中国城镇化已进入“下半程”,经济社会由追求高速增量转而追求高质量发展,社会主要矛盾已经转化为人民日益增长的美好生活需要和不平衡不充分的发展之间的矛盾。城乡融合发展是实施乡村振兴战略的根本途径,而重建乡村的生活空间是乡村振兴的深刻内涵所在[1]。因此,乡村生活空间作为城乡融合和乡村振兴的重要载体与抓手,乡村生活空间治理是推进城乡融合发展和乡村振兴战略实施的重要前提[2]。在具有显著地域差异性的乡村重构与转型背景下,乡村生活空间的治理逻辑注定要将乡村生活空间的转型特征与影响机理纳入参考,只有以此为基础才能考量如何协调乡村生活空间资源,整合要素、优化空间结构与功能[3]。因此,探究乡村生活空间的转型特征与机理,是明晰乡村生活空间治理路径、应对城乡融合和乡村振兴战略的现实要求[4]。
乡村重构与转型的背景下,人口、资金、技术等要素在城乡间快速流动,乡村正以与以往截然不同的态势加速参与到社会生产和消费的网络中[5,6]。外来定居者、旅游者与原住居民混杂于乡村,乡村地域功能也由单一的生产转向兼具生产、生活、消费等多元功能转变[7⇓-9]。从地理学者的角度来看,乡村生活空间是由居住、就业、消费和休闲等几类活动空间迭置而成的空间聚合体或多层次地域空间综合体[10,11]。据此,除了为乡村居民的居住、消费、休闲等日常活动提供场所或空间,广义的乡村生活空间也应包括为乡村居民提供生计基础的农业用地等生产空间。乡村生活空间是乡村要素流动和功能转型的重要载体,它的主体混杂和空间功能多元化趋势不仅对乡村空间治理提出了新挑战,还对乡村地理学的理论和研究框架提出了新要求[12]。
在当代城镇化和工业化的快速推进下,乡村居民生活行为模式以及地方人地关系发生剧烈变化,与乡村居民人居环境、生活质量直接相关的生活空间研究正当其时,但当前学界从地理学的视角解读乡村生活空间的变迁规律之研究仍稍显薄弱[13,14]。其次,当前的乡村地理学研究中,乡村转型与空间重构、农村居民点布局与演化、乡村生产空间等方面的乡村物质空间研究是主要议题[15⇓⇓⇓-19],且受传统的“物质—意象”二元乡村空间认知思维模式的影响,难以全面剖析乡村生活空间系统及其转型机理与治理路径。提升对乡村生活空间的多维度认知,系统地对乡村生活空间的转型过程和机理进行阐释,既是当前乡村转型与空间治理领域有待解决的重要议题,也有助于丰富乡村地理学的研究框架[20]。
综上所述,城乡融合发展和乡村振兴战略的实施均对乡村生活空间转型研究提出了现实需求。本文首先阐释当前乡村生活空间转型研究的现实需求与理论响应,归纳“乡村空间三元模型”对乡村生活空间转型研究的启示,进而构建基于“乡村空间三元模型”的乡村生活空间概念模型,最后提出包含转型过程—格局—机理的乡村生活空间转型研究框架。
1 乡村生活空间转型与乡村空间三元模型:现实需求与理论响应
1.1 乡村生活空间转型
国内学者认为,乡村空间转型发展研究主要包括乡村聚落转型、土地利用转型、经济社会转型以及城乡关系变迁等方面,且这几个方面同步发生、相互影响[24,25]。总体而言,当前对乡村生活空间的研究仍被纳入乡村重构—转型研究的背景与框架之下,主要包括乡村聚落、乡村居民点、乡村人居环境等,对日常生活层面的研究则主要包括居住、就业、消费、休闲等几个活动类型的空间分布特征与影响机制[26⇓-28]。实现乡村多元价值是乡村振兴战略实施的重要目标之一,而乡村生活空间转型是乡村多元价值实现的重要路径。后生产主义视野下,中国东部发达地区乡村的旅游消费、高品质居住和生态服务等多元价值空间不断产生、扩张和集聚[29⇓-31],乡村绅士化是典型表现之一,因资本入驻形成的乡村绅士化现象不仅改变了乡村的社会阶层,还驱动乡村生活空间异化和重构[32⇓-34]。受城市化的影响,中西部地区的农村居民点用地类型也渐趋多功能化[35],乡村的工业生产功能与生态旅游功能呈增强趋势[36]。与后生产主义的乡村多元价值发展相适应的是更多的学者呼吁应摆脱以往从城乡社会经济发展图谱来考察乡村发展和乡村性的宏观视野,而是从乡村的社会表征,即不同社会群体如何描述乡村,以及乡村在日常实践中被使用和建构的方式来表述乡村性[37,38]。与乡村多元空间和多元价值伴随而生的还有乡村转型中产生的各种空间现象或问题,如“专业村”“空心村”“数字乡村”等[39⇓-41]。为应对这些新现象或新问题,学界也提倡应构建包括物质空间治理、空间权属治理、空间组织治理的乡村空间综合治理体系[2],尤其是更为注重多元治理主体的参与协作、多层级网络化治理结构的构建[42,43]。
综上所述,以实现乡村多元价值为导向的乡村生活空间转型,以及为解决乡村生活空间转型中出现的问题而构建的乡村空间治理体系,均超出传统“物质—意象”的二元空间认知,对乡村生活空间研究提出新的要求,即构建一个不仅能测度多元空间和多元价值视野下的乡村生活空间转型过程,还能揭示其转型机理的乡村生活空间认知模式。
1.2 乡村空间三元模型
空间生产理论(Production of Space)认为空间的形成是社会生产的一部分,物质空间的变化是社会变迁的表象[48,50]。该理论构建了由“空间表征”“空间实践”与“表征空间”构成的三元一体的分析框架,三者之间存在相互影响的互动关系。空间三元论被引入不同地域类型的乡村空间生产研究中:其中一类为乡村居民点空间功能转型中存在的问题,如乡村旅游空间的生产被视为多元利益主体作用下的传统社区空间变迁过程,空间外来者(游客)的进入导致的主体多元化与社区空间生产过程如何联系是其理论推导的焦点[51,52];另一类是乡村居民点空间整合引致的空间正义等社会问题,如引用空间三元论分析乡村公共空间的生产过程及内在机制,以居民社会关系的变化为切入点,视乡村公共空间为国家权力与村民利益相互斗争的产物,阐释城镇化快速发展下变化的社会关系对乡村公共空间物质形态的影响机理[53]。
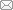
Halfacree[49]将这一“空间三元辩证法”运用于乡村研究领域,构建了“乡村空间三元模型”,对乡村空间认知的理论更新产生了广泛而深远的影响。根据该模型,乡村地方性、乡村的表征、乡村生活是构成乡村空间的三维要素,三者分别表示具有明显乡村特征的实践活动的物理空间,资本利益集团、规划者或者政客们对乡村的主观构想空间,以及乡村居民体验的、生活的空间。这一模型中日常生活实践的引入弥补了传统“物质—意象”的二元空间认知难以从微观的、人本的视角研究乡村生活空间转型特征与机理的缺陷。事实上,日常生活实践在乡村空间转型的研究中早已先于上述理论认知而引发关注。例如,乡村居民的公共服务消费、居住行为、就业选择等日常生活被用于映射城乡关系的新趋势,从而以微观的社会视角探索乡村性转型的表征与内在机制[54];乡村居民的休闲、就业、消费等日常活动为从微观人地关系视角透视当代乡村地域系统演变提供有益信息[26⇓-28];此外,乡村居民日常生活实践被用于测度乡村生活空间质量,并据此识别乡村生活空间网络结构特征[55]。总之,将日常生活实践纳入乡村生活空间转型的研究框架,无论是在实践需求还是研究积累上,均是正当其时。
由此可见,空间生产理论将“空间”视为过程而非物质的理念内核,契合当前混杂背景和多元价值导向下的乡村生活空间转型研究;而基于空间生产理论的“乡村空间三元模型”相较于传统的空间二元认知,前者可以还原快速城镇化影响下乡村生活空间内部多维主体和多类要素间的复杂相互作用,而不仅仅是物质与社会空间之间的简单相互关系,可以为揭示乡村生活空间的转型特征与机理乃至提出空间治理对策提供有益尝试。
2 乡村生活空间概念模型
图1
图1
基于“乡村空间三元模型”的乡村生活空间概念模型
Fig. 1
The conceptual model of rural life space based on the three-fold model of rural space
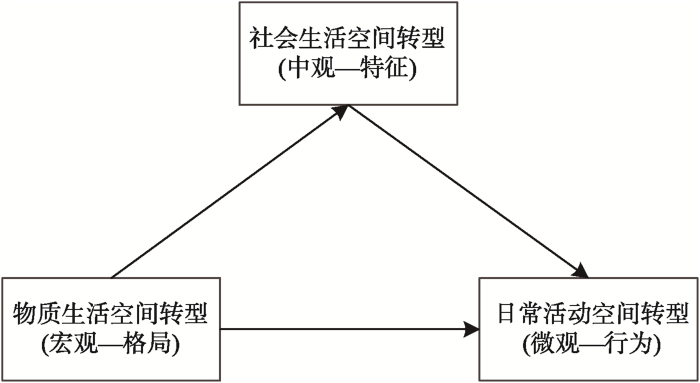
剖析乡村生活空间的多层尺度。乡村生活空间概念模型是包括宏观、中观和微观的多层尺度的概念模型,其中:乡村物质生活空间是宏观尺度下的乡村地域景观格局,包括乡村居民点、耕地、河流等;乡村社会生活空间是中观尺度下的乡村社会结构特征,如乡村居民在职业、收入、教育水平等方面的差异使乡村社会空间发生分异,相似社会经济属性特征的居民在空间上的集聚形成了乡村社会区,不同乡村社会区形成一定的乡村社会结构;乡村日常活动空间是乡村个体或家庭等微观主体的活动空间,主要由居住、消费、休闲等分散的点状空间组成。由此,乡村生活空间是蕴含了宏观格局、中观特征和微观行为的多层尺度概念模型。
透视乡村生活空间的多元空间。Halfacree的“乡村空间三元模型”中,乡村地方性回答“乡村生活空间内有什么”的问题,乡村表征回答“乡村生活空间是什么”的问题,乡村生活回答“乡村居民在乡村生活空间内做什么”的问题。据此,以乡村物质生活空间代表乡村生活空间的地方性,是乡村生活空间有别于其他类型人居环境的属性和特征;以乡村社会生活空间表示乡村生活空间表征,其本质是不同主体对乡村生活空间的想象抑或是期望,同时也是乡村生活空间对这些主体所呈现的差异性的价值或意义,因而乡村社会生活空间可以说是乡村居民的社会经济属性特征在空间上的投射;以乡村日常活动空间表示乡村生活,乡村生活空间是乡村居民日常生活实践形成的空间。
厘清乡村生活空间的多维主体。乡村生活空间的多层尺度和多元空间也意味着它具有多维的空间主体,具体包括人类活动者(如乡村本土村民、村集体、政府、游客等)和非人类活动者(如资本、政策、技术、人文与自然资源等)。从人地关系的视角来看,辨识乡村生活空间的关键活动主体,是研究乡村生活空间转型机理的关键环节之一。
3 乡村生活空间转型研究框架
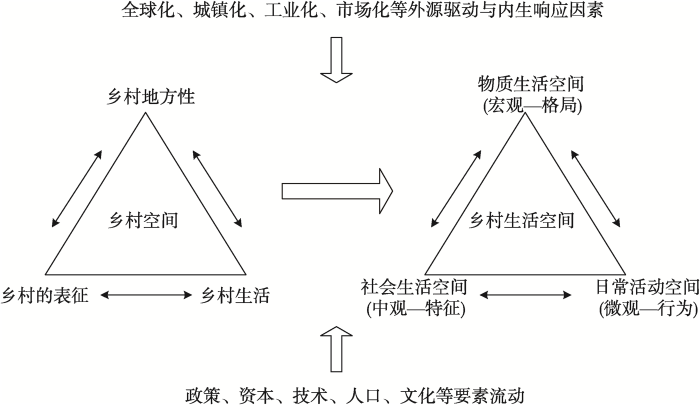
在全球化、城镇化、工业化和市场化等因素推动乡村重构与转型的背景下,乡村生活空间加剧转型。基于乡村生活空间概念模型提出乡村生活空间转型的研究框架,包括乡村生活空间转型的过程、格局与机理。其中,乡村生活空间转型过程是乡村生活空间系统内部各组成要素的结构变化,转型格局是这一变化的空间异质性表现,转型机理则包括乡村生活空间系统内多层尺度的传导机制、多边空间的交互作用和多维主体的混杂效应等三个方面(图2)。
图2
图2
乡村生活空间转型研究框架
Fig. 2
Research framework of the transformation of rural life space
3.1 乡村生活空间转型过程
表1 乡村物质生活空间转型指标体系
Table 1
| 显性指标 | 隐性指标 | 指标释义 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乡村物质生活空间 | 农村居民点面积占比 | 乡村常住人口占比 | 农村居民点面积占比=农村居民点面积/乡村地域土地面积; 农业用地面积占比=农业用地面积/乡村地域土地面积; 草地、森林、水域面积占比=草地、森林、水域面积总和/乡村地域土地面积 |
| 农业用地面积占比 | 第一产业增加值占比 | ||
| 草地、森林、水域面积占比 | 农村居民人均可支配收入 |
乡村社会生活空间转型度。在城镇化进程的影响下,乡村社区已呈现出不同于以往的异质性和复杂性,表现为乡村居民在年龄、性别、职业、受教育水平、经济收入水平、住房等社会经济属性的分异,如“空心村”“老年村”“绅士化乡村”等乡村社区的出现即为乡村居住空间和人口结构变化的空间映射。据此,乡村社会生活空间转型度可表征为乡村社区类型的变化。
