基于此,本文针对新时代中国实现乡村共同富裕的目标,从当前乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性出发,分析乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡的内涵、维度与关键问题,构建乡村旅游区域不平衡性测度指标体系,在传统经济要素之外引入社会、民生与环境等多维度要素,在此基础上拓展中观和微观要素的测度,为乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡问题的量化研究提供科学手段和测度工具,为乡村旅游的区域协同与全面发展奠定理论基础。
1 传统乡村旅游区域不平衡性研究
1.1 传统研究中乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性理论
传统不平衡研究主要从经济角度展开[9],代表性理论包括增长极理论、异速增长理论以及累积因果效应理论等。其中,新经济地理学中的循环累积因果理论指出区域经济发展中会形成“核心—边缘”的经济结构[11];增长极理论描述特定地区的经济发展出现增长极并形成外部效应[10],主要体现为辐射作用和虹吸作用[12];异速增长模型指一个局部与另一个局部之间的增长率存在一个恒定的比值[13]。在中国乡村发展中,不平衡理论研究主要从空间区域格局层面展开,指出区域不平衡表现在全国、区域与区域内部多个层面。全国范围看,中国乡村综合发展水平区域差异呈现自东向西递减规律[14];地区层面看,乡村内部发展的不平衡,已经成为新时期中国社会主要矛盾的一个重要方面[15];理论层面,学者重点对欠发达地区的乡村发展和社会差异进行分析[16],建立了欠发达地区贫困的发展地理学分析框架[17]。
在乡村旅游层面,国外研究者常通过量化或访谈方法,探索乡村旅游发展给周边地区带来的负面影响[18]和因此导致的区域不平衡性,也探讨遗产保护等在不同乡村旅游发展区域的水平差异,提出乡村之间公平分配中的制度、政治、社会和经济等问题[19]。国内研究者指出乡村旅游发展呈现出的区域不平衡性表现为乡村旅游发展水平差距较大,甚至出现两极分化现象。尤其体现在“老少边穷”地区,由于区位差异、经济水平、思想观念、地理特征等的不同,产生了与其他地区发展较为明显的不平衡现象[20]。可以看出,区域不平衡发展是地理视角下乡村旅游研究的重要主题。但是,当前研究大多以旅游资源、经济和产业指标等为主,存在注重经济性而轻社会性等问题[21]。因此,在共同富裕背景下的研究中,要将传统要素之外的公平性和人本性等纳入乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性指标体系。
1.2 乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性的原因研究
针对乡村旅游发展不平衡性的原因,以往研究从资源基础和经济水平、地理区位和交通、政策导向和思想观念,以及生态环境等方面进行分析[22,23]。首先,乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡源于区位和资源禀赋的差异,拥有优势资源的地区通过融入城镇化、工业化、信息化进程,实现了乡村现代化[24],而另一部分地区区位相对不佳、经济基础相对薄弱、现代化和信息化程度相对较低,乡村旅游景区在数量、规模、建设水平等方面不及区位良好的地区,从而造成不平衡格局。其次,发展顺序和发展能力的差异是导致乡村旅游发展不平衡的原因。部分乡村地区经济建设起步较晚,乡村旅游发展能力欠缺,发展成本较高,存在隐形发展壁垒。因此财政支出会更多地投入其他发展前景良好的区域,从而进一步导致缺乏文化和旅游资源优势的乡村走向衰退[25]。第三,在文化和民生层面,国家为支持乡村和旅游助力乡村振兴,出台了系列政策,但乡村地区部分观念落后,存在“等靠要”的依赖行为,旅游业发展的内生动力不足。第四,从环境角度,一些具有特色生态资源的乡村地区地理特征复杂多样,尤其是西部民族地区,虽然自然资源和文化资源丰富,但生态环境敏感脆弱,旅游资源开发受到限制,乡村旅游发展处于较低层次[26]。最后,研究者也发现了乡村旅游发展中同一地区内部的居住区和景区之间的不平衡[27]。在以上原因作用下,旅游发展的区域差异会影响区域经济发展的平衡性[6],成为制约乡村共同富裕的关键问题。
1.3 共同富裕视域下乡村旅游区域不平衡性的新挑战
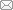
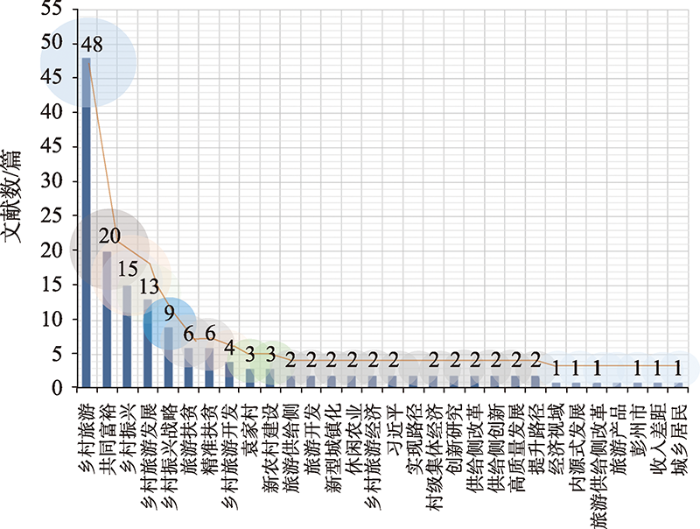
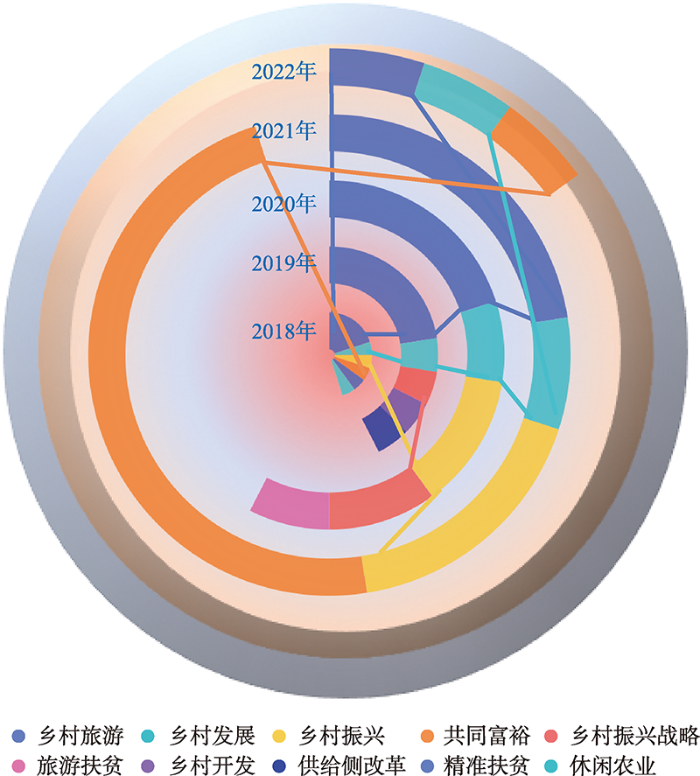
共同富裕包含物质和精神层面的双重富裕,包含社会和个体层面的多层富裕,实现共同富裕并非单一地提升收入,而是需要从解决社会主要矛盾入手[28]。对于乡村地区来说,区域发展的不平衡是阻碍实现共同富裕的突出问题[29]。乡村旅游与人民对美好生活的需求相契合,能够在经济发展、社会民生、区域协同治理等多个层面促进共同富裕目标的实现。但是,现有乡村旅游推动乡村发展的研究主要体现为经济层面的增收思维[30],并以经济要素为唯一指标衡量富裕程度。在中国知网对“乡村旅游”与“共同富裕”进行联合主题检索,可以发现二者的联合研究起始于近十年,研究主题服务于乡村振兴的国家战略,基于乡村资源分析探索产业开发路径,近年来开始关注精准扶贫(图1);次要主题更加具体,常见以民族村寨为分析对象,关注民宿产业和产品开发,并开始关注乡村居民及其感知(图2)。
图1
图1
乡村旅游与共同富裕研究主要主题分析
Fig. 1
Analysis of main themes of rural tourism and common prosperity research
图2
图2
乡村旅游与共同富裕研究次要主题分析
Fig. 2
Analysis of secondary themes of rural tourism and common prosperity research
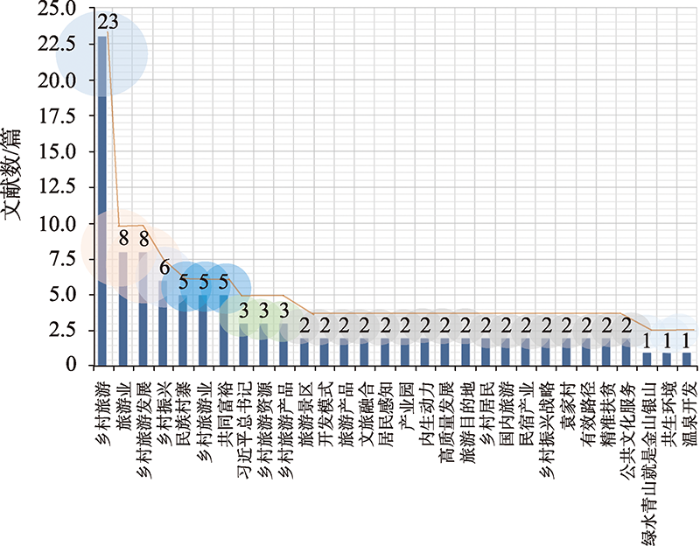
乡村旅游与共同富裕相关研究与中国国家战略需求存在一致性,因此也呈现出政策驱动和供给侧产业发展策略研究为主的特征(图3)。通过对近五年研究关注点分析,可发现乡村发展与振兴、战略研究、旅游扶贫与精准扶贫,以及供给侧改革和休闲农业研究日益丰富(图4),以乡村旅游推动共同富裕的研究处于理论积累的初期,也有研究创新提出推动区域内协同发展和共同富裕的重要方式包括协调人才振兴等[25]。总体可看出,现有以乡村旅游推动共同富裕的研究尚处于起始阶段,多从产业视阈出发,集中在经济策略研究,对共同富裕的人本性和民生性理论探索还比较缺乏,适用于乡村共同富裕研究的学理性和实证性分析亟待加强。但上述问题的核心都不能脱离乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性现象,在共同富裕视域下如何理解乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性及测度方法,需要学者给予更多的关注,为进一步以乡村旅游推进共同富裕提供扎实的理论参考。
图3
图3
乡村旅游与共同富裕研究主题共现矩阵
Fig. 3
Co-occurrence matrix of research topics of rural tourism and common prosperity
图4
图4
乡村旅游与共同富裕研究近五年关注点分析
Fig. 4
Analysis of focus of rural tourism and common prosperity research in recent five years
2 共同富裕视域下乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性内涵与维度
2.1 乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性基本内涵
在此实践基础上,共同富裕视域下解决乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性问题不仅在于解决绝对贫困,更要解决相对贫困问题[34,35],因此不仅要推动经济水平提升,更要超越经济指标,从环境系统、人文系统、乡风与治理系统等多维度综合评价[14];不仅要关注和解决不同地区宏观发展不平衡的问题,也要注重对不同区域主体间的感知差距进行合理控制与缩小[23],从而通过缓解不平衡问题,在客观物质层面和主观感知层面皆实现共同富裕。因此,在共同富裕视域下,要深入理解乡村旅游发展区域不平衡性的基本内涵,在于对绝对与相对贫困的双重考量;对经济与“超越经济”的全局筹划;对区域间与区域内多层空间的系统剖析,以及兼顾宏观与微观的人本理念指导。
2.2 乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性的维度及其特征
乡村旅游发展区域不平衡性的维度包含主客观维度和区域层级维度。主客观维度内含客观物质层面的不平衡和主观感知层面的[23]的不平衡性两种类型。区域层级维度内含区域间不平衡、区域内不平衡和区域主体感知的不平衡。就主客观维度分析,客观层面包括乡村发展的经济差异、区域水平差异、土地利用差异,以及空间格局差异等客观不平衡[36];主观层面体现为旅游区内不同主体感知到的不平衡,涉及社会议题、空间权利、利益和资源的非公平分配[37,38]、对旅游发展中对弱势群体的排斥、参与机会的不公平和权益侵犯[39]等问题。区域层级的不平衡包含三个层级,一是区域间不平衡,体现在部分乡村凭借良好的区位或资源[24]获得了相对其他地区更多的机会和发展成果,并导致对临近乡村的资源挤兑和人才虹吸等问题;二是乡村内部不平衡有所显现,乡村旅游发展区域空间重构中的优势经营区、原住民边缘集聚区、外来经营者区、空间衰退区等构成的不平衡格局[27];三是区域主体间的不平衡,体现为乡村旅游发展中的不同主体的收益分配、空间权力和个体权益等不平衡。
3 共同富裕视域下乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性关键问题
3.1 乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性的辩证分析
第二个辩证关系是乡村旅游与乡村不平衡性之间的辩证关系。一方面,乡村旅游的发展会导致不平衡的产生;另一方面,乡村旅游的合理发展能够推动原有的乡村不平衡性问题的解决。就前者来说,部分地区旅游发展会导致其他地区的相对落后问题[43],也会带来区域内外空间发展不平衡和空间主体权利不平衡等问题。就后者来说,旅游业作为兼具经济产业属性和社会文化属性的综合产业,能够促进乡村社会经济形态和地域空间重构[44],并在经济发展、社会结构、文化交往等层面缓解区域发展不平衡带来的负面影响[7]。乡村旅游可被视为乡村区域空间均衡优化发展的有力工具。当地方政府处理好旅游者、旅游企业和当地居民内部的结构关系时,旅游发展有助于实现区域经济、社会和文化在空间上共赢[45]。
3.2 乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性测度指标体系开发
在此基础上,共同富裕背景下的测度体系不仅要关注资源、经济和产业等指标,同样要关注人本性和民生性,应将传统要素之外的空间分配与参与公平性等指标纳入乡村空间重构和乡村旅游治理的考虑范畴,为实现乡村旅游区域协同发展提供科学依据和实证参考。在共同富裕视域下,学术研究需要探索如何基于多元要素构建有效的量化指标体系框架,科学地测度乡村旅游地发展的不平衡程度,才能为乡村旅游推动乡村共同富裕的实现提供学理基础。
3.3 乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性测度指标体系开发的应用实践
在明确了乡村旅游区域不平衡的内涵维度、测度与指标体系基础上,相关研究最终需落脚于应用实践,基于科学的量化评价定位不平衡性、解决不平衡性,实现发展机会、发展能力和发展结果的区域平衡[8]。从发展机会上,可探索如何为各乡村地区创造平等的发展机会,充分释放各地区的发展潜力,促进资源配置效率最大化。此外,乡村旅游区不同于景区的发展,可探索如何在空间格局重构中平衡乡村原住居民的利益。从发展能力上看,可在理论和实践层面探索如何联动、协调各乡村地区的财政能力、地方治理能力、开发规划能力、基础设施和服务水平,差异化资源优势。同时,可通过政策和实证分析研究如何丰富乡村社区居民的知识转移,如何提升乡村旅游发展的内生动力[48]。从发展结果上看,可探索外来企业投资主导模式与农民社区主导模式相平衡的理论模型,探索如何避免过度偏向,减少旅游漏损,促进乡村旅游发展成果共享[49],从而实现乡村旅游地区“人口—土地—产业”的耦合[50]和乡村旅游经济、社会、制度空间的协同发展[51]。此外,区域不平衡问题的解决落脚于空间问题,推动乡村发展的研究与实践需落实于具体的乡村地域空间,需要探索旅游系统与乡村地域系统内联外通且互促共融的路径模式[52]。在此过程中,更需要在以往的宏观、客观分析之外,注重区域间和区域内个体主观感知的平衡性,探索乡村旅游发展的不同主体间权利、利益和资源公平分配的路径[37,38],关注旅游发展中对弱势群体的排斥、参与机会的不公平和权益侵犯[39]等议题。
4 共同富裕视域下乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性测度体系
4.1 共同富裕视域下乡村旅游发展区域不平衡性测度框架
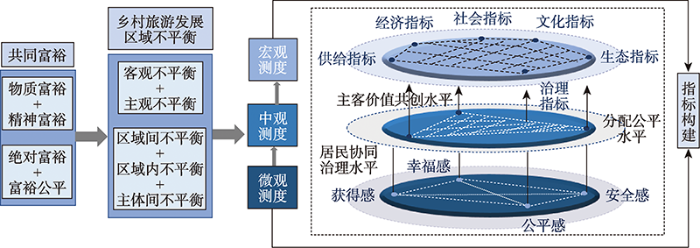
共同富裕包含物质和精神的双重富裕,兼顾人的发展与社会进步,强调成果共享和生活幸福[53]。因此,共同富裕视域下乡村旅游发展的平衡性既包含绝对量上摆脱贫困,也包括实现富裕过程中的公平性;既包含客观层面的富裕程度提升,也包含主观层面的富裕感知提升;既包含区域间平衡性的实现,也包含区域内和区域主体间平衡性的实现。在过去的研究中,中国共同富裕指标体系已经由经济收入分配延伸到经济、政治、文化、社会、生态等多维一体理念[54]。未来指标探索需进一步厘清指标构建的系统性思维方法,所建构的指标要反映人民主体共享性、共富内容全面性以及时代内涵[55]。基于以往研究,综合旅游发展特征,本文提出共同富裕视域下乡村旅游发展区域不平衡性测度从宏观、中观和微观三个层面进行(图5)。
图5
图5
共同富裕视域下乡村旅游区域不平衡性评价指标体系理论框架
Fig. 5
Theoretical framework of regional imbalance evaluation index system of rural tourism from the perspective of common prosperity
宏观层面需考虑乡村旅游区域的总体发展状况,从供给指标、经济指标、社会指标、文化指标、生态指标和治理指标六个维度衡量乡村旅游地区的发展情况,其中生态指标、供给指标和文化指标反映发展能力,社会指标表征乡村旅游地的发展机会,经济水平和治理成效则反映乡村旅游地的发展结果。中观层面需关注乡村旅游地各旅游主体,即政府、旅游企业、旅游地居民、旅游者等乡村旅游核心利益相关者[56]的关系,包括居民协同治理水平,主客价值共创水平和分配公平水平。居民协同治理强调各个主体之间的竞争和协作关系,治理主体与治理权威的多元化是其前提,多主体的协同与互动是其关键,共同的规则是各主体的行动准则[57]。该水平反映发展过程中政府、企业和旅游地居民之间的关系,衡量发展过程的民主性。主客价值共创水平反映旅游地居民和旅游者之间的关系。乡村旅游地居民与游客作为乡村旅游两大核心参与者,二者互动的本质是创造游客的体验价值[58]。分配公平水平衡量发展结果在各个主体间的公平共享程度,强调分配的起点公平、过程公平、结果公平[59]。微观视角方面,乡村旅游发展水平如何,归根结底要看人民是否满意,乡村旅游地居民的主观感受是判断乡村旅游区域发展平衡程度的最终落脚点。因此需关注乡村旅游地居民的幸福感、获得感、公平感、安全感等主观感受。
4.2 共同富裕视域下乡村旅游区域不平衡性测度指标构建
4.2.1 宏观层面测度指标体系
表1 乡村旅游区域不平衡性评价指标体系(宏观层面)
Table 1
