major function oriented zones, the proportion of tourism and leisure function gradually increased in various major function oriented zones, while agricultural production and ecological service function continued to decline. 2) The multi-functional development in rural areas gradually decreased from key development zones to key ecological function zones and agricultural production areas with the continual wider gap. But the multi-functional diffusion convergence and functional intensity of rural areas in different major function oriented zones are basically matched. 3) The rural multi-functional evolution of key development zones is urban-driven, which is mainly affected by urban radiation, industrial structure, and population agglomeration; the rural multi-functional evolution of agricultural production areas is modernized by agriculture, which is mainly controlled by natural conditions, policies and technology application; the rural multi-functional evolution of key ecological function areas has evolved into tourism development, which is mainly affected by tourism, ecological resources, and market demands. 4) Based on the results of the multi-functional measurement in the rural areas, seven types of polar development and four types of dominant development counties are identified, and the path of improvement is proposed from the perspective of urban-rural integration in the major function oriented zones.
贫困地区的精准扶贫与乡村振兴: 内在逻辑与实现机制
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190644
[本文引用: 1]

面向“两个一百年”奋斗目标的需要,当前中国贫困地区乡村发展正逐渐由低层次的脱贫向更高层次的振兴转变,两者的紧密关联使得减贫对于推动乡村振兴战略目标的实现具有重要意义。通过分析精准扶贫与乡村振兴的基本内涵,探讨两者的内在逻辑关系,进而从多个维度剖析贫困地区的精准扶贫实践如何助推其乡村振兴。结果表明:① 贫困地区的精准扶贫旨在科学诊断致贫因子的基础上采取针对性措施实施帮扶,从根本上消除导致贫困的各种障碍性因素;乡村振兴则重点在于通过构建城乡融合发展的体制机制,最终实现农业农村的现代化。② 精准扶贫与乡村振兴的内在一致性使得两者存在紧密的逻辑顺承性,精准扶贫是乡村振兴的关键和基本前提,而乡村振兴是精准扶贫的深化和保障,可以说农村减贫的过程也是乡村逐步振兴的过程。③ 通过要素资源合理流动和配置补齐乡村人、地、业等发展短板,贫困地区重塑了要素耦合、结构合理、功能复合的乡村地域系统,从而推动乡村产业、人才、文化、生态、组织等振兴,最终实现农业强、农民富和农村美的发展目标。
Targeted poverty alleviation and rural revitalization in poverty-stricken areas: Internal logic and mechanism
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190644
[本文引用: 1]

Targeting at the needs of Two Centenary Goals, rural development in poverty-stricken areas of China is gradually transforming from poverty alleviation to rural revitalization. Since there is a close relationship between these two stages, targeted poverty alleviation practices in rural areas are of great significance to promote the realization of rural revitalization. This study analyzed the connotations of targeted poverty alleviation and rural revitalization, and investigated the internal logic between them. Then it discussed how antipoverty practices promote the rural revitalization in poverty-stricken areas. Results show that targeted poverty alleviation aims at taking countermeasures to help those who truly need them based on scientific diagnosis of the factors leading to poverty, thus all kinds of factors causing poverty can be eliminated fundamentally. The key of rural revitalization lies in establishing the system and mechanism for urban-rural integrated development, eventually realizing the modernization of agriculture and countryside. In term of the relationship between targeted poverty alleviation and rural revitalization, the former is the key and basic premise of the latter since poverty reduction guided by targeted poverty alleviation makes up the shortboard of rural development, and the latter is the higher stage and guarantee of the former since it steadily improves the abilities of rural sustainable development. Therefore, it can be said that the process of poverty alleviation in rural areas is also a process of gradual rejuvenation of the countryside. Through the rational flow and allocation of factors, such as human, land and capital, poverty-stricken areas have constructed a benign rural regional system with enough elements, proper structure and multiple functions to promote the revitalization of industries, talent, culture, ecology and organizations. Eventually, it helps to achieve the goals of strong agriculture, beautiful countryside and well-off farmers. Rural development has obvious path dependence; thus, its cyclic accumulation effect determines that the current antipoverty in poor areas should focus on the effective connection with rural revitalization, laying a solid foundation for rural sustainable development.
大都市远郊衰败型村庄振兴探索: 以广州市莲麻村村庄规划为例
Regeneration of decayed villages in exurban zone: Lianma village, Guangzhou
城乡融合对小城镇区域专业化分工的影响: 以浙江省为例
Influence of urban-rural integration on regional specialization division of small towns: A case study of Zhejiang province
国土空间规划体系建构下乡村空间规划探索: 以江苏为例
The rural spatial planning under the construction of territorial spatial planning system: Take Jiangsu as an example
城乡融合视角下农村闲置建设用地拆旧复垦的资本化效应: 以广东省为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.011
[本文引用: 1]