3.2 乡村生活空间转型格局
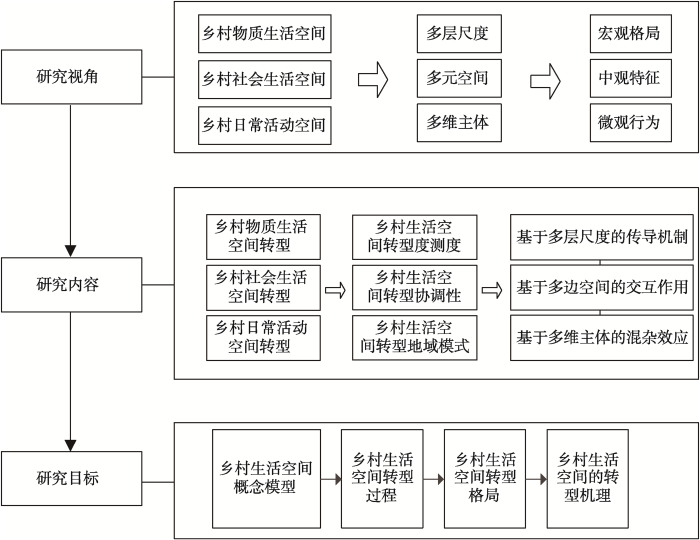
不同地域类型和发展阶段的乡村生活空间中,乡村物质生活空间、乡村社会生活空间、乡村日常活动空间的转型常处于不同步、不协调的状态。基于“乡村空间三元模型”的原理,动态变化着的乡村地方性、乡村表征、乡村生活之间存在结构化关联模式,当乡村空间内部表现为一致的和统一的结构化关联模式时,三者及其变化是协调关系,反之则为非协调关系。据此,从乡村物质生活空间、乡村社会生活空间、乡村日常活动空间的相互协调程度表征区域内的乡村生活空间转型格局,转型格局可以探析乡村生活空间转型在空间上的异质性和关联性,并进一步揭示乡村生活空间转型的地域模式。
将三个子空间之间的协调关系抽象为笛卡尔坐标系中三个不同方向作用力的矢量关系,并用三者的力学平衡结果定量测度乡村生活空间整体的协调状态,从而构建基于力学平衡模型的乡村生活空间协调性判别模型(图3)[61,62]。图3中,O点为合力作用点,当三个子空间的作用力均达到预期目标时合力为0,即表明乡村生活空间转型实现了均衡发展,O点为均衡点;反之则表示乡村生活空间偏离均衡点。由此定义乡村生活空间偏离度为研究单元在“物质生活空间—社会生活空间—日常活动空间”共同作用下偏离均衡点的程度,判别模型如图3所示。采用极坐标 (F合, θ) 来表征乡村生活空间转型的协调状态,其中F合为协调度,值越大说明该研究单元的乡村生活空间转型协调度越差;极角θ表征偏离方向,反映各要素间的匹配问题。OA、OB、OC分别为乡村物质生活空间、乡村社会生活空间和乡村日常活动空间等三要素的正向变化程度。当三要素均衡变化时,合力F合为0并且落在圆心处的均衡点O;当三要素的变化不均衡时,F合偏离均衡点O,F合的方向和大小可以定量化表征偏离程度。
图3
图3
基于力学平衡原理的乡村生活空间转型偏离度判别模型
Fig. 3
The mechanical model of the transformation of rural life space
3.3 乡村生活空间转型机理
(1)乡村生活空间的多层尺度及其传导机制
乡村生活空间转型不仅受外源宏观尺度因素的影响[63],也受内部微观尺度空间和微观主体活动的作用[46],乡村生活空间转型的影响因素之间也存在相互作用,且这些相互作用可能强化或削弱它们单独对乡村生活空间转型产生的影响[64]。乡村生活空间的多层尺度相互作用可选取结构方程模型[65],以日常活动空间转型度为因变量,物质生活空间转型度为自变量,社会生活空间转型度为中介变量,分析社会生活空间转型在物质生活空间转型对日常活动空间转型影响路径中的中介作用(图4)。这一模型的基本假设为,社会生活空间转型在物质生活空间转型对日常活动空间转型的影响中存在中介效应,由此构建了宏观格局→中观特征→微观行为这一影响路径的尺度传导作用。
图4
图4
基于结构方程模型的乡村生活空间尺度传导机制
Fig. 4
The scale effect between different dimensions of rural life space based on structural equation model
(2)乡村生活空间的多边空间及其交互作用
由于要素的跨区域流动现象,作用于乡村生活空间转型的影响因素及其转型结果存在空间上的溢出效应和区域间的交互影响,这也是乡村生活空间转型的影响机理之一[66]。全球化、城镇化、工业化和市场化等是推动人口、资金、技术、信息等要素在区域间流动的重要动力,要素流动下形成的区域内外联动乃至以区域为节点的多重网络化发展,使不同层级的区域主体均成为相互依赖、相互耦合的人地关系地域系统[67]。从要素流动和区域网络化发展的视角来看,乡村生活空间作为乡村地域系统的重要组成部分,其转型同时受乡村地域系统外源驱动和内生响应两个层面的影响作用[68]。据此,探测空间交互作用对乡村生活空间转型的影响机理时应考虑包括城镇化驱动及响应、工业化驱动及响应、全球化驱动及响应和市场化驱动及响应等四个方面的影响因素(表2),具体而言,该指标体系的构建依据如下[69,70]:① 城镇化驱动及响应。城镇化作用主要表现为城镇用地、城镇人口、经济发展水平的变化对乡村生活空间的外部驱动,以及乡村区域在用地类型、道路基础设施、居民收入等方面产生的内生响应。② 工业化驱动及响应。工业化作用主要表现为工业化水平进步带来的劳动生产率提升和先进技术输入对乡村生产、生活质量的改善。③ 全球化驱动及响应。全球化作用主要表现为乡村引入外资以实现乡村在空间、农业、生态等资源上的价值化利用,或将乡村生产的农产品、工业品并入全球产业链、价值链,使乡村生活空间成为更为开放的地域系统。④ 市场化驱动及响应。市场化作用主要表现为乡村外部市场条件的变化和乡村内部资源要素的市场流动、居民消费方式变化等,市场化驱动及响应与上述三个方面的作用相辅相成,共同促进乡村生活空间转型。
表2 乡村生活空间转型影响因素指标体系
Table 2
| 系统层 | 子系统层 | 外源驱动力 | 内生响应力 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乡村生活空间转型 | 城镇化驱动及其响应 | 城镇建成区面积占比 | 农村非农用地面积占比 |
| 城镇人口占比 | 农村道路网密度 | ||
| 人均GDP水平 | 乡村居民非农收入占比 | ||
| 工业化驱动及响应 | 第二产业劳动生产率 | 农业机械化水平 | |
| 规模以上工业R&D规模 | 生活垃圾无公害处理率 | ||
| 单位能耗地区生产总值能耗 | 互联网普及率 | ||
| 全球化驱动及响应 | 人均进出口贸易总额 | 农产品出口额 | |
| 实际利用外资水平 | 乡村旅游国际游客数量 | ||
| 市场化驱动及响应 | 第三产业从业人员数量 | 农村土地流转率 | |
| 基础服务设施数量 | 农村居民人均消费性支出 |
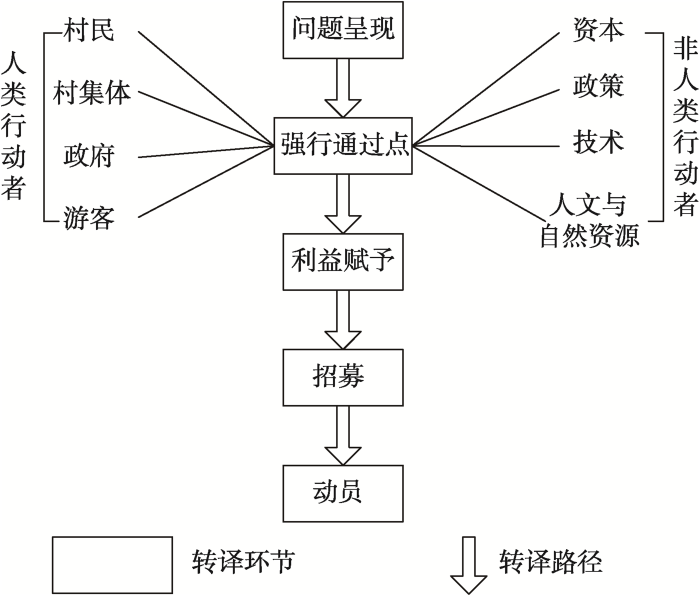
(3)乡村生活空间的多维主体及其混杂效应
首先,辨识乡村生活空间这一行动者网络中的行动者,尤其是处于网络中心的关键行动者。空间行为主体(行动者)的混杂是乡村生活空间混杂性的主要表现之一,除了村民、村集体、地方政府之外,乡村精英、企业、资本、外来人口等行动者也逐渐成为乡村生活空间网络的行动者,这些行动者的存在和关系变化推动着整个网络的演化。
图5
4 结论与讨论
4.1 结论
已有的乡村生活空间研究缺少对多元空间和混杂主体的关注,不利于复原乡村生活空间的转型特征与内在机理。沿循乡村生活空间的概念模型—转型特征—影响机理的逻辑思路,在构建乡村生活空间概念模型的基础上,提出乡村生活空间转型的研究框架。构建基于“乡村空间三元模型”的乡村生活空间概念模型和基于多层尺度、多元空间、多维主体的乡村生活空间转型研究框架,为探究乡村生活空间的转型机理提供系统化的思维模式,以期为乡村地理学研究扩展研究视野、丰富研究框架,并为乡村振兴和城乡融合发展提供科学依据。
(1)乡村生活空间是乡村居民居住并进行就业、消费、休闲等主要日常活动而形成的空间聚合体。基于“乡村空间三元模型”,构建包括物质生活空间、社会生活空间和日常活动空间的生活空间概念模型。该概念模型中,物质生活空间是宏观尺度下的乡村地域景观格局,是乡村生活空间有别于其他类型人居环境的属性和特征;社会生活空间是中观层面的乡村社会结构特征,表示乡村生活空间表征,是源于不同乡村居民的差异性社会经济属性特征形成的空间价值或意义;日常活动空间是乡村个体或家庭等微观主体的活动空间,是乡村居民日常生活实践形成的空间。乡村生活空间概念模型是多层尺度、多元空间和多维主体的构成。
(2)基于乡村生活空间概念模型提出乡村生活空间转型的研究框架,包括乡村生活空间转型的过程、格局与机理。乡村生活空间转型过程是乡村生活空间系统内部各组成要素的结构变化,转型格局是这一变化的空间异质性表现。乡村物质生活空间转型是乡村土地、产业、人口等要素的结构性变化导致的乡村物质生活空间的功能性变化;乡村社会生活空间转型表现为乡村居住空间和人口结构变化的乡村社区类型变化;乡村日常活动空间转型是乡村居民发挥主体能动性获得时空间资源变化的结果。乡村物质生活空间、社会生活空间和乡村日常活动空间的协调性关系及其空间异质性与关联性表征了乡村生活空间转型格局,用以揭示乡村生活空间转型的地域模式。
(3)与乡村生活空间概念模型形成呼应,乡村生活空间转型的影响机理从多层尺度的传导机制、多边空间的交互作用和多维主体的混杂效应三个方面阐释。其一,乡村物质生活空间的宏观尺度因素会通过乡村社会生活空间而对乡村日常活动空间产生影响,乡村生活空间转型受宏观格局→中观特征→微观行为这一影响路径的尺度传导作用;其二,在全球化、城镇化、工业化和市场化等的驱动下,当前城乡要素在区域甚至全球范围内加剧流动,不同地域类型的乡村生活空间转型具有空间溢出效应,从该角度探究乡村生活空间转型机理是地理学者的优势所在;其三,人类与非人类行动者构成的混杂主体及其相互作用形成的异质性网络形成微观主体层面下的乡村生活空间转型机理。揭示乡村生活空间的转型机理是乡村生活空间转型研究的关键问题与核心目标。
4.2 讨论
在当前乡村空间逐渐趋于分化、转型的背景下,乡村生活空间研究不仅尺度较为宏观,并且还流于或物质或社会的“二元化”的分析,不利于还原制度、资本、乡村居民等多元要素作用于乡村生活空间内部变化的复杂机制,也因此难以为乡村空间治理提出与之相对应的对策建议。一方面,乡村生活空间研究应融合多学科的理论视角和方法,为乡村生活空间研究注入新的活力;另一方面,未来应选取不同典型地域的乡村生活空间对其进行空间转型特征与影响机理研究,提炼乡村生活空间转型地域模式,以为乡村振兴与城乡融合发展提供科学借鉴。
乡村空间治理是国土空间治理的重要组成部分[74],全面实施乡村振兴战略对乡村空间治理也提出了新的要求,乡村生活空间转型特征与机理的研究可以为乡村空间治理提供科学借鉴。基于乡村生活空间转型机理分析,提出与多元空间认知研究框架相适应的乡村生活空间治理策略,为推进新时期背景下的乡村振兴与城乡融合发展提供科学依据,是本文力求达到的价值目标。
基于乡村生活空间转型特征与机理的分析有助于制定针对性的空间治理策略,为乡村生活空间治理提供理论指导与参考。(1)明晰乡村生活空间的治理方向。基于乡村生活空间转型度和协调性特征,识别多元空间中导致转型问题的目标“短板”,划分不同乡村生活空间转型地域模式。针对不同转型地域模式的乡村生活空间,以补足多元空间“短板”、增强多元空间的协调性作为乡村生活空间的治理方向。(2)制定乡村生活空间的治理路径。基于尺度传导、空间交互和主体混杂的乡村生活空间转型机理,制定差异化的乡村生活空间治理路径。针对多层尺度、多边空间和多维主体的乡村生活空间转型机理,可分别制定包括乡村生活空间系统治理、推进区域交流与协作、多主体协同治理等空间治理路径。
参考文献
重建乡村生活实现乡村振兴
The reconstruction of rural life and implementation of rural revitalization
论乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 2]