| 宏观指标 | 测量维度 | 宏观指标 | 测量维度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 经济指标 (Economic Index) | EI-1旅游总收入 | 社会指标 (Social Index) | SI-1返乡居民旅游参与率 |
| EI-2旅游年接待人次 | SI-2乡村旅游企业数量 | ||
| EI-3旅游产值占总产值比 | SI-3旅游扶贫村占比 | ||
| EI-4居民可支配收入 | SI-4居民非农就业比例 | ||
| EI-5恩格尔系数 | SI-5医疗保障水平 | ||
| 供给指标 (Supply Index) | SUI-1交通便利度 | 文化指标 (Cultural Index) | CI-1教育人口覆盖率 |
| SUI-2景区数量 | CI-2旅游从业知识普及率 | ||
| SUI-3乡村住宿容量 | CI-3历史文化名村比例 | ||
| SUI-4餐饮供给数量 | CI-4文化场馆建设水平 | ||
| SUI-5对外开放程度 | CI-5文化活动举办水平 | ||
| 治理指标 (Governmental Index) | GI-1居民旅游参与率 | 生态指标 (Ecological Index) | ECI-1绿化覆盖率 |
| GI-2区域内旅游特色村占比 | ECI-2垃圾处理能力 | ||
| GI-3旅游管理规范化 | ECI-3污水处理能力 | ||
| GI-4旅游扶持力度 | ECI-4空气质量指数 |
经济指标直接衡量乡村旅游产业发展的经济结果,包括乡村旅游总收入、乡村旅游年接待人次、旅游产值占总产值比例、居民可支配收入、居民恩格尔系数。旅游收入和乡村旅游年接待人次反映旅游的发展程度,收入的不平等程度进一步反映经济不平衡程度[61]。旅游产值占总产值的比例指乡村旅游总收入与区域生产总值之比,一方面体现旅游发展的产业效益[62],另一方面可以说明旅游业对于乡村旅游地发展的重要程度。居民可支配收入反映乡村旅游地居民内部的贫富差距,可用居民可支配收入的极差或标准差间接表征乡村旅游地的收入分配。恩格尔系数指乡村旅游地居民个人消费支出中食品支出所占的比例,用于判断居民的生活富裕水平,也可以说明经济增长和收入增加对居民生活质量和消费结构的影响程度[63]。
社会指标衡量乡村、社会、政府对发展乡村旅游的支持度,用于反映各乡村地区发展机会均衡与否,包括返乡居民旅游参与率、乡村旅游企业数量、旅游扶贫村占比、乡村旅游地居民非农就业比例和医疗保障水平。返乡居民旅游参与率指乡村旅游地外出务工人员返乡从事旅游业的人员数量占旅游从业人员总量的比例,反映出乡村旅游地居民对政策号召的响应程度和参与积极性。乡村旅游企业数量和旅游扶贫村数量占比,分别体现出社会和政府这两个强势主体对地区发展乡村旅游的支持力度。乡村旅游地居民非农就业比例,也即本地新型职业居民占农村劳动力的比例,反映乡村旅游地产业发展的多元性[64]。医疗保障水平不仅是近年来健康理念、康养旅游和老年人旅游发展中的重要变量,也是目的地安全形象建构和发展潜力的重要指标[65]。
乡村文化是旅游发展的关键禀赋资源,在旅游中发展中占据重要地位[66]。公共文化服务建设水平是精神生活共同富裕的重要标识[67]。从人的角度看,人才振兴是乡村振兴的关键,文化和人才基础的差异是乡村旅游发展区域不平衡的重要表现,也是造成差异的重要原因[68],因此测量指标包括教育人口覆盖率、旅游从业知识普及率。教育人口覆盖率反映乡村旅游地人群总体受教育程度,受教育程度和个人技能体现劳动力的素质与决策能力。旅游从业知识普及率指拥有旅游相关技能型知识的人群在乡村旅游地总人数中所占的比例,间接体现乡村旅游发展能力的差异。从文化建设水平看,历史文化名村比例、文化场馆建设水平、文化活动举办水平可反映乡村旅游地将本地文化资源转化为旅游文化产品的水平。
此外,还包括供给指标、治理水平和生态指标。供给指标中,交通便利度是决定发展机会的重要指标[69],景区数量与食宿设施是影响旅游持续发展的重要因素[68],对外开放程度表征乡村旅游地联动内外资源的整合协调能力,以上要素共同构成乡村旅游供给体系,反映乡村旅游资源丰富度及资源供给能力。治理水平影响乡村旅游发展过程和发展方向,采用居民乡村旅游参与率、区域内旅游特色村占比、乡村旅游管理规范化、旅游扶持力度作为治理指标衡量发展结果。居民乡村旅游参与率能够反应旅游地居民的支持度[70],表征旅游地居民参与旅游活动的积极度。区域内旅游特色村占行政村比例、年旅游接待人次反映乡村旅游地的发展规模,间接反映治理结果和发展结果的不平衡程度。旅游扶持力度能够反映出治理环境,不仅是影响旅游创业意愿的较强影响因素[71],也反映了政府作为治理主体的治理方式与结果。生态资源是乡村旅游资源的基本构成,生态文明是旅游高质量发展的重要理念,生态指标能表征乡村生态文明建设水平[72],包括绿化覆盖率、垃圾和污水处理能力、空气质量指数。
4.2.2 中观和微观层面测度指标体系
以共同富裕蕴含的人本性、公平性为基础,旅游区域不平衡性评价的中观和微观层指标体系建构如表2所示。
表2 乡村旅游区域不平衡性评价指标体系(中观和微观层面)
Table 2
| 中观指标 | 测量维度 | 微观指标 | 测量维度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 协同治理水平 (Cooperative Governance) | CG-1治理主体多元化程度 | 幸福感 (Sense of Well-being) | SW-1主观幸福感 |
| CG-2各主体间协同关系 | SW-2客观幸福感 | ||
| CG-3各主体共同决策量 | 获得感 (Sense of Gain) | SG-1能力获益感知 | |
| CG-4协同治理规范化程度 | SG-2经济利益感知 | ||
| SG-3自我身份感知 | |||
| 主客价值共创 (Host-Guest Value Co-Creation) | VC-1居民对旅游业/游客感知 | 公平感 (Sense of Justice) | SJ-1机会公平感知 |
| SJ-2互动公平感知 | |||
| VC-2游客对旅游地/体验感知 | SJ-3结果公平感知 | ||
| VC-3主客互动场景质量 | 安全感 (Sense of Safety) | SS-1个体层面的经济安全 | |
| 分配公平水平 (Distributive Justice) | DJ-1经济尺度(基尼系数) | SS-2社会层面的保障水平 | |
| DJ-2制度尺度(分配制度) | SS-3交往层面的人际安全 |
中观层面,政府、旅游企业、旅游地居民、旅游者等核心利益相关者之间的关系采用居民协同治理水平、主客价值共创水平、分配公平水平来衡量。刘培林等[28]指出共同富裕的实现要从让人民公平积累人力资本、公平参与共创共建入手。基于此,本文所选取的协同治理水平能够反映居民在乡村旅游发展中的地位和作用,根据协同治理理论的四个特征,可以从治理主体的多元化程度、各主体间的协同关系、各主体共同做出重大决策的数量等角度来测度。主客价值共创主要指旅游地居民与游客积极互动,与游客共同创造的体验价值[73],能够反映主客权力的平衡性。主客价值共创水平以主客互动场景质量为基础,既表现为乡村旅游地居民对旅游业和游客的态度,也表现为游客对旅游体验的感知[58]。衡量分配公平可以采用科学尺度和经验尺度[59]。科学尺度主要是基尼系数,以收入为切入点测度经济成果分配公平水平。经验尺度即通过民意调查判断居民的满意度,从而判断分配公平程度,可用于评估乡村旅游发展中权力和空间等的分配公平水平。
微观层面,共同富裕与幸福生活紧密联系,政策努力的目的在于增进人民的幸福感[74],在2018年中央一号文件即提出促进共同富裕需提升农民的获得感、幸福感、安全感,即代表的精神层面的满足[75]构成了个体对共同富裕的感知。与此同时,公平正义是共同富裕最根本的价值取向[76]。因此,本文从幸福感、获得感、安全感、公平感角度衡量乡村旅游地居民对旅游发展的满意度。幸福感可以从主观幸福感与客观幸福感两个角度进行测度,前者是从居民感知角度分析其对当前生产生活状况的满意程度、情感状态等,后者则从全局视角出发测度乡村区域的生活舒适度、生活质量等[77]。获得感指居民对发展乡村旅游的能力获益感知,例如对观念型、技能型知识的获得[26],对经济利益增加的感知,对自我身份认同度的提升等。机会公平、互动公平、结果公平为测量公平感的三个主要维度[78],可以将居民对乡村旅游发展中的参与公平、利益共享公平度的认知作为衡量指标。安全感体现旅游地居民对生活保障和安全状况的认知,主要来源于个体层面的社会经济水平和社会层面的保障水平,如居民的风险敏感度与承受能力、乡村公共资源建设水平;以及交往层面的人际安全,例如乡村内部居民的友好关系与凝聚力等[79]。
5 结论与讨论
研究立足于乡村旅游发展的不平衡实践,指出其是制约乡村共同富裕的突出问题,探讨乡村旅游区域不平衡的内涵、关键问题和测度指标体系构建,旨在为共同富裕视域下乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡研究提供理论基础与方向。研究结论为:第一,在共同富裕背景下,乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性问题面对新的挑战,解决该问题具有迫切性。第二,研究创新指出,在共同富裕视域下,研究乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性的基本内涵在于对绝对和相对贫困的双重考量;对经济与“超越经济”的全局筹划;对区域间与区域内多层空间的系统剖析,以及兼顾宏观与微观的人本理念指导。第三,研究指出乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性的维度包含主客观维度和区域层级维度。其中,主客观维度体现为客观物质层面的不平衡和主观感知层面的不平衡性;区域层级维度体现为区域间不平衡、区域内不平衡和区域主体感知的不平衡。第四,研究指出了共同富裕视域下乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性关键问题,包括乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性的辩证分析、指标与测度体系的建构,以及不平衡性问题的解决。第五,研究对共同富裕视域下乡村旅游区域不平衡性测度指标构建提出了初步探索,建构了宏观、中观和微观指标体系,宏观层面包括供给指标、经济指标、社会指标、文化指标、生态指标和治理指标六个维度;中观层面包括协同治理、主客价值共创水平、分配公平水平;微观视角关注乡村旅游地居民的幸福感、获得感、公平感、安全感等主观感受,并进一步针对不同层级的指标提出了初步的测量维度探索。
本文超越以往区域发展不平衡研究中的经济视角,以共同富裕的物质和精神富裕双重性为基础,对绝对与相对贫困进行双重考量,对区域间与区域内多层空间进行系统剖析,兼顾宏观与微观的人本理念指导,综合宏观、中观、微观视角,对乡村旅游发展区域不平衡的内涵进行更新,对其衡量指标进行探索,旨在为乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性研究提供理论模型和测度工具。研究有助于充实乡村旅游助力乡村振兴的理论框架,为推动中国乡村共享发展成果、逐步实现共同富裕提供关键理论依据。但同时,本文仍存在不足之处,例如对测度指标体系的具体化和实操化探索有待深入、对区域不平衡发展的机理涉足不深等,因此未来研究可从以下几个方面进一步实现创新探索。首先,可基于乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性测度指标体系,因地制宜地探索更具体的代理变量及计算方法;第二,对不同区域进行实地测度,采集典型乡村旅游案例地的关键数据,发现和揭示乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性的空间格局;第三,综合采用量化分析、地理方法和心理研究等多元方法探索乡村不平衡性的演化过程和演化特征,从空间格局和动态演化综合视角破解乡村旅游发展的区域不平衡性,促进共同富裕。
参考文献
湖南省乡村旅游地空间分异及影响因素: 以五星级乡村旅游区为例
Spatial differentiation and influencing factors of rural tourism destination in Hunan province: A case study of five-star rural tourism areas
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210406 URL [本文引用: 1]
西部民族地区乡村旅游高质量发展的现实需求、丰富内涵和实现路径
The realistic demand, rich connotation and realization path of high-quality development of rural tourism in western minority areas
生活空间重构旅游者的乡村游憩影响因素与路径: 一个模糊集的定性比较分析
Influencing factors and path analysis of rural tourism: Based on tourists' living space changes: A fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200709 URL [本文引用: 1]
促进共同富裕的内涵、战略目标与政策措施
The connotation, strategic goals and policy measures to promote common prosperity
中国共产党推进全民共同富裕思想演进研究
The evolution of CPC's thought of promoting the common prosperity
区域旅游发展空间差异变化对经济发展平衡性的影响
The impact of spatial differences in regional tourism development on the balance of economic development
旅游发展、空间溢出与区域经济不平衡
Tourism development, spatial spillover and regional development imbalance
对我国区域不平衡发展的多视角观察和政策应对
Multi perspective observation and policy response to China's regional unbalanced development
贫困治理、产业结构与区域经济发展不平衡
Poverty governance, industrial structure and unbalanced regional economic development
产城分离视野下对增长极理论的重新审视
Reexamination of growth pole theory from the perspective of industry city separation
循环累积因果机制与我国区域协调发展
Circular cumulative causal mechanism and regional coordinated development in China
京津冀城镇体系的位序—规模与异速生长标度分析
An scaling analysis of allometry and size distributions of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban system
作为增长极的省会城市经济、人口和用地的集聚机制分析及对策建议. 城市发展研究
The agglomeration mechanism of economy, population and land use of provincial capital cities as growth poles
中国乡村地域类型及分区发展途径
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180981
[本文引用: 2]

