21世纪以来,人类的持续作用成为影响地球系统变化的关键力量[1]。在进入“人类世”(Anthropocene)新纪元的过程中,人民生活水平逐步提升,来自生态环境惠益的幸福感增强[2];但同时,人类社会又以超越边界的、无节制的、不可逆转的方式破坏着地表环境,生态系统退化与人类需求提升间的矛盾愈发激烈[3]。究其实质,就是生态系统服务供给与人类福祉需求的失调问题,是自然系统与人类系统耦合失衡的结果。为此,国际社会陆续开展了国际地圈与生物圈计划(IGBP)、生物多样性与生态系统服务政府间科学政策平台(IPBES)、“未来地球计划”、联合国《2030年可持续发展议程》等行动,中国也适时提出了生态文明建设、“绿水青山就是金山银山”、美丽中国建设、“共建地球生命共同体”等命题,以期推进新时代的可持续发展。如何将其与人地系统耦合研究衔接,在生态适宜承载性的基础上谋求不同层次福祉的提升,促进生态系统服务与人类福祉的科学协调,以达成人与自然的和谐共生,成为现今人地关系及可持续性研究的核心主题。
生态系统服务(Ecosystem Services,ES)指人类从生态系统功能与过程中获取到的各种惠益[4],目前对生态系统服务价值的研究已超越了传统的经济产出导向,转而强调人类福祉(Human Well-being,HWB)的综合提升,即在良好生活质量的基础上实现个人需求的满足[5,6]。随着2005年联合国千年生态系统评估(Millennium Ecosystem Assessment,MA)的推进,生态系统服务与人类福祉之间的关系研究成为主流,且主要呈现出三个阶段的演进[7]:(1)生态系统服务对人类福祉的贡献(“影响链条”,impact chain),分析不同时空尺度变化下不同类型服务的影响作用,如典型的环境库兹涅茨曲线(EKC)[8]和“生态魔咒”现象[9]等;(2)人类福祉对生态系统服务的反馈(“反馈链条”,feedback chain),主要关注支付意愿[10]、农户生计[11]、区域决策[12]等,通过人类社会对生态系统服务的主观感知和使用需求差异来反映不同的福祉效应[13];(3)生态系统服务与人类福祉的相互影响,在整合上述两个链条的基础上,聚焦资本流动、供需联系、尺度依存、获得性差异等双向动态演变关系[14,15],应用于生物多样性、景观可持续性、区域管控等实践[16,17]。
随着国内外人地关系研究向人地系统耦合(Coupled Human and Natural Systems,CHANS)的方向深化,近年来围绕城镇化与生态环境、城镇化与生态系统服务等主题的耦合研究成果逐渐丰硕,提出了社会—生态系统(SES)[18]、服务弹性反馈框架[19]、人与自然耦合系统[20]等创新性理论框架,技术方法上既有较为经典的耦合度指标[21],也有动态耦合度模型[22]、耦合魔方[23]、耦合圈及耦合器[24]等前沿探索。在这些研究中,生态系统服务与人类福祉的关系是现代人地系统耦合的关键表征[25],二者在相互影响、反馈中趋于协调统一,即耦合(coupling)。不过目前直接面向服务与福祉相互作用、甚至耦合关系测度的实践极少,大多仅从供需流动、权衡/协同博弈、文化服务价值化、生态补偿与付费、优化调控与可持续管理等方面进行交互关系具体表现的探讨[7],远没有达到系统耦合的高度和深度。综上,生态系统服务与人类福祉关系(耦合)研究虽已从理论探索走向了区域实践,但在人地系统耦合范式下又存在着明显不足:缺乏服务与福祉耦合的理论构建,过于侧重服务的供给端;缺少服务与福祉耦合关系评估的技术方法,多停留在影响作用的质性探讨层面,较少揭示其空间异质性;研究对象或关注大洲、国家、流域、省域等宏观格局,或聚焦生态功能区的农户生计、工程移民等微观行为和“三生”关系,缺少城镇尺度下的定量化应用。
城镇化地区既是中国经济社会转型最为快速,又是生态系统退化与人类福祉提升之间冲突最为强烈的区域,人地矛盾激烈。为此,中国提出了以人为本的新型城镇化建设,要求构建新发展格局、引领高质量发展、缔造高品质生活,其核心目的是增进人民福祉[26]。因此,针对上述不足及区域实际,如何以生态文明和高质量发展为导向,以城镇化地区为对象,开展生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合研究,解理其空间分异特性,科学辨析人地关系的区域协调路径,愈发成为现今可持续发展与人地系统耦合研究亟待解决的关键问题。由此,本文首先明确“从级联到耦合”的服务与福祉关系研究新思路;然后以快速城镇化的典型地区——广州市为例,分析服务与福祉耦合的空间格局特征,揭示空间分异问题;再立足于人地系统耦合范式,搭建服务与福祉耦合的逻辑框架,在此基础上通过识别出的耦合类型区探析耦合关系的驱动方式,为实现人与自然和谐共生的新时代城镇可持续发展提供科学依据和决策参考。
1 生态系统服务与人类福祉:从级联到耦合
自MA以来,国内外生态系统服务与人类福祉关系研究基本上都以生态系统结构、过程与功能—服务—人类收益与福祉的级联框架(cascade)[27]为范式,在环境管治、国土优化规划、人地可持续协调等方面贡献了大量成果。级联框架很好地处理了生态系统服务向人类福祉的传导作用,通过“影响链条”和“反馈链条”逐步揭示了服务与福祉的交互胁迫效应[7]。但随着自然生态系统与人类社会经济系统之间的复杂交互作用逐渐深化,服务与福祉的关系趋于非线性化、网络化[14,19],级联框架开始显现出理论上的缺陷:侧重于单要素、单向的线性关系分析,尚不能理清“反馈链条”的具体作用机理;难以处理“多对多”非线性传导关系,疲于揭示服务与福祉相互作用的内在动力机制。为此,亟需跳脱于传统级联框架,提出“从级联到耦合”的新思路,从更高层次、更系统集成的视角——耦合来重新梳理生态系统服务与人类福祉的交互关系。
耦合指两个或以上要素、运动体系间通过物质传输、能量传递的相互作用而达到联合促进的结果,现多用于地理学与环境科学等研究中,以表现人与环境之间、不同系统之间相互依赖、影响、反馈而趋于协调统一的复杂交互关系[23,28]。从内涵本质上看,生态系统服务与人类福祉分别源于自然生态、人类社会经济两个系统,唯有耦合才得以实现“系统对系统”的非线性复杂交互。生态系统服务与人类福祉在愈发强化、复杂化和网络化的交互作用中形成了以耦合为表征的非线性竞合关系:内部各要素间存在着非对称关联[14],其发展演变呈非同步性,如时序变化的滞后性、空间分异的非均衡性、路径依赖的自封闭性等[9,29]。这种竞合关系多通过时空权衡[29]、供需流动[14]、韧性响应[19]等方式来表现,耦合系统的良性演化可最终推动人与自然耦合系统的协调发展[3,30]。
2 研究方法与数据来源
2.1 研究区概况
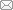
广州市地处珠江三角洲中部,是中国的“南大门”,土地总面积7433.3 km2,河流水系发达,森林覆盖率达42%以上。2018年末,全市常住人口1490.44万人,人均GDP为155491元,城镇化率高达86.38%;第三产业占比71.75%,高新技术产品产值占规模以上工业总产值的47.98%,现代产业发达;三甲医院数量约占全省31%,现代商贸发达,基础服务设施完善,文化开放包容,居民幸福感较强。随着广州城镇化的高速发展,建设用地大幅扩张,其面积在2005—2018年间增长了22.6%,由此带来了严重的生态用地破碎、萎缩等问题(图1),生态系统功能和结构受到剧烈扰动,人地矛盾突出。
图1
2.2 研究方法
首先从“系统”概念出发,分别从自然生态系统的供给端、人类社会经济系统的需求端定量评估广州市生态系统服务与人类福祉的水平,深入微观格网尺度识别其空间分布特征及差异;其次对两个“系统”进行耦合分析,通过耦合协调阶段、不同维度的耦合分异等辨析生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合的现状格局;然后筛选出典型的耦合类型区,探讨其驱动方式及路径,诊断当前的突出问题,为实现新时代人与自然和谐共生提供实践参考。空间异质性是本文分析耦合空间格局的核心落点,其空间尺度选择尤为重要。通过对比不同尺度下的空间格局发现,随着尺度下推生态系统服务与人类福祉的空间集聚与异质性愈加精细化,其中100 m×100 m是判析人与自然系统交互作用最直接的微观尺度①(①参考前人研究成果[33⇓-35],本文对比了3 km×3 km、1 km×1 km、500 m×500 m、300 m×300 m、100 m×100 m尺度下的生态系统服务价值空间格局,发现100 m×100 m尺度下的Moran's I值最大、变异系数最小。但若尺度小于100 m×100 m,则不利于表征人类福祉水平的分布,难以梳理城市视角下的耦合关系。),易于探寻二者耦合的内在驱动机理,因此成为本文最合适的研究尺度。
2.2.1 生态系统服务价值评估
土地是生态系统服务的直接载体,基于土地利用/土地覆盖变化(Land Use/Cover Change,LUCC)的生态系统服务价值(Ecosystem Service Value,ESV)评估能快速准确地获知不同区域生态系统服务的格局特征,已成为当前生态系统服务定量评估研究最常用的方式之一。其中,国内学者最普遍使用的是谢高地等[36]所提出的当量因子评估法,因此本文采用谢高地等[37]最新提出的当量因子改进方法进行ESV评估。将生态系统服务划分为4类11种,根据广州实际状况进行以下修正:(1)将土地利用分类与当量表衔接,耕地当量因子取表中旱地和水田的面积加权均值,林地取森林的对应数值,未利用土地取荒漠和裸地的面积加权均值,建设用地中供给、调节、支持服务取0,文化服务(美学景观)取森林和水域的均值;(2)运用原方法中的NPP、降水、土壤保持三大时空调节因子进行地域修正[37],考虑到数据的可得性和应用性,分别使用全球生态系统总初级生产力(GPP)②(②数据来源于国家青藏高原科学数据中心,Doi: 10.6084/m9.figshare.12981977.v2。)、水土流失面积减少率③(③数据来源于《中国水土保持公报》《中国水利统计年鉴》《第一次全国水利普查公报》等。)代替NPP和土壤保持因子;(3)每个ESV当量因子所对应的经济价值一般近似于当年单位面积平均粮食单产市场价的1/7[38],结合广州的实际情况,计算得到2005年、2010年、2015年、2018年当量因子价值量分别为2028.73元/hm2、1798.27元/hm2、1897.39元/hm2、1887.44元/hm2(2018年可比价格)。在ESV评估过程中,同时对上述4个时相的空间格局进行对比,目的是通过生态系统服务的时空动态演变以更好地理解其与人类福祉的耦合关系。
为验证ESV评估的准确性,通常还需进行敏感性指数(Coefficient of Sensitive,CS)分析,即当生态系统服务价值系数发生变动时所引起的ESV变化,计算方式为:
式中:
2.2.2 人类福祉综合指标体系构建
当前中国社会的主要矛盾已经转变,更加强调人民对更高层次美好生活的向往,这也成为新时代人民福祉的核心发展目标。为此,以人为本新型城镇化要求通过新发展理念来引领高质量发展,缔造人民的高品质生活[26]。因此,新发展理念——创新、协调、绿色、开放、共享应成为理解中国特色城镇化背景下人民福祉的关键导向。在此引领下,中国近年开展了城市体检评估工作,旨在诊断城市问题、提升人居福祉、推进高质量发展[42]。人类福祉是人民需求满足程度的综合反映,在城市体检过程中“城市人”是否达到“自存”与“共存”的平衡[43],实际上就是某一区域福祉发展水平的综合体现。因此,城市体检评估体系既能弥补现有人类福祉评价体系的不足,又能紧跟中国城镇化发展动态,还能着重表现人类福祉的空间异质性,自然成为本文测度人类福祉水平的可靠抓手。综上,本文以新发展理念为导向,借鉴自然资源部国土空间规划城市体检评估体系④(④中国自然资源部在《国土空间规划城市体检评估规程》(TD/T 1063-2021)中,共划分出安全、创新、协调、绿色、开放、共享6类23个二级类122项指标。),以人的多层次发展需求为细则,结合相关文献经验和广州发展实际,构建了广州市人类福祉综合指标体系,共6维度22项一级指标(表1)。需要说明的是:(1)本文测度的人类福祉仅聚焦于客观福祉,主要考虑到主观福祉多内化在客观福祉中,相应地精神、文化空间也以物质空间为依托,且在服务与福祉耦合研究中暂且不需要区分不同人群主体的差异;(2)为辨析人类福祉的空间异质性,该指标体系采用了微观尺度的矢量化测量手段,一方面综合数据的多源化、尺度的精细化、指标的本土化等方式保证其科学性,另一方面着重测度居民潜在需求的空间实现程度,涵盖了不同主体、地域、利益关联方的主观差异。各指标的基础尺度由数据来源来划定,人口与经济统计数据的尺度为街道,服务/覆盖范围参考国土空间规划城市体检评估体系来确定,再空间插值到100 m×100 m格网中,最后再将各指标的数据统一到现状水平。为尽可能减少数据误差,综合指标体系的权重由主客观赋权法相结合的方式来确定,取主观的层次分析(AHP)法和客观的熵值法之间的均值作为最终的权重。
表1 广州市人类福祉综合指标体系
Table 1
| 维度 | 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 方向 | AHP法 | 熵值法 | 综合权重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 创新A | 知识人才A1 | 高等教育学历人口占比 | + | 0.1423 | 0.0900 | 0.1161 |
| 活力创造A2 | 人均专利拥有量 | + | 0.0384 | 0.0158 | 0.0271 | |
| 先进经济A3 | 高技术制造业及规模以上服务业营收、工业高新技术产品产值占比 | + | 0.0299 | 0.0114 | 0.0207 | |
| 创新氛围A4 | 众创空间、创新产业园区、孵化器、开发区覆盖率 | + | 0.0413 | 0.0044 | 0.0228 | |
| 协调B | 人口红利B1 | 人口抚养比 | - | 0.0327 | 0.0584 | 0.0455 |
| 城乡协调B2 | 城乡居民人均可支配收入比、城镇居民自由分配收入差距 | - | 0.1461 | 0.0534 | 0.0998 | |
| 职住平衡B3 | 职住比 | - | 0.0512 | 0.0130 | 0.0321 | |
| 绿色C | 洁净大气C1 | 空气质量综合指数 | - | 0.0553 | 0.0102 | 0.0328 |
| 良好生态C2 | 公园绿地服务半径覆盖率 | + | 0.0396 | 0.0302 | 0.0349 | |
| 绿色出行C3 | 公共交通、人行道覆盖率 | + | 0.1639 | 0.1292 | 0.1466 | |
| 开放D | 交往吸引D1 | 实际利用外资金额、外资到达率、领事馆和国际组织机构覆盖度 | + | 0.0671 | 0.0004 | 0.0337 |
| 对外联通D2 | 主要对外交通方式的服务范围 | + | 0.0546 | 0.0753 | 0.0649 | |
| 文化包容D3 | 中、外餐厅菜系多样性 | + | 0.0422 | 0.0536 | 0.0479 | |
| 共享E | 住房可靠E1 | 人均住房建筑面积 | + | 0.1206 | 0.2256 | 0.1731 |
| 生活便利E2 | 商业便民服务设施覆盖率 | + | 0.0444 | 0.0105 | 0.0274 | |
| 交通便捷E3 | 市内交通综合路网密度 | + | 0.0338 | 0.0238 | 0.0288 | |
| 休闲多元E4 | 休闲文旅游憩服务设施覆盖率 | + | 0.0424 | 0.1913 | 0.1169 | |
| 就业安稳E5 | 失业人员再就业率 | + | 0.1403 | 0.3095 | 0.2249 | |
| 社会可依E6 | 养老设施、幼儿园、无障碍设施、社区服务中心覆盖率 | + | 0.0386 | 0.0604 | 0.0495 | |
| 安全F | 应急庇护F1 | 应急避难场所、避暑防寒场所覆盖范围 | + | 0.0125 | 0.0457 | 0.0291 |
| 消防救援F2 | 消防站点5分钟可达范围 | + | 0.0120 | 0.0568 | 0.0344 | |
| 医疗救助F3 | 各级医院服务范围 | + | 0.0077 | 0.0452 | 0.0264 |
2.2.3 耦合协调度模型
式中:C为耦合度;E与W分别为生态系统服务与人类福祉综合指数,即ESV总量或人类福祉综合水平的标准化值;R为耦合协调度;T为系统综合协调指数;
表2 生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合协调阶段与发展水平划分
Table 2
| 耦合协调度 | 耦合协调阶段 | 符号 | 相对发展度 | 耦合特征 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 严重失调 | Ⅰ | 系统严重失调,生态系统服务发展滞后 | ||
| 系统严重失调,二者低水平均衡发展 | ||||
| 系统严重失调,人类福祉发展滞后 | ||||
| 中度失调 | Ⅱ | 系统中度失调,生态系统服务发展滞后 | ||
| 系统中度失调,二者较低水平均衡发展 | ||||
| 系统中度失调,人类福祉发展滞后 | ||||
| 拮抗 | Ⅲ | 系统拮抗,生态系统服务发展滞后 | ||
| 系统拮抗,二者基本均衡发展 | ||||
| 系统拮抗,人类福祉发展滞后 | ||||
| 磨合 | Ⅳ | 系统缓慢磨合,生态系统服务发展滞后 | ||
| 系统较强磨合,二者较高水平均衡发展 | ||||
| 系统缓慢磨合,人类福祉发展滞后 | ||||
| 高度协调 | Ⅴ | 系统高度协调,生态系统服务发展滞后 | ||
| 系统极度协调,二者高水平均衡发展 | ||||
| 系统高度协调,人类福祉发展滞后 |
2.3 数据来源
本文所使用的LUCC数据来源于中国多时期土地利用土地覆被遥感监测数据集(CNLUCC),Kappa系数在0.8以上,地类综合检验精度在95%以上,总体解译效果较好。人类福祉综合指标体系涉及的数据主要包括:(1)人口与社会经济数据,来源于全国第六次人口普查、2015年1%人口抽样调查、全国第四次经济普查、广州市及各区统计公报、《广州年鉴》《广州统计年鉴》及各区年鉴、广州市及各区“十三五”专项规划、广州市政府数据统一开放平台等,缺失数据通过线性内插获取;(2)矢量空间数据,来源于1∶100万全国基础地理数据库、天地图广州、OSM(Open Street Map)开源平台、高德地图POI数据以及矢量化自绘数据等。
3 结果分析
3.1 空间格局分析
3.1.1 生态系统服务与人类福祉的格局分析
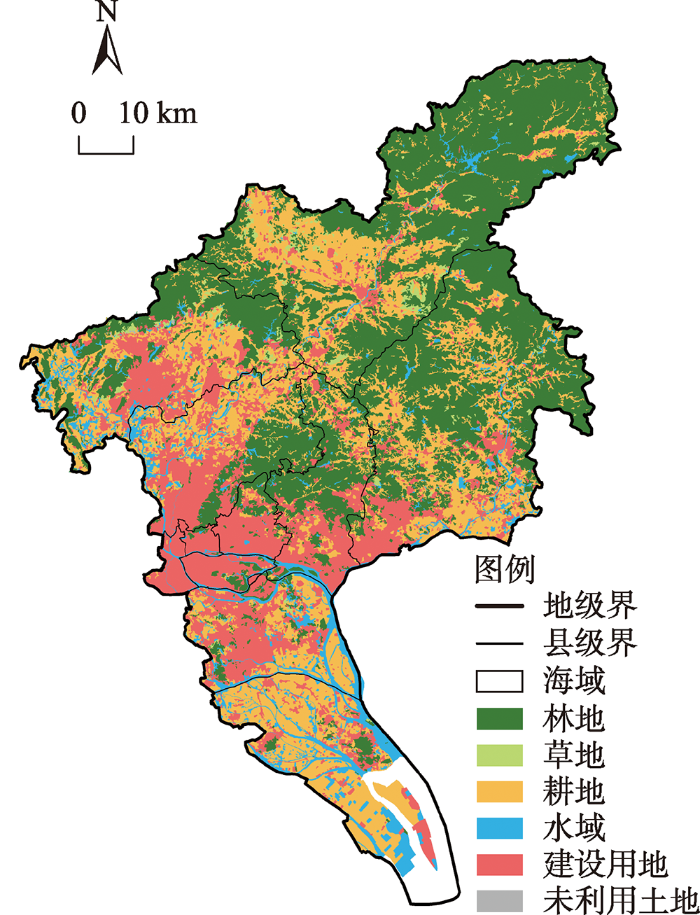
(1)生态系统服务价值严重萎缩,低值区连片蔓延。2005—2018年间广州市ESV总量的降幅高达21.09%,其中水域和林地是贡献广州市ESV的两大地类,但也是引起服务萎缩的主要载体。ESV分布的Moran's I值在0.5左右,高值区主要沿中部的珠江水系连绵延伸,得益于水环境质量的稳步提升(2020年地表水水质优良断面占比超过75%,劣Ⅴ类全部清零⑤(⑤资料来源于广州市生态环境局2020年广州市生态环境保护工作总结。))。但同时,13年间ESV分布的空间异质性又较为显著(图2):轴带延伸的高值区有所萎缩,多受城镇用地的侵占式扩张影响;低值区呈连片蔓延趋势,由广州现代中心都会区向各个方向拓展,与多中心、网络化的城市发展战略相匹配,区域分异加大。
图2
图2
2005—2018年广州市生态系统服务价值分布
Fig. 2
Spatial distribution of ESVs in Guangzhou during 2005-2018
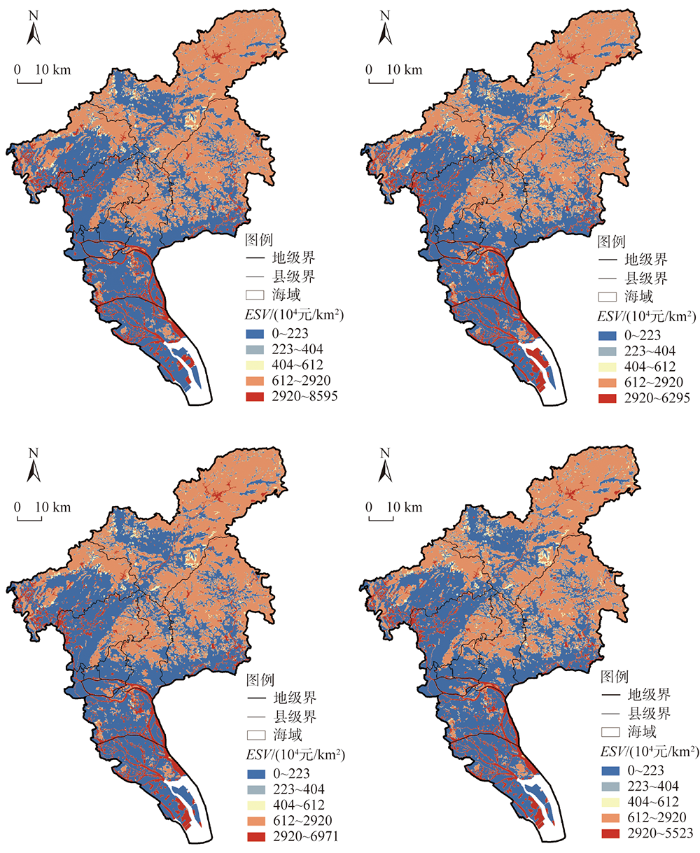
(2)人类福祉呈单核集聚、圈层式递减,趋同化增进较为显著。人类福祉空间分布的Moran's I值高达0.99,但其变异系数仅为0.18,反映出极强的空间集聚性与区域层面上的趋同化增进趋势。整体上形成了以越秀区为中心的单核区,在珠江前、后主航道附近出现了较高的福祉轴带(图3),滨水空间因而成为快速城镇化地区居民实现宜居、舒适、和谐福祉的关键依托。但局域离散与区际不平衡现象并存:创新福祉在空间广度、水平高度、内涵深度上均有不足;协调福祉在中心城区的水平最低,与其高密度布局、职住分离、收入差距大以及老城区老龄化严重等问题密切相关;绿色福祉较高的区域多破碎分布在城市边缘的生态涵养地、公园绿地等附近,广州都市核心区的福祉多通过绿色出行方式和碧道建设来实现;开放福祉的水平低、空间分异强,文化包容福祉的空间转化效应有待深化;共享福祉的分异性最弱、结构最复杂,辐射联动效应不强,宜养福祉的空间缺失明显;安全福祉呈城央集聚、圈层递减的趋势,区域之间显著不平衡,空间品质较低。