土地问题是乡村振兴战略落实的关键。土地整治和资本化作为提升土地质量、促进城乡融合的重要手段,一直是各方探讨的热点。论文以广东省实施的农村拆旧复垦政策为切入点,分析农村建设用地拆旧复垦模式资本化效应的形成机制,梳理其与乡村振兴、城乡联动的关系。研究发现:首先,在农村建设用地拆旧复垦模式实施中,以市场机制为主的“弱关系”和土地流转为主的“强关系”分别在整治腾退建设用地和复垦农业用地中发挥重要作用,是实现土地资本化的主要路径;其次,农村建设用地拆旧复垦模式主要通过结构重组、空间重构、生产方式变革和生态环境优化等推动乡村振兴;最后,农村建设用地拆旧复垦模式以跨地区市场交易平台为载体,引导城乡之间土地、资金等要素流通,通过设置最低保护价和优先购买权等方式保障乡村的发展权利,实现城乡等价要素联动。
Capitalization effect of rural land reclamation from the perspective of rural-urban integration: A case study of Guangdong province
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.011
[本文引用: 1]

Addressing the land issue is the key for implementing the rural revitalization strategy. Land consolidation and capitalization as important means to improve land quality and promote rural-urban integration have been the hot topic of discussion. This study took the demolition and reclamation policy in Guangdong Province as a case, analyzed the mechanism of capitalization effect of rural construction land reclamation, and clarified its influence on rural revitalization as well as rural-urban integration. First, during the implementation of rural construction land reclamation, the "weak relationship" dominated by market mechanism and the "strong relationship" dominated by land circulation play important roles in the renovation and reclamation, which are the main ways to realize land capitalization. Second, rural construction land reclamation mainly promotes rural revitalization through structural reconstruction, spatial reorganization, production mode transformation, and ecological environment optimization. Finally, rural construction land reclamation takes cross-regional market trading platforms as the carrier to guide the circulation of land, capital, and other factors between urban and rural areas. Meanwhile, it guarantees the development right of rural areas by setting the protection price and the right of preemption, which realizes the smooth flow of factors between urban and rural areas.
城乡等值: 新时代背景下的乡村发展新路径
Urban and rural parity: A new path of rural development in the New Era.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 1]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the New Era in China
全民所有自然资源资产“三权分置”产权体系研究: 基于委托代理理论的视角
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211016
[本文引用: 1]

建立健全自然资源资产权利体系,是开展自然资源统一确权登记,推进自然资源资产价值核算和编制自然资源资产负债表的基础和前提。基于委托代理理论,按照“制度安排与市场建设欠佳——委托代理与资源监管低效——权能分解与委托代理耦合——三权分置设计”的逻辑思路,试图建构具有中国特色的新时代自然资源资产产权体系。研究发现:自然资源资产产权制度安排失灵,产权市场建设滞后,委托代理机制弱化以及资源监管失调等因素,是自然资源有效利用的主要障碍。通过对自然资源资产产权的权能分解与管理机制耦合,建立自然资源资产“三权分置”的产权体系,有利于明晰自然资源资产的所有者、代理者和使用者之间权、责、利的关系。
Design of property right system of "three rights separation" of natural resource assets of the whole people: From the perspective of principal-agent theory
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211016 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于结构方程模型的南方丘陵山地农户福祉与生态系统服务关系: 以广东省乐昌市为例
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003266
[本文引用: 1]

以农户福祉和生态系统服务关系为研究视角,选取地处南方丘陵山地重点生态功能区的广东省乐昌市的8个地形地貌相似、但发展存有差异的村庄为研究对象,基于实地调研、问卷访谈等,采用模糊综合评价法对其2005及2018年农户福祉发展水平进行综合评价;并利用结构方程模型,对农户福祉与生态系统服务之间的关系进行耦合分析。结果表明:1)2005—2018年,农户福祉水平各指标均有一定程度的提升,其中农户收入水平、居住条件等显著增加,其评价值分别由2005年的0.294和0.245增加到2018年的0.385和0.422,同时农户对生态保护的意识逐渐加强。2)农户对生态系统服务功能的认识程度整体呈上升趋势,特别是对文化服务功能的感知有较大的提升,其感知值由2005年的0.251增加到2018年的0.370。3)生态系统四大服务功能与农户福祉水平均存在一定的耦合关系,其中供给服务、文化服务与农户福祉的关系密切。4)加强提升生态系统的文化服务能力,大力发展“特色种植+林下经济+生态旅游”等低影响经济发展模式,有利于生态系统服务维护与农户福祉的提高,促进重点生态功能区生态环境和农村经济社会的持续发展。
Relationship between farmer's well-being and ecosystem services in hilly and mountainous areas of south China based on structural equation model: A case study of Lechang in Guangdong province
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003266
[本文引用: 1]