由于我国乡村地域差异显著,乡村振兴需分类有序推进。本研究立足于人地关系地域系统理论,从资源、环境、人文、经济等维度构建了度量乡村综合发展水平的指标体系和计量模型,划分了乡村地域类型,明确了分区发展途径。结果表明,我国乡村综合发展水平区域差异显著,呈现明显的自东向西递减规律;全国乡村地域类型可以划分为11个一级区和45个二级区,不同类型区制约因子各异;乡村发展水平差异是资源禀赋、功能定位、区位条件、政策文化等因子交互作用的综合体现。地理环境是乡村地域类型分异的决定性因素,资源禀赋状况是乡村地域分异的关键因子,人文和经济因素在乡村系统转型发展中扮演着重要作用。通过对乡村地域类型、特征及其分异机制的研究,为乡村振兴战略的顺利推进提供了理论依据。
Areal types and their development paths in rural China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180981
[本文引用: 2]

Rural revitalization strategy is the general starting point for China's agriculture, rural areas and farmers in the new era. Because of the significant differences in rural areas in China, it is necessary to promote rural revitalization strategy according to local conditions, regional guidance and classification. Based on the theory of regional system of human-land relationship, this study constructs a comprehensive index system and measurement model to measure the level of rural development from the perspectives of resource endowments, geographical environment, humanistic elements and economic level, divides the areal types in rural China, and suggests the regional development ways. The results show that the level of rural comprehensive development in China varies significantly from east to west and that level in the eastern region is generally higher than that in the central and western regions. China's rural areal types can be divided into 11 first-class zones and 45 second-class zones, and there are distinct regional differences among different types. Geographical environment is the decisive factor for the differentiation of rural areal types, and resource endowment or resource type is the key factor for rural regional differentiation, and human and economic factors play an important role in the transformation and development of rural areal system. The connotation of rural areal differentiation lies in the difference of development level and industrial structure. The difference of rural development level is the comprehensive reflection of the interaction of many factors such as resource endowment, function orientation, location condition, national or regional policy, and historical background. From the perspective of human-land relationship, this study analyzes the characteristics, problems and development strategies in different types of rural areas so as to provide theoretical basis and decision-making guidance for the smooth promotion of the rural revitalization strategy in the new period.
走向共同富裕的解决相对贫困思路研究
A study on the approach of reducing relative poverty and achieving common prosperity
Mapping determinants of rural poverty in Guangxi: A less developed region of China
DOI:10.1007/s11629-019-5760-9 URL [本文引用: 2]
发展地理学视角下欠发达地区贫困的地方分异与治理
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910011
[本文引用: 2]

