乡村振兴战略自党的“十九大”报告提出之后,在“二十大”报告中再次被强调,产业振兴作为乡村振兴的首要任务成为社会各界共同关注的热点。农业产业发展路径的探讨是农业产业高质量发展的关键,学者们在农业产业结构调整[1]、农业绿色生产转型[2]、农业产业集群演化与形成机理[3⇓-5]、农业型专业村地域类型分化[6]等农业产业发展的途径进行了深入探索,为农业产业发展的研究奠定了坚实的基础,但现有研究大都集中在本地层面,对区域内外部联系作用下的外源型农业产业的形成与发展关注较少。在发展基础薄弱、内生动力缺乏的乡村地区,外源性要素(资金、政策等)的嵌入具有重要作用[7]。在此背景下,外商直接投资形成的外源型农业产业的演化路径[8,9]、技术扩散[10]等研究受到重视,但对其新路径形成与发展作用机制的研究仍显不足。
区域产业发展的新路径可能来自危机和创造性破坏事件,也可能来自适应和渐进变化的过程[11],指一个地区新经济活动的出现和发展[12]。区域新路径发展规律和机制的研究是演化经济地理学的重要议题[13],也是经济地理服务于国家发展战略与政策需求的主要研究方向之一[14]。近几年来,演化经济地理学在区域新路径发展机制的研究中取得了较大进展,深入研究多元主体参与[13]、多层级制度举措[15]、跨区域地理尺度(外部联系或外部力量)[16]、路径间关系[17]等不同因素对区域发展路径的作用机制,同时亦尝试将不同影响因素整合纳入综合框架进行研究[18,19]。值得注意的是,未来期望视角在演化经济地理学新路径发展的研究中开始受到关注[20],其研究视角突破了演化经济地理学基于历史和惯例的局限,尝试延伸演化经济地理学的时间尺度,但目前鲜见综合期望视角与已有不同要素系统共同探讨中国语境下的区域新路径的发展,更鲜见其在外源型产业新路径发展机理上的研究。
路径创造关注路径本身变化和路径转变的可能性,强调创新主体之间、创新主体与区域情境的互动关系对于路径演化的重要性[21]。那么外源型农业产业在其路径创造过程中各主体之间以及各主体与区域情境(区域内外部资产、制度环境等)之间的关系演进如何作用于新路径发展?在双循环新发展格局下如何有效利用和整合外部市场与资源要素服务于区域产业新路径发展?同时在不同阶段新路径发展的作用机制和资源、要素、市场等的整合内容与利用方式又有何变化?为探讨这些问题,本文在结合已有关于区域内外部联系、多元主体参与、路径创造机制、制度环境等研究的基础上同时考虑未来期望对新路径发展的作用,构建路径创造视角下外源型农业产业新路径发展的分析框架,以永福台湾高山茶产业为例,利用实地调研与访谈数据,从微观层面分析外源型农业产业的路径创造与新路径发展的演化机理,丰富演化经济地理学的新路径发展理论,同时亦为制定乡村农业产业发展政策提供参考。
1 理论基础与分析框架构建
1.1 演化经济地理学与区域产业新路径发展
因此,学者们近期试图从更为广泛的视角讨论新路径的发展,例如对新路径发展进行多尺度、多因素的综合性分析,探讨新路径发展和政策行动的外源性来源[29]、外部知识的引入[16]、多尺度制度动态[15]以及多尺度政策干预[30]等在区域产业新路径发展中的作用。总体而言,区域产业新发展路径的形成是涉及内生与外生力量、多元主体参与、知识与非知识互动和制度变革的多主体、多要素和跨尺度的复杂过程[31]。同时,也正是由于演化经济地理学存在因过于强调区域内生基础与结构、存在单一尺度等局限导致对区域路径发展新现象解释的薄弱,从而出现了与其他领域理论相融合的趋势,包括区域创新系统理论、地理政治经济学、转型研究与期望社会学等[13],如与区域创新系统理论结合理解专业化地区的路径更新和路径创造过程[32]以及区域绿色发展路径的实现[22];与地理政治经济学理论融合提出路径创造的五个关键维度:区域与区域外资产、关键参与者、路径创造机制、市场建设和制度环境[18];与技术创新系统理论结合构建路径创造过程中区域动态与技术特征之间相互联系的框架[33];与全球生产网络理论结合提出更广泛的路径创造演化视角,强调区域资产、关键经济和组织行动者、路径创造机制以及多层次的制度环境和政策举措不同要素之间的动态相互作用[19]。以上成果对演化经济地理学在区域产业新路径发展的研究提供了有益的理论基础与更广阔的视角。
演化经济地理学强调时间和历史对解释区域经济演化与产业新路径发展的重要性[34],但都集中于惯例和历史的影响,对于“未来”的潜在影响却较少涉足,即期望和愿景如何作用于新路径发展尚未清晰[12]。区域过去累积的资产会影响未来产业发展方向,同样对未来的预期亦会影响现在的决策[35]。因此,有学者指出演化经济地理学的实证研究对象倾向于特定的历史发展过程,实际上这种历史研究视角应该拓展到预期和未来方向对参与者策略与活动的影响,即关注期望与愿景在区域产业新路径发展的作用[13,20]。因此,本文基于演化经济地理学关于区域产业新路径发展的研究成果并尝试结合期望社会学的相关理论基础,构建外源型产业新路径发展演化机理的理论分析框架。
1.2 外源型产业新路径发展的理论框架构建
1.2.1 区域与区域外资产
区域资产是区域路径创造的重要基础[19],主要包含五个领域:自然资产(涵盖资源)、基础设施和物质资产、产业资产(包括技术和企业能力)、人力资产(劳动技能、成本和知识)和制度资产(规则、惯例等)[36]。它们在很大程度上反映出地区已有的经济发展形式和模式,代表了区域路径发展在预成型阶段的特征[23]。但这些特征只体现区域内部资产结构,而从全球生产网络理论角度看,区域发展被视为区域资产与全球生产网络“战略耦合”的结果[37],区域内外行动者通过寻求、评估、移植和固定区域外资产以及对旧资产的战略性破坏也可能在新路径发展中发挥关键作用[19,38]。因此了解区域外资产如何影响特定区域新路径发展的形成至关重要,尤其是在其早期阶段[28]。对于外源型产业而言,其在区域新路径创造过程中,本身起着具有联系区域内外的“管道”作用[27],能够将区域外的相关资产引入区域内部,促进区域产业新路径发展。此外,与区域外资产的联系往往对外围和后发地区起着关键作用,因为其有可能通过创造新路径发展使区域实现跃升[39]。因此在区域发展路径创造与演化过程中,区域与区域外资产之间的相互作用是路径创造与演化的重要动力[16,40]。
1.2.2 关键经济与组织行动者
1.2.3 路径创造机制
现有文献认为技术关联性、区域分支(相关多样化)与路径依赖是区域产业演化的主要机制,但有研究指出这一结论存在一定局限性[16,29],其一强调可分化衍生出新产业的区域现有产业与衍生产业之间存在较强的技术关联或相关性[48],其二该结论主要基于发达国家及地区,而后发地区/外围地区并不具备内生产业分化条件,在区域产业分化能力上存在较大困难[49]。针对上述局限,学者们对区域产业新路径发展作出进一步的细分,提出路径扩展、路径革新、路径移植、路径分支、路径创造、路径多样性等概念[50,51]。这些区域新路径发展的不同途径主要基于区域产业演化中路径“解锁”机制,分为五个方面(表1):基于新技术范式的本土路径创建;通过代理、技术、制度和社会网络之间的异质性促进多样性与创新;通过引进和传播新技术、企业或产业进行移植;向相关产业多样化发展;在现有产业基础上升级[52]。这些机制在形成前阶段过渡到路径创建阶段以及随后的路径发展阶段等整个过程发挥着至关重要的作用[23],且不同路径发展的机制在区域内也可以同时存在[13]。
表1 路径创造的五种机制
Table 1
| 新路径的来源 | 特征 |
|---|---|
| 本土创造 | 区域内出现了在该区域没有先例的新技术和新产业 |
| 异质性和多样性 | 当地产业、技术和组织的多样性促进了不断的创新和经济重组,避免了固定结构的锁定 |
| 从区域外移植 | 从其他地方引进新的技术或产业,然后形成区域增长新路径的基础 |
| 向(技术)相关行业的多样化 | 现有产业走向衰落,但其核心技术被重新部署或扩展,为该地区相关新产业提供基础 |
| 现有产业升级 | 通过注入新技术或引进新产品和服务来振兴和加强一个地区的产业基础 |
注:来源于Martin等[
1.2.4 制度环境与政策举措
在演化经济地理学与地理政治经济学的研究中,强调制度和政策在区域产业演化路径与区域新路径发展的作用[30,53]。制度指的是“经济主体之间在规则和法规基础上发展的相关且相对稳定的社会互动”[54]。不同地区的制度安排与政策举措会直接影响外源企业及其外部资源在本地的嵌入程度[55]。近期的研究关注了制度在多层次与跨尺度的作用,认为区域新路径发展既依赖本地独特的制度环境与制度设计,同时也嵌入不同尺度及不同层级的制度体制中[15,56]。制度与产业协同演化是一个跨尺度过程,全球尺度或其他地区产业与制度变化可以影响(促进或阻碍)本地产业与制度,因此需要对不同地区制度与产业的协同演化作跨尺度分析[12,57]。
1.2.5 未来期望
区域行动者的活动和战略是由经验与期望的组合构成,期望与愿景的表达被视为一种重要资源,其能够引导投资和经济活动选择,是理解和解释区域新路径发展的关键[20,59]。期望和愿景有助于吸引潜在的未来技术、促进资源调动、创造合法性、构建创新网络以及建立硬基础设施与软基础设施,并使新行业与监管、规范保持一致性[20,28]。例如在区域行动者寻求、利用区域资产促进路径创造的同时,也参与了一系列合法化实践,其中包括阐明未来区域发展的愿景和期望,进而将自己的诉求与更广泛的政治和经济议程相结合,以吸引更多的资源和支持[60]。此外,期望与愿景对企业(以及其他行动者,如研发机构、政府等)的活动和战略规划产生影响,进而影响路径创造过程的势头、速度与方向[20]。因此,理解区域新路径发展也要面向未来期望,通过融合未来与期望的研究进而延伸演化经济地理学的时间观点[13]。期望被认为是企业或其他主体的战略活动,旨在实现特定目标而开展的活动[20]。鉴于此,本文以企业以及其他关键经济与组织行动者所实现特定的效应(如经济效应、政治效应、社会效应等)为切入视角,分析期望与愿景对区域新路径发展的作用。
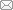
基于以上理论分析,本文结合演化经济地理学与期望社会学的相关内容,构建路径创造视角下外源型农业产业新路径发展演化的理论分析框架(图1)。
图1
图1
外源型农业产业新路径发展
Fig. 1
New path development of exogenous agricultural industry
2 研究设计
2.1 研究区概况与产业选定
20世纪80年代末以来,在海峡两岸逐步开放的背景下,两岸在农业交流合作方面得到进一步发展,而福建省由于与台湾地区在地理上的邻近性,跟台湾的农业交流合作更具优势,其中位于福建省龙岩市漳平市(县级市)的永福镇成为国家级台湾农民创业园核心区。该地平均海拔780 m,年平均气温17.3 ℃,农业种植条件较好,园区目前已成为最大的台式高山乌龙茶生产基地,是海峡两岸茶业合作重点示范基地。
本文以漳平国家级台湾农民创业园(以下简称“台创园”)为研究案例地,以台湾高山茶产业为研究对象,具有较好的典型性与代表性:其一,该台创园成立于2006年,2008年升格为最早一批的国家级台湾农民创业园,并在全国28个国家级台创园发展建设考评中连续五年(2016—2020年)获得第一名,其“大陆阿里山”品牌已成为两岸交流合作的重要品牌之一。其二,截至2021年,台创园共入驻台企82家,台湾茶农、花农600多人,是台资农业个体在大陆投资最密集的区域,台湾高山茶种植面积达5.5万亩(1亩≈667 m2),年产茶1600多t,产值8亿元,2022年园区共接待游客近30万人次,实现旅游收入近亿元。依托园区的建设与产业的发展,近年来台创园被评为“全国十大赏樱基地”“中国最美樱花胜地”“全国休闲农业与乡村旅游示范点”,也是首批“全国绿色食品一二三产业融合发展示范园”。其三,台湾高山茶产业自20世纪90年代末在永福兴起至今经历了从无到有再到多元化发展的发展历程,选择这一案例能够脉络清晰地分析其通过路径创造促进新路径发展的演变进程。
2.2 研究方法与资料来源
研究实证数据主要来自对地方政府相关部门、台商茶企与龙岩文化旅游发展集团有限公司(龙岩市属国有企业之一,以下简称“国企”)的深度访谈和实地调研获得的第一手数据,采用质性研究的方法分析永福台湾高山茶产业的新路径发展机理。访谈与实地调研分为三个阶段,第一阶段在2021年7月对漳平市农业农村局、漳平市住房和城乡建设局、漳平市永福镇政府、漳平台湾农民创业园区管理委员会、漳平闽台缘高山茶产销专业合作社及1家代表性永福台湾高山茶企业进行访谈,与政府相关部门的访谈主要围绕永福台湾高山茶产业发展的规划和相关政策等,重点关注台创园发展现状及本地各级政府对永福台湾高山茶产业的政策扶持情况;第二阶段和第三阶段分别在2022年1月和7-8月对15位永福台湾高山茶代表性企业家(其中第一家落地企业用初创企业指代,其余企业用企业一、企业二等依次指代)及国企负责人进行访谈,了解企业发展历程、产品市场情况、企业发展困境与需求、国企与台企的合作情况以及企业未来发展规划等。统计数据以及相关文字资料主要来自政府相关法规、文件、统计资料以及海峡两岸农业合作网。
3 永福台湾高山茶产业新路径发展演化研究
3.1 第一次新路径发展演化:永福台湾高山茶产业的从无到有
3.1.1 “闲置”资产与“稀缺”资产的整合
在20世纪90年代,永福的反季节蔬菜种植是其农业主导产业,其中就包括芥末的原材料——山葵的种植(台湾阿里山地区是山葵与台湾高山茶的主要种植地,两者的种植条件相似),这说明永福独特的纬度位置与山地环境,形成了与阿里山类似的自然条件,也反映出永福具有丰富的自然资产与一定的产业资产。永福的山葵种植成为第一代台湾高山茶企业落地的依据(据永福台湾高山茶初创企业的访谈)。与此同时,拥有丰富农村剩余劳动力资源也十分适合典型劳动密集型产业的高山茶生产,永福当时处于“闲置”状态的丰富土地资产和人力资产也为台湾高山茶的种植提供了本地先决条件。“当时荒山每亩地租2元,小工一天20元,制作一斤高山茶种植成本200元左右,在台湾制作相应成本在800~1000元之间”(永福镇政府官员)。
两岸在文化上的同根同源能够为台商在大陆的投资带来便利。除了地域上的邻近,文化与社会的邻近性是永福特殊的本地资产,如语言与习俗的相同,社会关系网络的作用等能够促进两地间的交流,因此两地间非正式制度的“厚度”也是其重要的资产之一。初创企业曾到越南等东南亚地区考察,尽管在东南亚地区的劳动力成本低于永福,但永福与台湾在文化与社会上的邻近性对台商更具吸引力,由此促成台商在永福投资(据永福台湾高山茶初创企业的访谈)。因此,永福本地丰富的自然资产、人力资产以及深厚的非正式制度资产为引入稀缺的台湾高山茶产业、生产设备、资金与技术奠定了区域基础。两者的资产整合能够实现两地的资源优势互补,从而促成台湾高山茶在永福的从无到有。
3.1.2 企业与政府的双驱动
在永福台湾高山茶产业的新路径发展中,企业是变革的关键因素,对路径的早期发展产生了重大影响。一方面,台商茶企在寻求、评估与利用区域内外资产时企业家精神的发挥对永福产生“创造性破坏”,通过对当地“闲置”资产进行开发与利用,使永福出现新的发展路径;另一方面,企业家的到来与初创企业的成立扮演着吸引区域外其他企业的“磁石”角色,通过社会关系网络及其示范效应,促使集聚作用与自增强机制得以发挥,进而促进永福台湾高山茶产业的成长。“老板(初创企业)是南投(县)人,南投是重要茶区,他第一个进来之后,通过与他有销售联系的台商进一步扩大这一信息,然后引导其他台商陆续进来,2004年进来的最多”(永福台湾高山茶企业一、二)。
此外,台商企业家同时也是永福台湾高山茶产业路径合法化的主动力量,其在永福承包的当地土地通常拥有30~50年的土地使用权,这也是台商企业家获得合法与稳定经营的基础。
在永福台湾高山茶产业发展过程中,不同层级的政府自上而下的作用不可忽视,其在招商引资、管理与服务等方面起着重要作用。以国家级台湾农民创业园的发展历程为例,当永福台商集聚到一定规模时,为更好地实现台商茶企的在地化,其首先受到龙岩市政府的高度关注与建设,而后成立省级台湾农民创业园直至提升为国家级台湾农民创业园,并设立台创园管委会,为永福台湾高山茶产业进一步发展设立支持性平台。这种“筑巢引凤”的建设模式能够更好地“以台引台”,吸引台商台资落地,同时通过推荐台商在管委会担任职务这一重要实践创新使得永福台湾高山茶产业发展在政府层面亦具合法性(据台创园管委会官员访谈)。
因此,在两岸交流合作的背景下,企业与政府是永福台湾高山茶产业新路径发展的关键行动者和路径倡导者,他们以各自不同的方式和手段影响新路径发展的速度与方向。
3.1.3 台湾高山茶产业的移植
从战略耦合[61]的角度看,无论是区域内资产还是区域外资产,本身并不是区域新路径发展的充分条件,而需要关键行动者通过路径创造机制的选择及其与已整合资产的耦合实现区域新路径发展。永福台湾高山茶产业是基于台湾高山茶产业的移植而形成的。在台湾,高山茶的主要产区在南投县,其茶叶种植技术先进,产业管理体系完善。来自南投县的初创台商企业负责人将台湾高山茶产业移植至没有植茶历史的永福,产业的移植是永福台湾高山茶产业早期阶段的主要路径创造机制。“这些茶山的茶树刚开始都是从台湾来。茶叶无性繁殖很快,等长大再剪枝,经过两三年就形成一大片”(永福台湾高山茶企业一、三)。虽然对永福本地而言,高山茶产业的出现主要是台商企业利用本地廉价劳动力与自然禀赋的结果,属于低级的依附式耦合,并未实现互惠式耦合以及更高层次的自主性耦合,由于低级依附性耦合的“弱根植性”,本地区域处于弱势地位,但台商茶企将台湾本地发展成熟的高山茶产业成功移植到永福,永福的“闲置”资产得以利用,同时也促进了企业在永福的根植与生产网络的在地化。
3.1.4 开放的制度环境及两岸关系的缓和
改革开放之后的一系列政策制度的实施,促使中国经济的全球化、市场化与分权化的过程创造了市场力量,激活了地方力量,引入了全球力量[62]。以上三个过程的共同作用为台湾高山茶产业在永福的根植创造了包容性的制度环境,促进外源知识在本地的积累,从而实现永福台湾高山茶产业新路径的创造与发展。此外在土地制度方面,根据国家法律规定(《中华人民共和国宪法》《中华人民共和国土地管理法》),农村土地原则上归农民集体所有,且土地使用权可以依法转让,同时《中华人民共和国农村土地承包法》规定林地的承包权期限可达三十年至七十年,这为台商依法获得土地使用权及长久合法经营提供制度上的保障。