The south hilly and mountainous area is an important ecological functional area in China. As the main economic activity subject, farmers' perception of ecosystem services directly affects the eco-environment behavior, economic production activities, social life style and so on. The contribution of well-being is the core of ecosystem services. In order to explore the relationship between farmers' well-being and ecosystem services and promote the healthy development of ecosystem, eight villages in Lechang city of Guangdong Province, which are located in the key ecological functional areas of hilly and mountainous areas in south China, are selected as the research objects. Based on field survey and questionnaire interview, the structural equation model was used to comprehensively analyze the relationship between the development level of rural communities and farmers' welfare and the changes in ecosystem services, emphasizing the changes in that occurred between 2005 and 2018. The results show the following: 1) From 2005 to 2018, the well-being level of farmers has somewhat improved. The income level and living conditions of farmers have increased significantly; their evaluation values have increased from 0.294 and 0.245 in 2005 to 0.385 and 0.422 in 2018, respectively. Meanwhile, the awareness of farmers on ecological protection has been gradually strengthened. 2) The awareness of the four major service functions of the system is rising; particularly, the degree of understanding of cultural service functions and support service functions has improved significantly. The perceived value of farmers increased from 0.251 in 2005 to 0.370 in 2018. 3) The four service functions of the ecosystem have a certain coupling relationship with the level of community development, among which the relationship between supply services, cultural services and farmers' well-being is close. 4) To enhance the cultural service capacity of the ecosystem and develop the low impact economic development mode is conducive to the maintenance of ecosystem services and the improvement of farmers' well-being, and promote the sustainable development of ecological environment and rural socio-economic in key ecological function areas.
长三角重点生态功能县域生态资产损益核算
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220802
[本文引用: 1]

限制开发的重点生态功能县域承担着生态保护与经济发展双重使命,如何实现生态与发展互促共进及生态产品价值化是当前面临的极大难点,生态资产损益核算为量化区域资源有偿使用、生态保护修复、生态文明绩效评价等提供了有效途径。以浙江省嵊州市作为长三角地区重点生态功能区的典型县域,基于栅格尺度评估了近20年生态资产存量与流量时空动态变化,并利用地理探测器结合人类活动类型监测分析了生态资产损益的驱动因素。结果表明:2000—2018年,由于森林生态资产质量降低及面积减少,嵊州市近60%区域的生态资产存量呈减少趋势,而生态资产流量总价值与单位面积价值均增益10%以上。相对于自然因素,社会经济因素对嵊州市生态资产损益平均贡献度更大,为17%。县域城镇化导致粮食供给轻微减损,70%以上乡镇生态资产增益,特别是石璜镇生态保护成效较突出。
Accounting of gains and losses of ecological assets in counties of key ecological function regions in Yangtze River Delta
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220802 URL [本文引用: 1]
喀斯特生态系统服务价值评价: 以贵州花江示范区为例
采用频度法对喀斯特生态系统服务类型及指标进行分析,结合中国南方喀斯特环境特征、生态功能区位等因素,构建了石漠化生态系统服务价值评估指标体系;并以贵州花江示范区为例,基于实测和调查数据,采用物质量和价值量相结合的方法对其2010年生态系统服务价值进行评估。结果表明:示范区生态系统服务价值为19 604.71万元。其中,固碳制氧价值11 181.25万元、土壤肥力价值3 051.56万元、产品供给价值为2 850.40万元、涵养水源价值2 521.13万元、土壤保持价值为0.37万元。示范区生态系统服务价值以间接价值为主,占85.5%,直接价值仅占14.5%;生态功能价值主要依靠灌丛、经济林、耕地和疏林生态系统提供,裸岩荒坡尽管是研究区的优势景观,但提供服务价值较低。
Valuation of karst ecosystem service value: A case study of Huajiang Gorge of Guizhou province
长江三角洲跨界流域生态产品交易机制: 以天目湖流域为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220616
[本文引用: 1]