图3
图3
广州市人类福祉水平空间分布
Fig. 3
Spatial distribution of comprehensive HWB in Guangzhou
3.1.2 生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合格局分析
(1)耦合协调性的空间格局
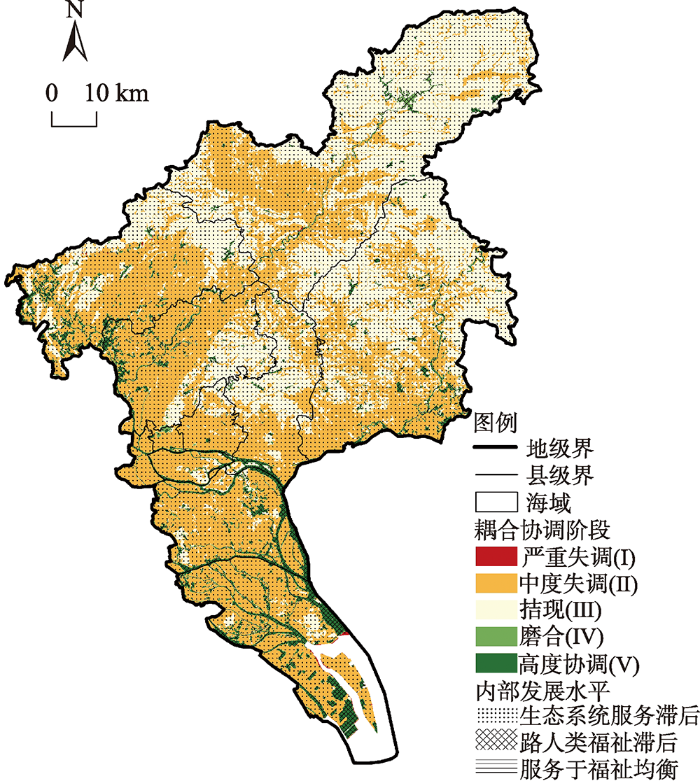
结果显示,广州市约89.7%的区域处于中度失调和拮抗阶段,处于高度协调阶段的仅占5.2%,生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合协调性较差,二者呈胁迫式关联。从空间分布看,耦合失调区(阶段Ⅰ和阶段Ⅱ)在广州中、南及西北部等区域连片蔓延,边界模糊效应显著(图4);区内生态系统服务价值较低,但人类福祉水平高,反映其对生态系统服务形成了较强的胁迫效应。拮抗区(阶段Ⅲ)破碎内嵌在失调区之间,多集中在广州东北部;该区正处于系统耦合演进转换期,较强的调节和支持服务对人类福祉起到了稳定的承载作用,减弱了福祉胁迫所带来的系统衰退风险。耦合协调区(阶段Ⅳ和阶段Ⅴ)主要沿珠江水系进行线状或轴带延伸,多为水域分布区(包含江河湖湾、水库湿地等);生态系统服务与人类福祉的发展水平均较高,彼此形成了较好的空间协同作用以促进系统的良性共振。
图4
图4
广州市生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合协调阶段分布
Fig. 4
Distribution of ES-HWB coupling coordination phases in Guangzhou
从内部发展水平来看,广州市90%以上区域的生态系统服务发展水平滞后于人类福祉,而生态系统服务又是相对稳定不变的一方,来自人类福祉的需求分异较易对其造成不同程度的胁迫作用,二者之间的供需空间失衡问题严峻。人类福祉滞后的区域基本上都分布在耦合协调区,表明较高耦合协调性的实现需要依赖于较强的生态系统服务。综上,耦合格局整体上呈现出显著的低失调同化趋势,且耦合协调阶段的分布基本上与ESV空间格局相契合,说明耦合关系的空间表征以生态系统服务为刚性主导,人类福祉则是起到弹性的促进/约束作用。
(2)维度分异下的对比分析
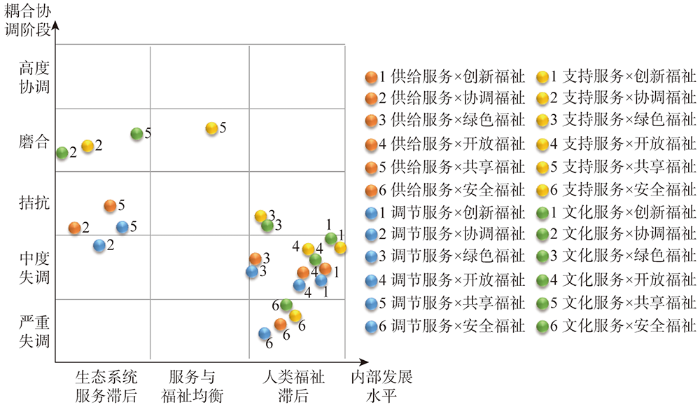
从维度分异的角度来看(图5),支持服务与共享、协调福祉,以及文化服务与共享、协调福祉之间的耦合协调性较强,高水平的福祉对服务起到了正向促进作用,以此促成了城市滨水空间较为显著的耦合协同效应。供给服务与共享、协调福祉,调节服务与共享福祉,支持服务与绿色福祉以及文化服务与绿色福祉的耦合关系处于拮抗阶段,其中前三者的服务水平相对滞后,福祉需求的跨域营造作用对服务供给造成了一定的空间胁迫,以组团、成片的方式扩展了耦合失调的范围;后两者的服务水平高,但耦合协调关联的空间辐射效应较弱,受绿色福祉破碎化分布的影响,服务与福祉的耦合处于博弈波动之中。剩下的关系均处于中度和严重失调阶段,除调节服务与协调福祉外,其余都是福祉滞后于服务,且耦合度基本较低,生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合的系统共振性较弱,供需空间不匹配问题导致了系统的失调发展。值得注意的是,创新、开放福祉与四种生态系统服务的耦合关系均呈中度失调,而安全福祉与四种生态系统服务的耦合关系则为严重失调,主要是由于这些福祉的空间分异性较强,很难与生态系统服务形成较好的空间关联。尤其是安全福祉呈现出了显著的圈层式递减分布趋势,边缘地区的低水平福祉远不能与生态系统服务相匹配,而服务供给又较难直接与居民的安全发展需求对接,彼此之间的耦合关系趋于无序失调。
图5
图5
维度分异下生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合协调阶段对比
Fig. 5
Comparisons of ES-HWB coupling coordination phases by dimension differentiation
3.2 驱动方式差异探析
3.2.1 生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合的逻辑框架
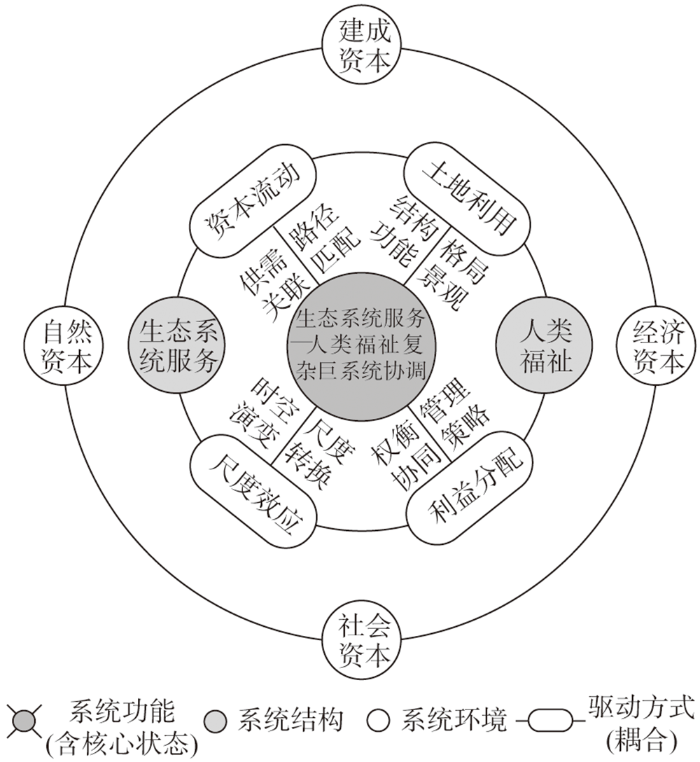
生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合即是基于二者紧密交互作用而形成的非线性复杂关系。对此进行科学辨析时,若仅从生态系统服务或人类福祉的一方来判断耦合状态,而不是基于“系统”和“关系”导向,则容易出现“以部分推知整体”的逻辑问题,难以准确认识复杂耦合系统的综合状况。“关系”(模糊作用方向)是影响系统状态和效果的关键,这种理解与系统科学论有很大程度的契合[47],尤其是以钱学森为代表的系统科学学者认为,应通过定量综合集成的方法、从关系的视角“自下而上”来研究开放的复杂巨系统(Open Complex Giant System,OCGS),包括地理系统、社会系统等[48]。因此,生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合关系可被理解为在生态系统服务—人类福祉复杂巨系统(简称“服务—福祉巨系统”)中表现出来的耦合状态。借助系统科学方法论,可构建起生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合的逻辑框架(图6),以更好地探析其驱动方式差异。
图6
从系统的组成维度来看,系统结构、系统环境和系统功能是系统形成的三大基础[49]。系统结构是指系统内部的构成要素,这里的两大核心要素即生态系统服务和人类福祉。系统环境侧重于系统外部起支撑或承载作用的环境条件,应为自然生态系统和人类社会经济系统中的“资本”(capital),通过主流研究成果[50,51]的梳理,可归纳为自然资本(主要来自生态环境的功能、过程、资源等)、经济资本(财富、市场、生产关系等)、社会资本(服务、人口、文化、制度等)和建成资本(建筑、设施、建成环境要素等)。这些资本输入后可转化为生态系统服务,再通过资本流动的方式凝聚为人类福祉。系统功能是系统整体性的外在表现,由系统结构和系统环境及其作用关系决定,是影响系统健康发展的核心。这里的整体性表征即服务—福祉巨系统的耦合状态,其核心发展状态是协调(与人地耦合系统的协调相辅相成),对应的核心发展目标是人与自然和谐共生。
为达成系统功能的核心状态,需要通过生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合关系来实现,具体的驱动因素主要包括资本流动、土地利用、尺度效应、利益分配等。其中,资本流动是来自几种资本的生物物理过程,多通过供给—需求关联、路径的匹配分异、可得性(access)差异等方式促成服务与福祉的耦合[16,52];土地利用(LUCC)是生态系统服务的直接作用载体和关键驱动力,也是人类福祉的空间响应表征,更是人地系统耦合的集成基底,通过其结构、功能、格局与景观的配置来促成可持续的系统运行效率[1,53];尺度效应(scale effect)从时空尺度的动态演变、不同尺度的转换与匹配等角度整合服务与福祉的关联作用[17,32],如生态系统服务变化时人类福祉将如何出现不同尺度的演变(或反之),与人地耦合系统的多尺度嵌套性互馈[30]等;利益分配(benefit allocation)侧重于生态系统服务惠益与人类福祉受益之间的配置,以权衡/协同、管理策略等为主要表征[53],既包括不同类型服务之间、不同层次和群体福祉之间的分配,更包括服务与福祉之间的复杂分配关系[52]。在不同区域,这些驱动因素及其作用方式各异,由此形成了各具特色、各具异质性的耦合关系。
此外,OCGS是基于非线性关系的自组织系统,以非平衡的自组织性为前提,以系统的协同为终极目标,且不断地处于涌现演化的进程之中[54]。在服务—福祉巨系统中,耦合关系会不断受到外部环境、跨域资本、远程耦合等的“开放式”影响,因此要重点关注外部负熵流的输入[55],主要通过生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合路径的调整,或(及)人类社会经济系统对系统功能的合理控制与管治,以促进系统向协调状态涌现,实现人与自然和谐共生。根据此逻辑框架,可从人地系统耦合的视角来探索性分析生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合的驱动方式及其内在机理,试图突破级联框架对于解构相互作用关系及其动力过程的不足,拓展生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合关系研究的新理论体系。
3.2.2 典型耦合类型区的驱动方式差异
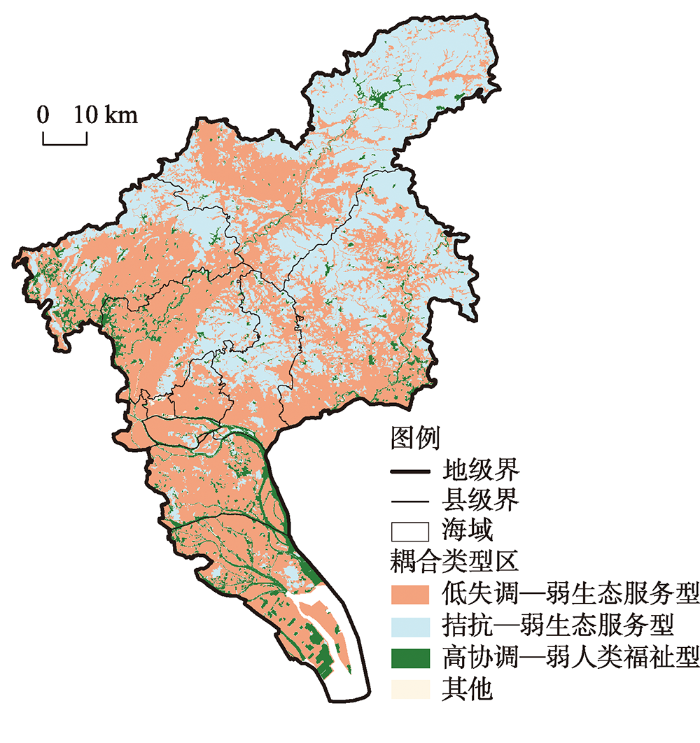
基于上述逻辑框架,在耦合关系现状格局中,根据生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合协调关系的阶段划分及相对发展水平差异,基于空间分异视角,提炼出三种典型的耦合类型区:低失调—弱生态服务型、拮抗—弱生态服务型和高协调—弱人类福祉型(图7)。分别剖析微观尺度下三者耦合关系的驱动方式差异。其中,将
图7
图7
广州市生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合的典型类型区分布
Fig. 7
Spatial distribution of typical ES-HWB coupling types in Guangzhou
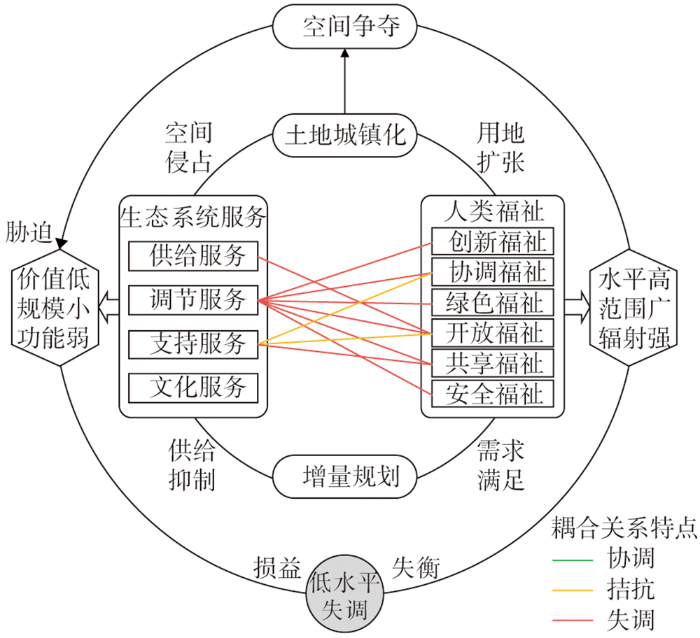
(1)低失调—弱生态服务型
该类型的面积占比最大,主要分布在广州中心城区、黄埔和增城的南部、白云西北侧和花都中南部、番禺和南沙建成区、知识城附近以及流溪河水系、增江水系沿岸等区域,呈跨域连片蔓延的趋势。区内人类福祉水平高,生态系统服务则较弱,福祉需求对服务供给形成了显著的负胁迫效应,二者的耦合呈现出权衡式的空间争夺,系统处于低耦合失调状态。受快速城镇化的驱动影响,“城市人”多元福祉的实现要以充足的发展空间为保障,由此水域、耕地被大量转变为建设用地,导致生态系统的结构和功能受损严重,服务破碎化。21世纪初广州市城市总体规划以多中心、网络型扩展为主要策略,这无疑加强了福祉侧的空间胁迫,进而造成了生态系统服务的低值蔓延,面积缩减36%的水域和耕地却导致ESV降低了60.7%。与此同时,资源要素的空间集聚又提升了人类福祉水平,促使共享福祉对支持服务、开放福祉对供给服务产生了较强的抑制作用,13年间水文调节、生物多样性、养分循环等服务价值萎缩超过20%。最终,以土地城镇化和增量规划为主导的压制式管治偏向造就了显著失衡的供需耦合关系,复杂巨系统趋于低失调的混沌发展(图8)。该类型的耦合失调源于人类福祉“发展”的绝对主导,系城镇化地区最常见的问题,其关键在于人类福祉需求对生态系统服务供给的空间侵占,“供小于求”或“供求分离”的空间不匹配关联亟待改善。
图8
图8
低失调—弱生态服务型耦合关系的驱动方式⑥
⑥ 图中的“耦合关系特点”仅标注出显著性较强的内部关联作用,下同。
Fig. 8
Driving pathway of low uncoordinated-weak ES coupling type
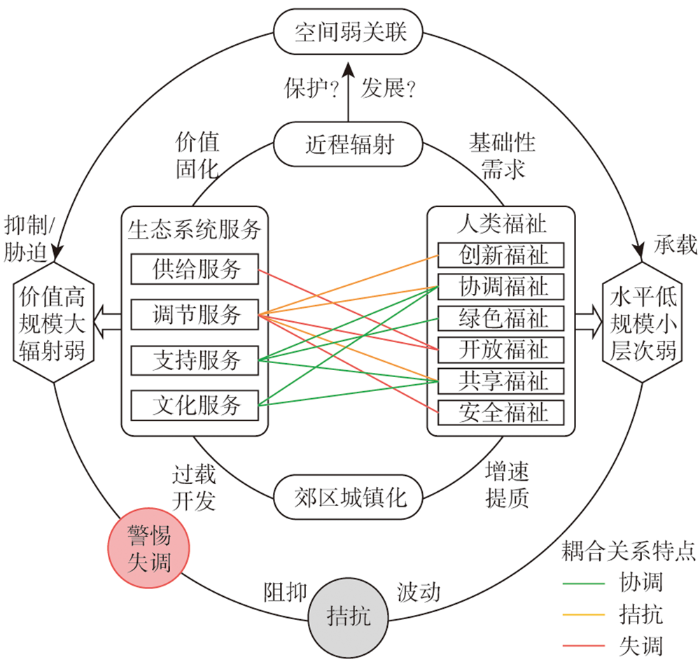
(2)拮抗—弱生态服务型
该类型主要分布在广州东北部、黄埔中部、增城东部、花都和白云交界的林区和山区,以及天河北部、海珠、番禺、南沙的森林公园等,与低失调—弱生态服务型区域错落内嵌。区内多为城郊及城市边缘的林地,生态系统服务价值高、规模大、质量优,人类福祉水平低但增速快,福祉需求愈发显现出对服务供给的抑制甚至胁迫作用,而服务对福祉的直接承载较弱,二者在空间上形成了弱关联,系统处于拮抗状态。林地提供了稳定高质的生态涵养功能和支持、调节服务,但此过程具有较显著的价值固化效应,主要通过近程辐射作用于人类社会经济系统。服务供给大多支撑的是绿色、协调、共享等基础性福祉(占比超过85%),主要满足的是洁净大气、稳定住房、小农自足等较低层次的福祉,由于这种承载不够直接和强大,因此难以适应城镇居民的多元发展需求。在这种情形下,郊区城镇化逐步强化,必然就要以林地等生态空间的牺牲为代价,导致林地ESV锐减21.1%,通常是在超出生态环境承载性的基础上谋求发展,造就了人类福祉对生态系统服务的阻抑作用。由此低福祉区域连片拓展,彼此之间以低—低集聚的方式进行破碎化关联,占据了该类型的42.3%。实际上,生态系统服务供给与人类福祉需求之间尚未形成较为匹配的资本流动,二者交互作用后自然就难达到“1+1>2”的效果,复杂巨系统趋于转折波动的演化(图9)。该类型耦合的实质是“保护”与“发展”的矛盾,其关键在于生态系统服务与人类福祉的供需弱关联与空间阻抑问题,需要特别警惕系统耦合过程中的失序、失衡风险。
图9
图9
拮抗—弱生态服务型耦合关系的驱动方式
Fig. 9
Driving pathway of antagonistic-weak ES coupling type
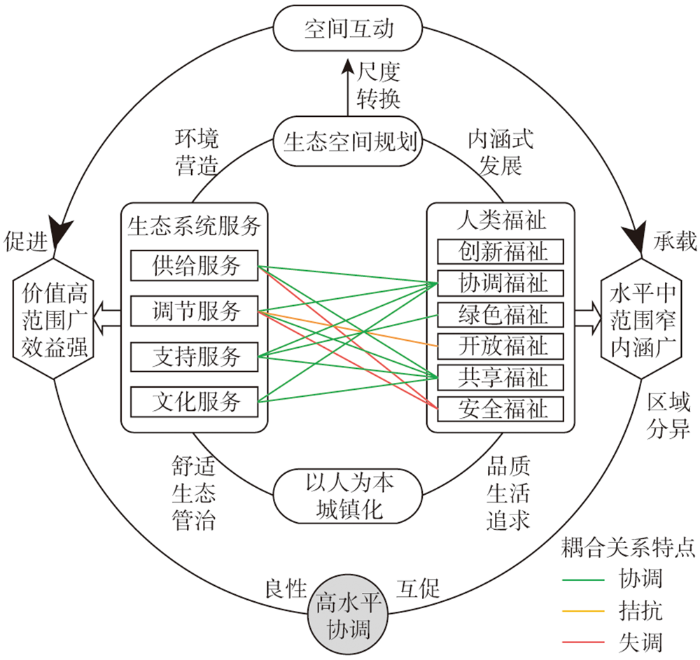
(3)高协调—弱人类福祉型
该类型的规模最小,多分布在广州中、南部的珠江主航道、入海水道,流溪河、增江、巴江、白云湖等水域,以及城市外缘的水库、湿地、河湾等,除中心的珠江水系呈轴带延伸外,整体分布较为零散。以水域为主要依托,生态系统服务价值高、效益强,贡献了ESV总量的54.6%;同时人类福祉得到较好满足,二者在良性空间互动的基础上形成了相互促进的耦合关系,系统处于高水平的协调状态。水域是影响广州市ESV最重要的地类,能提供重要的水文调节、净化环境、碧水资源等服务,辐射范围广。在碧道建设、珠江景观带、河网水系保育等生态空间规划的推进下,水域对人居环境的生态营造效应逐渐强化,促进了环境舒适、生态宜居、绿色健康、生活便利等的福祉实现,尤其是占比仅3%的支持和文化服务价值就以较强的耦合协调性产出了32.5%的人类福祉,成为“城市人”缔造高品质生活的必要支撑。由此打造的城镇滨水空间具备较强的内涵可塑性和生态韧性,在以人为本新型城镇化的战略推动下,城央区域“人水共生”的和谐环境逐渐形成。在此过程中,生态系统服务对人类福祉形成了良性承载作用,而人类福祉又能促进生态系统服务的稳定供给,二者通过和谐的供需协同、景观共塑、惠益互促等作用形成了相互匹配的良性空间互动,复杂巨系统趋于有序协调的方向涌现(图10)。该类型区在恰当的管治策略之上达成了耦合互促的协调,也是新时代广州城镇化迈向高质量发展的前沿阵地。因此,要继续加强因地制宜的耦合互促,但同时也需注意区域分异过大的问题:随着尺度转换的推移,生态系统服务与人类福祉的空间强关联可能在远程耦合之下显现出供需之间的约束分异,尤其是安全福祉的空间分异性强,将会对供给、调节等生态系统服务造成较大的阻抑压力。
图10
图10
高协调—弱人类福祉型耦合关系的驱动方式
Fig. 10
Driving pathway of high coordinated-weak HWB coupling type
4 结论与讨论
4.1 结论
本文将生态系统服务与人类福祉的关系研究从级联提到耦合的新高度,深入微观尺度,定量识别了生态系统服务与人类福祉的空间格局特征,分析了二者耦合关系的空间分异表现,最后基于人地系统耦合的范式构建了生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合的逻辑框架,探讨了典型耦合类型区的驱动方式差异。研究结果发现:
(1)广州市生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合协调性差,在快速城镇化的驱动下,人类福祉依托于建设用地的高速扩张而呈现出趋同化增进的趋势,对生态系统服务造成了胁迫式关联。随着人类福祉的强力集聚与局域离散化,服务价值严重萎缩,低值区连片蔓延,来自福祉需求的空间权衡效应较强,造成了二者耦合失调性的空间蔓延。
(2)广州市生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合关系以前者为刚性主导,生态系统服务受抑制,形成了低失调的同化格局。共享、协调福祉的广域实现损害了生态系统服务的空间功能发挥,创新、开放、安全福祉难以与生态系统服务形成较强的空间关联,服务供给与福祉需求间存在着显著的空间失衡。
(3)生态系统服务与人类福祉通过资本流动、土地利用、尺度效应、利益分配等驱动因素的差异形成了不同发展阶段和不同空间关联性的耦合。在增量城镇化阶段,人类福祉的“发展”占主导,通过对生态系统服务的空间侵占而形成空间不匹配的损益失调关系;在郊区城镇化区域,生态系统服务的价值固化,难以承载多元、高层次的福祉需求,形成空间弱关联的拮抗关系;当以人为本新型城镇化深化时,以滨水空间为纽带,生态系统服务与人类福祉形成了协同互促效应,在良性空间互动之中趋于协调发展。
4.2 讨论
突破传统的级联框架,从耦合这一系统集成的视角来审视生态系统服务与人类福祉的交互作用关系,是“人类世”背景下解构复杂人地系统耦合问题的必然选择。本文运用耦合协调度模型进行耦合格局的空间异质性分析,识别出了较为显著的生态系统服务与人类福祉耦合失调问题。其中,既有生态系统服务的积极承载作用,也有人类福祉的促进、阻抑、胁迫等多种效应,更有二者之间基于不同空间匹配特性的强、弱关联和权衡、协同关系。相较于级联的单向交互视角而言,耦合研究显然能更深入地揭示服务与福祉内在非线性关联的动力机理,更易于明晰其空间异质性的演变过程以及耦合形成的关键要素,有助于直观解耦人与自然耦合系统间的复杂交互作用,进而可为服务—福祉巨系统下的耦合空间实践提供切实可行的响应策略。面对广州市当前生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合失调问题,要夯实生态基底,刚性管控生态用地空间,丰富城镇发展空间的多元内涵,强化生态系统服务稳定供给与人类福祉趋同增进;将“三线管控”与“三生空间”有机衔接,统筹人地系统综合管理,在生态适宜承载性的基础上实现不同层次福祉的提升;创设生态系统服务与人类福祉良性空间互促的调控机制,快速城镇化区域严控城镇空间的无序外扩、弱化空间争夺,郊区城镇化的拮抗区域进行保护式开发与内涵式城镇建设,城央滨水空间的高协调区域注意加强服务的广域外溢与福祉的高质营造,深化高质量发展下生态系统服务与人类福祉的空间供需强关联。
为研究生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合关系,务必要理清二者的发展水平及其空间表现,其中对人类福祉的测量,尤其是其空间化识别问题,是耦合研究的重点和难点。本文以新发展理念为导向,基于“城市人”的发展需求构建了人类福祉综合指标体系,将评价尺度突破到100 m×100 m的微观单元。结果显示,广州市人类福祉的分布出现了以越秀为主导的单核区,集聚性强,圈层递减、局域离散、趋同化增进等特征明显。这些表现与居民福祉水平或客观福祉要素分布的相关研究成果[56,57]基本一致,能较好地印证广州城市发展的现状,表明人类福祉的高度集聚实际上也是各种资源要素和动力资本内化集中的过程,本文的体系与方法具有较好的科学合理性。不过,对于二级指标的细化、不同空间的差异化修正、不同时间上的动态演变、主客观福祉融合等问题亟待更多的区域实践以检验和完善。此外,受数据可得性、系统复杂性、技术不成熟性等影响,本文尚未能深入揭示服务与福祉间的非线性交互胁迫效应、非同步性时空异质演化、弹性传导动力路径、系统预警响应机理、综合集成反馈机制等问题,后续研究还需强化远程耦合、时空耦合,从多尺度嵌套、多维度反馈、多系统胁迫、非线性网络化涌现等深入研究。
参考文献
现代人地关系与人地系统科学
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 2]