两岸关系在永福台湾高山茶产业的形成中也具有特殊意义。20世纪80年代以来,在“海协会”与“海基会”的协商中促成了“九二共识”的达成与两岸“三通”(通邮、通商、通航)的逐步开放,两岸关系趋于缓和,同时出台一系列政策措施鼓励与支持两岸经济交流合作,如1988年《关于鼓励台湾同胞投资的规定》与1994年《中华人民共和国台湾同胞投资保护法》的出台等,台商直接投资成为改革开放初期重要投资来源之一。永福台湾高山茶产业正是在此契机下形成的。
3.1.5 经济效应、社会效应与政治效应
台湾在20世纪80年代开始,茶叶需求量增大,但受工业化进程影响导致其茶园面积缩小,同时劳动力与土地成本升高,台湾茶叶生产出现向外迁移趋势。福建与台湾在地理上的邻近,相似的自然禀赋与文化社会特征成为承接台湾茶产业的最佳区域之一,台商企业家的社会责任感与乡土情怀也在某种程度上驱动着企业家返乡投资家乡。“当初我爷爷回到家乡,看到这么落后,就建议我父亲回来投资建设家乡,这里适合种茶成立了这家企业”(永福台湾高山茶企业四)。因此永福台湾高山茶产业新发展路径的产生,不仅仅是经济利益驱动着企业家寻求创业之地,同时也带有建设与回报家乡的美好期望和社会情怀。
从区域本地层面来看,永福台湾高山茶产业属于劳动密集型产业,其在永福的落地产生明显的社会效应,表现在能够解决当地剩余劳动力,为农民创收,从而逐步实现地区的脱贫。此外,由于两岸的特殊关系,永福台湾高山茶产业在促进两岸经济交流与合作方面也具有示范作用。因此,从区域本地或政府层面的期望角度看,台湾高山茶产业在永福的落地,兼具经济、社会与政治效应的驱动。
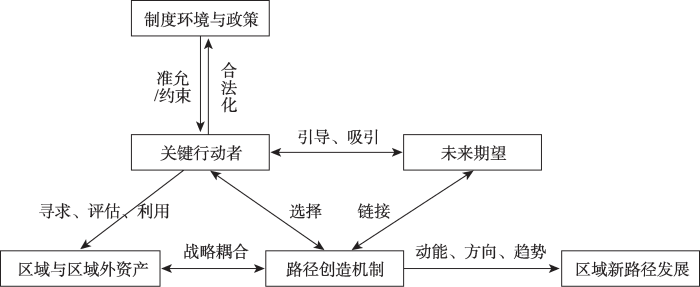
总体而言,永福台湾高山茶产业第一次新发展路径的产生是以下因素共同作用的结果:在改革开放及两岸关系缓和的背景下,受经济、社会与政治效应驱动,台商茶企利用永福本地的“闲置”资产与本身所具有的优势进行整合,将台湾高山茶产业发展经验移植并复制到永福;同时在这过程中,地方政府也起到了重要的推动作用,从而实现永福台湾高山茶产业从无到有的发展过程(图2)。永福台湾高山茶产业的第一次新路径发展虽然仅仅是初级阶段的依附式耦合,但其“在地化”的过程实现了产业的专业化与规模化发展。
图2
图2
永福台湾高山茶产业的从无到有
Fig. 2
Yongfu Taiwan High Mountain Tea Industry from scratch
3.2 第二次新路径发展演化:永福台湾高山茶产业的从一到多
3.2.1 区域内外资产的再整合
在永福台湾高山茶产业的第二次新路径发展演化中,要素配置得到重构与升级,区域内外部资产得以再整合,实现更深层次的融合发展。其中区域内部资产主要表现在以下几个方面:(1)在产业资产上,高山茶产业已形成一定规模,成为区域内的重要资产。产业发展所需资金来源也更加多样化,不仅来源于台商投资,还来源于本地,如政府支持、银行贷款、本地企业(国企)的参与等。(2)在人力资产上,本地劳动力已积累一定的生产技术与管理经验,劳动力水平与素质得到提高,能够深度参与永福台商企业的生产与管理。(3)在制度资产上,台商在永福深耕多年,当地的熟人网络基本形成,更加根植于当地的社会网络,并以此逐步打开了本地市场。(4)在基础设施与物质资产上,一方面表现在道路等基础设施的完善,另一方面生产设备的本地化供应,不再依赖于外部资产来源。“机器刚开始都是从台湾运过来,后来采用台商在本地生产的设备,现在也有采用大陆本地企业生产的设备”(永福台湾高山茶企业三、五)。
在区域外资产方面,一方面是台湾休闲农业发展经验的传入,使永福台湾高山茶产业开始走向多元化发展道路;另一方面是青年台商的参与,主要表现在台二代、台三代的接班,“子承父业”的家庭经营模式特征明显。产业的多元化发展及经营的代际传承为区域内外部资产的再整合提供途径,也能够保证经营的连续性,从而为永福台湾高山茶产业的持续发展注入活力。
3.2.2 企业、政府与国企的三方驱动
在永福台湾高山茶产业的第二次新路径发展演化中,企业仍然起到重要作用,一是表现在龙头企业的示范与带动作用,其在永福台湾高山茶产业基础上结合台湾休闲农业发展经验,实现永福台湾高山茶多元化发展路径,例如通过茶园套种樱花形成生态旅游观光茶园,既优化茶园生态环境又带动休闲农业发展。另一方面是台二代、台三代的继承与发展,目前已入驻台湾青年近百名,台湾青年创办企业近30家,负责台企管理或担任高管职务的台湾青年20多名,被授予国家级“海峡两岸青年就业创业基地”“台湾青年产业融合创业示范基地”、省级“台湾高校学生农业教学实践基地”“台湾青年就业创业基地”。台湾青年在原有的茶产业基础上引入新技术发展多种产业形式,如茶叶+观光休闲、电商、文旅、研学等,推动永福台湾高山茶产业的结构升级。此外,由5位永福台商企业参与制定的《台式乌龙茶》《台式乌龙茶加工技术规范》两项国家标准在2021年6月正式颁布实施,这意味着在台商推动下永福台湾高山茶产业的合法化发展获得更为权威的支持,帮助永福台湾高山茶产业的发展在市场中更具主动权。
相较于前期的重视平台建设,政府在永福台湾高山茶产业的第二次新路径发展演化过程中服务功能更为突出。“服务型”政府的积极有为使政府与企业的联系更为紧密,一是表现在完善基础设施建设方面,为推动永福台湾高山茶产业发展提供基础支撑。“我们道路硬化,都是政府提供的。还有节水灌溉、农械购买补助等,能够补一半金额”(初创企业)。二是表现在充当永福台湾高山茶产业的“推广员”角色,如与高山茶产销合作社一起举办“永福杯”台式乌龙茶茶王赛等赛事以加强台商企业间的交流,提升制茶技术,同时促进永福台湾高山茶的品牌营销,扩大永福台湾高山茶产业的市场知名度。
此外,国企与台企于2018年达成合作意愿,共同开发台品樱花茶园,并在原有基础上扩大规模。“我们当时投资台品时樱花园游客已经稳定了,第一期投了约1500万,建了人行天桥,停车场,游客服务中心,人工湖夜景等”(国企管理人员)。相比于一般企业,国企与政府间的紧密联系对新产业发展路径的合法化更具能动性作用,更容易动员地方政府与其他不同层级组织的协商(如对村集体土地的征收、村委与村民的荒山迁坟协商等)以此获得更多主体的支持,同时本地专业旅游企业拥有丰富的本地市场资源,有助于永福台湾高山茶产业品牌的营销与市场的开拓。
3.2.3 路径创造机制的多元化
永福台湾高山茶产业多种路径的发展得益于路径创造机制的多元化。一是台湾休闲农业发展经验的移植,复制阿里山休闲观光模式,同样以樱花、火车等观光娱乐形态出现;二是相关产业多样化的实现,如种植本地茶叶——漳平水仙茶,“现在本地的漳平水仙茶效益还可以,所以也有种植一些”(永福台湾高山茶企业一);三是产品异质性与多样性,除原有以软枝乌龙与金萱为主的传统品种,还发展出茉莉乌龙茶、桂花乌龙茶等特色新品种;四是现有产业基础的升级,主要形式有观光工厂、文旅融合等产业链延伸,同时也向电商模式拓展,实现销售模式的多元化,“我06年过来的,一开始是想卖奶茶的,但是我们想茶叶自己种,所以才拿这个基地种植高山茶,想把台湾小吃、奶茶、茶叶融合,如果融合成功,我们就大力推广”(永福台湾高山茶企业六)。由此可见,永福台湾高山茶产业第二次新发展路径的实现,是移植、相关产业多样化、产业基础升级等多种路径创造机制共同演化的结果。
3.2.4 制度与政策的支持及两岸关系的紧张
近年来休闲农业与乡村旅游成为乡村振兴的重要支点并出台了一系列相关支持性政策,如2018年中央一号文件《关于实施乡村振兴战略的意见》与《乡村振兴战略规划(2018—2022年)》相继发布,提出构建农村一二三产业融合发展体系,推动农村产业的深度融合;同年,国务院办公厅在关于促进全域旅游发展的指导意见中指出推动旅游与农业、林业等融合发展,大力发展观光农业、休闲农业。此外2021年乡村振兴促进法的实施与2022年中央一号文件再次强调全面推进乡村振兴。这一系列关于促进乡村振兴战略的意见与措施,为永福台湾高山茶产业的多元化路径发展提供了制度与政策的支持。
进入新时代以来,深化两岸融合发展是当前大陆对台工作的政策主轴。积极推进两岸经济合作制度化,打造两岸共同市场仍是当前两岸融合发展的目标之一。在司法与金融保险等方面也给予大力支持,如龙岩市漳平台湾农民创业园区人民调解委员会、龙岩市中级人民法院“涉台司法服务工作站”以及漳平台湾农民创业园司法服务中心在园区的陆续成立,为调解台资企业矛盾纠纷提供更完善的司法服务;2020年台创园管委会促成闽台缘产销专业合作社与中国人寿财险龙岩市中心支公司签订万亩茶园茶叶低温指数保险项目合作协议,有效保障了台商茶农的经济利益。“当初没有贷款政策,这个政策差不多是11年、12年出来的,可以用茶树抵押贷款,但茶树抵押贷款一家公司也贷不多”(永福台湾高山茶企业三)。“当时没有贷款,资金都是从台湾汇过来的,这几年就有贴息贷款支持了”(初创企业)。在农业产业多元化发展、两岸融合、司法与金融保险等不同制度层级给予永福台湾高山茶产业制度与政策支持,有效促进了永福台湾高山茶产业与制度的协同发展。
外源型农业产业的发展不仅受当地制度与政策环境的影响,同时也受到来源地政治环境的影响。自蔡英文上台以来两岸关系趋于紧张[63],大陆地区的农产品难以进入台湾,永福台湾高山茶产业需经第三方市场进行转口贸易(通常经东南亚国家)才能进入台湾市场。同时在新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情冲击下,进出口贸易受到阻滞,旅游业也受到较大影响。永福台湾高山茶产业在受到政治环境与疫情的双重冲击下,就短期来看,永福与台湾两地的联系与贸易往来都受到明显影响,造成区域间网络的局部断裂,不利于两者的长久发展。但这一背景反而促进了永福台湾茶商本地市场的开拓,加速区域内市场网络的构建以推动区域内外多尺度市场网络达到新的空间平衡。近几年在大陆市场的销售占比大幅提高,总体达70%~80%左右,仅个别企业仍以台湾市场为主,部分企业的产品已完全在大陆市场销售。
3.2.5 经济效应、社会效应、政治效应与生态效应
自2012年党的“十八大”以来,乡村振兴战略和生态文明建设成为农业发展的主基调。在此背景下,永福台湾高山茶产业利用休闲农业与乡村旅游实现第二次新路径的发展,一方面借鉴台商“精致农业”的理念促进农业现代化,另一方面通过产业链的进一步延长促进乡村振兴以实现城乡融合。“比较大的台企,(在采茶季的时候)工人量大概在300~500人,现在一年的工资量大概就要600万~800万元”(台创园管委会官员)。“跟台商合作,对方很强调生态要保护,不会轻易同意在茶园增加一些设施(如民宿)”(国企管理人员)。与此同时,国企与永福的合作对于两岸融合发展具有重要的推动和示范作用,并对当地基础设施的完善也起到重要的帮助。“这里包含社会效益,如果做好了,永福的面貌改变,就是我们最大的成绩”(国企管理人员)。永福台湾高山茶产业向休闲旅游方向拓展的第二次新路径可以说是在生态、经济、政治与社会等多种效应驱动下的结果。
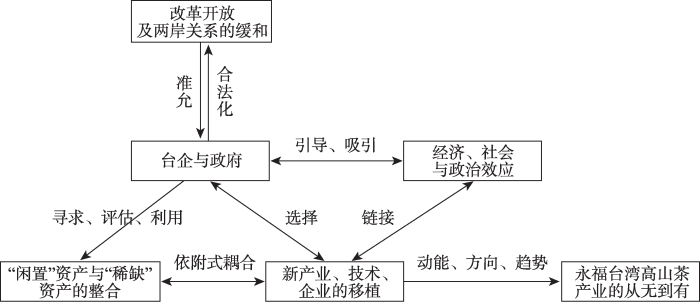
总体而言,永福台湾高山茶产业第二次新发展路径的产生是以下因素共同作用的结果:在改革开放与乡村振兴的背景下,台商茶企将区域内外的资产进行再一次整合,将台湾休闲农业发展经验移植永福的同时,相关产业多样化、现有产业升级以及产品多样性等多种路径创造机制也作用于永福台湾高山茶产业。同时在当前两岸关系及疫情的影响下,永福台商积极开拓大陆市场,区域内市场网络的构建进程加快,推动永福台湾高山茶产业的市场网络达到新的空间平衡。此外政府的助推作用以及国企的加入,也为实现永福台湾高山茶产业的第二次新路径发展起到了重要作用。在实现原有经济、社会与政治效应的基础上,生态效应逐渐显现(图3)。永福台湾高山茶产业的第二次新路径发展通过“再地化”实现了更高层次的合作式耦合,产业模式从原来的单一化转变为更为多样化的形态。
图3
图3
永福台湾高山茶产业的从一到多
Fig. 3
Yongfu Taiwan High Mountain Tea Industry from one to more
综上所述,永福台湾高山茶产业的发展过程中经历了两次路径创造与发展,而两次新路径发展的关键要素存在显著差异(表2),第二次的新路径发展是在第一次新路径发展基础上进行的,相比于第一次的新路径发展,第二次新路径发展的关键要素构成更为多样化与复杂化。
表2 永福台湾高山茶产业新路径发展的比较
Table 2
| 第一次新路径发展 | 第二次新路径发展 | |
|---|---|---|
| 区域与区域外资产 | 自然资产:典型的山地与气候条件 产业资产:反季节蔬菜(山葵)的种植 人力资产:丰富的廉价劳动力 制度资产:文化与社会上的接近 基础设施与物质资产:土地 外部资产:高山茶种植知识、资金、茶苗、技术型与管理型人才、先进生产设备 | 自然资产:典型的山地与气候条件 产业资产:高山茶产业、资金 人力资产:廉价劳动力、本地管理人员 制度资产:文化与社会上的接近、熟人网络 基础设施与物质资产:土地、道路、生产设备 外部资产:资金、休闲农业发展模式、青年台商(台二代、台三代) |
| 关键经济与组织行动者 | 台商企业、政府 | 台商企业(台湾青年)、政府、国企 |
| 路径创造机制 | 新技术、企业和产业的移植 | 移植、相关产业多样化、异质性与多样性、现有产业升级 |
| 制度环境与政策举措 | 国家层面:改革(市场化、分权化)与开放(全球化) 地方层面:招商引资、平台建设 政策环境层面:鼓励台商到大陆地区发展与促进两岸合作及两岸“三通” | 国家层面:改革开放、乡村振兴 地方层面:招商引资、平台建设、服务功能 政策环境层面:两岸融合发展及两岸关系的紧张 |
| 未来期望 | 企业层面:获取经济利益、返乡投资(经济与社会效应) 政府层面:脱贫攻坚、两岸交流合作(经济、社会与政治效应) | 企业层面:获取经济利益、返乡投资(经济与社会效应) 政府(国企)层面:乡村振兴、两岸融合发展(社会、政治、经济与生态效应) |
4 结论与讨论
4.1 结论
本文融合演化经济地理学与期望社会学理论,以永福台湾高山茶产业为例,以路径创造视角探讨外源型农业产业新路径发展的演变机理,从区域内与区域外资产、关键经济与组织行动者、路径创造机制、制度环境与政策举措、未来期望等五个维度进行分析,并强调未来期望因素对外源型农业产业新路径发展的重要价值。永福台湾高山茶产业两次新路径发展的案例反映出:(1)外源型农业产业新路径发展的实质是区域内外资产的不断匹配重组与升级,关键行动者的多主体参与(本地主体的逐渐参与),路径创造机制的多元化,制度与政策环境的多尺度变革(同时受地区间的横向尺度和区域内不同层级纵向尺度的影响),经济、社会、政治、生态乃至文化不同期望效应间相互呼应的多维度综合作用的结果。(2)将未来期望视角纳入研究框架,探讨关键经济与组织行动者所实现特定效应对区域发展路径的影响,丰富现有演化经济地理学关于区域新路径发展的视角。(3)永福台湾高山茶产业从“在地化”到“再地化”、从“依附式耦合”到“合作式耦合”不断深化的过程为外源型农业产业实现产业兴旺和乡村振兴提供了一种可能的路径。此外,针对外商直接投资存在“弱根植性”“松脚性”等问题,路径创造视角下的产业新路径发展能够为破除根植性不足和减少路径依赖带来的负面影响提供理论新解与案例实证。
4.2 讨论
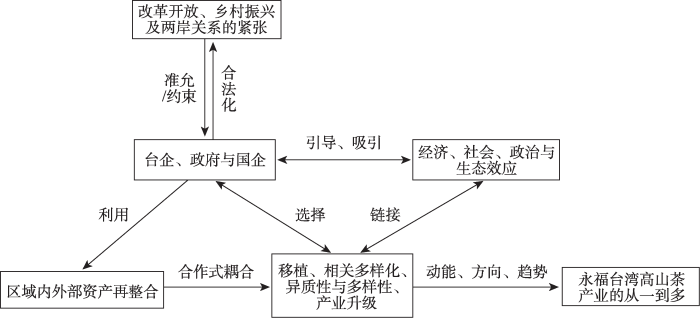
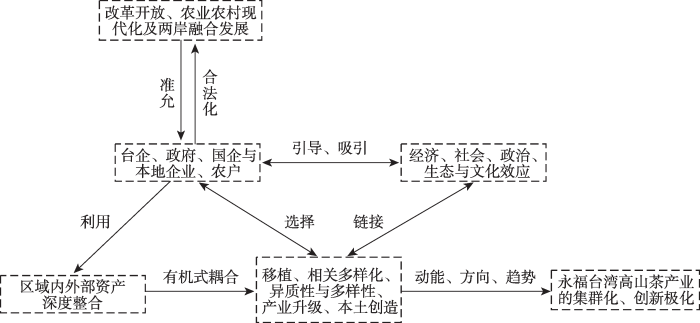
因地制宜、因时制宜结合乡村资源禀赋和发展基础,有助于明确乡村振兴愿景,制定乡村振兴路径[7]。对永福台湾高山茶产业的未来愿景与路径进行初探(图4):(1)永福台湾高山茶产业是通过与区域外的外部资产建立联系,从而为区域内外部资产的整合提供途径。区域内外部资产的整合过程是外部资产逐渐转化为内生资源的过程,但至今为止本地尚有丰富的资产待挖掘待整合,如与永福本地发展成熟的花木产业资产进行产业间的合作(如茶园与本地花木的搭配、樱花茶园与本地旅游景点的线路规划等)以及利用其成熟的市场网络等,亦是永福台湾高山茶产业未来进一步发展的有益探索。(2)永福台湾高山茶产业的关键参与者仍然集中在企业(台企与国企)个体层面,未来应考虑不同经济主体的参与互动,尤其加强与本地企业、农户层面的联系,促进不同尺度和层级的多主体协调共生能够与本地产业、企业共同构成产业生态系统,从而实现产业的集群化发展。此外,与相邻地区的同行业集群的正式与非正式交流亦有助于集群间的共位发展[9]。永福台湾高山茶产业和邻近的本地漳平水仙茶的交流与合作能够加强本地网络的根植,强化产业发展的能动性。(3)永福台湾高山茶产业从第一次新路径发展的单一移植到第二次新路径发展实现了路径创造机制的多元化,但仍局限在其产业(移植、相关产业多样化、现有产业升级)或技术(异质性与多样性)本身,未能与本土创造元素结合在一起,即其创新能力对区域内部的溢出效应仍显不足,这需要产品、技术、制度、组织和空间的协同创新,形成农业创新体系,实现向“创新极”的转变[4],而其中关键是本地企业与农户的参与进而通过深度整合区域内外资产实现有机式耦合从而实现本土创造。(4)永福台湾高山茶产业作为外源型农业产业,其产业的发展受来源地与本地制度的双重影响。在本地制度层面,仍需坚持改革开放以及加快推进农业农村现代化发展,为永福台湾高山茶产业在本地的发展保驾护航;在两岸关系层面,应推动两岸实现经济、社会、文化等全方位的融合发展。同时,在当前双循环背景下,积极开拓国内市场,构建区域内市场网络,减小外部环境冲击所带来的不确定性。(5)文化振兴是乡村振兴的重要内容之一[64]。据考证,台湾高山茶是在明朝由福建引入台湾的,如今再次回到福建,这其中蕴含丰富的历史渊源与文化底蕴。此外在台湾,台湾奶茶与台湾小吃等饮食文化结合茶文化方面也具有一方特色。因此如何讲好茶叶故事并融合台湾文化发挥文化效应,实现文化上的再一次赋能是永福台湾高山茶产业新路径发展未来需要考量的。
图4
图4
永福台湾高山茶产业的集群化与创新极化
Fig. 4
The clustering and innovation polarization of Yongfu Taiwan High Mountain Tea Industry
个体案例的研究具有特殊性。永福台湾高山茶产业的特殊性一方面在于两岸逐步开放背景下的两岸关系,两岸关系很大程度上影响着产业是否能与制度协同发展;另一方面在于来源于台湾的农业产业可能具有一定的特殊性,尤其表现在闽台文化与社会上的邻近性,这与一般外源型农业产业的特性不尽相同。本文的研究仅是一个案例管窥,仍需更多相关实证研究加以验证和予以丰富。
参考文献
农业结构调整与中国乡村转型发展: 以河南省巩义市和鄢陵县为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.013
[本文引用: 1]