生态价值多元化实现是落实区域一体化生态保护格局的经济政策保障。针对当前生态产品交易制度不完善与市场活跃度问题,以天目湖流域水质净化服务产品为例,提出一条生态保护市场化与生态产品增值的双向促进道路:基于长序列监测数据与水文水质过程模型,提出流域生态保护基准概念及其约束下生态产品交易边界,精准核算基准年水质净化产品的可交易量为1.37 t,基准价格为1186.71万元/t/年;面向近10年产品实际供需主体的内在联系,揭示了“三类五种”生态产品交易机制类型,并选择设计了低端产品退出—高端产品激励的典型交易模式。生态产品交易实施为研究区生态价值实现提供市场化路径,为国内同类地区一体化生态保护格局保障提供思路。
Ecosystem service products trading in the transboundary basin of the Yangtze River Delta: An example of Tianmu Lake Basin
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220616 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于PPT战略的广东省乐昌市生态旅游扶贫模式探讨
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003352
[本文引用: 1]

以贫困人口受益为出发点,基于有利于贫困人口发展的旅游(Pro-Poor Tourism, PPT)战略,以广东省乐昌市为例,开展适用于中国南方林区生态旅游扶贫开发的发展模式和旅游扶贫产业的发展路径研究。结果表明:1)政府部门、旅游企业、乡村社区和非营利社会组织都应在提升贫困人口参与度、减轻贫困和生态保护方面承担责任,具体为:政府部门应主导搭建平台和监管落实,旅游企业合理利用生态资源,乡村社区和非营利社会组织相互支持并协助以推进拟定的旅游扶贫发展模式;2)针对乐昌市“生态林木、高山名茶、特色蔬果”等3种特有生态资源,提出以“茶、林、蔬果”三大特色农林资源为抓手的生态旅游发展方式,并提炼出三条适用于乐昌市的产业发展路径,具体为:“休闲农业+特色林果产业+旅游电商产业”“林下休闲业+林下经济产业+林产品初加工”和“森林生态旅游+特色林业种植+自然生态教育”。基于PPT战略,旅游扶贫开发需协调好政府部门、旅游企业、乡村社区和非营利社会组织的关系,只有这四大参与主体共同兼顾生态旅游扶贫开发中的经济、社会和环境效益,才能最终实现PPT战略的经济发展、贫困社区发展、贫困人口与生态可持续发展这三大层次目标。
Proposing a conceptual framework for ecotourism based on pro-poor tourism strategy in Lechang city, Guangdong province
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003352
[本文引用: 1]

Eliminating poverty and exploiting natural resources are sustainable development goals for modern society, especially for developing countries or regions. To achieve these targets, development-oriented eco-tourism planning and design can empower rural areas with rich available natural resources to eventually achieve the aforementioned goals. Pro-Poor Tourism (PPT), an initiative proposed by the UK's Department for International Development in 1999, is regarded as an effective pathway that benefits, through tourism, the underprivileged population living in poor areas. For the purpose of attracting the participation and increasing the income of the poor population, we conducted research, in the present study, on possible models of development-oriented poverty reduction via ecotourism in forest zones. We then proposed several development paths for PPT industries in Lechang city, Guangdong province, southern China, by utilizing the literature review method and conceptual analyses and comprehensively adopting the PPT strategy. The results indicated that: 1) four stakeholders [(i.e., government departments, tourism enterprises, rural communities, and non-profit social organizations (NGOs)] are responsible for engaging the poor population, alleviating poverty, and protecting the environment in different ways. Specifically, government departments are expected to play a leading role in setting up platforms and supervising the situation, tourism can maximize its usage of various ecological resources rationally and sustainably, and the rural communities and NGOs are recommended to serve as an organic unit, working together to push forward certain PPT tasks and form practical development models. 2) In consideration of the availability of three featured types of ecological resources (i.e., natural forests, high mountain tea, and characteristic vegetables and fruits) in Lechang city, the present study put forward a compound development model of ecological tourism consisting of the above three featured agro-forestry resources.Furthermore, we proposed three possible pathways suitable for the industrial development of Lechang city; that is, (i) "leisure agriculture + characteristic forest fruit industry + e-commercial tourism industry," (ii) "understory leisure industry + understory economic industry + initial processing of forest products," and (iii) "forest eco-tourism + characteristic forest planting + natural ecological education." In conclusion, our study suggests that the rational utilization of the PPT strategy and the effective integration of government departments, tourism enterprises, rural communities, and NGOs could facilitate subsequent tasks. The study also emphasized that achieving the anticipated three goals (i.e., comprehensive development of economy, comprehensive development of poor communities, as well as poor population and ecological sustainability) might largely rely on the full consideration of benefits for the economy, society, and the environment during the process of development-oriented poverty reduction via eco-tourism by the four stakeholders.