人地关系地域系统理论系统提出30 a来,对促进地理学综合研究、学科建设和服务国家重大战略决策发挥了重要的科学支撑与导向作用。深入解析了人地关系地域系统理论的科学内涵及时代价值,诠释了现代人地系统的类型与环境,提出了“人地圈”与人地系统科学研究的主要内容和前沿领域。初步研究表明:① 现代人地系统具有复杂性、地域性和动态性特征,人?地交互作用过程、格局及其综合效应正在发生深刻变化,地球表层人地系统成为现代地学综合研究的核心内容和重要主题。② 科学认知和有效协调人地关系,亟需深入探究人地系统耦合格局与机理,探明人地关系地域系统类型、结构及其动力机制。依据城乡关系将人地关系地域类型划分为城市地域系统、城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统。乡村地域系统可细分为农业系统、村庄系统、乡域系统、城镇系统等子系统,分别对应于作土关系、人居关系、居业关系、产城关系。③ 现代人类活动强烈地作用于地球表层人地系统,形成了人地系统耦合与交互作用的地表圈层——“人地圈”,其实质是现代人类活动与地表环境相互联系、耦合渗透而形成的自然–经济–技术综合体或人地协同体。④ 人地系统科学或人地科学是研究人地系统耦合机理、演变过程及其复杂交互效应的新型交叉学科。它是现代地理科学与地球系统科学的深度交叉和聚焦,以现代人地圈系统为对象,致力于探究人类活动改造和影响地表环境系统的状态,以及人地系统交互作用与耦合规律、人地协同体形成机理与演化过程。人地系统耦合与可持续发展是人地系统科学的研究核心。传承创新人地关系地域系统理论和发展人地系统科学,更能凸显地球表层人类的主体性、人地协同的过程性和可持续发展的战略性,为人地系统协调与可持续发展决策提供科学指导。
Modern human-earth relationship and human-earth system science
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 2]