农业转型升级是中国乡村转型发展的主要引擎。而规模化、专业化生产是国际农业转型升级的方向。本文以两个不同乡村转型道路的典型县域(工业化转型的巩义市和农业现代化转型的鄢陵县)为例,利用区位熵、结构变化指数和专业化指数,在乡镇尺度深入分析新世纪以来乡村经济转型发展背景下乡村农业结构调整状况,以及由此带来的乡村景观再造。主要结论为:①基于市场需求的农业结构调整与乡村转型之间的相互作用是农产品提质增效倒逼耕地利用方式的现代化转变,并引致乡村景观的多功能再造。未来中国农业的转型方向将是规模化大宗农业与专业化精细农业并存;②无论是乡镇的非农化转型还是农业现代化转型,均可带来乡镇耕地的规模化、专业化利用以及农业内部的结构调整,并引致乡村的进一步转型。工业转型县农业结构以粮食作物为主要调整方向,农业现代化转型县以粮食和特色农作物为主要调整方向,并形成了特色专业村或产业集群;③农业结构调整方向更加与自然条件和资源禀赋相匹配,空间配置更加合理。
Agricultural structure adjustment and rural transformation development in China: Taking Gongyi city and Yanling county as examples
农业生产转型及其环境效应的研究进展与展望
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220703
[本文引用: 1]