在梳理发展地理学的发展过程、基本理论、分析模式和方法的基础上,结合中国解决区域性整体贫困目标和可持续发展本地化与减贫的学术探索,构建了欠发达地区贫困的发展地理学分析框架,建立了由经济地理资本、社会地理资本、文化地理资本、生态地理资本和政治地理资本构成的“五位一体”地理资本指标体系,提出了数据处理集成方法和技术流程,系统分析欠发达地区贫困的地方分异与治理方案。实证研究显示:① 地理探测可以确定作用地方贫困的主导地理资本,各主导地理资本对贫困发生率的决定力L<sub>A</sub><sub>, </sub><sub>P</sub> ≥ 0.15;② 在不同主导地理资本作用下,5个单维地理资本指数及其合成的区域地理资本指数地方分异明显,存在阻隔和时滞特征;③ 贫困的地方分异可分为经济地理资本约束型、经济—社会地理资本约束型、经济—社会—生态地理资本约束型、经济—社会—文化—生态地理资本约束型4大类共7小类;④ 立足发展特征,挖掘地方动力,提出不同贫困分异类型的地方治理对策和模式。乡村振兴和2020年的减贫转向,应重视欠发达地区贫困的空间分异与空间扩散、空间整合的综合研究,为可持续发展本地化与减贫提供发展地理学解决方案。
Local differentiation and alleviation of poverty in under developed areas based on development geography
Impacts and social implications of landuse-environment conflicts in a typical Mediterranean watershed
People, power, and the coast: A conceptual framework for understanding and implementing benefit sharing
2020年后中国农村贫困的类型、表现与应对路径
Types,appearances and countermeasures of poverty in rural China after 2020
发展地理学视角下中国区域均衡发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102002
[本文引用: 1]