构建现代乡村治理体系成为推动城乡融合发展和乡村振兴的重要内容。破解乡村空间利用过程中出现的发展空间受限、权属关系不明和组织体系不畅等系统性问题,成为乡村空间治理的首要任务。本文从乡村空间“物质—权属—组织”综合治理的视角出发,尝试解析乡村空间治理在推动乡村空间重构、权属关系重塑和组织体系重建中的作用机制,并进一步探讨乡村空间治理优化城乡格局、改善城乡互动关系、推动城乡融合发展的可行路径。结论如下:物质空间治理可作为乡村空间结构和功能优化的重要手段,空间权属治理有助于保障乡村空间不同参与主体的发展权利,空间组织治理可提升乡村空间的组织效率;乡村空间治理导向的“人口—土地—产业”转型过程为“深化空间治理—活化乡村空间—优化人地关系—改善城乡格局”的分析思路创造条件;乡村空间治理推动城乡发展格局不断演化,城乡互动关系改善成为推动城乡融合发展和破解乡村发展困境的重要依据。最后,本文构建了乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展互动分析框架,并探讨了乡村空间治理与国土空间规划的内在关系及研究趋势。
Rural spatial governance and urban-rural integration development
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 2]

The construction of the modern rural governance system becomes an important part in promoting the urban-rural integration development and rural vitalization. Solving systemic problems such as limited development space, unclear ownership relationship and inefficient organization in the process of using rural space has become the primary task of rural spatial governance. Based on the breakthrough of the comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space, this paper attempts to analyze the mechanism of rural space governance in promoting rural space restructuring, ownership reshaping and organizational system reconstruction, and further explores the feasible path of rural space governance to optimize the urban-rural pattern, improve the urban-rural interaction, and promote the urban-rural integration development. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Physical space governance facilitates the optimization of rural spatial structure, the space ownership governance safeguards the development rights of different stakeholders, and the space organization governance enhances rural organizational capabilities. The comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space helps to impel the restructuring of rural space, the reshaping of ownership relations and the reconstructing of organizational system, to achieve the goals of the modern rural space governance system with clear rural space ownership. (2) The "population-land-industry" transformation path guided by rural space governance creates conditions for the analysis of "deepening space governance-activating rural space-optimizing human-land relationship-improving the urban-rural pattern". (3) Rural space governance promotes the continuous evolution of urban-rural development, and the improvement of urban-rural interaction becomes an important basis for upgrading urban-rural integration development and solving the dilemma of rural development. Finally, this paper constructs an analytical framework and feasible path for the interaction between rural space governance and the urban-rural integration development, and explores the internal relationship and research trends of rural space governance and territory spatial planning.
发展转型视域下的乡村空间分化、重构与治理研究进展及展望
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003240
[本文引用: 1]

在工业化、城镇化、信息化和经济全球化的宏观背景下,乡村地域的经济结构、社会结构、景观结构、用地结构、城乡关系、消费结构和治理格局等出现了多元分化,同时不同地域类型乡村面临着传统村落空间消亡、地域认同感消失、村民自主性缺失等问题。乡村复兴和振兴成为新时期区域发展和农村发展的核心目标,理清乡村空间分化的内外动力的交互作用机制,深化归纳总结乡村多维空间重构的地域规律,发掘乡村综合治理的科学途径,有助于深化乡村建设和治理的理论框架。文章围绕乡村空间分化、重构与治理的国内外研究进展进行系统梳理,发现国际乡村地理学界在研究视角切入上更加多元,研究方法以质性为主,大量应用政治经济学和社会学的理论和方法,重点关注乡村空间认知、分化与重构的行动者网络建构和转译的学理解释,乡村社区治理主体和治理框架分析较为深入。国内的研究主要从乡村物质空间的分化和重组入手,研究方法偏向定量化,乡村空间分化、重构与治理的地理学研究内容框架和方法体系仍显不足。基于此,文章提出以人地关系地域系统理论为指导,在宏观尺度上系统研究多元外部性环境下的中国乡村发展转型的空间分化类型与动力机制;在中微观尺度上重点从乡村人地关系地域系统的要素结构、功能变化与要素重组及空间治理等方面展开全方位的研究,全面采用城乡连续谱空间梯度分析手法,剖析不同区位不同类型的乡村空间内部多维空间分化与重构治理的学理逻辑,综合集成地理学、社会学、政治学和管理学等学科理论和方法,搭建独具特色的中国乡村空间转型理论框架。乡村空间治理是国土空间管制和社会治理的重要组成部分,揭示其空间治理主体和参与共同体之间的协同机制,以及村庄建设管理与空间治理的途径与模式亟待归纳总结。
Progress and prospects in rural space diversification, reconstruction, and governance from a development perspective
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003240
[本文引用: 1]

With industrialization, urbanization, informatization, and economic globalization, there is significant diversification in rural areas, including the social and economic devolopment and rural landscape, land-use structure, urban—rural relationship, consumption structure, and governance pattern. Development and evolution are types of spatial transformation, and their differentiation is significant in rural areas. With changes in the relationship between human beings and the environment in rural areas, problems such as the gradual disappearance of traditional villages, loss of regional identity, precariousness of villagers’ development prospects, and loss of autonomy tend to arise. The renaissance and revitalization of rural areas have become the core target of regional and rural development in this new era. Development, together with the theoretical construction of rural geography, now faces a critical period of opportunity. The mechanism of interaction between the internal and external motivations of rural spatial differentiation needs to be clarified, and geographic parameters concerning the reconstruction of rural multidimensional space need to be examined carefully, as they take a scientific approach in exploring comprehensive rural governance. These are beneficial in strengthening both rural construction and the framework of governance theory. This paper systematically reviews the progress of research on rural spatial differentiation, reconstruction, and governance both at home and abroad. We found that, internationally, research on rural geography is more diverse, and theories and methods from the field of political economics and sociology are widely used. These research methods are mainly qualitative, focusing on the theoretical interpretation of the construction and translation of the actor-network of cognition, differentiation, and reconstruction of rural space. Further, the main body and framework of rural community governance are analyzed deeply. Domestic research, in contrast, focuses on the differentiation and reorganization of rural material space, but the content framework and methodology of rural spatial differentiation, reconstruction, and governance remain insufficient. Accordingly, this paper—guided by the theory of territorial system of human—environment interaction on a macro scale—systematically examines the spatial differentiation types and dynamic mechanism of rural development and transformation under multiple external environments in China. On a medium-micro scale, the comprehensive study of the rural human—environment relationship in a regional system is implemented, focusing on element structure, function change, element reconstruction, and space governance. We performed a space gradient analysis using urban—rural continuous spectrum geographic transects, which analyzed internal multidimensional space differentiation and reconstructed the scientific logic of governance in different locations and with different types of rural space. By integrating geography, sociology, politics, management, and other subjects, we constructed a unique theory framework for the transformation of rural space in China. Rural space governance is an important part of territorial space control and social governance, and is of interest across multiple academic disciplines. The collaborative mechanism between the governance of space and the participating community, as well as the approaches and models of village construction management and spatial governance used, needs an urgent conclusion and summary.
论农村人居环境整治与乡村振兴
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220107
[本文引用: 1]