农业绿色转型已经成为乡村振兴与农业农村深化改革的关键路径,亟待探索农业生产转型与其环境效应的耦合关系与机制,从而推进农业的高质量发展。近年来,学者们基于不同的空间尺度,对农业生产转型及其环境效应的过程、格局、机理与优化调控开展了广泛探讨。为系统梳理该方面研究的相关进展,识别出相应的研究不足,本文采用文献分析与系统归纳相结合的方法,分析了农业生态环境问题的识别、测度与成因等方面的研究态势,从关键要素的视角解析了农业生产转型对生态环境影响的研究进展,并对农业经济增长与农业面源污染和农业生产转型与农业生态效率的相互关系进行了总结。研究指出:未来农业生产转型及其环境效应研究应加强从系统科学的视角解读二者的互馈关系,并关注二者互馈响应的区域异质性,深化基于土地系统科学视角的耕地利用转型的环境影响研究,通过多学科交叉融合加强对中国特色“小农”生产方式转型所引发的环境问题的微观机理探析。
Agricultural production transition and its environmental effects: Research progress and prospect
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220703 URL [本文引用: 1]
农业产业集群的演化阶段与形成机理分析: 以宁夏中宁县枸杞加工产业为例
Formation mechanism and evolution stage of agricultural industrial cluster: A case of medlar products processing industry of Zhongning county
中国农业产业集群演化过程及创新发展机制: 以“寿光模式”蔬菜产业集群为例
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.04.014
[本文引用: 2]