In the past 30 years, the theory of human-earth areal system has played an important support and guidance role in promoting the comprehensive research, disciplinary development and serving national strategic decision of geography. This study analyzes the scientific connotation and era value of human-earth areal system, explores the types and environment of modern human-earth system, and puts forward 'human-earth sphere' and the main contents and frontier fields of human-earth system science. The results show that: 1) The modern human-earth system is characterized by complexity, regionalism and dynamicity. The processes, pattern and comprehensive effect of human-earth interaction are undergoing profound changes, and the human-earth system on the surface of the earth has become the critical content and important theme of modern geosciences. 2) To scientifically understand and effectively coordinate the human-earth relationship, it is urgent to explore the coupling pattern and mechanism of human-earth relationship and to analyze the type, structure and dynamic mechanism of human-earth areal system. Based on the urban-rural relationship, the human-earth areal system can be divided into urban regional system, urban-rural integration system and rural regional system. Furthermore, the rural regional system is subdivided into agricultural system, village system, rural system and township system. 3) Modern human activities strongly affect the human-earth system on the surface of the earth, forming a new surface with the coupling and interaction between human and earth. In essence, it is a natural-economic-technological synthesis or human-earth coordination. They are also the main contents of deepening the researches on the coupling of human-earth system and supporting decision-making for coordinated development of human-earth system. 4) Human-earth system science or human-earth science is a new interdisciplinary subject which studies the coupling mechanism, evolution process and complex interaction effect of man earth system. It is the deep intersection and focus of modern geographic science and earth system science. Taking the modern human-earth sphere system as the research object, it is committed to exploring the state of human activities transforming and affecting the surface environment system, the interaction and coupling law of human-earth system, the formation mechanism and evolution process of human-earth coordination.Human-earth system coupling and sustainable development is the core of human-earth system science. Inheriting and innovating the theory of human-earth areal system and developing the human-earth system science will highlight the subjectivity of human on the earth surface, the process of human-earth coordination and the strategy of sustainable development, thus providing scientific guidance for the coordination of human-earth system and sustainable development decision-making.
Global change and the ecology of cities
DOI:10.1126/science.1150195
PMID:18258902
[本文引用: 2]