区域差异大、发展不平衡是中国的基本国情,研究区域均衡发展问题是发展地理学领域的重大课题。本文首先回顾了中国的区域均衡发展历程,总结了各时期区域均衡发展的特征,研究指出,中国区域间发展呈现出均衡发展与非均衡发展演替的状态,每次演进使得社会的发展质量迈进新的台阶,逐渐走向高质量发展与区域均衡发展的状态。其次,本文探讨了当前区域均衡发展的科学内涵,强调要以可持续发展理论为指引,关注不同地区资源禀赋差异,解决经济、人、自然三者间的矛盾,促进区域发展的空间均衡与生态经济协调的绿色发展,最终落脚到区域人民生活福祉的均衡提升为区域均衡发展的最终目标。最后,本文以发展地理学的思维从社会、经济、生态三个方面探讨中国区域均衡发展的路径,为中国区域均衡发展和国民福祉的提升提出若干建议。
Chinese balanced regional development strategy from the perspective of development geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102002
[本文引用: 1]

Large regional differences and uneven regional development is fundamental of China. Regional balanced development is an important topic in the field of development geography. This study reviews the course of regional balanced development in China and summarize the characteristics of regional balanced development in each period. This study suggests that inter- regional development of China shows a state of succession between balanced development and non-balanced development. Each succession brings the quality of social development to a new level and gradually make social development move towards the state of high- quality development and balanced regional development. Then, this study discusses the scientific connotation of regional balanced development. Under the guidance of sustainable development theory, we should pay attention to the resource endowment difference in different area, solve the problem among economy, human and nature and promote spatial balance of regional development and green development of ecological economic coordination. The balanced promotion of regional people's well-being is the ultimate goal of regional balanced development. In the end, based on the thinking of development geography, this study discusses the path of regional balanced development in China from three aspects of society, economy and ecology. Suggestions are put forward for the balanced development of China's regions and the improvement of people's well-being.
江苏省星级乡村旅游区的空间分布特征及影响因素研究
Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of star-level rural tourism areas in Jiangsu province
共同富裕路上的乡村振兴: 问题、挑战与建议
Rural revitalization on the path of common prosperity: Problems, challenges and suggestions
西方国家乡村空间转型研究及其启示
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.08.003
[本文引用: 2]

西方国家对乡村空间的认识经历物质、意象再到三元综合体的深化,后者作为西方学界理解乡村空间的系统性理论框架,为研究从生产主义到后生产主义的转型过程提供全新视角。西方国家的乡村分化表明,乡村空间转型的功能与价值重塑,在全球乡村视角下有一般规律性,对中国乡村空间转型研究有重要启示。当前中国正处于城乡空间加速重构的关键时期,加强乡村空间及其转型在多维度认知、多功能趋势和多主体机制等方面的研究,形成具有中国特色的乡村地理学研究范式,响应乡村振兴的时代主题。
Rural space transition in western countries and its inspiration
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.08.003
[本文引用: 2]

Recognition of rural space in western countries has undergone a profound turn from material and ideational space to the three-fold model of rural space proposed by Halfacree. Fundamentally influenced by “the production of space” and widely accepted as the systematic theoretical framework of rural space in western world, this model provides a whole new perspective on the transition of rural space in western countries from productivism to post-productivism. Differentiated rural space in western countries manifest that affected by interwoven forces of globalization, urbanization and modernization, dynamics and patterns of rural space transition development has been regenerated by combination and reorganization of essential productive factors, as well as its functions and values. Process of rural space transition in western countries reflects general rules in the view of “global countryside” proposed by Woods, which offers a great and significant enlightenment for studies in China. Based on the situation that urban and rural space is going through a critical period of accelerated reconstruction, theoretical guidance is urgently needed for newly emerging problems, patterns and forces, especially more studies on multi-dimensional cognition, multi-functional trend and multi-agent mechanism of rural space and its transition. In the end, this paper calls for establishing research paradigm of rural geography with Chinese characteristics, so as to better respond to the theme of the times on rural revitalization
新型农村集体经济创新发展的战略构想与政策优化
Strategic conception and policy optimization of innovative development of new rural collective economy
普适道路还是隐形门槛? 不同类型乡村旅游发展路径的外源因素
Universal road or invisible threshold? Exogenous factors indifferent development paths of rural tourism
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220308 URL [本文引用: 2]
基于社会网络分析的旅游地乡村社会空间重构研究: 以南京世凹“美丽乡村”为例
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.014
[本文引用: 2]

在商品经济影响下,乡村社会关系正发生多途径、多层次重构,由于社会关系与空间形态辩证统一,社会关系的异化将引起空间形态的变化。以南京市世凹美丽乡村示范村为案例,从传统社会结构观念与市场经济之间的冲突出发,建立研究假设,通过2014年、2016年和2018持续跟踪调查,运用社会网络分析方法揭示乡村经济社会空间交互过程。结果表明:① 所选乡村社会网络发展符合社会资本与市场制度相互作用的发展规律,具有替代效应、挤出效应与互补效应3个明显阶段,符合研究假设;② 网络模式由轮轴模式演化到“结构洞”模式再到合作与分派模式,且分别对应扩散型、分支型与簇群型网络结构,伴随行动者的淘汰与迁出与市场经济规则的增强;③ 空间重构主要表现为土地利用格局重构与乡村空间衰退现象,形成优势经营者区域、原住民的边缘集聚区、外来经营者区域与空间衰退区域。
Reconstruction of rural social space in tourist destinations based on social network analysis: A case study of Shiwa beautiful village, Nanjing city
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.014
[本文引用: 2]

Today, affected by the transformation of China’s rural development mode, rural social relations are being reconstructed from many aspects, which includes not only rational improvement but also problems such as ‘constructive destruction’ and ‘disintegration of rural social structure’. Due to the dialectical unity of social relations and spatial forms, the alienation of social relations will cause changes in spatial forms, which contributes to the two main research purposes of this paper.The first is to comb the development process of rural tourism and explore the interactive relationship between economic development and social transformation by means of social networks. The second is to explore whether there is a correlation between social relations and spatial changes by investigating and recording the process of spatial change in the countryside, so as to reveal the spatial effects brought about by the evolution of social relations.To this end, following the continuous follow-up investigations of the beautiful countryside of Nanjing Shiwataoyuan village (Hereinafter referred to as Shiwa Village) in 2014, 2016, and 2018, this paper calculates each social network parameter index via social network analysis methods and analyzes the interactive process of rural economic and social space from 2012 to 2018 in detail. The results indicate: 1) The development of the selected rural social network conforms to the development law of the interaction between social capital and the market system, and has three distinct stages: substitution effect stage, crowding-out effect stage and complementary effect stage; 2) The network model evolves from the wheel and axis model to the ‘structure hole’ model and then to the cooperation and faction model, which corresponds to the diffusion, branch and cluster network structures respectively, accompanied by the elimination of actors and the enhancement of market economic rules; 3) Spatial reconstruction is mainly manifested in the reconstruction of land use pattern and the decline of rural space, during which process a dominant operator area, a marginal agglomeration area of aborigines, a foreign operator area and a spatial recession area are accordingly formed.
共同富裕的内涵、实现路径与测度方法
The connotation, realization path and measurement method of common prosperity for all
新时代共同富裕的理论发展与实现路径
Theoretical development and realization path of common prosperity in the New Era
乡村振兴战略下民族地区农民可持续增收路径研究: 以广西龙胜各族自治县为例
A Study on the sustainable income-increase path of farmers in ethnic areas under the rural revitalization: Taking Longsheng multi-ethnic autonomous county as an example
旅游开发的正义反思与求索
Reflection and pursuit of justice in tourism development
Attached to or bound to a place? The impact of green space availability on residential duration: The environmental justice perspective
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.10.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
贫困、他者与平等: 反贫困中乡村旅游发展的文化解读
Poverty, the other and equality: A cultural interpretation of rural tourism development in Anti-poverty
中国乡村旅游研究历程与新时代发展趋向
The research process and trend of development in the New Era of rural tourism in China
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211012 URL [本文引用: 1]
面向2035年的中国反贫困战略研究
China's anti-poverty strategy towards 2035
土地利用转型与乡村转型发展耦合研究进展及展望
Progress and prospects of the coupling research on land usetransitions and rural transformation development
乡村社区旅游空间不正义及其“住改商”制度症结: 波兰尼嵌入性视角下的西江苗寨实证研究
Spatial in justice in rural community tourism and the negative impacts of the residential-to-commercial conversion system: An empirical research on Xijiang Miao village from the perspective of Polanyi's embeddedness
多维贫困视角下的旅游扶贫与空间正义研究: 以贵州施秉喀斯特世界遗产地社区为例
Research on spatial justice and pro-poop tourism from the perspective of multidimensional poverty: The case study of the community in Shibing Karst World Heritage Site in Guizhou province
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704001
[本文引用: 2]

快速城镇化进程驱动中国乡村地域发生巨大变化。乡村重构,即为适应乡村内部要素和外部调控的变化,通过优化配置和有效管理影响乡村发展的物质和非物质要素,重构乡村社会经济形态和优化地域空间格局,以实现乡村地域系统内部结构优化、功能提升以及城乡地域系统之间结构协调、功能互补的过程。本文在界定乡村重构的概念内涵,构建基于“要素—结构—功能”演变助推乡村重构的理论框架基础上,从空间重构、经济重构、社会重构视角探讨了乡村重构的实现路径,并着眼于服务当前国家重大战略需求和解决城乡转型发展进程中乡村地域系统面临的现实困境,提出了未来中国乡村重构研究需重点关注的内容。最后,就现有旨在促进乡村社会经济发展的重大引导性战略和政府干预性政策及其在实践操作中引发的一系列问题,展开批判性分析和讨论。
Rural restructuring: Theory, approach and research prospect
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704001
[本文引用: 2]