在对农业产业集群理论探讨的基础上,以山东寿光蔬菜产业集群为例,分析中国农业产业集群形成演化的“四阶段”模型及可持续创新发展的内在机制,并挖掘了“寿光模式”的“集群”本质。结论表明: ① 中国农业产业集群的形成与创新发展:首先是从农业产业集聚开始,并经由专业村到产业集群,再到乡村创新极演化; ② 促进农户的企业化演变是农业集群及其创新体系形成的第一步。创建产业网络是农业产业集聚和专业村向农业产业集群升级的必备步骤,农业创新体系的形成标志着农业集群走向成熟; ③ 山东寿光蔬菜产业集群的形成演化也经历了这4个阶段。各类各层主体通过知识增长、知识流动和知识采纳提高自己的内生能力和外部契约关系,并通过知识和创新网络实现五大维度上的协同创新,一起促进企业(农户)、产业(网络)、技术、制度和空间“五位一体”的协同演化,是农业集群可持续创新发展的内在机制。
The formation, evolution and innovative development of agricultural clusters in China: Case of the cluster nature of "Shouguang Mode"
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.04.014
[本文引用: 2]

As a new tool of global agricultural transformation, agricultural cluster has become an important strategy for developing countries to revitalize rural areas and integrate into agricultural global value chain. China has also been promoting the construction of the industrial clusters with advantages. However, the existing literature is not enough to discuss the theory of agricultural industrial cluster with Chinese characteristics. On the basis of theoretical analysis of agricultural cluster, taking the vegetable cluster in Shouguang, Shandong as an example, this article discusses the "four-stage model" of the formation and evolution and the sustainable innovative mechanism of Chinese agricultural industrial cluster. The conclusion shows that: 1) The formation and innovative development of agricultural cluster starts from agricultural agglomeration, specialized village to the industrial cluster and then to the rural innovation pole; 2) It is the first step for the formation of agricultural cluster and its innovation system to promote the transformation of farmers into enterprises. The establishment of industrial network is a necessary step for agricultural industry agglomeration and the upgrading of specialized village to agricultural industry cluster. The formation of agricultural innovation system marks the maturity of agricultural cluster; 3) The formation and evolution of Shouguang vegetable cluster in Shandong has also gone through 4 stages. The knowledge growth and knowledge flow within the cluster improve the endogenous ability and external contractual relationship of enterprises or farmers, promote the collaborative evolution of enterprises (farmers), industry (network), technology, system and space, and realize collaborative innovation in five dimensions, which is the internal mechanism of sustainable innovative development of clusters.
基于生命周期阶段的农业产业集群形成和演化机理分析
Analysis on the agriculturai industry's cluster composing on lifecycle stage and evolvement mechanism
农业型专业村地域类型分化特征及对乡村产业振兴的启示: 以广东省为例
The differentiation characteristics of regional type of agricultural specialized villages and comprehensive enlightenment to the revitalization of rural industry: A case study of Guangdong province
新时代中国乡村振兴: 探索与思考: 乡村地理青年学者笔谈
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190417
[本文引用: 2]

乡村振兴是新时期国家重大战略,是一项系统工程。中国地域广阔,资源禀赋和经济发展区域差异显著,乡村振兴路径需要体现乡村发展的综合性、复杂性和区域性。来自乡村地理学领域的16位青年学者,以笔谈方式,对中国乡村振兴的科学路径开展了深入讨论。核心观点如下:(1)乡村振兴需要遵循时空分异规律,重点关注乡村发展的时空传承与现实需求之间的衔接,建立彰显地域特色和具有可操行性的理论和技术体系,分类、有序地推进乡村的人居环境、产业体系、生态环境和治理模式等转型。(2)力求城乡融合和联动,构建城乡复合多中心网络体系,创新采用“乡村群”空间组织模式,以乡村内生力、城镇辐射力与规划约束力共同驱动乡村振兴。(3)在中国“大国小农”的基本国情下,农业承载着食品安全、社会稳定和生态产品等多重功能,需要构建农业“全价值链”的发展路径,促进一二三产业深度融合,助力乡村产业兴旺。(4)在能源富集区,在保障国家能源安全需求前提下,需从根本上解决农村发展不平衡不充分问题;在西南地区,依托山区特色生态、人文资源打造山区现代农业产业体系、重塑乡村旅游新品牌、构筑山水田园乡村家园;在东北地区,乡村振兴应与“东北振兴”战略协同推进,有序分类推进;在长三角地区,应在全面认知乡村工业化到乡村城镇化,再到乡村特色化,到乡村的社会、文化和生态建设的阶段演化特征基础上,寻求差异化的乡村振兴路径;在西北地区,应在生态保护的前提下有效提升乡村“自主脱贫”的能力,实现从“输血”扶贫向“造血”扶贫转变;在京津冀地区,需以城乡基本公共服务均等化为目标,推动城乡融合与乡村振兴;在资源型地区,乡村振兴核心将以一二三产业融合的高效农业体系替代以资源开采为核心的产业体系;在传统农区,优化耕地利用转型同农村劳动力结构变化的耦合格局是实现乡村振兴的关键;在经济发达地区,具有“混杂性”特征的乡村,需激活农村土地资源的资产和资本属性,推进空间有序整合与活化,寻求多主体共同参与和缔造的现代乡村治理模式。
Discussions and thoughts of the path to China's rural revitalization in the New Era: Notes of the young rural geography scholars
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190417
[本文引用: 2]