21世纪以来,中国乡村社会经济发展与基础设施建设取得明显成效,但城乡发展不平衡、乡村发展不充分的问题仍较突出。特别是与乡村生活密切相关的人居环境仍为乡村发展的短板。2018年初,国家出台了《农村人居环境整治三年行动方案》,以着力改善农村人居环境,建设美丽宜居乡村,助力乡村振兴战略。本文解析了农村人居环境及其整治的概念与内涵,阐释了农村人居环境整治与乡村振兴的相互作用机理,剖析了农村人居环境整治的运行模式,梳理了整治成效的评价方法与结果,并展望了农村人居环境整治研究的重点领域。农村人居环境科学在过去十余年取得了快速发展,在基本理论、演化机理、质量评价、调控策略等方面有明显进展。但是,当前研究对于实践的指导性和支撑性仍存在明显不足,地方具体整治工作仍存在一些认识上或实践上的误区。面向乡村振兴战略需求,新时期的农村人居环境整治在认识和实践方面要形成“八项共识”。在研究层面,应强化乡村地理学与工程技术科学、城乡规划学、管理学、社会学等的交叉与融合,着力形成集理论研究、技术研发、机制剖析、成效评估、模式优化等于一体的系统性研究体系,可更好地支撑农村人居环境整治,实现乡村地域功能显化和价值提升,进而有效助力乡村振兴。
Rural living environment improvement and rural revitalization
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220107 URL [本文引用: 1]
土地整治供给侧结构性改革与乡村重构: 潜江“华山模式”实证研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.016
[本文引用: 1]

在厘清供给侧结构性改革提出的背景、内涵基础上,运用实地观察法和深度访谈法,探讨如何通过开展土地整治助推乡村重构等问题,并以湖北省潜江的“华山模式”作为实证。结果表明:①需要构建“背景—手段—路径—目标”的土地整治供给侧结构性改革体系;②土地整治供给侧结构性改革从调结构、去库存、补短板、降成本、促融合五个方面着手,核心在于实现“劳动力、土地、资本、制度、产业、技术”六大要素的合理配置;③“华山模式”实现了土地流转—虾稻共作—镇企共建—市场引导—多方共赢的目标,是土地整治供给侧结构性改革助推乡村重构的成功样板。建议在实施土地整治时,应贯彻绿色理念、注意全域规划、依托科技支撑、因地制宜发展当地产业、加强制度供给等,确保土地整治助推乡村重构的有效性和持续性。
Structural reform on the supply side of land consolidation and rural restructuring: An empirical study of the Huashan Model in Qianjiang city, Hubei province
市场资本驱动下的乡村空间生产与治理重构: 对婺源县Y村的实证观察
Rural space production and governance restructuring driven by market capital: A case study of Y village in Wuyuan
混杂性: 关于乡村性的再认识
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201710005
[本文引用: 2]

乡村性一直是西方乡村地理研究的核心。传统认识中的乡村性被认为是一种乡村本身既有的平面化和单向度的性质。然而,在社会现实和学术思潮的后现代转向下,乡村性被置于“后乡村”的语境中进行重新理解,强调了一种多元化和异质性意义上的不断生产和再生产的动态过程。当今,“后乡村”的重构牵涉多元主体、跨越多重尺度、交织流动关系,镶嵌于混杂的过程、话语和实践之中,“混杂性”成为理解日益复杂的乡村性的有益视角。从主体混杂与再物质化、网络混杂与关系乡村、意义混杂与融入现代性三个方面,对近年西方研究关于“后乡村”的混杂性视角进行系统评述,重新解读有关乡村性的认识,并探讨其对国内乡村研究的启示。
Hybridity: Rethinking rurality
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201710005
[本文引用: 2]

Rurality has always been a central topic of rural studies in the West. Discussions on its definitions have been quite complex, contested and even ambivalent, reflecting recent dramatic changes occurring in rural economies, politics and social cultures. In tradition, rurality has been regarded as a given nature that is self-evident, generalized and one-dimensional. However, with the post-modern transformation of social realities and academic trends, the concept of rurality now focuses on dynamic processes through which diversified and heterogeneous meanings are produced and reproduced. Many scholars have called for a 'post-rural' context from which to understand rural reconstruction in a new era. Just as 'post-modernity' refers to the reflexivity of modernity, the concept of the 'post-rural' has been advanced not to partition phases of rural development, but to realize the reflexive turn occurring in rural studies. The 'post-rural' can be regarded as a 'complex', as multiple actors, events, discourses and practices co-exist and interplay. Hybridity refers to a process of recreation based on the integration of heterogeneous elements together with the elimination of borders between systems. Thus, hybridity is considered to be one of the most useful theoretical perspectives for understanding the essence of rurality in an increasingly complex context. Hence, based on interpretations and analyses of previous literature of the West, this paper proposes a framework on hybridity in 'post-rural' settings based on the following three aspects: (1) hybridity produced by human and non-human actors and trends of rematerialization emphasizing performances and practices in post-rural everyday life; (2) hybridity embedded in fluid networks and relations and dialectical relationships between rurality, globality, and urbanity; (3) hybridity stimulated through rural area's integration into processes of modernization and processes of negotiation occurring between the de-alienation of traditional local cultures and the alienation of modernity. Finally, considering the particularities of the context of rural China, this paper discusses ways in which the perspective of hybridity offers new insights into the studies and practices of Chinese rural reconstruction.
Multifunctional rural development in China: Pattern, process and mechanism
基于多功能理论的中国乡村发展多元化探讨: 超越“现代化”发展范式
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502007
[本文引用: 1]

传统的乡村现代化发展范式和地理学关于乡村的区域差异研究之间存在缝隙,不足以为快速演化分异的乡村地域发展提供直接理论支撑。本文引入西方近20年来逐渐兴起的多功能农业与多功能乡村理论,从新的视角观察思考中国乡村多元化发展的目标、路径及对策。首先从经济、社会和环境三个方面反思中国乡村现代化的基本历程与得失,以及西方国家乡村现代化产生的问题,指出传统的农业农村现代化发展在很大程度是以牺牲乡村环境和乡村社会机理脆弱化为代价的,也造成了乡村经济对外部支持的过度依赖,仅仅强调“现代化”发展范式显然是不够的;然后简要介绍了国外多功能农业与多功能乡村理论;在此基础上,从功能角度提出中国农业农村发展的多元目标,推演探讨农业农村发展的区域差异化路径及对策。
Diversified agriculture and rural development in China based on multifunction theory: Beyond modernization paradigm
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502007
[本文引用: 1]

There is a big gap between general rural modernization paradigm and huge empirical rural geography studies. This gap results in impotent development strategies on regionally differentiated countryside. Based on multifunctional agriculture theory and multifunctional rural theory which emerged in Western World as a new paradigm, this paper discusses the multiple objectives, differentiated pathways and policies of agriculture and rural development in China. Firstly, this paper reflects the problems and challenges caused by modernization paradigm in rural China on economic, social, and environmental aspects, as well as that of western developed countries. It can be concluded that conventional agricultural and rural modernization is developed largely at the expense of rural environment, social fabric and economic viabilities. Obviously, "modernization development paradigm" alone is not enough for healthy agricultural and rural development in such booming economy as China. A better paradigm should be developed which takes economic development, social justice and environmental sustainability into account at the same time. After a brief review of multifunctional agriculture theory and multifunctional rural theory overseas, the multiple objectives of agriculture and rural development in China are put forward. These multiple objectives, however, should not and could not be a burden on rural space indiscriminatingly due to the enormous differentiation of natural and socio-economic conditions. Thus, the final but main part of this paper envisions the differentiated pathways and policy portfolios of agricultural and rural development in China from the perspective of territorial division.
乡村生活空间研究进展及展望
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.03.007
[本文引用: 1]

乡村生活空间是一定地域乡村居民居住、就业、消费和休闲等日常活动迭置而成的空间聚合体,也是一定乡村地域空间形式、空间内涵和空间意义内在关联的有机统一体。近期西方学术界对乡村生活空间的关注主要集中于两个方面:一是后生产主义乡村的生活主体多元化和生活空间异质化,二是被城市社会生活他者化和空间边缘化的不同弱势群体的乡村生活体验及空间建构。国内乡村生活空间研究具有两个鲜明特点:从研究内容看,注重乡村居民居住及就业空间变化研究,但乡村消费空间和休闲空间研究成果很少见;从研究方法看,空间形式的实证分析始终占据主导地位,空间内涵的结构分析和空间意义的人本分析有待深化。乡村生活空间研究能够丰富乡村地理学的研究视角,并可能为乡村发展政策制定提供理论指导。西方乡村生活空间研究难以提供标准模版,中国乡村生活空间研究资源得天独厚,“形式-内涵-意义”相统一的空间观能够帮助构造有效分析框架,基于空间行为分析的多种方法集成能够提供有力分析工具。
Progress and prospect on rural living space
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.03.007
[本文引用: 1]

In the context of both contemporary human development transformation and humanism booming, ‘living space’ has become a new perspective for human geographers to investigate the change of human-environment relationship, and the spatial view of integrating ‘pattern-connotation-implication’ has also become a new thinking to interpret the interaction of human activities and environment. So far, the researches on living space have focused mainly on the urban areas and their element space and space form. In contrast, little attention has been paid on the rural areas, juxtaposition space and three-dimensioned research. Rural living space refers to a polymer formed by the overlapping of everyday activities for rural residents in a certain territory, such as dwelling, employment, consumption and leisure, and also an organic body where spatial form, spatial implication and spatial meaning are inherently associated with each other. Due to differences in development environment and concrete national situations, post-modernization and counter-urbanization in developed countries has contributed to the post-rurality in rural space. There have been two highlights on rural living space in western academic circles. One indicates the diversification of living subjects in rural area in the context of post-productivism and the heterogenization of living space, and the other refers to life experience and spatial construction with respect to vulnerable groups who are “otherized” by urban social living or marginalized in space. Rural region in China has kept going through function transformation and spatial reconstruction, so it is a unique significance for the livable construction of rural living space. At the present stage, there are also two distinct characteristics studying on rural living space at home. From the view of contents, studies on changes in dwelling space and employment space of rural residents have been played more attention, while studies on consumption space and leisure space are as sparse as morning stars. From the view of methods, the empirical analysis in spatial forms has occupied a leading position, while the structural analysis in spatial implication and humanistic analysis in spatial meaning are expected to carry forward. Notably, it is hard for western studies on rural living space to be standardized. Studies on China’s rural living space own their distinct context. Effective analysis framework can be made from the view of space mutually unified by form, implication and meaning, applying the rational of deconstructing spatial pattern by environment, perceiving spatial connotation by relationship and interpreting spatial implication by impacts, and powerful analysis tools can be created based on various methods of spatial behavior analysis, employing the research methods of combing quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis, spatial analysis and statistical analysis; Which will focus on mainly exploring the features, mechanism and effects of the changes of the rural living space to reveal the change laws of rural human-environment. The expected achievements might amplify the research viewpoints, contents and methods of rural geography, and provide theoretical support for the sustainable development of the rural areas.
中国乡村生活空间研究溯源及展望
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.04.013
[本文引用: 1]