Urban areas are hot spots that drive environmental change at multiple scales. Material demands of production and human consumption alter land use and cover, biodiversity, and hydrosystems locally to regionally, and urban waste discharge affects local to global biogeochemical cycles and climate. For urbanites, however, global environmental changes are swamped by dramatic changes in the local environment. Urban ecology integrates natural and social sciences to study these radically altered local environments and their regional and global effects. Cities themselves present both the problems and solutions to sustainability challenges of an increasingly urbanized world.
The value of the world's ecosystem services and natural capital
DOI:10.1038/387253a0 URL [本文引用: 1]
Twenty years of ecosystem services: How far have we come and how far do we still need to go?
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.09.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Conceptualizing and operationalizing human well-being for ecosystem assessment and management
人地系统耦合下生态系统服务与人类福祉关系研究进展与展望
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.06.015
[本文引用: 4]

21世纪以来生态系统服务退化与人类需求提升间的矛盾愈发激烈,如何有效推进生态系统服务与人类福祉的协调平衡成为当前可持续发展的核心主题。论文通过梳理生态系统服务与人类福祉关系研究的阶段演进发现,现有研究主要从服务对福祉的影响与福祉对服务的反馈切入,逐步聚焦到供需关系与空间流动、权衡/协同的利益博弈、文化服务的价值化、生态补偿与付费、优化调控与可持续管理等二者相互作用关系的实践上。但目前的关系研究仍以“级联框架的‘影响链条’”为主导,缺少测度直接交互作用的技术路径,理论体系匮乏,面向可持续管理的应用支撑较弱,而同时二者逐渐形成非线性交互关系,亟需在人地系统耦合框架下寻求综合集成范式经验以推进理论创新。因此,论文提出从级联到耦合的关系研究新思路,以生态系统服务与人类福祉的耦合研究来系统辨析其交互胁迫效应及内在动力演化机理,同时探索性构建耦合研究的理论框架与技术思路,丰富人地系统耦合的关键命题。以此为基础,未来研究还需着重从交互作用关系的梳理出发,深化耦合效应解耦、传导机制与动态集成、基于服务与福祉协调的可持续优化等领域研究,促进有序协调的生态文明发展。
Research progress and prospect of the interrelationship between ecosystem services and human well-being in the context of coupled human and natural system
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.06.015
[本文引用: 4]