The rural revitalization, as a national strategy in the new era, puts forward the requirements and goals of the thriving industry, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance and prosperity. China is a country with a vast territory, marked by regional differences in resource and economic development levels. What's more, rural areas are complex, diverse, and have many problems. Rural revitalization is a systematic project with comprehensive, complex and regional characteristics. Sixteen young scholars in the field of rural geography across the country have conducted in-depth discussions and reflections on the scientific path of rural revitalization in China. The core points are as follows: (1) In accordance with the law of time-space distribution, we should fully understand the connection between the historical basis of rural development and the practical needs, establish a theoretical and technical system that highlights regional characteristics and has operability, and promote the transformation of rural residential environment, industrial system and governance mode in a classified and orderly manner. (2) Rural revitalization strives for the integration between urban and rural areas to build a compound multi-center network system, which breaks through the village and town systems of traditional linear "central place", and innovate the spatial organization mode of "village cluster". Rural endogenous force, urban radiation force and planning binding force jointly drive rural revitalization. (3) The agriculture has multiple functions such as food safety, social stability, and ecological products. Its development needs to create the whole value chain of agriculture to promote the integration of primary, secondary and tertiary industries. (4) In energy-rich areas, we should fundamentally solve the problem of unbalanced and inadequate rural development under the premise of ensuring the national energy security demand. In Southwest China, we should take advantage of ecology and human resources to build a modern agricultural industry system, remodel the brand of rural tourism, and build landscape rural homes. In Northeast China, rural revitalization must proceed in an orderly and classified way in the process of synergistic promotion of the "northeast revitalization" strategy. In the Yangtze River Delta region, it is necessary to cognize the evolutionary stages from rural industrialization to rural urbanization, and then to rural characteristics with more and more emphasis on the social, cultural and ecological construction of rural areas, seeking a scientific path of rural revitalization. In Northwest China, we propose to effectively improve the ability of "independent poverty alleviation" in rural areas under the premise of ecological protection, and realize the transformation from "transfusing blood" to "producing blood". In the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, oriented by equalization of basic public services in urban and rural areas, we will promote the development of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. In resource-oriented areas, rural industries will replace the industrial system formed around resource exploitation with an efficient agricultural system integrating primary, secondary and tertiary industries. In traditional agricultural areas, it is necessary to optimize the coupling pattern between farmland use transformation and rural labor structure change, which is an important means to achieve rural revitalization. In economically developed areas, villages with "mixed" characteristics need to activate the assets and capital attributes of rural land resources, promote the integration and activation of spatial order, and comprehensively explore the modern rural governance mode with the participation of multiple subjects.
演化经济地理学视角下台湾高山茶产业在大陆的集聚与演化过程: 以漳平市永福镇为例
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.02.2019466
[本文引用: 1]

20世纪90年代以来,台湾地区对中国大陆的农业投资快速增长,两岸不同制度背景下台资农业在大陆发展的时空过程值得关注。基于演化经济地理学的路径依赖理论和共同演化理论,借鉴制度经济地理学与关系经济地理学的相关理论,构建“企业-网络-制度-政府”共同演化的分析框架,以漳平国家级台湾农民创业园永福高山茶产业为例,通过实地调研和深度访谈,分析台湾农业在大陆不同制度背景下的集聚与演化过程。研究发现:台湾高山茶产业在永福镇的集聚与演化过程可看作是路径依赖的结果,整个过程可以划分为路径创造(1996—2003年)、路径发展(2003—2012年)和路径锁定与解锁(2012年至今)三个阶段;在永福高山茶产业发展的不同阶段,企业、网络、制度和政府相互适应,共同演化,不断推动产业优化升级。
Agglomeration and evolution of Taiwan High Mountain Tea Industry in Mainland China from the perspective of evolutionary economic geography: A case study in Yongfu town, Zhangping city
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.02.2019466
[本文引用: 1]

Since the 1990s, Taiwan's agricultural investment in mainland China has been rapidly growing, and the spatio-temporal development of Taiwan-funded agriculture industries in the mainland China in context of the different systems across the Taiwan Straits is worth the attention. Based on the path dependence theory and co-evolution theory of evolutionary economic geography, drawing on theories of institutional economic geography and relational economic geography, this paper constructs the analytical framework of the co-evolution of "enterprise-network-system-government", takes the Yongfu high mountain tea industry of The Taiwan Peasant's Innovation Park in Zhangping city as an example, analyzes agglomeration and evolution of Taiwan's agricultural enterprises under the background of different institution in mainland China through field research and in-depth interviews. This study found that the agglomeration and evolution of Taiwan's high mountain tea industry in Yongfu Town can be regarded as the result of path-dependence, which can be divided into three stages: path creation, path development and path locking and unlocking; enterprises, networks, institutions, and governments adapt to each other and co-evolve to continuously promote industrial optimization and upgrading at different stages.
“共位集群”视角下的农业产业集群演化路径与网络: 以福建省漳平市茶产业为例
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003318
[本文引用: 2]

结合实地调研与半结构访谈法,从集群演化生命周期视角出发,建立“路径-网络-制度”演化研究框架,在此基础上对比两种不同类型农业产业集群形成演化路径与特征,探究其共位发展的演化过程,并探讨形成“共位集群”的潜力与发展路径。结果表明:1)漳平永福高山茶集群作为外资驱动型集群,其发展显示出较强的“初动能”与正式制度依赖性,在台资驱动下经历两端在外、原生路径移植的萌芽期,叠加多级政策外力进入成长期,并逐步实现三产融合发展的路径突破,其间伴随由原生关系网络转向本地生产网络,逐步嵌入全球生产网络的演化过程,但其本地溢出效应有限且存在用地资源限制等路径锁定风险因素;2)作为本地内生型集群,漳平水仙茶产业集群具备更强的“能动性”与社会制度依赖性,在原有历史积淀及地区禀赋基础上萌芽,通过政府扶持实现路径修复,逐步恢复由地方关系网络主导的集群生产网络而进入成长期,初步形成专业化分工格局,成熟的产业氛围及较强的地方根植性使得集群创新网络已初现雏形,但因企业规模有限、外部力量不足等限制存在路径锁定风险;3)集群的共位发展可辅助消除路径锁定风险,而两者由萌芽阶段的独立共生,演化至成长阶段前期的共位竞争,并最终形成共位竞合关系,表明其具备形成“共位集群”的发展潜力与潜在路径。由此,推动地区农业“共位集群”的发展,地区正式制度安排是关键推力,而龙头企业、中小企业与农户组织在其中扮演着重要角色。
The evolution path and network of agricultural clusters from the perspective of "Co-Location Clusters": A case study of the Zhangping Tea Industry in Fujian province
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003318
[本文引用: 2]

The formation and evolution of agricultural industrial clusters experience a life cycle comprising different stages, accompanied by different paths, networks, and institutional characteristics. Foreign capital-driven agricultural industrial clusters and local endogenous clusters show different development characteristics at different life cycle stages. This study aims to provide a useful reference for promoting the local embeddedness and innovation network construction of clusters, thus strengthening the cooperation and co-innovation evolution between foreign capital-driven clusters and local endogenous clusters. Taking Zhangping City, Fujian Province, as the research area, combined with field research and a semi-structured interview, this paper establishes the research framework of "path-network-institution" evolution. Further, it attempts to analyze the evolution process of their co-development based on the comparative study of the evolution paths and essences of Zhangping Yongfu High-mountain tea and the Narcissus tea industrial cluster. In doing so, it adopts the perspective of the life cycles of cluster evolution. The results showed that the trigger mechanism of the Yongfu High-mountain tea cluster drives by the Taiwanese agricultural investment. Therefore, the Yongfu High-mountain tea cluster shows stronger initial kinetic energy and institutional dependence than the Narcissus tea industrial cluster. Driven by Taiwanese agricultural investment, it experienced the embryonic stage of original path transplantation by both ends of the outside world. It has entered its growth stage by superimposing multi-level policy forces, and gradually accomplished the path breakthrough of the integration of the three industries. During this period, it was accompanied by the evolution process from the original relationship network to the local production network and was gradually embedded into the global production network. However, its local spillover effect is limited and there are risk factors that engender path locking. The development history of the Narcissus tea industry in Zhangping can be traced back to the early 20th century. As it was affected by war and other factors, this industrial development was interrupted in the 1950s. Hence, the trigger mechanism for the formation of the Zhangping Narcissus tea industrial cluster is the path repair of the original agricultural cluster. It includes the inheritance of traditional technology, the advantages of local resources, and the promotion of the market and government in the new era. The Zhangping Narcissus tea industrial cluster shows stronger "initiative" and social system dependence than the Yongfu High-mountain tea cluster. On the basis of the original historical accumulation and regional endowment, it has achieved government-sponsored path restoration. With the path extension and dependence, the local production network has gradually formed, and the prototype of the innovation network of the cluster has developed. However, certain path locking risks remain, such as the limited scale of enterprise and the insufficient external force. The two clusters evolved from an independent symbiosis in their incubation stage to co-competition in the early stage of growth. Finally, they formed a relationship of "competition-cooperation," which indicates the potential and path of the development of "co-location clusters." To promote the development of a regional agricultural "co-location cluster", regional institutional arrangement is critical, in which leading enterprises, minor enterprises, and farmers' organizations are instrumental.
农户视角下台湾农业技术在大陆扩散影响因素分析: 以广东韶关粤台农业合作试验区兰花种植业为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200713
[本文引用: 1]

以广东韶关粤台农业合作试验区兰花种植业为例,基于农户视角,构建三个维度下7个外因潜在变量,利用问卷调查数据,通过结构方程模型对台湾农业(兰花)技术扩散效果(内因潜在变量)的影响因素进行了分析。结果表明:农户社会网络与主观规范因素、农户对台湾农业的认知因素、台湾农业特点因素、台湾农业技术服务特点因素及基础条件因素等对兰花技术扩散效果具有显著正向影响,相应假设通过检验;农户创业特征及政策环境等两个因素对兰花技术扩散效果的影响不显著,相应假设未通过检验;试验区特殊的地域文化在促进兰花技术扩散的同时,也带来了一些消极影响;试验区应结合当地实际情况,根据兰花技术扩散的影响因素,制定合理的兰花产业发展对策。
Analysis on the influencing factors of the diffusion of Chinese Taiwan's agricultural technology in China's Mainland from the perspective of farmers: Taking orchid planting industry in Guangdong-Taiwan agricultural cooperative experimental zone in Shaoguan of Guangdong province as an example
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200713 URL [本文引用: 1]
Beyond strategic coupling: Reassessing the firm-region nexus in global production networks
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbr009 URL [本文引用: 1]
Towards a comprehensive understanding of new regional industrial path development
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2019.1566704 URL [本文引用: 5]
演化经济地理学视角下区域新路径发展的研究评述与展望
Review on study of regional new path development from the perspective of evolutionary economic geography
区域发展的“全球—地方”互动机制研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.10.001
[本文引用: 1]

建立对外联系、利用外部资源有助于弥补区域发展新经济活动所面临的资源与技术缺口,为区域发展注入新活力,避免陷入路径锁定导致发展停滞甚至衰退。对外联系的建立势必与本地已有联系相互作用,表现为“全球-地方”之间多类型行为主体在特定空间支持与约束下的互动,涉及4个基本问题:发生条件、区域差异、互动内容与行为主体。梳理现有研究发现:① 本地与非本地要素的相似性或互补性决定了互动发生的可能性,本地能力则进一步决定互动发生的程度;② 互动对于优势地区和后进地区2类极端类型地区更为有效;③ 互动内容以知识、贸易、资本等要素为主,日益强调非本地劳动力和非本地制度的影响;④ 互动主体以企业为中心。近年来研究一方面强调企业家等个体作用,另一方面关注非经济主体的作用。整体而言,既有研究在区域发展中“全球-地方”互动的尺度结构、动态变化和行为主体等方面仍面临挑战。结合中国当前区域经济转型与主动全球化并行的发展现状,论文提出理解中国区域发展“全球-地方”互动的关键问题与潜在方向。
A review of global-local interactions for regional development
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.10.001
[本文引用: 1]