For the sake of adapting to the changes of elements in both kernel system and external system of rural development, rural restructuring is a process of optimally allocating and efficiently managing the material and non-material elements affecting rural development, reshaping social and economic structures in rural areas and optimizing spatial pattern in rural territory, and approaching the structure optimization and function promotion of rural territorial system as well as the structure coordination and function complementation of urban-rural territorial system. Based on elaborating the concept and connotations of rural restructuring and the mechanism of promoting rural restructuring due to the evolution of "elements-structure-function", the paper probed the approaches of rural restructuring from the aspects of spatial restructuring, economic restructuring and social restructuring. In order to meet the current national strategic demands and meet the challenges of rural development in the process of urban-rural development transformation, it is in great urgency to strengthen the study on the patterns and processes, dynamic mechanism, differentiated development models, rural planning technology systems, strategies and policies for rural development, and the impacts of globalization on China's rural restructuring in the future. Finally, focusing on a series of problems in the implementation of some important government intervention policies, which is aimed at boosting the social and economic development of rural areas in recent years, a critical analysis and discussion is carried out.
江苏省乡村地域功能与振兴路径选择研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180919
[本文引用: 1]

乡村振兴战略背景下,探索乡村振兴的差异化路径成为研究热点。乡村地域功能具有空间的差异性,明晰乡村地域功能的空间格局对于准确定位乡村发展模式、实施差异化的乡村振兴路径具有重要意义。本文以江苏省为例,采用定量评价方法,构建了包含生产发展、生活保障和生态保育为核心的乡村地域多维功能评价指标体系,以县级尺度识别了乡村地域功能的空间格局和地域类型,在此基础上探索各类型区差异化的乡村振兴路径。结果表明:江苏省乡村生产发展功能尚需完善、空间集聚程度低;生活保障功能空间格局和社会经济发展的地带性规律基本一致,呈现由苏南向苏北渐进衰退的趋势;生态保育功能高值区的区县数量较少,大部分区县的生态保育功能还有待加强;乡村地域总体功能由苏南向苏北呈现先行发展区、优化升级区、转型提升区和滞后欠发达区四种地域类型。此外,根据乡村地域总体功能呈现的差异化地域类型分别提出了相应的乡村振兴路径。
Detecting the pathways towards rural vitalization from the perspective of territorial functions in Jiangsu province
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180919
[本文引用: 1]

Detecting a pathway towards rural vitalization has drawn considerable attentions from both governments and scholars in China within the context of rural restructuring. Given that territorial functions of rural areas varies cross the country, it is essential to clarify the spatial pattern of territorial functions for demystifying the model and pathway of rural development. Taking Jiangsu - one of the most developed provinces in eastern China - as an example, this paper proposes an indicator system for rural territorial function covering triple dimensions of economic development, life support, and ecological conservation. Thereafter, we conduct an empirical study at the county and district level followed by a discussion about potential pathways towards the vitalization of villages in different zones. The findings imply that: 1) the function of economic development in rural Jiangsu is not as good as expected, and the degree of spatial agglomeration is relatively low. Coincidently, the pattern of life support is consistent with that of economic development, which is regarded as a trend of gradual decline from south to north. Few districts or counties can be detected with high values of ecological conservation, which suggests an urgent demand for sustainable development in rural Jiangsu. 2) Taking the spatial heterogeneity of rural areas in respect of their overall functions into consideration, we further divide the province into four zones, namely primarily developed zone, optimized developing zone, transformation zone, and lagging underdeveloped zone. Finally, we put forward some suggestions for rural vitalization in the aforementioned functional zones, and argue that rural revitalization is a long-term project that cannot be done overnight.
国土空间规划体系下乡村空间规划管控途径: 以4个典型村为例
Approaches of rural spatial planning and governance under the land spatial planning system: A case study of four typical villages
农家乐发展的地域空间格局及其影响因素: 基于浙江、湖北、四川的比较研究
Regional spatial disparity and influencing factors of the development of agritainment: A comparative study of Zhejiang, Hubei and Sichuan provinces
DOI:10.2307/142511 URL [本文引用: 1]
Incorporating indigenous rights and environmental justice into fishery management: Comparing policy challenges and potentials from Alaska and Hawaii
DOI:10.1007/s00267-013-0021-0 URL [本文引用: 1]
典型村域乡村重构的过程及其驱动因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201902009
[本文引用: 1]

乡村重构是实施推进乡村振兴战略的重要手段,一个完整的乡村重构过程通常由初始期、发展期、趋稳期、稳成期等不同阶段组成。本文在构建乡村重构过程分析的理论框架基础上,探索引入乡村发展指数、乡村重构强度指数和乡村重构贡献率的概念,选取大都市郊区和平原农区典型村域开展乡村重构过程的定量研究和驱动因素的对比分析。研究表明:① 20世纪90年代以来,伴随产业结构由传统农业向工业采矿业、旅游服务业转型,黄山店村社会经济形态和地域空间结构发生了剧烈重构,乡村重构过程依次经历了初始阶段、发展阶段,目前处于趋稳阶段;杨桥村产业发展经历了传统农业主导、农业兼业化生产阶段,自2000年以来开始出现社会经济重构迹象,近年来在地方政府推动下生活空间发生重构,但经济形态尚未发生明显改观,目前村域整体上仍处于低水平发展阶段。② 黄山店村快速的乡村重构是市场需求牵引、政府宏观政策引导等外源性因素及资源环境、区位条件、行为主体、经济基础、文化特质等内源性因素综合作用的结果;杨桥村的重构历程主要受城镇化、工业化、技术进步等社会经济发展进程以及“新农村建设”“增减挂钩”等外源性政策因素主导,缺乏内生发展动力是导致其重构速度相对缓慢的根源。
Process and driving factors of rural restructuring in typical villages
旅游对全面脱贫与乡村振兴作用的途径与模式: “旅游扶贫与乡村振兴”专家笔谈
Ways and patterns of tourism's role in poverty alleviation and rural revitalization: Expert discussion on "Tourism for Poverty Alleviation and Rural Revitalization"
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211011 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国区域旅游业发展不平衡的演变特征研究
A study of the evolution characteristics of the unbalanced development of China's regional tourism industry
湖南乡村生活质量的空间格局及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201812009
[本文引用: 1]

认知乡村生活质量的地域分异规律及形成原因,既是新时代乡村地理学研究的新内容,也是科学实施“乡村振兴”战略的内在要求。以湖南省101个县(市、区)为研究单元,构建由6个维度组成的乡村生活质量评价指标体系,运用熵权法、探索性空间数据分析(ESDA)及地理探测器等研究方法,研究湖南乡村生活质量的空间格局特征及其影响因素。结果表明:湖南乡村生活质量总体上呈现出东高西低并由东向西依次递减的空间分布态势;从空间关联格局来看,HH区和LL区在空间上集聚格局明显,显著HH区主要分布在长株潭城市群地区和周边临近县域,显著LL区主要分布在大湘西地区;影响湖南乡村生活质量空间格局的重要因素为人均GDP、城镇化水平、离省会城市距离、海拔,次重要因素为坡度、第二第三产业占比、农村非农劳动力占比、农业机械总动力。振兴乡村,提高乡村生活质量应在充分保护乡村生态环境的基础上,把乡村产业振兴和经济振兴放在优先的位置,应积极改善广大乡村地区的互联互通条件,促进乡村地区基础设施和公共服务设施的现代化。
Spatial pattern and influencing factors of quality of life in rural areas of Hunan province
以知识转移促进后脱贫时代乡村旅游产业与人才双振兴
Promoting the dual revitalization of rural tourism industry and talents in the post poverty era with knowledge transfer
乡村振兴中的旅游乡建与包容性发展
Rural tourism construction and inclusive development in rural revitalization
中国乡村地理学研究的主要热点演化及展望
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.004
[本文引用: 1]

以地理学主要中文期刊近40年来刊发的有关乡村研究的文献为分析对象,采用Citespace软件文献计量分析及文献归纳方法,对中国乡村地理学研究主要热点进行识别和阶段性划分,并梳理其主要热点的研究进展。结果发现,伴随20世纪80年代的乡镇工业和21世纪初以乡村旅游业兴起的乡村两次产业结构调整,以及国家乡村发展和建设的战略和政策不断调整,乡村地理学的研究热点演化大致可分为3个阶段:①1978-2000年,主要聚焦于乡村城市化、城乡关系、乡村聚落、农业发展、农村经济等研究,为国家和地区的农业与农村发展做出了基础性和战略性贡献。②2000-2008年,开始转向以乡村旅游、农村居民点、新农村建设、村庄规划、空心村等研究热点话题,中国乡村地理学发展改变了“重城轻乡”的学科格局,逐渐走向繁荣。③2008年至今,研究热点转向多元化,涉及乡村转型、乡村重构、乡村性、空间重构、乡村社区、乡村治理等,研究主题逐渐接轨于国际乡村地理学。未来中国乡村地理学的研究应以建设乡村地理学学科基础理论和方法体系为核心目标,服务于国家实施乡村振兴战略需要,积极关注乡村发展、转型、分化、重构与治理等核心话题,深化乡村多元空间价值理论研究,形成独具中国特色的乡村地理学理论框架和研究范式。
Change in key research area and prospect of Chinese rural geography
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.004
[本文引用: 1]