乡村生活空间是乡村发展的缩影,透视了乡村地域的人地关系。随着城乡融合战略、乡村振兴战略的实施,加之新型城镇化和全球化进程的不断推进,包括乡村生活空间在内的乡村空间发生整体性重构,乡村进入新的发展时期。在此过程中,乡村生活空间如何映射和影响乡村发展,是值得多角度探讨的话题。论文在梳理历史文献的基础上,认为乡村生活空间是承载乡村居民日常生活行为的场所空间,是乡村居民居住、休闲、社交、消费以及公共服务活动的多层次地域综合体,也是乡村社会空间的重要组成部分。国内学界对乡村生活空间的研究自20世纪20年代至今约百年,论文按照中国不同经济社会发展阶段特征,将乡村生活空间研究历程分为4个阶段:1949年前的探索时期、改革开放前的停滞时期、改革开放后的复兴时期、21世纪以来的快速发展时期。但相比于国外乡村生活空间的研究和国内城市生活空间的研究,国内乡村生活研究内容偏向实证,缺乏全面的深度总结和理论构建。新时期中国乡村生活空间的研究应该构建完整的研究框架体系,分别从基础理论、研究主体和多元化研究视角进行多层次、全方位的探索展望。
Historical development and prospect of rural living space research in China
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.04.013
[本文引用: 1]

Rural living space is the microcosm of rural development, which reflects the human-environment relationship in rural areas. With the implementation of the Urban-Rural Integration Strategy and the Rural Revitalization Strategy, coupled with the development of the new-type urbanization and globalization, rural space, including rural living space, has been restructured as a whole, and the countryside has entered a new period of development. In this process, how rural living space map and influence rural development is a topic worthy of discussion from multiple perspectives. Based on the review of literature, this article holds that the rural living space is the space of the daily life behavior of rural residents, a multi-level territorial complex of rural residents' living, leisure, socializing, consumption, and public service activities, and an important part of rural social space. The study of rural living space in Chinese academia started in the 1920s. According to the characteristics of different stages of economic and social development of China, this study divided the research of rural living space into four periods: the exploration period before the founding of the People's Republic of China; the stagnation period before the Reform and Opening-up; the revival period after the Reform and Opening-up; and the rapid development period since the 21st century. However, compared with international rural living space research and Chinese urban living space research, the study of rural life in China tends to be empirical, lacking comprehensive deep examination and theoretical model construction. In the new era of development, the study of rural living space in China should construct a complete research framework and carry out multi-level and all dimensional exploration on basic theories, research subjects, and diverse research perspectives.
新时代中国乡村振兴: 探索与思考: 乡村地理青年学者笔谈
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190417
[本文引用: 1]

乡村振兴是新时期国家重大战略,是一项系统工程。中国地域广阔,资源禀赋和经济发展区域差异显著,乡村振兴路径需要体现乡村发展的综合性、复杂性和区域性。来自乡村地理学领域的16位青年学者,以笔谈方式,对中国乡村振兴的科学路径开展了深入讨论。核心观点如下:(1)乡村振兴需要遵循时空分异规律,重点关注乡村发展的时空传承与现实需求之间的衔接,建立彰显地域特色和具有可操行性的理论和技术体系,分类、有序地推进乡村的人居环境、产业体系、生态环境和治理模式等转型。(2)力求城乡融合和联动,构建城乡复合多中心网络体系,创新采用“乡村群”空间组织模式,以乡村内生力、城镇辐射力与规划约束力共同驱动乡村振兴。(3)在中国“大国小农”的基本国情下,农业承载着食品安全、社会稳定和生态产品等多重功能,需要构建农业“全价值链”的发展路径,促进一二三产业深度融合,助力乡村产业兴旺。(4)在能源富集区,在保障国家能源安全需求前提下,需从根本上解决农村发展不平衡不充分问题;在西南地区,依托山区特色生态、人文资源打造山区现代农业产业体系、重塑乡村旅游新品牌、构筑山水田园乡村家园;在东北地区,乡村振兴应与“东北振兴”战略协同推进,有序分类推进;在长三角地区,应在全面认知乡村工业化到乡村城镇化,再到乡村特色化,到乡村的社会、文化和生态建设的阶段演化特征基础上,寻求差异化的乡村振兴路径;在西北地区,应在生态保护的前提下有效提升乡村“自主脱贫”的能力,实现从“输血”扶贫向“造血”扶贫转变;在京津冀地区,需以城乡基本公共服务均等化为目标,推动城乡融合与乡村振兴;在资源型地区,乡村振兴核心将以一二三产业融合的高效农业体系替代以资源开采为核心的产业体系;在传统农区,优化耕地利用转型同农村劳动力结构变化的耦合格局是实现乡村振兴的关键;在经济发达地区,具有“混杂性”特征的乡村,需激活农村土地资源的资产和资本属性,推进空间有序整合与活化,寻求多主体共同参与和缔造的现代乡村治理模式。
Discussions and thoughts of the path to China's rural revitalization in the New Era: Notes of the young rural geography scholars
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190417
[本文引用: 1]

The rural revitalization, as a national strategy in the new era, puts forward the requirements and goals of the thriving industry, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance and prosperity. China is a country with a vast territory, marked by regional differences in resource and economic development levels. What's more, rural areas are complex, diverse, and have many problems. Rural revitalization is a systematic project with comprehensive, complex and regional characteristics. Sixteen young scholars in the field of rural geography across the country have conducted in-depth discussions and reflections on the scientific path of rural revitalization in China. The core points are as follows: (1) In accordance with the law of time-space distribution, we should fully understand the connection between the historical basis of rural development and the practical needs, establish a theoretical and technical system that highlights regional characteristics and has operability, and promote the transformation of rural residential environment, industrial system and governance mode in a classified and orderly manner. (2) Rural revitalization strives for the integration between urban and rural areas to build a compound multi-center network system, which breaks through the village and town systems of traditional linear "central place", and innovate the spatial organization mode of "village cluster". Rural endogenous force, urban radiation force and planning binding force jointly drive rural revitalization. (3) The agriculture has multiple functions such as food safety, social stability, and ecological products. Its development needs to create the whole value chain of agriculture to promote the integration of primary, secondary and tertiary industries. (4) In energy-rich areas, we should fundamentally solve the problem of unbalanced and inadequate rural development under the premise of ensuring the national energy security demand. In Southwest China, we should take advantage of ecology and human resources to build a modern agricultural industry system, remodel the brand of rural tourism, and build landscape rural homes. In Northeast China, rural revitalization must proceed in an orderly and classified way in the process of synergistic promotion of the "northeast revitalization" strategy. In the Yangtze River Delta region, it is necessary to cognize the evolutionary stages from rural industrialization to rural urbanization, and then to rural characteristics with more and more emphasis on the social, cultural and ecological construction of rural areas, seeking a scientific path of rural revitalization. In Northwest China, we propose to effectively improve the ability of "independent poverty alleviation" in rural areas under the premise of ecological protection, and realize the transformation from "transfusing blood" to "producing blood". In the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, oriented by equalization of basic public services in urban and rural areas, we will promote the development of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. In resource-oriented areas, rural industries will replace the industrial system formed around resource exploitation with an efficient agricultural system integrating primary, secondary and tertiary industries. In traditional agricultural areas, it is necessary to optimize the coupling pattern between farmland use transformation and rural labor structure change, which is an important means to achieve rural revitalization. In economically developed areas, villages with "mixed" characteristics need to activate the assets and capital attributes of rural land resources, promote the integration and activation of spatial order, and comprehensively explore the modern rural governance mode with the participation of multiple subjects.
中国乡村地理学研究的主要热点演化及展望
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.004
[本文引用: 1]

以地理学主要中文期刊近40年来刊发的有关乡村研究的文献为分析对象,采用Citespace软件文献计量分析及文献归纳方法,对中国乡村地理学研究主要热点进行识别和阶段性划分,并梳理其主要热点的研究进展。结果发现,伴随20世纪80年代的乡镇工业和21世纪初以乡村旅游业兴起的乡村两次产业结构调整,以及国家乡村发展和建设的战略和政策不断调整,乡村地理学的研究热点演化大致可分为3个阶段:①1978-2000年,主要聚焦于乡村城市化、城乡关系、乡村聚落、农业发展、农村经济等研究,为国家和地区的农业与农村发展做出了基础性和战略性贡献。②2000-2008年,开始转向以乡村旅游、农村居民点、新农村建设、村庄规划、空心村等研究热点话题,中国乡村地理学发展改变了“重城轻乡”的学科格局,逐渐走向繁荣。③2008年至今,研究热点转向多元化,涉及乡村转型、乡村重构、乡村性、空间重构、乡村社区、乡村治理等,研究主题逐渐接轨于国际乡村地理学。未来中国乡村地理学的研究应以建设乡村地理学学科基础理论和方法体系为核心目标,服务于国家实施乡村振兴战略需要,积极关注乡村发展、转型、分化、重构与治理等核心话题,深化乡村多元空间价值理论研究,形成独具中国特色的乡村地理学理论框架和研究范式。
Change in key research area and prospect of Chinese rural geography
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.004
[本文引用: 1]

Since the reform and opening up in 1978, human geography in China has experienced important developments. As a branch of human geography, rural geography has carried out a series of research on the rural regional system of human-environment relations. Taking the geography research articles published in the past 40 years in major Chinese journals of geography as the analysis object and using bibliometrics and literature summarization methods assisted by Citespace tools, this study identified the key research areas, divided the themes into stages, and summarized progress in the major research areas. The results show that under the background of globalization, urbanization, modernization, and informationization, as well as rural industrial structure adjustment and rural development policy change, great changes have taken place. From 1978 to 2000, rural geography mainly focused on the research themes of rural urbanization, urban-rural relations, village clusters, agricultural development, and rural economy. The academic community showed greater interest in urban than rural research, which has made fundamental and strategic contributions to the agricultural and rural development of the country and regions From 2000 to 2008, rural geography began to shift to topics such as rural tourism, rural settlements, new rural construction, village planning, and hollow village, and the development of the discipline gradually progressed. Since 2008, rural geography has shifted to more diverse topics, mainly including rural transformation, rural restructuring, rurality, rural governance, rural community, and spatial restructuring, which converge with rural geography research internationally. In the future, the research of rural geography in China should be based on the construction of theories and methods of rural geography and serve the rural vitalization strategy. More attention should be paid to the development, transformation, differentiation, restructuring, and governance of rural areas, deepening theoretical research on the value of diversified space in rural areas and developing a theoretical framework and research paradigm of rural geography with unique Chinese characteristics.
从“四地”期刊载文审视中国农业与乡村地理学研究发展特征
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.09.015
[本文引用: 1]

基于中国学术期刊出版总库所提供的《地理学报》《地理科学》《地理研究》《地理科学进展》(简称“四地”期刊)创刊以来至2020年12月间的农业与乡村地理学论文数据,采用Citespace可视化科学文献计量方法,对566篇文献的主题、引文和关键词等特征进行可视化分析。系统梳理了农业与乡村地理学术论文所反映的主题脉络、知识演进、历史热点、研究机构发展和发文作者分析。这些分析充分体现出了中国农业与乡村地理学研究的发展历程、目前的主要研究议题与未来的发展趋势。研究结果显示,农业地理、聚落与古村落、土地利用及其发展模式、乡村居民点及其空间格局、城乡一体化、新农村建设、乡村重构、乡村振兴和城乡融合发展等主要研究议题是不同时期的研究聚焦点。从研究热度看大致经历了由以农业地理研究为主,转向农业地理与乡村聚落地理并驾齐驱,再到城乡融合与乡村振兴研究3个阶段。其研究发展过程呈现出3大转向:① 由单一的农业地理和乡村聚落地理转向综合的农业与乡村地理学研究;② 从单一的农业生产要素、社会经济要素格局研究转向区域城乡人地系统融合的过程、机制和影响研究;③ 由传统的调研统计、田野观测、数字模拟技术方法转向大数据、多源时空监测模拟和农业地理工程实践。乡村转型-城乡融合-乡村振兴-高质量发展将成为未来城乡发展的大逻辑、新常态,也是未来农业与乡村地理学研究的重点和方向。主要研究议题方面有乡村地域类型、乡村功能转型、乡村空间重构、乡村聚落重构、乡村人居环境质量、乡村发展的新因素及其作用机制、乡村弹性与可持续性发展、乡村产业结构调整与升级、城乡基础设施与服务统筹规划建设等。学科发展应注重综合研究,深化对农业与乡村发展新驱动力的认识,切实加强乡村地理学研究的理论与方法创新,借以更好地服务于国家乡村振兴战略。
Characteristics of research in agricultural and rural geography in China: Review from papers in four geographical periodicals
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.09.015
[本文引用: 1]