Extra-regional linkages can benefit regional development by introducing supplement resources and technologies. They also enrich the local knowledge base, keeping regions away from depression due to lock-in effects. Global-local interaction (GLI) research represents the academic effort to theorize this process by examining the interplay between a wide array of actors at multi-scales within particular territorial confines. It raises four critical questions regarding the conditions, regional differences, channels, and actors for interaction. The literature has documented that the relatedness between local and nonlocal inputs determines the probability of GLI. Local capabilities determine the extent of GLI. The literature also reveals that the leading and most lagging behind regions tend to benefit from GLI. Knowledge diffusion, foreign investment, and international trade are primary elements that support GLI. As one region continues to develop, the immigrants and nonlocal institutions may enrich the GLI. Conventionally, the literature on GLI is firm-centric. Recent advances highlight the role of individuals, such as entrepreneurs and employees. There is also increasing awareness of the non-economic agency, especially the institutional agency. Overall, an in-depth examination is still required for understanding the scales, dynamics, and agencies of GLI for regional development. Grounded in the context of China's regional restructuring and opening-up, this study proposes a framework to model GLI in China and discusses its potential for future studies.
The geography of technology legitimation: How multiscalar institutional dynamics matter for path creation in emerging industries
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2020.1842189 URL [本文引用: 3]
Exogenous sources of regional industrial change: Attraction and absorption of non-local knowledge for new path development
DOI:10.1177/0309132517700982
URL
[本文引用: 5]

The role of exogenous sources of new path development has been underplayed in the literature on regional industrial change so far. The aim of this article is to explore in a conceptual way under which conditions and in what ways non-local knowledge can lead to new path development in different regional innovation systems (RISs). We distinguish between organizationally thick and diversified RISs, thick and specialized RISs and thin RISs and argue that these types vary substantially in their needs for exogenous sources as well as in their capacities to attract and absorb knowledge generated elsewhere.
Beyond the single path view: Interpath dynamics in regional contexts
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2019.1685378 URL [本文引用: 1]
Rethinking path creation: A geographical political economy approach
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2018.1498294 URL [本文引用: 2]
Path creation, global production networks and regional development: A comparative international analysis of the offshore wind sector
DOI:10.1016/j.progress.2018.01.001 URL [本文引用: 4]
Reconsidering path creation in economic geography: Aspects of agency, temporality and methods
DOI:10.1080/09654313.2016.1204427 URL [本文引用: 6]
演化经济地理学视角下创新网络研究进展与展望
Progress and prospect of research on innovation networks: A perspective from evolutionary economic geography
Unravelling green regional industrial path development: Regional preconditions, asset modification and agency
DOI:10.1016/j.geoforum.2020.02.016 URL [本文引用: 2]
Roepke lecture in economic geography-rethinking regional path dependence: Beyond lock-in to evolution
DOI:10.1111/ecge.2010.86.issue-1 URL [本文引用: 3]
Towards a theory of regional diversification: Combining insights from evolutionary economic geography and transition studies
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2016.1258460 URL [本文引用: 1]
Evolution in economic geography: Institutions, political economy, and adaptation
DOI:10.1111/ecge.2009.85.issue-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
A geographical political economy of evolution in economic geography
DOI:10.1111/ecge.2009.85.issue-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Clusters and knowledge: Local buzz, global pipelines and the process of knowledge creation
DOI:10.1191/0309132504ph469oa
URL
[本文引用: 2]

The paper is concerned with spatial clustering of economic activity and its relation to the spatiality of knowledge creation in interactive learning processes. It questions the view that tacit knowledge transfer is confined to local milieus whereas codified knowledge may roam the globe almost frictionlessly. The paper highlights the conditions under which both tacit and codified knowledge can be exchanged locally and globally. A distinction is made between, on the one hand, the learning processes taking place among actors embedded in a community by just being there dubbed buzz and, on the other, the knowledge attained by investing in building channels of communication called pipelines to selected providers located outside the local milieu. It is argued that the co-existence of high levels of buzz and many pipelines may provide firms located in outward-looking and lively clusters with a string of particular advantages not available to outsiders. Finally, some policy implications, stemming from this argument, are identified.
Path creation as a process of resource alignment and anchoring: Industry formation for on-site water recycling in Beijing
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2015.1103177 URL [本文引用: 3]
Exogenously led and policy-supported new path development in peripheral regions: Analytical and synthetic routes
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2016.1154443 URL [本文引用: 3]
Policy activism and regional path creation: The promotion of offshore wind in North East England and Scotland
DOI:10.1093/cjres/rsu036 URL [本文引用: 3]
演化经济地理学与区域发展
Evolutionary economic geography and regional development
Understanding processes of path renewal and creation in thick specialized regional innovation systems. Evidence from two textile districts in Italy and Sweden
DOI:10.1080/09654313.2019.1610727 URL [本文引用: 1]
Expanding analyses of path creation: Interconnections between territory and technology
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2020.1756768 URL [本文引用: 1]
Time should tell (more): Evolutionary economic geography and the challenge of history
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2018.1515481 URL [本文引用: 1]
Trinity of change agency, regional development paths and opportunity spaces
DOI:10.1177/0309132519853870
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The study of regional growth paths is a key theme in economic geography and of elemental interest for regional development. This paper addresses the interplay between path-dependent, structural forces and the construction and utilization of opportunities through agentic processes. Extending the evolutionary framework, it is argued that not only history but also perceived futures influence agentic processes in the present and thus shape regional development paths. The paper discusses the relevance and interdependencies of three types of agency with distinct theoretical roots, namely Schumpeterian innovative entrepreneurship, institutional entrepreneurship and place-based leadership, as main drivers of regional structural change.
The competitiveness of firms and regions: 'Ubiquitification' and the importance of localized learning
DOI:10.1177/096977649900600102
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In traditional location theory there is a distinction between factors of production for which the costs differ significantly between locations, on the one hand, and production inputs which are in practice available everywhere at more or less the same cost (i.e. so-called ubiquities) on the other.
'Globalizing' regional development: A global production networks perspective
DOI:10.1111/tran.2004.29.issue-4 URL [本文引用: 1]
Embracing the future: Path transformation and system reconfiguration for self-driving cars in West Sweden
DOI:10.1080/09654313.2019.1652570 URL [本文引用: 1]
How to jump further and catch up? Path-breaking in an uneven industry space
Regional industrial evolution in China
DOI:10.1111/pirs.12246
[本文引用: 1]

Evolutionary economic geography (EEG) indicates that regional industrial development is path dependent. The empirical studies in EEG however have not paid sufficient attention to the importance of global linkages nor the role of regional institutions in driving industrial dynamics. Based on firm level data of four-digit manufacturing industries during 1998 to 2008 in China, we find that Chinese regions branch into new industries technologically related to the existing industrial portfolio and related industries are less likely to exit. Further analysis reveals that global linkages, economic liberalization and state involvement not only create favourable conditions to allow a larger role of technological relatedness but also generate opportunities for Chinese regions to create new paths of industrial development.
Relatedness as driver of regional diversification: A research agenda
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2016.1254767 URL [本文引用: 1]
Doing evolution in economic geography
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2015.1108830 URL [本文引用: 1]
东南亚华人华侨网络与中国企业海外投资的区位选择关系研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201808005
[本文引用: 1]

随着“走出去”战略的实施和“一带一路”倡议的提出,中国在全球化经济中逐渐成为国际投资的主要力量之一。海外华人华侨网络曾经积极促进外商对华的直接投资,是否在这个过程中再次扮演积极的作用,是当前经济地理领域尚未充分探究的问题。因此,本文从经典的区位选择问题切入,探究海外华人华侨网络与中国企业海外投资的区位选择的关系,利用2001-2016年中国企业投资东南亚国家的数据,通过混合逻辑模型回归分析海外华人华侨对中国企业投资区位的影响。结果表明:① 从整体上看,东南亚各国的华人华侨规模和中国企业对外直接投资的区位选择之间存在显著的正相关关系;② 从投资时间上看,海外华人华侨规模与中国企业对外直接投资区位选择之间的关系显著性呈现扩大趋势,说明华人华侨在促进中国企业对外投资方面存在较大潜力;③ 从投资的行业和环节上看,不同行业和不同职能部门的企业在东南亚投资中海外华人华侨在其投资区位选择中所起的作用不同。
Relationship between the location choices of Chinese outbound enterprises and overseas Chinese networks: The case study of Southeast Asia
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201808005
[本文引用: 1]

With the implementation of the strategy of "Going Global" and the Belt and Road Initiative, China is playing a critical role in the global economy. Along with the increasing globalization of Chinese enterprises, China has gradually become an influential force in the global market. The contemporary literature has revealed how overseas Chinese networks and communities promoted foreign investments into China in the past four decades. Whether these networks and communities can drive Chinese capital to expand overseas once again is ambiguous. Employing the classical location theory, this study examines Chinese corporate investments in Southeast Asia from 2001 to 2016. Data were collected from official information of Chinese corporations released by the Ministry of Commerce of China. This research covers 10 countries located in Southeast Asia including Malaysia, Philippines, Thailand, Singapore, Indonesia, Brunei, Vietnam, Cambodia, Myanmar and Laos. Utilizing the discrete-selection logit regression model, the study analyzed the correlation between overseas Chinese social networks and the site selection of Chinese outbound investment. The results show that: (1) overall, the positive correlation between the number of overseas Chinese in Southeast Asian countries and the location choice of Chinese outbound investment is apparently significant; (2) in terms of time sequence, the significance of the correlation is soaring up, indicating that overseas Chinese have potentials in imposing positive impact on the promotion of locational choice of Chinese enterprises while the impact is potentially on the rise; (3) as for industrial structure and corporate functions, the impact is various and significant only in some industries and corporate segments. These findings affirm the positive value of overseas Chinese social networks on the globalization of Chinese corporations. Considering the implementation of the Belt and Road Initiative, this paper suggests that Chinese government should pay more attention to the improvement of the interactions between Chinese enterprises and overseas Chinese networks.
Creating new paths? Offshore wind, policy activism, and peripheral region development
DOI:10.1111/ecge.12028 URL [本文引用: 2]
Regional agency and constitution of new paths: A study of agency in early formation of new paths on the west coast of Norway
DOI:10.1080/09654313.2016.1276159 URL [本文引用: 1]
Regional industrial restructuring resulting from individual and system agency
DOI:10.1080/13511610.2018.1496322 URL [本文引用: 1]
Related variety, unrelated variety and regional economic growth
DOI:10.1080/00343400601120296 URL [本文引用: 1]
Industrial development in thin regions: Trapped in path extension?
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbu026 URL [本文引用: 1]
Unrelated knowledge combinations: The unexplored potential for regional industrial path development
DOI:10.1093/cjres/rsy012 URL [本文引用: 1]
Path dependence and regional economic evolution
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbl012 URL [本文引用: 2]
Advancing evolutionary economic geography by engaged pluralism
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2014.889815 URL [本文引用: 1]
Institutional change in economic geography
DOI:10.1177/0309132513507823
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper develops a rigorous concept of institutions to investigate the interrelationships between institutional and economic change from the perspective of economic geography. We view institutions neither as behavioural regularities nor as organizations or rules, but conceive institutions as stabilizations of mutual expectations and correlated interaction. The paper discusses how economic interaction in space is shaped by existing institutions, how this leads to economic decisions and new rounds of action, and how their intended and unintended consequences impact or enact new/existing institutions. The paper explores three modes of institutional change – hysteresis, emergent change, and institutional entrepreneurship.
中国区域产业结构演化的路径突破
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.08.006
[本文引用: 1]