Since the reform and opening up in 1978, human geography in China has experienced important developments. As a branch of human geography, rural geography has carried out a series of research on the rural regional system of human-environment relations. Taking the geography research articles published in the past 40 years in major Chinese journals of geography as the analysis object and using bibliometrics and literature summarization methods assisted by Citespace tools, this study identified the key research areas, divided the themes into stages, and summarized progress in the major research areas. The results show that under the background of globalization, urbanization, modernization, and informationization, as well as rural industrial structure adjustment and rural development policy change, great changes have taken place. From 1978 to 2000, rural geography mainly focused on the research themes of rural urbanization, urban-rural relations, village clusters, agricultural development, and rural economy. The academic community showed greater interest in urban than rural research, which has made fundamental and strategic contributions to the agricultural and rural development of the country and regions From 2000 to 2008, rural geography began to shift to topics such as rural tourism, rural settlements, new rural construction, village planning, and hollow village, and the development of the discipline gradually progressed. Since 2008, rural geography has shifted to more diverse topics, mainly including rural transformation, rural restructuring, rurality, rural governance, rural community, and spatial restructuring, which converge with rural geography research internationally. In the future, the research of rural geography in China should be based on the construction of theories and methods of rural geography and serve the rural vitalization strategy. More attention should be paid to the development, transformation, differentiation, restructuring, and governance of rural areas, deepening theoretical research on the value of diversified space in rural areas and developing a theoretical framework and research paradigm of rural geography with unique Chinese characteristics.
乡村旅游社区可持续发展研究: 基于空间生产理论三元辩证法视角的分析
Sustainable development of rural tourism community: Based on the analysis from the perspective of ternary dialectics on production of space
文旅融合导向下的乡村振兴发展机制与模式
Mechanism and model of rural vitalization guided by culture tourism integration
基于多维测度的共同富裕评价指标体系研究
Research on evaluation index system of common prosperity based on multidimensional measures
新时代“以人民为中心”共同富裕指标体系的构建
Construction of "people-centered" common prosperity index system in the New Era
扎实推动共同富裕指标体系构建: 理论逻辑与初步设计
Achieving solid progress in establishing an index system for common prosperity: Theoretical logic & preliminary design
村落遗产地利益相关者界定与分类的实证研究: 以开平碉楼与村落为例
An empirical study on the definition and classification of stakeholders in village heritage sites: A case study of Kaiping watchtower and village
社会—生态韧性视角下城乡治理的逻辑框架
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.009
[本文引用: 1]

伴随着快速城镇化,生态环境剧烈变化与社会经济结构深刻转变使中国城乡发展问题愈发突出,城乡治理面临新挑战。社会—生态韧性理论与城乡治理实践存在紧密关联,但对两者关系的研究欠缺。论文以中国城乡发展问题为导向,厘清社会—生态韧性与城乡发展的关系,构建社会—生态韧性视角下城乡治理的逻辑框架。将社会—生态韧性的核心理念(耦合、自组织和学习)引入城乡规划、个体参与和政策制定,将促进城乡融合和可持续发展。在未来的城乡治理中,需要将社会与生态问题统筹考虑,贯彻人地耦合的理念,形成多层级的城乡协同治理网络,促进适应性治理,培育不同尺度城乡治理主体的合作和创新,尤其要重视城乡社区的学习、适应能力构建。实践中需要充分利用空间规划工具,将生态系统服务纳入城乡空间治理范畴,协调城乡生态系统服务与居民福祉的关系,增强城乡对不确定性的缓冲和应对能力。
A logical framework of rural-urban governance from the perspective of social-ecological resilience
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.009
[本文引用: 1]

Along with the rapid progress of urbanization, dramatic changes in the ecological environment and profound changes in the social and economic systems have made issues related to China's urban and rural development more prominent. Urban and rural governance faces new challenges. The concept of social-ecological resilience may shed some light on changes in the practice of rural-urban governance, but there is a lack of research on the relationship between them. Focusing on major issues of urban and rural development in China, this study clarified the relationship between social-ecological resilience and urban and rural development, and constructed a logical framework of rural-urban governance from the perspective of social-ecological resilience. The framework aims to promote urban and rural integration and sustainable development by introducing the key characteristics of social-ecological resilience (coupling, self-organization, and learning) into rural-urban governance mechanisms (planning, participation, and policy). In the future, social and ecological issues should be taken into overall consideration in rural-urban governance, with the idea of human-earth system coupling. A multiple-tiered network of coordinated rural-urban governance should be established. Attention should be paid to the cultivation of cooperation and innovation of the participants at different scales, especially to the construction of learning and adaptability of urban and rural communities. In practice, it is necessary to make full use of spatial planning, to incorporate ecosystem services into rural-urban spatial governance and take them as a priority. The goal of enhancing the resilience and adaptive capacity of urban and rural areas to uncertain challenges will be achieved by coordinating the relationship between ecosystem services and human well-being.
旅游感知与地方依恋对主—客价值共创的影响
The impact of tourism perception and local attachment on the co creation of host guest value
初次分配公平满意度研究: 基于起点公平、过程公平、结果公平的微观证据
A research on the satisfaction of initial distribution fairness: Based on the microeconmic evidences of starting point fairness, procedural fairness and outcome fairness
共同富裕指数模型的构建
Construction of common prosperity index model
The impact of tourism on income inequality in developing economies: Does Kuznets curve hypothesis exist
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2016.09.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
乡村旅游发展水平评价与障碍因素分析以长株潭城市群为例
Evaluation of rural tourism development level and analysis of obstacle factors: A case study of Changsha Zhuzhou Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration
共同富裕视域下我国农村居民生活质量测度及其时空演变
Measurement of rural residents' quality of life and its temporal and spatial evolution from the perspective of common prosperity
乡村农户旅游适应效果、模式及其影响因素: 以西安市和咸阳市17个案例村为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180913
[本文引用: 1]

乡村旅游地面临人地交互作用的剧烈变迁,内部要素适应社会-生态系统变化,趋利避害降低脆弱性具有重要现实意义。本文重新界定基于恢复力和脆弱性的农户适应性理论内涵,构建旅游开发适应力指标体系,以西安市和咸阳市17个不同类型的城郊型乡村旅游地为例,评价和分析农户旅游适应效果与空间差异规律,探讨和归纳适应行为与对策模式,建立BP神经网络辨别和揭示适应性影响因素与重要性关系。研究表明:① 西安市和咸阳市农户适应旅游开发综合效果呈现中等偏下水平的偏态分布趋势,分别处于旅游地生命周期快速发展阶段和探索起步阶段。② 乡村旅游地农户适应效果形成“圈层辐射、两翼包络、外围联动”的县域尺度空间分布格局;村域尺度圈层分化现象显著。③ 经营模式划分的旅游乡村农户适应效果股份制模式>“公司+农户”模式>“政府+公司+农户”模式>个体农庄模式>“农户+农户”模式;常年外出务工和农家乐经营是农户主要适应行为选择,季节性务工、本地上班以及农业生产是辅助适应行为选择,且适应行为组合方式表现为旅游专营型、旅游主导型、均衡兼营型、务工主导型和务农主导型五种适应对策模式。④ 旅游发展机会认知、技能培训机会、社会联结度、劳动力总量、政策知晓度、旅游就业人数、收入来源种类、生活主要能源、受教育程度、公共服务设施是农户主要旅游适应性影响因素。据此,提出后续社会-生态整合研究亟需突破方向和适应旅游开发的政策路径。
Adaptation effect, mode and influencing factors of rural tourism: A case study of 17 typical villages in cities of Xi'an and Xianyang
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180913
[本文引用: 1]

Rural tourism sites have witnessed dramatic changes in human-land interaction, and their internal factors are adapting social-ecological system changes. It is of great practical significance to avoid disadvantages and reduce vulnerability. This paper redefines the theoretical connotation of farmers' adaptability based on resilience and vulnerability, and constructs an adaptability indicator system of tourism development based on a case study of 17 tourist villages in the cities of Xi'an and Xianyang, so as to examine the adaptation effect and spatial difference law of rural tourism, explore the adaptive behavior and countermeasure mode, and establish a back-propagation network to reveal the relationship between adaptive influencing factors. The results are obtained as follows: (1) The comprehensive effect of farmers' adaptation on tourism development in Xi'an and Xianyang shows a trend of skewed distribution at the middle-lower level in the stage of rapid development of tourism life cycle and the initial stage of exploration. (2) The adaptation effect of households in the rural tourism area forms a spatial pattern of “scale circle radiation, two-wing envelope and peripheral linkage”; the segmental differentiation of the village scale is significant. (3) The adaptation mode of rural households is identified by business model: shareholding system model > “company + farmer” mode > “government + company + farmer” mode > individual farm mode > “farmers + farmers” model; migrant workers and farmhouse management are the main adaptation of farmers. Behavior choice, seasonal work, local work and agricultural production are auxiliary adaptation behavior choices, and the adaptation behaviors are characterized by five types of adaptation strategies: tourism franchise, tourism-oriented, balanced, labor-oriented and agricultural-oriented. (4) Tourism development opportunity cognition, skills training opportunities, social connection degree, total labor force, policy awareness, tourism employment, income source types, primary energy sources, education level, and public service facilities are the main factors affecting farmers' tourism adaptability. Based on this, we proposed that the follow-up social-ecological integration research should adapt to the policy path of tourism development.
西藏旅游目的地品牌评价体系构建及营销策略研究
Research on brand evaluation system construction and marketing strategy of tourism destination in Tibet
Cultural rural tourism: Evidence from Canada
DOI:10.1016/S0160-7383(02)00061-0 URL [本文引用: 1]
精神生活共同富裕的基本内涵与指标体系
The basic connotation and index system of common prosperity in spiritual life
乡村旅游开发的现实困境、不足及其化解
Development and solution of rural tourism
贫困地区乡村经济韧性研究及其启示: 以河北省阳原县为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.11.004
[本文引用: 1]