Supported by China Academic Journal Network Publishing Databas, this study collected 566 articles fromActa Geographica Sinica,Geographical Research, Scientia Geographica SinicaandProgressinGeography (four geography periodicals for short) of CNKI. The selected articles were all related to agricultural geography, and their publication dates covered from the establishment of the four geography periodicals to December 2020. Taking the 566 articles as the analysis object and using bibliometrics and literature summarization methods assisted by Citespace, this study identified the topic context, knowledge evolution, historical hotspots, development of research, institutions, and authors. The analyses reflected that the past development history, the current main research topics, and the future development trend of agricultural and rural geography in China. The results showed that agricultural geography, settlements and ancient villages, land use and development patterns, rural settlements and its spatial pattern, urban-rural integration, new rural construction, rural restructuring, rural revitalization, and urban-rural integration all played important leading roles in different periods. Although the research on these topics has been flourishing for a long time. However, it has experienced 3 stages: the agricultural geography stage, the agricultural geography and settlement geography stage, and the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization stage. The process has presented four major transformations. First, research perspective modified from single agricultural geography and rural settlements to integrated agricultural and rural geography. Second, research content transformed from agricultural and social elements to the process, mechanism, and influence of regional urban-rural integration. Third, research methods and techniques changed from survey statistics, the field observation and digital simulation to big data, multi-source spatiotemporal monitoring simulation and agricultural geoengineering practice. The path from rural transformation, urban-rural integration, rural revitalization, to rural high-quality development will become the general logic and new normal of future urban-rural development. It will be the focus and direction of agricultural and rural geography research in the future. The main research topics include rural areal types, rural functional transformation, rural spatial restructuring, rural settlements reconstruction, rural human settlements quality, new factors and mechanisms of rural development, rural elasticity and sustainable development, and rural industrial structure adjustment and upgrading, overall planning and construction of urban-rural infrastructure and services, and so on. To serve national rural revitalization strategy better, the comprehensive research should be emphasized in disciplinary development, the understanding of the new driving forces of agriculture-rural development should be deepened, and the theoretical and methodological innovation of rural geography research should be effectively strengthen.
乡村重构的理论认知
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.002
[本文引用: 1]

面向快速城镇化进程中乡村地域日益复杂的人地关系,乡村重构成为地理学研究的重要前沿课题。乡村重构即行为主体通过优化配置和有效管理影响乡村发展的物质和非物质要素,重构乡村社会经济形态和优化地域空间格局的过程。本文在已有研究基础上,基于乡村地域系统的“要素—结构—功能”视角,从乡村重构的行为主体、价值取向和目标定位等方面进一步阐释了乡村重构的概念内涵,剖析了由诱发机制、支撑机制、约束/促进机制、引导机制、引擎机制构成的乡村重构作用机制框架。最后,基于政府行为对推动城乡资源要素优化配置和乡村重构的引领作用,认为有必要重构乡村社会经济的政府干预框架,并对未来中国乡村重构需进一步重点关注的研究内容展开探讨。
Theoretical thinking of rural restructuring
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.002
[本文引用: 1]

With its focus on the increasingly complicated human-environment relationship under the background of rapid urbanization, rural restructuring study has become an important frontier research area of geography. Rural restructuring is a process of reshaping the socioeconomic forms and spatial patterns in rural areas in respond to the changes of factors both internal and external of the system, by optimally allocating and efficiently managing the material and non-material elements of rural development. It aims at ultimately optimizing the structures and improving the functions within rural territorial systems as well as realizing the structural coordination and functional complementation between urban and rural territorial system. Based on the perspective of "elements-structure-function" of rural territorial system, this article first elaborated the concept of rural restructuring from the aspects of behavioral mainstream, value system, and targets. Then, a framework of rural restructuring mechanism was analyzed, which consisted of inducing mechanism, supporting mechanism, constraining/promoting mechanism, guiding mechanism, and driving mechanism. Furthermore, in view of the guiding role of governments in optimal allocation of critical resources and rural restructuring, this article argued that it is necessary to restructure the contours of state intervention in rural societies and economies. Finally, the research contents of rural restructuring in the future were prospected.
城乡融合背景下乡村转型与可持续发展路径探析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912010
[本文引用: 1]

探究乡村转型发展规律对于系统认识乡村发展阶段、研判乡村发展趋势、明确乡村可持续路径、促进乡村转型与振兴具有重要意义。首先基于马斯洛需求层次理论、产业结构演变理论、区域空间结构理论等演绎乡村转型发展阶段,然后结合典型乡村发展历程分析进行实证检验,进而探讨对于新时期乡村可持续发展的启示。研究结果:① 乡村转型发展在理论上可分为4个阶段,一是生产力均匀分布下以实现温饱需求为目标的土地整治促增产阶段,二是城乡联系增强下以改善生活水平为目标的农业结构调整促增收阶段,三是区域联系增强下以提升生活质量为目标的产业结构调整促致富阶段,四是城乡互动融合下以城乡等值为目标的公服设施建设促均等阶段。② 典型发达乡村的发展历程在一定程度上印证了乡村转型发展阶段特征。③ 因资源基础、区位条件、市场规模、发展主动性等因素的差异,乡村实际发展过程可能存在阶段的跃迁或并行的现象。根据发展过程中不同主体发挥作用的变化,每个阶段又可细分为初始阶段、过渡阶段和成熟阶段。④ 基于乡村转型发展规律分析,城乡融合背景下不同类型地区乡村可持续发展路径可分为土地整治集聚路径、特色产业发展路径、产业平台集散路径和社区功能集约路径等4类。
Approaches to rural transformation and sustainable development in the context of urban-rural integration
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912010
[本文引用: 1]

Exploring the evolution rules of rural transformation is significant for systematically understanding stages of rural development, judging trends of rural development, determining paths of rural sustainable development and promoting rural vitalization. Based on Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, industrial structure evolution theory, and regional spatial structure theory, this paper deduced the evolutionary stages of rural transformation. The evolutionary stages were verified by analysis of the development process of typical villages. Further, this paper explored the implication for rural sustainable development in the new era. The results showed that: (1) Evolutionary process of rural transformation included four stages. The first was the cropland-engineering stage, aiming at realizing the need for food and clothing under the uniform distribution of productivity. The second was the agricultural structure adjustment stage, aiming at increasing income under the intensifying urban-rural relationship status. The third was the industrial restructuring, aiming at improving the quality of life under the strengthening of regional linkages. The fourth was the stage of promoting the equalization of public service facilities with the goal of urban-rural equivalence under the urban-rural integration. (2) The development course of typical developed villages confirmed the evolution rules of rural transformation to some extent. (3) In practice, the evolutionary process of rural development presented skip or parallel phenomena because of regional differentiation of resources, location, market size, and willingness. According to the changes of the roles of different groups in development course, each stage could be subdivided into initial stage, transition stage, and maturation stage. (4) Based on the analysis of evolutionary rules of rural transformation, the paths of rural sustainable development in different types of region included land consolidation and agglomeration path, specialty industrial development path, industrial platform for collection and distribution path, and community function intensification path in the context of urban-rural integration.
乡村重构与转型: 西方经验及启示
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181133
[本文引用: 1]

20世纪80年代以来,乡村重构与转型成为西方国家乡村地理学研究的重要前沿课题。在揭示西方国家乡村重构过程、梳理转型特征、探析驱动因素的基础上,聚焦于乡村发展的系统总结及其提供的经验借鉴与启示。西方国家乡村重构经历了从“资本、土地、产权”主导的经济维度重构到“话语、他者、建构”主导的社会维度重构、再到“主体、文化、网络”主导的综合维度重构阶段;乡村转型特征可凝聚为生产性乡村-消费性乡村-多功能乡村-全球化乡村的逻辑主线;后工业化、逆城市化、全球化是推动西方国家乡村重构与转型的主要因素。中国乡村发展具有迥异于西方国家的背景和特征,但相关经验及认识仍然能够为理解中国乡村实践发展、推动相关理论建设提供启示,并从“要素/重构/过程”-“功能/转型/结果”视角对当代中国乡村重构与转型进行了系统思考。
Rural restructuring and transformation: Western experience and its enlightenment to China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181133
[本文引用: 1]

Rural restructuring and transformation has been frontier in Rural Geography studies of Western countries since the 1980s. Our objective in this paper is to draw lessons from the rural development of Western countries for the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy of China. The paper reveals the rural restructuring process, the characteristics of rural transformation, and the driving factors of Western countries, and summarizes the rural development practice in Western countries and its enlightenment to China. The energy crisis and post-industrialization in the 1970s, and technological progress (especially the rapid development of the Internet) since the early 1990s constituted important contexts for the rural restructuring and transformation in Western countries in three phases. The first phase is the economic dimension of restructuring dominated by "capital, land, and property rights". The second phase is the social dimension of restructuring dominated by "discourse, otherness, and construction". The third phase is the comprehensive dimension of restructuring dominated by "subject, culture and network", the essence of which is the reorganization of rural elements and their relationships as a result of the insertion of the exogenous subject, or urban area, capital and culture. The transformation characteristics have been concluded in a logic line which starts from productive countryside to consumptive countryside, then to multifunctional countryside, and lastly, to current global countryside. Rural transformation, of which the substance is the change of rural nature, is the direct result of rural restructuring. Post-industrialization, counter-urbanization, and globalization are the main factors that drive rural restructuring and transformation. Meanwhile the evolution of global geopolitical pattern has an impact on rural restructuring. Finally, despite the difference of background and characteristics of rural development between China and Western countries, it is believed that the experience from Western countries can contribute to providing enlightenment for understanding the practice of rural China's development and promoting its theory construction. In consideration of the issue that there is not unified conceptual framework for rural restructuring and transformation in China, which is a disadvantage of the relevant studies on rural China, the rural development practice and theoretical understanding in Western countries can provide some beneficial help for deepening the recognition of rural restructuring and transformation. It is noteworthy that because of different contexts between China and Western countries, Western practice and experience should not be directly copied by China without taking the differences into account. In addition, rural restructuring and transformation in contemporary China can be discussed from the perspectives of factors, reconstruction, process and function, transformation, consequence. Specifically, the paper proposes a rural revitalization blueprint for China, which sets global countryside, productive countryside, and multifunctional countryside as development orientations for eastern, central and western China, respectively.
山东省农村居民点转型的空间特征及其经济梯度分异
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201710009
[本文引用: 1]