Since the beginning of the 21st century, the conflict between the degradation of ecosystem services (ES) and the increase of human needs has become increasingly intensified. How to improve the interrelationship between ecosystem services and human well-being (HWB) towards a coordinated and balanced state naturally becomes a core theme of sustainable development. Based on the reviews of ES-HWB interrelationship through three phrases, the existing research mainly started from the influences of ES on and responses to HWB, and further focused on the practices of their interrelationship through some key fields including supply-demand relationship and spatial flows, trade-offs/synergies, valuation of cultural ecosystem services, payments for ecosystem services, and optimized regulation and sustainable management. However, the interrelationship research is still led by "influence chain" of the ES cascade while distinct deficiencies exist in terms of theoretical framing, technical methods of direct interrelationship measurement, and support applied for sustainable management. Moreover, the ES-HWB interrelationship tends to become more nonlinear, which urges for certain theoretical innovation from synthetic integration paradigm of the coupled human and natural system framework. This article, therefore, proposed a new path for the ES-HWB interrelationship research—from cascade to coupling, with which the interactive coercing effect and its intrinsic dynamic change mechanism are clear to distinguish in a systematic way. On this basis, an exploratory theoretical research framework of ES-HWB coupling was built with a main thread of "interactive coercing effect measurement-coupling relationship deconstruction-coupled pattern and process evolution-coordinated management and application", so were the technical coupling approaches. In such regards, the ES-HWB coupling research is bound to develop as a pivotal issue enriching the coupled human and natural system studies. First, there is a need to untangle ES-HWB interrelationship as a foundation. Then, further in-depth research should be enriched to achieve the orderly and coordinated development oriented by ecological civilization, including the decoupling of coupled interactions, transmission mechanism and dynamic integration, human needs-oriented differentiated evolution, and sustainable optimization based on the ES-HWB coordination.
Taking the "U" out of Kuznets: A comprehensive analysis of the EKC and environmental degradation
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.08.006 URL [本文引用: 1]
Untangling the environmentalist's paradox: Why is human well-being increasing as ecosystem services degrade?
DOI:10.1525/bio.2010.60.8.4 URL [本文引用: 2]
Valuing recreational ecosystem services in developing cities: The case of urban parks in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
Disaggregating livelihood dependence on ecosystem services to inform land management
Human well-being differs by community type: Toward reference points in a human well-being indicator useful for decision support
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.04.003 URL [本文引用: 1]
Getting the measure of ecosystem services: A social-ecological approach
DOI:10.1890/120144 URL [本文引用: 1]
Relationships between ecosystem services and human well-being changes based on carbon flow: A case study of the Manas River Basin, Xinjiang, China
Frontiers in coastal well-being and ecosystem services research: A systematic review
Linking biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human well-being: Three challenges for designing research for sustainability
DOI:10.1016/j.cosust.2015.03.007 URL [本文引用: 2]
Ecosystem services-human wellbeing relationships vary with spatial scales and indicators: The case of China
Ecosystem services in coupled social-ecological systems: Closing the cycle of service provision and societal feedback
DOI:10.1007/s13280-015-0651-y URL [本文引用: 1]
Elasticity in ecosystem services: Exploring the variable relationship between ecosystems and human well-being
Modeling the complex associations of human wellbeing dimensions in a coupled human-natural system: In contexts of marginalized communities
Spatio-temporal evolution scenarios and the coupling analysis of ecosystem services with land use change in China
DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.136 URL [本文引用: 2]
The spatial differentiation of the coupling relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment in countries globally: A comprehensive assessment
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.07.009 URL [本文引用: 1]
城镇化与生态环境“耦合魔方”的基本概念及框架
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908001
[本文引用: 2]

城镇化与生态环境耦合系统是人地关系地域系统的重要一环,面对新时代全球尺度的远程联系、时空压缩与社会经济重构,传统的研究框架急需转型和升级。借鉴人地关系地域系统、远程耦合和星球城市化等理论,从复杂性科学视角出发,首先解析了城镇化与生态环境耦合系统的内涵,进而从空间、时间、表象和组织四个维度,提出了一个解释城镇化与生态环境耦合机理的分析框架——“耦合魔方(CHNC)”,并论述了其概念、内涵、演化规律和分析框架:魔方中的系统与系统、系统与要素、要素与要素间通过各种“耦合线”相互联系与作用,形成一个彼此嵌套、相互联系、对立统一的有机整体;魔方的旋转代表了不同地域间城镇化与生态环境的时空非线性耦合作用,系统通过不断能量交换,产生临界相变与整体涌现性,长期处于有序与无序之间的中间状态;“耦合魔方”包括近远程耦合、近远期耦合、组内间耦合和显隐性耦合,共四个维度,八种类型。重点剖析了远程、远期、组间和隐性耦合的科学内涵、研究方法与典型案例,并形成更具普遍意义的人地关系耦合矩阵。“耦合魔方”为揭示城镇化与生态环境耦合系统的演化和机理提供一个更加全面系统的跨学科研究范式,拓展了人地系统耦合研究的分析维度,为面向人类福祉的区域可持续发展政策制定提供科学支撑。
The coupled human and natural cube: A conceptual framework for analyzing urbanization and eco-environment interactions
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908001
[本文引用: 2]