韧性是乡村地域系统的基本属性,对于推进乡村振兴与高质量发展具有重要支撑作用。截至2020年底,中国如期完成了新时代脱贫攻坚目标任务,然而,一些脱贫地区乡村发展水平不高,面临外界风险与挑战冲击时存在返贫风险,亟需提升乡村韧性。论文选取燕山—太行山集中连片贫困区的阳原县为研究对象,构建了“压力—状态—响应”模型(PSR),综合评价了14个乡镇、264个行政村的经济韧性。研究发现:① 阳原县乡村经济韧性平均值为0.13 (总分为1),水平偏低,乡村经济基础薄弱、发展质量不高;② 经济韧性水平较高的村庄主要分布于邻近交通干线地区,山地区和距离交通干线较远地区的乡村经济韧性水平较低;③ 农户家庭年人均纯收入偏低、人均耕地面积较少、乡村人均固定资产投资不足是经济韧性的关键制约因素。论文指出,应构建“农户个体—乡村集体—城镇中心体”的多级发展体系,强化乡村交通、通讯等基础设施建设和农户技能培训,壮大村集体经济,推进以重点镇、中心村、新型农村社区为载体的村镇化发展,实现村镇化与城市化“双轮驱动”。
Rural economic resilience in poor areas and its enlightenment: Case study of Yangyuan county, Hebei province
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.11.004
[本文引用: 1]

Resilience is a basic characteristic of the rural system, which plays a crucial role in rural revitalization. By the end of 2020, China had completed the mission of poverty alleviation in the new era. However, rural development in some areas is of low quality and when facing external risks and challenges, these areas have the risk of returning to poverty. Therefore it is urgent to improve rural resilience. This study selected Yangyuan County of Hebei Province in the contiguous poverty-stricken area of Yanshan-Taihang Mountains as the research object. The "Pressure-State-Response" (PSR) model was constructed to comprehensively evaluate the rural economic resilience. The study found that: 1) The average value of rural economic resilience in Yangyuan County is 0.13 (total score is 1), which indicates that the quality of rural economic development is not high. 2) The areas located near the town and township seats and close to the main traffic lines display high economic resilience. In contrast, mountainous areas and areas far from the main traffic lines display low economic resilience. 3) Low per capita income of rural households, low per capita arable land, and insufficient investment in rural fixed assets are the main constraints to economic resilience. The article proposed four aspects to improve rural resilience: establishing multi-level development system of "individual farmers-rural collectives-urban centers", strengthening the development of infrastructure such as rural transportation and communication systems, promoting farmers' skill training, and strengthening the collective economy of the villages. Developing key towns-central villages-new rural communities effectively accelerates the development of ruralization, which drives rural development together with urbanization.
Rural tourism and residents' well-being in Cyprus: Towards a conceptualised framework of the appreciation of rural tourism for islands' sustainable development and competitiveness
DOI:10.1504/IJTA.2019.098105 URL [本文引用: 1]
乡村旅游地居民政府信任对旅游发展支持度的影响: 地方依恋的调节效应
Influence of residents' trust in government on support for tourism development in rural tourism destinations
中国旅游业高质量发展水平测度及时空演化特征
Measurement and spatial temporal evolution characteristics of high quality development level of China's tourism
旅游凝视视角下城市边缘型社区居民: 游客价值共创研究
The value co-creation of resident and tourist in urban fringe communities form tourism gaze perspective communities from tourism gaze perspective
在促进共同富裕中增进农民幸福感: 基于经济收入—社会网络—生态环境框架的分析
Enhancing farmers' happiness in common prosperity: Analysis based on economic income-social network-ecological welfare framework
农村宅基地制度对农户主观获得感、幸福感、安全感的影响
Effect of rural residential land system on farmers' subjective sense of gain, happiness and security
公平正义原则下共同富裕的核心要义
The core meaning of common prosperity under the principle of fairness and justice
城市居民压力源对幸福感的影响研究: 基于乡村旅游休闲参与的角度
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180660
[本文引用: 1]

居民幸福感研究日益受到重视,以往研究多是从自然环境、社会人文环境和城市化进程等方面探讨大尺度空间环境因素对城市居民幸福感的影响。结合乡村旅游的角度探讨城市居民幸福感的影响研究,目前还较少。运用SEM分析方法,探究处于多维压力之下的城市居民旅游者如何通过前往乡村进行旅游休闲活动提升幸福感,进行模型构建与分析,结果显示:① 压力源对调适策略有显著正向影响,对休闲参与不显著,但不同群体影响差异显著,压力调适对休闲参与有显著正向影响;② 休闲参与对心流体验和幸福感具有显著正向关系,且心流体验对幸福感具有显著正向影响;③ 心流体验对休闲效益具有正向显著影响,且休闲效益对幸福感具有正向显著影响;④ 心流体验在休闲参与对幸福感、休闲效益在心流体验对幸福感均具有显著中介效应;⑤ 旅游者不同背景变项在压力调适、休闲参与及幸福感等分别呈现不同程度的显著差异。
The influence of multidimensional deconstruction of stressors on enhancing urban residents' well-being: From the perspective of rural tourism and leisure involvement
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180660
[本文引用: 1]

In recent years, the well-being of residents has attracted increasing attention from the public. Previous studies have focused on the impact of large-scale space environment on urban residents' well-being by analyzing the natural environment, social and humanistic environment and the process of urbanization. Few studies have conducted research on the mechanism of urban residents' well-being from the perspective of rural tourism. Based on SEM, this study explores how rural tourism and leisure involvement enhance well-being of urban residents who are under multidimensional stress. SEM shows that: (1) Stressor has a significant positive impact on the adjustment strategy, but not significant to leisure involvement. The impact on different groups is significant. Stress adjustment has a significant positive effect on leisure involvement. (2) Leisure involvement has a significant positive relationship with flow experience and well-being. Flow experience has a significant positive impact on wellbeing. (3) Flow experience has a significant positive impact on leisure benefits, which then have a positive impact on well-being. (4) Flow experience has a significant mediating effect on leisure involvement and well-being. Leisure benefits have a significant mediating effect on flow experience and well-being. (5) There are significant differences in stress adjustment, leisure involvement and well-being among different tourist groups.
公平感对农民工流入地政府信任的影响研究: 基于公民权意识的调节效应分析
The impact of perceived justice on rural migrant workers' trust in government of migrant places: Based on moderating effect of citizenship awareness
居民城市公共安全感知与社区环境: 基于北京大规模调查问卷的分析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202108009
[本文引用: 1]

新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情的爆发使得民众对公共安全问题的关注到了前所未有的程度,社区作为社会治理基本单元,在防疫减灾中所发挥的作用尤为突出。本文基于北京2019年城市体检问卷调查数据,采用多层线性模型检验个体属性及社区环境指标对公共安全感知的影响。研究发现,公共安全感知的差异主要来自个体属性的不同,老年人及健康状况一般或较差的群体,以及低收入、低学历、待业人群的安全感相对较低;安全感的社区差异显著,人口稠密、公交线路密集的社区居民安全感较低,道路交叉口较多的社区安全感较高;社区离Ⅰ型应急避难设施和医院的距离越近,居民安全感越高,但中小型设施影响不显著;良好的社区社会环境对居民安全感具有非常明显的正向影响,但租户很难从物业管理水平的提高中获益。据此本文提出了建设安全韧性社区的若干建议。
Residents' sense of urban public security and community environment: Analysis based on a large-scale questionnaire survey of Beijing
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202108009
[本文引用: 1]

The novel coronavirus epidemic has led to an unprecedented concern regarding public security. Communities, as the basic units of social governance, play a prominent role during this period. However, little is known about the relationship between residents' sense of public security and their community environment in the existing geography and planning literature. To fill this gap in the research, this paper builds a theoretical framework to identify personal and community-level factors that influence the sense of public security. Based on a large-scale survey conducted in Beijing in 2019, we use multilevel linear models to analyze how and to what extent personal and community features impact this sense. The results show that (1) most of the personal attributes have significant effects on the sense of public security. Those who are older or less healthy are more likely to report a lower sense of security, and residents with lower incomes or education levels are also liable to suffer from insecurity. Stable employment has a positive effect on people's sense of security, and unemployed people report the lowest sense of security compared to others. Migrants feel safer than local residents, the main reason is that they compared their current city with their hometown and found Beijing to be much safer. (2) There is significant difference in residents' sense of public security across communities. The model results suggest that a built environment with a denser population and a bus route has a negative effect on the sense of security, while open space with more road crossings can improve residents' safety perception. Additionally, residents will feel more secure if their community gets closer to type I emergency shelters and hospitals. However, the influences of small- and medium-sized facilities are not significant, such as type II/III emergency shelters and community healthcare centers. (3) The social environment of the community plays a more important role in promoting residents' sense of public security than the built environment. However, it is found that renters can hardly benefit from the improvement of property management. Based on these findings, the paper provides some suggestions for improving the community's safety and resilience.