为探究农村居民点转型的空间结构及其与经济发展的关联性,以山东省为例,基于农村宅基地转型的理论假设与测度方法,运用空间关联分析方法研究农村居民点转型的空间布局和集聚特征,并以人均GDP作为特征指标划分各县级行政区的经济发展梯度,从省级全域层面和“点、线、面”特征单元综合的角度,揭示农村居民点转型与经济发展的相关性及其耦合关系。结果显示,在空间分布上,2005-2014年山东省农村居民点转型指数呈现西高东低和南高北低的态势;在全局趋势上,Moran's I指数达到0.6317,说明农村居民点转型存在显著的空间集聚现象;在局部趋势上,农村居民点转型的热点区和次热点区集中分布在鲁西黄泛平原、鲁西南淮河平原以及鲁中沂蒙山区,次冷点区分布在次热点区外围,冷点区分布在胶东丘陵地区和鲁北黄河三角洲地带;在相关性分析上,农村居民点转型与经济发展水平具有明显的数理统计相关性和空间耦合性,无论是全域层面还是特征单元,农村居民点转型均表现出从低级到高级经济梯度的递减规律、且乘幂变化趋势显著。本文探索了农村居民点转型的空间特征,弥补了土地利用转型空间性分析的不足;同时研究结果也较好地验证了前人提出的理论假设。
Spatial characteristics of rural residential land transition and its economic gradient differentiation
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201710009
[本文引用: 1]

In order to explore the spatial structure of rural residential land transition and its relevance to economic development, the spatial layout and agglomeration characteristics of rural residential land transition in Shandong Province were studied by applying theoretical hypothesis on rural housing land transition and spatial correlation analysis methods, such as global spatial autocorrelation analysis and hot spot analysis. Economic growth stages at county scale were divided based on per capita GDP, and the coupling relationship between rural residential land transition and economic development were revealed from the integrated angle of global scale at the provincial level and "point-line-face" feature unit. The results showed that, the rural residential land transition index from 2005 to 2014 displayed a significantly increasing trend in the east-west direction and a gradually descending trend from south to north. Based on the global spatial autocorrelation analysis, Moran's index, which reached 0.6317, indicated that the rural residential land transition showed a significant pattern of high-high and low-low spatial clustering. Furthermore, by applying hot spot analysis, it was found that the hot spots and hot sub-spots were intensively distributed in the western inadated plain of the Yellow River, southwest Huaihe plain and central Yimeng Mountains of Shandong Province; the cold sub-spots were distributed in the periphery of the hot sub-spots, such as cities of Zaozhuang, Jinan, Zibo, Binzhou and Weifang; and the cold spots were mostly distributed in Jiaodong hilly region and the northern Yellow River Delta. Moreover, obvious correlation of mathematical statistics and spatial coupling between rural residential transition indices and economic development level were indicated. The decreasing tendency from low to high economic gradient at both global scale and provincial level and feature units of "Five counties - Three belts - Four regions" were revealed by all rural residential land transition characteristics, with the significant relationship of power exponent trend. This paper explored the spatial characteristics of rural residential land transition, and made up for the deficiency of the single non-spatial analysis of land use transition; and the results verified the previous theoretical hypothesis successfully.
乡村生产空间系统的概念性认知及其研究框架
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

中国乡村发展正步入转型的新阶段,乡村生产空间正经历以家庭为单元的土地细碎化经营向多种形式的适度规模化经营转变,呈现出乡村多元主体利益竞合的空间博弈及乡村生产空间资源配置不匹配等新型矛盾。本文将系统论思想引入乡村生产空间,提出“乡村生产空间系统”理念,并从地理学与空间、行为空间和空间行为、“空间的生产”理论和人地关系地域系统学术思想出发厘清了乡村生产空间系统的思想缘起,凝练乡村生产空间系统的核心内涵;并对乡村生产空间系统的学理辨析、演化机制、形成机理、优化调控等基本问题域进行讨论,初步构建乡村生产空间系统的研究框架;进而提出未来研究需重点关注乡村生产空间系统的要素构成及其关系界定、“人”与“地”之间的相互作用机理及人地关系行为机制、探讨多学科融合多方法集成、辅以长时序数据支持的方法体系,旨在为乡村生产空间可持续发展由基础研究走向实践应用提供理论基石。
Conceptual and research frameworks of rural production space system
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

As China enters a new stage of rural transformation, rural production space is changing from household-based fragmented land management to moderate-scale land management of various forms. New conflicts due to the spatial competition of multiple stakeholders in the rural area and disordered spatial allocation of rural production resources have arisen. By introducing system theory thinking into the study of rural production space, this research puts forward the concept of rural production space system. Inspired by a series of theories and concepts, including the space concept in geography, behavior space and spatial behavior, the theory of "production of space," and the thoughts of regional system of human-land relation, this study traced the theoretical origin of rural production space system and proposed its core connotation. Following the logic of conceptual development to operation and regulation, this study proposed four basic problem domains of rural production space system, including its theoretical analysis, mechanism of change, mechanism of formation, and optimization and regulation. After briefly outlining a research framework of rural production space system, this article prospects three important objects of future research. We need to understand the essential factors that rural production space system consists of, as well as the definition of their relationships; focus on the mechanism of interactions between "human" and "land"; and pay close attention to the behavioral aspect of human-land relationship. Also, we should explore the use of new approaches that are multidisciplinary and integrate multiple methods. On these bases, this study aimed at providing a theoretical basis for the research of sustainable development of rural production space, expanding from basic research to practical applications.
乡村空间辨析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.003
[本文引用: 1]

伴随着城镇化、信息化、全球化等多种内外因素的交互作用,中国的乡村正经历着社会经济形态重组、地域功能提升等一系列转型与重构的过程,乡村地域面临着前所未有的机遇与挑战,而“乡村振兴战略”的提出也给乡村发展及乡村地理学的研究提出了新要求,全面系统地认识乡村空间系统,准确把握乡村空间是开展进一步研究的必要前提。本文在系统梳理国内外对乡村空间的认知与发展基础上,指出国内乡村地理学在乡村社会—文化空间研究上的不足。本文以人地关系地域系统为理论基础,尝试建构了由“物质空间—社会空间—文化空间”组成的乡村空间系统,以期为全面认识日益复杂的乡村地域提供理论指导。
On the analysis of rural space
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.003
[本文引用: 1]

Influenced by the interaction of various internal and external factors including urbanization, informatization, and globalization, rural areas in China are experiencing socioeconomic restructuring, regional function upgrading, and a series of transformations and reconstructions. Rural areas face a range of unprecedented opportunities and challenges, and the proposal of "rural revitalization strategy" puts forward new requirements for rural development and rural geography. Therefore, a comprehensive and systematic understanding of rural space system and accurate depiction of rural space are necessary prerequisites for further studies. Existing Chinese research focused more on the material space and to some extent placed less focus on the study of social-cultural space. Using a single material space view is very difficult to understand and interpret a large number of increasingly complex rural geographical problems. Based on a systematic analysis of the thinking on rural space and development in China and abroad, this article points out the deficiency of Chinese rural geographical research about rural society and culture. This article preliminarily expounds the complexity of rural territorial system and argues that the rural space system that is derived from the rural territorial system should not be limited within the range of rural material space but be understood through the multi-dimensional perspective of space. According to the human-environment system theory, this study tried to construct a rural space system that consists of three progressive layers including material space-social space-cultural space and clarify the connotations of every layer and the logical relations between them to fully understand the increasingly complex rural area. This article also highlights the necessity that multi-dimensional rural spatial restructuring should be developed. Based on the construction of multi-dimensional rural space system, forming an overview of the historical process and realistic situation of rural spatial restructuring and predicting the future path of rural development are very important research tasks to carry out in the future. In the end, this article appeals that Chinese geographers should continue to discuss and analyze concepts of rural issues in order to constantly improve our understanding about the changing countryside, and deepen the studies of rural spatial restructuring by using the theories and methods of related subjects from the perspective of multi-dimensional space. Finally, for the comprehensive empirical research of rural geographical issues, Chinese rural geographers should strengthen micro scale studies, actively devote themselves to field study, be observant of rural daily life, and understand the rural society and culture to make up for the deficiency of Chinese rural geographical research about rural society and culture.
演变与重塑: 中国农民生活空间的变迁
Evolution and restructuring: Changes in rural living space in China
欠发达地区农户消费行为空间结构演变特征: 以湖北省黄冈市为例
The evolution of spatial structure of rural households' consuming behaviors in undeveloped rural areas and its influencing factors: A case of Ercheng town in Hubei province
国内村域尺度乡村转型发展与重构的现状述评及展望
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.05.012
[本文引用: 1]

乡村转型发展与重构是解决乡村衰落的重要抓手,乡村振兴是国家破解新时代“三农”问题的重大战略部署。论文通过对现有乡村发展相关文献的梳理与分析,从研究范式、演进过程、机理探析和路径探索等4个方面总结了国内乡村转型发展与重构的研究现状及展望。发现乡村转型发展与重构研究具有多学科交叉的研究视角、多元融合的研究内容、综合多样的研究方法与手段。未来需重视不同类型村域转型发展与重构中乡土文化的研究,加强欠发达区不同类型村域转型发展与重构的实证研究,深化多学科理论与方法的综合研究,优化不同发展模式下乡村转型发展与重构的路径。
Progress of research on the transformation and restructuring of rural development in China
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.05.012
[本文引用: 1]

Transformation and restructuring of rural development is an important starting point to solve the problem of rural decline, and rural revitalization is an important strategic deployment for China to address the "sannong issues" in the new era. This article summarized the progress of research on the transformation and restructuring of rural development from four aspects: research paradigm, evolution process analysis, mechanism analysis, and path exploration. It is found that the research on the transformation and restructuring of rural development took interdisciplinary research perspectives and covered diversified and integrated research contents and used comprehensive and diverse research methods and approaches. In the future, it is necessary to pay attention to the research of local culture in rural development of different villages, strengthen the empirical research on rural development of different villages in the west, innovate the theory and research methods of transformation and restructuring of rural development, and optimize the path of rural transformation and restructuring under different development modes.
中国地理学对乡村发展的多元视角研究及思考
Pluralistic perspectives and thinking of Chinese rural development in geography study
乡村转型发展影响因素及其作用效应的空间分异: 以陕西省为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220808
[本文引用: 1]

以陕西省为例,围绕人口、土地、产业等乡村社会经济发展要素构建乡村转型发展评价指标体系,借助ArcGIS平台分析陕西省乡村转型发展时空格局演化特征;利用逐步回归、地理加权回归模型(GWR模型)对陕西省乡村转型发展影响因素及作用效应的空间分异进行探究,以期为陕西省乡村高质量发展路径设计与政策制订提供参考依据。研究结论如下:(1)2005—2017年间,陕西省乡村转型发展程度呈现持续上升趋势,在空间上整体呈现西安及其周边以及榆林北部能源区发展程度高,其余地区发展程度低的特点,且乡村转型发展经历了低度转型主导到较低、中度转型主导的发展过程。(2)地均固定资产投入、加权路网密度、人均生产总值、规模以上工业企业个数和人均耕地资源量是陕西省乡村转型发展的主要影响因素。(3)影响因素中除人均耕地资源量对乡村转型发展整体呈现负向影响外,其余因素均呈现正向影响,且对不同县域影响程度不同,影响效应的空间分异明显。研究对因地制宜地制定陕西省乡村转型发展的差异化政策措施具有重要的参考意义。
The study on influencing factors of rural transformation development and their spatial differentiation of effects: Take Shaanxi province as an example
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220808 URL [本文引用: 1]
江汉平原农户日常休闲变迁及其影响因素研究
Research on the changes and influencing factors of farm households' daily leisure in Jianghan Plain
江汉平原乡村农户就业变迁及其影响因素研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.12.011
[本文引用: 2]