The coupled urbanization and eco-environment system is an important aspect of coupled human and natural systems. However, the time-space compression, long range interactions, and reconstruction of socio-economic structure at the global scale pose great challenges to the traditional analysis frameworks for human-nature systems. We are in urgent need of developing a brand new analysis framework. In this paper, based on the connotation of the coupled urbanization and eco-environment system and its four dimensions — space, time, appearance and organization, we propose a conceptual framework "Coupled Human and Natural Cube (CHNC)" to explain the coupling mechanism between urbanization and eco-environment, which is inspired by the theories including human-earth areal system, telecoupling, planetary urbanization, and perspectives from complexity science. We systematically introduce the concept, connotation, evolution rules and analysis dimensions of the CHNC. It is worth noting that there exist various "coupling lines" in the CHNC, which connects different systems and elements at multiple scales, and forms a nested, interconnected organic bigger system. The rotation of the CHNC represents the spatiotemporal nonlinear fluctuation of the urbanization and eco-environment system in different regions. As the system exchanges energy with the environment continually, the critical phase transition occurs when fluctuation reaches a certain threshold, and leads to emergence behaviors of the system. The CHNC has four dimensions — pericoupling and telecoupling, syncoupling and lagcoupling, apparent coupling and hidden coupling, intra-organization coupling and inter-organization coupling. We mainly focus on the theoretical connotation, research methods and typical cases of telecoupling, lagcoupling, hidden coupling, and inter-organization coupling, and finally put forward a human-nature coupling matrix to integrate multiple dimensions. In summary, the CHNC provides a more comprehensive and systematic research paradigm for understanding the evolution and coupling mechanism of the human-nature system, which expands the analysis dimension of coupled human and natural systems, and provides some scientific supports to formulate regional sustainable development policies for human wellbeing.
城镇化与生态环境耦合圈理论及耦合器调控
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912008
[本文引用: 1]

城镇化与生态环境之间客观上存在着极其复杂的近远程非线性耦合关系,如何协调城镇化与生态环境的关系问题已上升为全球性战略问题和世界性科学难题。本文从理论上揭示了城镇化与生态环境交互作用的耦合性、耦合关系和耦合度;根据主控要素总结出了城镇化与生态环境耦合的10种关系和交互方式;根据耦合度强弱将耦合性分为低度耦合、较低耦合、中度耦合、较高耦合、高度耦合和完全耦合6种类型,分别对应随性耦合、间接耦合、松散耦合、协同耦合、紧密耦合和控制耦合,进而形成城镇化与生态环境耦合塔;创建了城镇化与生态环境耦合圈理论,按每旋转10°生成一个图谱构建了由直线图谱、指数曲线图谱、对数曲线图谱、双指数曲线图谱和“S”型曲线图谱等组合而成的45种耦合图谱,不同图谱对应着不同的城市发展阶段和发展模式。在多种耦合图谱中,认为“S”型曲线耦合图谱是最佳图谱,代表着多种图谱中体现城镇化与生态环境相互作用的最佳耦合状态。以“S”型曲线耦合图谱为依托,借助SD模型及各变量之间存在的一对一、一对多和多对多的复杂关系,构建了由11个调控要素和201个变量构成的耦合调控器(UEC),只要一个变量发生变化,就会牵一发而动全身,影响整个耦合调控器的结构、功能和调控结果。这种耦合调控器包括同一时间多个城市城镇化圈与生态环境圈之间的静态调控、不同时间同一城市城镇化圈与生态环境圈之间的动态调控、不同时间多个城市城镇化圈与生态环境圈之间的动态调控3种时空尺度,通过调控将逐步推动城镇化圈与生态环境圈之间由低级耦合向高级耦合方向演进。
Theoretical analysis of urbanization and eco-environment coupling coil and coupler control
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912008
[本文引用: 1]

There is an extremely complex nonlinear coupling relationship between urbanization and eco-environment. How to coordinate this relationship has become a global strategic problem and a worldwide scientific problem. First, based on theoretical analysis, this paper revealed the coupling, coupling relationship, coupling degree and coupling tower of interaction between urbanization and eco-environment. Second, by analyzing the main controlling factors, ten kinds of interaction modes between urbanization and eco-environment are summarized. Third, according to the strength of coupling degree, we have identified six coupling types, including low coupling, slight coupling, moderate coupling, high coupling, excellent coupling, and full coupling, which correspond to the random coupling, indirect coupling, loose coupling, synergistic coupling, tight coupling and control coupling, respectively. Then, urbanization and eco-environment coupling tower was formed. Finally, the theory of urbanization and eco-environment coupling coil was established. Through rotating the graph by 10°, we built 45 kinds of coupled graphs, including linear graph, index curve graph, logarithmic curve graph, double index curve graph and S-shaped curve graph. Different graphs represent different urban development modes, stages and characteristics. Among them, S-shaped curve coupled graph is optimal, and it reflects the best state of urbanization and eco-environment coupling. After that, we amplified the S-shaped coupled graph, and then constructed a coupler (UEC) based on the SD model and the complex relationship between different variables. The coupler consists of 11 regulatory elements and 201 variables, and can control the coupling state between urbanization coil and eco-environment coil. In general, the above control types include static control of multiple cities at the same time, dynamic control of a single city at different times, and dynamic control of multiple cities at different times. Through coupler control, urbanization coil and eco-environment coil can keep the best dynamic and orderly state. In addition, if one variable changes, the structure, function and simulation results of the coupler will also be affected. Finally, with the increase of control intensity, the coupler will gradually improve the coupling degree between urbanization coil and ecological environment coil.
人地系统耦合与可持续发展: 框架与进展
Human-natural coupling system for sustainable development: Framework and progress
新型城镇化、居民福祉与国土空间规划应对
New-type urbanization, well-being of residents, and the response of land spatial planning
Understanding the role of conceptual frameworks: Reading the ecosystem service cascade
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.05.015 URL [本文引用: 1]
Investigation of a coupling model of coordination between urbanization and the environment
DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.12.025
PMID:22265813
[本文引用: 1]

China's coastal cities are experiencing rapid urbanization, which has resulted in many challenges. This paper presents a comprehensive index system for assessment of the level of urbanization based on four aspects: demographic urbanization, economic urbanization, social urbanization and spatial urbanization. The developed index system also characterizes the environment based on three factors: environmental pressure, environmental level and environmental control. Furthermore, a coupling coordination degree model (CCDM) focusing on the degree of coordination between urbanization and the environment was established using panel data collected from 2000 to 2008 for Lianyungang, China. The results showed that: (1) the dynamic of coordination between urbanization and the environment showed a U-shaped curve, and both sub-systems evolved into a superior balance during rapid urbanization; (2) social urbanization and environmental control make the greatest contribution to the coupling system, indicating that they are the critical factors to consider when adjusting coordination development during decision-making; and (3) the two parameters (α-urbanization, β-environment) that have been widely used in previous studies had less of an effect on the coupling coordinated system than the other factors considered herein.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Applying the ecosystem services concept to poverty alleviation: The need to disaggregate human well-being
DOI:10.1017/S0376892911000506 URL [本文引用: 2]
城镇化与生态环境耦合动态模拟理论及方法的研究进展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201906002
[本文引用: 2]

城镇化与生态环境耦合是当前研究热点,而其动态模拟将是未来的重要方向。基于系统科学与跨尺度耦合理论揭示城镇化与生态环境耦合系统的本质,即一个非线性的、具有高低阶多重反馈的开放的复杂巨系统。通过综述城镇化与生态环境耦合动态模拟的理论、方法与应用的研究进展,可知:① 动态模拟成为趋势,相关理论与机理解析不断完善;② 动态模拟技术趋向多元化、精细化、智能化和集成化;③ 应用研究基于多类型案例区、多要素以及近远程与跨区域3个方面。当前研究不足包括:① 理论发展与整合不足;② 方法集成与数据共享力度滞后;③ 耦合关系链条和主控要素的动态特征未被完整揭示,远程耦合模拟缺乏定量表达、系统性整合以及与区域联动层面的应用衔接。今后,应以理论为根基,推动多科学交叉融合;以方法为支撑,推动动态模拟技术整合与数据共享;以应用为导向,揭示城市群等重点地区的近远程关系链条与主控要素的动态演化模式,为区域可持续城镇化提供决策支持。
Dynamic simulation of urbanization and eco-environment coupling: A review on theory, methods and applications
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201906002
[本文引用: 2]

At present, urbanization and eco-environment coupling has become a research hotspot. Owing to the complexity of the coupling mechanism, as well as the limitation of mathematical statistics methods, the process simulation of urbanization and eco-environment coupling needs to be strengthened. Based on the systems science and cross-scale coupling theory, we can define the coupled urbanization and eco-environment system as a nonlinear open system with multiple feedbacks. Based on the above analysis, the progress of dynamic simulation for urbanization and eco-environment coupling is reviewed. (1) As dynamic simulation has become a trend, the relevant analysis of theory and mechanism is being improved. (2) Dynamic simulation technologies have shown a trend of diversified, refined, intelligent and integrated pattern. (3) The simulation application mainly focuses on three aspects, including multiple-case regions, multiple elements, local coupling and telecoupling, and regional synergy. In addition, we found some shortcomings. (1) The development and integration of basic theories are insufficient. (2) The method integration and data sharing is lagging. (3) The coupling relational chains and dynamic characteristics of the main control elements are not fully revealed. Besides, telecoupling simulation is not quantified and systematically integrated, and could not be effectively applied to spatial synergy. In future, we should promote the intersection of research networks, technology integration and data sharing, and then uncover the evolution process of coupling relational chains and the main control elements in urban agglomerations. Finally, we should build decision-making support systems for regional sustainable urbanization.
生态系统服务研究动态及地理学研究范式
The research trends of ecosystem services and the paradigm in geography
DOI:10.11821/xb201112004
[本文引用: 1]

As studies on ecosystem services are becoming a hot spot among scientists, a research paradigm needs to be built in related discipline fields such as geography. This paper reviewed the progress, problems and trends of studies on ecosystem services at home and abroad. Furthermore, aiming at the topics and problems in current ecosystem service studies, we proposed a geographical paradigm and priority themes in this field. It is suggested that spatial heterogeneity and regional difference should be taken as entry points to study ecosystem services from geographical perspectives. Researches should be focused on the theme of ecosystem structure and function-ecosystem services-human well-being, and take the coupling connections between "ecosystem services offered by natural system and then internalized consumption of socioeconomic system" as the core research theme for comprehensive analysis of the response of socioeconomic system to the internalization of natural capital. We can promote integrated research on geographical sciences by constructing the geographical study paradigm of ecosystem service, which can not only expand the study capacity for ecosystem services, but also raise the level of comprehensive studies on social-ecological system. In addition, we should offer an important practical field for the study of human-land relationship, which is the core issue of geography.
Science for managing ecosystem services: Beyond the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
DOI:10.1073/pnas.0808772106
PMID:19179280
[本文引用: 2]