在经济转型新阶段,如何突破已有资源条件的束缚,创造新的产业发展路径是区域经济增长的突破口。路径依赖和路径突破是区域创造产业发展路径的两种途径,已有演化经济地理学研究证实区域生产结构的演化依赖地区已有生产能力,是一种路径依赖的结果,而谁是突破区域现有生产能力实现新路径创造的开拓者却尚未得知。本文基于1999-2012年中国337个地级城市的424个四位数产业数据,沿用Hidalgo等人对生产能力的定义,研究中国产业演化过程中路径突破的可能,结果发现:地区新产业的进入以及已有产业的退出有助于地区突破对原有生产结构的依赖,是区域产业发展新路径的创造者。政府补贴一方面有利于地区现有生产能力的提升,增强地区路径依赖趋势;另一方面可为地区带来新的路径,实现路径突破并为区域创造新的发展机会。此外,政府补贴影响产业演化路径选择的效用受地方财政能力限制,并在空间上存在显著差异。
Path creation in China's industrial evolution
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.08.006
[本文引用: 1]

In evolutionary economics, the notion of path creation has attracted much attention in recent years. Previous research has expounded the possibility of path dependence and path creation in the process of regional industrial evolution, but it remains unknown that who changes the existing production capacity and accomplishes path creation. This article focuses on regional production capacity, and applies the indicator of density defined by Hidalgo. Based on the data of 424 four-digit industry of 337 prefecture-level cities in China from 1999 to 2012, this article discusses the path creation of China's industrial evolution. It is found that the entry and exit of an industry would break the original production structure of a region and become the creator of a new path. Governmental subsidies, on the one hand, can promote the development of a region's existing production capacity to enhance the regional's path dependence trend, but also can influence industry dynamics and accelerate the process of path creation. The selection of evolutionary path has significant regional differences. This study will help deepen the understanding of the change of China's industrial structure and its regional differentiation, and provides new evidence from developing countries for the development of evolutionary economic geography.
Do institutions matter for regional development?
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2012.748978 URL [本文引用: 1]
Co-evolution in contemporary economic geography: Towards a theoretical framework
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2018.1494824 URL [本文引用: 1]
Towards an evolutionary perspective on regional resilience
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2014.959481 URL [本文引用: 1]
Normative expectations in systems innovation
Niche construction and empowerment through socio-political work. A meta-analysis of six low-carbon technology cases
DOI:10.1016/j.eist.2015.02.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
战略耦合的研究脉络与问题
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807013
[本文引用: 1]

在回顾经济地理学中较为前沿的战略耦合概念的起源、发展与研究现状的基础上,对战略耦合研究的优点与问题展开评述,认为当前研究在战略耦合模式的探讨中,主要基于经验总结而缺乏对影响变量,特别是空间变量的阐述,存在一定的模糊性。为理解该问题的根源,追溯了全球生产网络和全球价值链两个学派的争论和最新进展。在认可全球价值链理论解释力的同时,认为当前全球生产网络2.0版本的研究框架仍然没有解决模糊性的问题,而且全球生产网络的分析框架主要侧重于主导企业视角来构建战略耦合的发生机制,忽略了后发地区和企业的主动性。因此,借鉴传统经济地理学研究,充分考虑主导企业和后发地区的行为逻辑,提出经济活动的空间粘性和区域的区位优势这两个变量,重构了战略耦合的分析框架,并进行理论阐述。该项理论构建有助于更好地厘清战略耦合的发生机制,帮助发展中国家和地区判读发展机遇,确立产业发展与升级战略。
Theoretical thread and problems of strategic coupling
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807013
[本文引用: 1]

This paper critically reviews the theoretical thread, contribution and problems of the studies of strategic coupling. By examining the conceptualization, explanatory variables and the analytical framework of this concept, it finds that the spatiality of strategic coupling is ambiguous. The three-fold typology and mechanism is based on empirical observation, while lacking of theoretical reasoning based on spatial variables. By learning from the studies of global production network and global value chain, this paper argues that the strategic coupling studies shall be advanced by absorbing spatial variables from traditional studies in economic geography, rather than from other disciplines. As an attempt, this paper proposes two spatial variables, locational advantage (LA) and spatial stickiness (SS), for explaining the formation, variety and impacts of strategic coupling in the globalization of latecomer regions. Leveraging the low-high weight of the proposed new variables, there are three potential types of strategic coupling. When LA and SS are both low, captive coupling tends to happen in which later-comer firms and regions play as a follower of global leading firms. When LA and SS are both high, absorptive coupling become possible in which late-comer actors have high bargaining power to negotiate for ideal partnership with global leading firms. When LA is high while SS is low, cooperative coupling may happen in which both counterparts exchange resources under a relatively balanced power relationship. In contrast, when LA is low while SS is high, strategic coupling will not happen. This paper contributes to the literature of global production network by fixing the problem of spatial ambiguity of strategic coupling. The proposed new variables are derived from traditional studies in economic geography so that the strategic coupling can draw upon many classical theories and studies. This effort reminds the disciplinary position of strategic coupling for being an economic geographical study. This renewed framework has salient implication for latecomer economies. On the one hand, by analyzing the spatial stickiness of an industry, we can evaluate the potential of industrial relocation or upgrading within a region and then strategize relevant policies to slow or facilitate the process. On the other hand, for fostering regional assets, a region shall focus on immobile resources such as domestic market environment, regionalized production networks and local talents, rather than using replicable policies such as fiscal incentives.
1978年改革开放以来中国工业地理格局演变
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910002
[本文引用: 1]

回顾改革开放40年,在深刻的制度变革环境下,中国工业实现快速发展,中国工业地理格局也在经济转型中得到重塑。中国工业总体上经历了从内陆扩散到沿海地区集聚,再向内陆转移的过程。但不同类型产业地理格局及变化受制于不同力量,显现出一定的行业差异性。与改革开放之初相比,中国工业在不同地理尺度上呈现出明显的集聚趋势,但集聚程度较欧盟和美国低。产业的聚集与分散驱动不同尺度下的产业迁移,导致区域产业频繁进入和退出,促使地方产业呈现多样化态势,推动中国工业地理格局演变。从经济转型的视角出发,改革开放可概括为市场化、全球化和分权化三个过程,这些过程创造市场力量,激活地方力量,引入全球力量,共同重塑了中国工业地理格局。
Evolution of Chinese industrial geography since reform and opening-up
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910002
[本文引用: 1]

Looking back on the 40 years of reform and opening-up, Chinese industry has achieved rapid growth and development, and Chinese industrial geography has been profoundly reshaped under the profound institutional evolution environment. Chinese industry has undergone a process of spreading in the inland to agglomeration in the coastal areas and then dispersion towards the inland again. However, the geographical pattern of different types of industries is influenced by different forces, leading to differences in the spatial restructuring process. Since the beginning of reform and opening-up in 1978, Chinese industries have been increasingly more agglomerated at different geographical scales, but still much lower than the European Union and the United States. Industrial agglomeration and decentralization drive industrial migration at different scales. In spite of the heterogeneity of industries, industrial migration has generally changed from a scattered layout to an agglomeration pattern in coastal areas; and in recent years, industrial migration has gradually shifted from developed eastern provinces to central provinces, indicating a new round of industrial migration. Remarkable regional industrial entries and exits have promoted the evolution and diversification of local industries. Overall, Chinese industrial space tends to be more complex and concentrated, the links between industries are further strengthened with a more obvious "path dependence" characteristics of industrial evolution in coastal areas. Theoretically, Chinese economic reform is not only the reform of development mode, but also the reform of institutions in essence. The fundamental triple process of marketization, globalization and decentralization has introduced market forces, local forces, and global forces to reshape Chinese industrial geography. And for the study of Chinese industrial geography, besides continuing to summarize patterns and dynamics from multiple perspectives, it is necessary to reveal the deep-level mechanism of the evolution of industrial geography pattern through phenomena, and evaluate the multiple effects of the reshaping of industrial geographical pattern systematically.
基于事件数据分析法的两岸关系测度及影响因素研究
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2022.03.2020714
[本文引用: 1]

海峡两岸同根同源,发展两岸关系、推进祖国统一是实现中华民族伟大复兴的必然要求。从政治互动、经贸往来和文旅交流3个维度构建两岸关系综合评价指标体系,利用事件数据分析法和熵值法,对2000—2018年的两岸关系进行定量测度、演化阶段划分及影响因素分析,进而对两岸关系的良性发展提出建议。结果表明:①21世纪以来,两岸关系经历了低谷波动期(2000年1月—2008年5月)、全面发展期(2008年6月—2016年5月)和冷却回落期(2016年6月—2018年12月),呈现整体周期性、局部突变性的演化特征;②两岸关系主要受区域地缘环境、大陆综合实力、台湾政党轮替以及非传统安全因素等4个方面的影响;③大陆应当持续优化两岸关系地缘环境、继续提升综合实力、推进两岸社会融合以及建立防范非传统安全风险的机制。
Study on the measurement and influencing factors of cross-strait relations: Based on event data analysis