The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) introduced a new framework for analyzing social-ecological systems that has had wide influence in the policy and scientific communities. Studies after the MA are taking up new challenges in the basic science needed to assess, project, and manage flows of ecosystem services and effects on human well-being. Yet, our ability to draw general conclusions remains limited by focus on discipline-bound sectors of the full social-ecological system. At the same time, some polices and practices intended to improve ecosystem services and human well-being are based on untested assumptions and sparse information. The people who are affected and those who provide resources are increasingly asking for evidence that interventions improve ecosystem services and human well-being. New research is needed that considers the full ensemble of processes and feedbacks, for a range of biophysical and social systems, to better understand and manage the dynamics of the relationship between humans and the ecosystems on which they rely. Such research will expand the capacity to address fundamental questions about complex social-ecological systems while evaluating assumptions of policies and practices intended to advance human well-being through improved ecosystem services.
Uncovering the relationships between ecosystem services and social-ecological drivers at different spatial scales in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region
1970—2015年大别山区生态服务价值尺度响应特征及地理探测机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201909015
[本文引用: 2]

生态系统服务功能对于区域生态平衡、生态系统健康、国土生态安全及全球气候变化等方面具有重要作用,生态服务价值的尺度效应及空间分异机制问题值得探讨。以大别山区为研究对象,基于土地利用分类等数据,应用空间统计、热点分析和地理探测器等方法探讨1970-2015年大别山区生态服务价值动态演变、尺度响应特征及生态服务价值的空间分异机制。结果表明:① 1970-2015年,大别山区生态服务价值整体上升9.51亿元,但2010-2015年下降3.95亿元,占总增加值的41.54%,下降热点区主要位于大别山边界处(湖北省境内)及核心区东北部(安徽省境内);② 4种类型9级幅度的尺度对比分析表明,乡镇单元尺度是大别山区生态服务价值空间分异的特征尺度,其生态服务价值空间差异信息量丰富;③ 地理探测机制表明,16个影响因子中的生态用地占比、土地利用程度和人为影响综合指数对生态服务价值空间分异的解释力q值近40%,是导致空间分异的主要原因;高程和坡度因子q值近30%,为次要影响因素。交互探测q值达50%以上的交互组合主要有三大类30种,自然因子和人为干扰因子、景观格局因子交互协同作用增强了对生态服务价值空间分异的解释力。研究结果可为大别山区生态系统服务功能的精准、多元化调控提供一定的理论依据。
Scale response characteristics and geographic exploration mechanism of spatial differentiation of ecosystem service values in abie Mountain area, central China from 1970 to 2015
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201909015
[本文引用: 2]

Ecosystem services play an important role in regional ecological balance, ecosystem health, land and ecological security, and global climate change. The response characteristics of scale and the spatial differentiation mechanism of the ecological service value are worth discussing. Taking the Dabie Mountain area located in central China as the research object, based on the data of land use classification, this paper applied the methods of spatial statistics, hot spot analysis and geographical detector to examine the dynamic evolution characteristics, scale effect and spatial differentiation mechanism of the ecological service value of Dabie Mountain area from 1970 to 2015. The results show that over the 50 years, the overall value of ecological services in the Dabie Mountain area increased by 951 million yuan, while in recent years it decreased by 395 million yuan, accounting for 41.54% of the total value added. Scale is helpful for understanding the pattern and process of ecosystem. To strengthen the study of scale characteristics in the evaluation of ecosystem service function can improve the objectivity, credibility and practicability of the evaluation results. Therefore, in this paper, we made a comparative analysis through the scale of four types, which includes 9-level amplitude. The results show that the unit scale of township is the characteristic scale of the spatial differentiation of ecological service value in Dabie Mountain area, and the spatial difference information of the ecological service value at the township unit scale is rich, and the type of township unit scale is a more appropriate research scale level in the study area. To strengthen the geographical exploration of the spatial differentiation of ecosystem service value will be helpful to carry out regional ecological planning and ecosystem regulation. In this study, we analyzed the spatial differentiation mechanism of ecosystem service value in Dabie Mountain area by using the geographical detector. The results show that the explanatory power q value of the ecological land use proportion, land use degree and human influence composite index among the 16 influencing factors contributing to the spatial differentiation of ecological service value is nearly 40%, which is the main reason for the spatial differentiation. Elevation and slope factor q value is nearly 30%, which is a secondary factor. There are mainly three categories and 30 types of interaction combinations with an interactive detection q value of more than 50%. The interaction and synergistic effects of natural factors, human disturbance factors and landscape pattern factors enhance the explanatory power of spatial differentiation of ecological service value. Our work may provide a theoretical basis for the precise and diversified regulation of ecosystem functions in Dabie Mountain area.
土地利用/覆盖变化对生态系统服务的影响: 空间尺度视角的研究综述
A review on the impact of land use/land cover change on ecosystem services from a spatial scale perspective
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200513 URL [本文引用: 1]
一个基于专家知识的生态系统服务价值化方法
Expert knowledge based valuation method of ecosystem services in China
基于单位面积价值当量因子的生态系统服务价值化方法改进
Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area
青藏高原生态资产的价值评估
Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau
The concept, dimensions and methods of assessment of human well-being within a socioecological context: A literature review
DOI:10.1007/s11205-013-0320-0 URL [本文引用: 2]
Measuring quality of life: Economic, social, and subjective indicators
DOI:10.1023/A:1006859511756 URL [本文引用: 1]
A review of the elements of human well-being with an emphasis on the contribution of ecosystem services
DOI:10.1007/s13280-012-0256-7 URL [本文引用: 1]
面向高质量发展的中国城市体检方法体系探讨
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

改革开放40 a来,中国的城市规划、建设和管理水平发生了质的改变,但快速城镇化所引发的城市问题日益突出。城市体检概念应运而生,并逐渐从国家战略落实到城市高质量发展的具体实践中。在梳理和解析城市体检背景及其作用的基础上,详细阐述城市体检指标设计的逻辑框架,梳理城市体检各指标间的关系,辨析不同尺度间城市体检的异同,提出中国城市体检的方法,旨在对中国城市体检提供理论依据。
Method system of urban physical examination for high quality development in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

Over the past 40 years of reform and opening up, the urban planning, construction and management in China has undergone qualitative changes, but the urban problems caused by rapid urbanization are still increasingly prominent. The concept of urban physical examination arises at the historic moment and is gradually implemented from the national strategy to the concrete practice of urban high-quality development. On the basis of sorting out and analyzing the background and function of urban physical examination. This article starts from the core connotation of high-quality urban development in China, which is eco-livable, distinctive, diverse and inclusive, innovative, healthy and comfortable, safe and resilient, convenient transportation, clean and orderly. We design the index logical framework of urban physical examination from the above eight aspects and sorts out the relationship among various indicators of urban physical examination. Urban physical examination must be a ‘global physical examination’ rather than a ‘department physical examination’, so the urban physical examination has the dual function of ‘examination of general planning’ and ‘physical examination of a city’. The article points out that we should adopt the trinity of physical examination, third party physical examination and social satisfaction survey, and apply the closed-loop mode of ‘evaluation-feedback-governance’. It also analyzes the similarities and differences of urban physical examination in different scales, proposes the methods of urban physical examination in China. This article aims to provide theoretical guidance for urban physical examination in China and provide a research framework and scientific support for future urban physical examination research topics
再谈“城市人”: 以人为本的城镇化
Further discussion on homo-urbanicus: Human-based urbanization
Exploring the interactive coercing relationship between urbanization and ecosystem service value in the Shanghai-Hangzhou Bay Metropolitan Region
黄河流域生态保护与高质量发展的耦合关系及交互响应
Coupling relationship and interactive response between ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210112 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国省域生态文明建设与城市化的耦合协调发展
Coupling coordination development between ecological civilization construction and urbanization in China
Fifty years of systems science: Further reflections
DOI:10.1002/sres.711 URL [本文引用: 1]
钱学森系统科学思想的形成和发展
The formation and development of Qian Xuesen's system science thought
系统科学和系统工程的发展与应用
Development and application of system science and system engineering
Changes in the global value of ecosystem services
DOI:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.04.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
Relating ecoystem services to domains of human well-being: Foundation for a U.S. index
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.02.032 URL [本文引用: 1]
Mechanisms mediating the contribution of ecosystem services to human well-being and resilience
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.09.011 URL [本文引用: 2]
基于土地系统科学的土地利用转型与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 2]

土地系统科学的研究视角可为促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型研究提供参考借鉴。本文在梳理国际上土地系统科学发展历程基础上,基于土地系统科学研究视角探讨了土地利用转型影响城乡融合发展的理论框架、方式与路径以及促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控途径与措施。土地系统科学致力于监测土地变化,解释驱动因素和反馈机制,理解发生于土地上的人类—环境相互作用,实现将对土地系统的科学发现转化为可持续土地利用解决方案。土地系统运行以土地可持续利用与人类福祉为准绳,显化为土地利用的多维效应。通过科学管控土地利用转型实现土地系统的良好运行能够影响城乡融合发展进程。土地利用转型通过效率提升、价值显化、要素流通与结构优化4大渠道,在“强整体”效应与“补短板”效应的作用下助推城乡融合发展。基于土地系统科学视域下促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控需要重塑土地权能体系,推进国土空间综合整治,健全土地利用转型管控体系。
Urban-rural integrated development and land use transitions: A perspective of land system science
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 2]

The research perspective of land system science can provide a reference for the study of urban-rural integrated development promoted by land use transitions. Based on the review of the development of land system science, this paper discusses the theoretical framework concerning land use transitions affecting urban-rural integrated development guided by land system science, the influential ways and paths of land use transitions on urban-rural integrated development, and the measures of promoting urban-rural integrated development via adjusting and controlling land use transitions. Land system science is committed to monitoring land use change, explaining the driving forces and feedback mechanism, understanding the human-environment interactions occurring on land, and translating scientific findings on land system into solutions for sustainable land use. The operating of land system takes sustainable land use and human well-being as the criterions, and manifests as multi-dimensional effects of land use. Operating well the land system via scientifically adjusting and controlling land use transitions can affect the process of urban-rural integrated development. Land use transitions promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas under the effects of strengthening the whole and reinforcing weak links through four channels, i.e., efficiency improvement, value embodiment, development elements circulation and structure optimization. In order to promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas from the perspective of land system science, the adjustment and control of land use transitions need to reshape the land use rights system, to promote the integrated consolidation of territorial space, and to improve the management and control system of land use transitions.
系统科学哲学理论范式的发展与构建
The development and construction to the paradigm of philosophy of systems science
论地理学的研究核心: 人地关系地域系统
Man-earth areal system: The core of geographical study
DOI:10.2307/140646 URL [本文引用: 1]
Supply and demand assessment of urban recreation service and its implication for greenspace planning: A case study on Guangzhou
The location of retail stores and street centrality in Guangzhou, China
DOI:10.1016/j.apgeog.2018.08.007 URL [本文引用: 1]