当代乡村就业变迁是透视乡村人地关系变化的重要视角。论文基于湖北省京山市乡村常住农户抽样调查和实地访谈数据,沿循类型—空间—模式的逻辑主线,通过变化率指数、就业转移矩阵揭示案例地区农户就业变迁特征;同时运用无序多分类Logistic回归模型进行影响因素分析。研究表明:① 2007—2017年乡村农户就业类型已由纯农就业主体演变为兼业就业主导,非农就业增加显著;② 农户就业区位距离衰减特征弱化,村域作为农户就业转移的出发源与回流汇地位突出;③ 村域纯农就业仍是乡村农户就业的主流模式,但就业方式多元化成为农户就业新趋势;④ 农户就业模式选择是农户就业需求、地方就业供给、环境就业媒介多因素综合作用的结果。研究结果能够为中国农区人地关系变化及乡村振兴战略实施提供科学信息。
Change of farming households' employment and influencing factors on the Jianghan Plain
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.12.011
[本文引用: 2]

The change of contemporary Chinese rural employment is an important perspective for understanding the change of rural human-land relationship. In this study, taking the rural households of Jingshan City on the Jianghan Plain as an example, we examined the characteristics of rural households' employment change in the research area through the change rate index and employment transfer matrix. This article described the changing characteristics of employment in three aspects: Employment type, employment space, and employment pattern. A multinomial Logistic regression model was used to analyze the influencing factors of rural households' employment pattern. The results show that: 1) From 2007 to 2017, the employment type of the surveyed rural households evolved from agricultural employment to part-time agricultural employment, with significant increase in non-agricultural employments. 2) Correspondingly, the distance attenuation characteristics of rural households' employment location choice weakened. The role of village as the starting point and returning sink of rural households' employment transfer is still prominent. 3) During the study period, pure agricultural employment in the rural area is still the main type of employment for the surveyed households, but the diversification of employments has become a new trend. 4) The choice of farmers' employment is the result of a combination of factors including farming households' employment demand, local employment opportunities, and environmental factors. Specifically, age of the head of the household, ratio of migrant workers, family dependency ratio, and family employment habits were taken as farming households' employment demand factors; the developing level of township and village development opportunities were taken as local employment opportunity factors; and distance from a village to town centers and regional employment satisfaction, and information and communication system development level were taken as environmental factors in the model. The results may shed some light on the change of human-land relationship and provide a theoretical support for the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy in typical agricultural regions of China.
江汉平原农户日常消费空间演变及影响因素研究
Research on spatial evolution and influencing factors of rural households' daily consumption in Jianghan Plain
经济发达地区乡村地域多功能空间分异及影响因素: 以江苏省为例
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201406007
[本文引用: 1]

随着经济社会发展和土地利用格局变化,乡村地域功能和发展定位的多元化和空间差异特征日益明显。以经济发达的江苏省为例,采用定量化价值评价方法,研究县域尺度乡村地域生态保育、农业生产、工业发展和社会保障功能的空间差异,识别各县市区主导功能类型,揭示不同类型乡村地域功能的影响因素。结果表明:乡村地域多功能特征明显,工业发展功能占据主导;4 类乡村地域功能空间集聚程度均较低,生态保育功能高值区集中于沿湖、沿海或苏南山丘地区,农业生产功能集中于苏北和苏中,工业发展功能以苏南最强,社会保障功能则集中于市辖区及其临近市县;乡村地域功能组合类型多样,共可分为9 种;4 类乡村地域功能的影响因素存在较大差异,自然地理、空间区位、经济社会发展等因素的影响在强度和影响方向上明显不同。研究可为针对性地定位乡村功能和发展导向、增强县域乡村功能特色和竞争力提供参考依据。
Spatial differentiation and influencing factors of rural territorial multifunctions in developed regions: A case study of Jiangsu province
后生产主义乡村多元价值空间重构研究: 基于无锡马山镇的实证分析
Study on the reconstruction of multi-value space in post-productivist countryside: A case study of Mashan town in Wuxi
中国乡村旅游重点村的空间分布与影响因素研究
The spatial distribution and influencing factors of key villages of rural tourism in China
快速城市化背景下乡村绅士化的时空演变特征
DOI:10.11821/xb201208004
[本文引用: 1]

乡村绅士化是指移民从城市迁入乡村地区, 通过对一定的经济资本的利用, 来达到对乡村的自然环境与独特的生活方式及文化氛围的体验与消费的过程。乡村绅士化过程造成了乡村地区人口结构的重构以及物质景观的变迁。本文选取广州小洲村作为研究案例, 对乡村绅士化的时空特征及其演变过程进行了深入分析。研究发现, 小洲村乡村绅士化过程分为艺术先锋绅士化及学生化两个阶段。由于空间需求、付租能力、群体数量等方面的差异, 两类绅士化过程对当地的物质环境、文化、社会、经济等方面产生了不同的影响。但两者的发展紧密相连, 在时间和空间上经历了延续、重叠、更替等阶段。乡村绅士化的过程, 在一定程度上缓解了乡村社区经济发展的困境, 也没有造成对本地居民的置换。但是随着社区住房成本的上涨, 先期迁入的艺术家群体正在被付租能力更强的学生群体逐渐替换。值得注意的是, 本地村民通过积极的寻租行为成为乡村绅士化的重要推动者, 而非被置换者。研究发现, 乡村绅士化现象的中西方差异主要体现在4 个方面:经济和物质层面的影响、与城市化的关系、人口置换的后果、绅士化的推动者。这些差异主要与乡村绅士化发展的社会经济背景、机制和特殊的土地政策等密切相关。这一研究对于探讨转型期中国乡村绅士化现象的特征与机制以及乡村社区发展的模式具有重要的理论与现实意义。
Spatial-temporal evolution of rural gentrification amidst rapid urbanization: A case study of Xiaozhou village
乡村绅士化进程中旅游型村落生活空间重塑特征研究: 以北京爨底下村为例
The characteristics of the life space remodeling of tourism village during rural gentrification: The case of Cuandixia in Beijing
多重资本驱动下西安市秦岭北麓S村的空间生产与收缩: 基于布尔迪厄理论的管窥
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211010
[本文引用: 1]

引入布尔迪厄的资本理论,构建多重资本概念模型;以西安市秦岭北麓S村为例,对其在不同类型资本综合影响下的空间生产与收缩过程及机制进行质性研究和可视化分析。结果表明:(1)经济资本的三级循环推动S村物质空间商品化程度不断加深,商户金融资本的差异造成村内经济阶层分化与空间分异,外来经济资本的进入则易诱致社会风险。(2)新生的业缘关系与亲缘、地缘关系交织而成的社会网络等结构性社会资本的变化,引致S村社会空间的混杂和地方认同的分化;社会信任等认知性社会资本的下降造成村民交往空间的内移,并促成新的空间治理秩序。(3)商户个人品味等身体化文化资本创造出多样化的文化空间,政府赋予村庄的集体称号等制度化文化资本推动形成农家乐专业村品牌。(4)元资本主导下,村内三大旅游项目被拆除,S村由空间持续再生产转向空间收缩。(5)自然垄断地租、小规模集体行动优势、元资本的间接调控与直接影响以及双重锁定效应,共同构成S村空间生产与收缩的机制。
Space production and shrinkage of S village at the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains in Xi'an driven by multiple capitals: Based on Bourdieu's theory
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211010 URL [本文引用: 1]
农村居民点用地的多功能性划分及其农户利用差异性评价
Multifunction compartmentalization of rural settlement land use and its peasant household utilization difference evaluation
城乡融合区乡村地域多功能空间分异及影响因素: 以福州东部片区为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20221015
[本文引用: 1]

乡村地域多功能是有效破解城乡二元结构、促进城乡融合发展的重要途径。本文以国家城乡融合发展试验区——福州东部片区为研究区,基于乡镇域尺度分析研究区乡村地域多功能空间分异规律与特征,使用地理探测器分析空间分异的影响因素。结果表明:(1)研究区各乡镇的乡村单一功能空间格局特征表现为农业生产功能在沿海小范围聚集,工业发展和生活保障功能主要集中分布在福州城区边缘郊区和南部乡镇,生态保育功能西部山区大于东部乡镇,而旅游休闲功能主要分布在中北部乡镇和平潭岛;(2)依据LSE模型,将研究区乡镇划分为五功能、四功能、三功能、双功能复合区和单功能主导区,其中拥有五、四功能复合区的乡镇共计58个,占比45.68%,说明研究区乡村地域多功能整体上处于较高水平,城乡融合发展基础良好;(3)乡村地域多功能的空间分异受自然环境、社会经济等内外因素的共同影响,自然环境因素塑造了乡村地域初始与特色功能,地理区位因素促进乡村功能的形成与分化,社会经济是优化乡村功能的基础因素,政策资金是推动乡村多功能转型的主导因素。研究结果为进一步推进区域城乡融合发展与乡村振兴提供科学依据。
Spatial differentiation and influencing factors of rural territorial multi-functions in urban-rural integration area: A case study of Eastern Fuzhou
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20221015 URL [本文引用: 1]
Talking about rurality: Social representations of the rural as expressed by residents of six English parishes
西方乡村性研究进展
Progress in western rurality research in China
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002847
[本文引用: 1]

Rurality is the core concept of Western multi-disciplinary rural studies, especially rural geography. The combination and conflict among rural sociology, agrarian political economy, rural geography saw the diversity and abundance of rurality topics. The evolution of academic trends in social science and the transformation of rural society respectively in the terms of theory and practice pushed the development of rurality studies. In popular discourse, rurality simply represents different features, which distinguish the rural from the urban, like lifestyle, economy structure, land use and so on. The ways of ‘knowing’ rurality are under the constantly fluid condition: from the ontology of rurality and the macro social economic structures at the early stage to the existence of rural ‘others’ finally to the hybrid complexity of modernized rurality. With the deepening of rurality studies, a series of hot topics came into being one after another: rurality index, discourse of rurality, social difference, daily performance. Though approaches to rurality are various, the power relations and social differentiation rather than the social spatial features became main research directions with the influence of cultural turn and rocketing-up of post-modernism in rural studies. In another word, against the background of the multi rural interests, the representation and reproduction of rurality rather than ‘objective’ rural index have a great importance to understand the representative and material production and reproduction of rurality and politics of rural change under the context of modern capitalism. This review, based on social and academic background of rurality studies, focuses on the social construction of rurality and its burgeoning trends in Chinese rurality studies. The social constructionist treats rurality as the process and product of social, cultural construction not the existed reality, stresses on power relations and otherness. The transition from the former approaches to the social constructionist could be viewed as the transformation from materiality of rurality to its representation, from the rurality itself and macro structural dynamics to the ‘knowing’ means of rurality. The present China rurality study focuses on rurality index and its quantitative models, the concerned researches contain important practical meanings for governmental departments to understand rural problems and make the reasonable solutions for rural planning and rural regeneration. In western rural studies, due to its indication of linear development view and lack of interpretive potential for rural change, rurality index is criticized greatly. In nowadays rural China, the modernization discourse of rural development dominates, while the unequal power relations and ‘othering’ of disadvantaged peasants are overlooked at some degree. Under such social, academic context, social construction of rurality could provide alternative and critical lens to deconstruct dominant discourses of rurality and discover power relations and interest conflict among different social groups.
广州市城郊典型乡村空间分化过程及机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908010
[本文引用: 1]

全球生产方式变革和社会制度改革加速了城市化进程,城乡要素流动加快了城郊乡村空间分化,以空间生产和博弈论为理论基础,针对广州市城郊北村的空间分化过程及机制进行解析,以期丰富乡村空间分化和治理的理论。结果表明:① 20世纪80年代以来,北村的发展经历了农业发展、工业发展和服务业发展等3个阶段,业态结构从单一的农业逐渐转向为多元,兼有农业去中心化向农村社区化发展转变过程。② 伴随村域经济发展转型,北村土地利用类型和结构趋向多元分化,各类用地空间关系变得更加复杂化,呈现出商住混合和工商混合的用地新特征,空间上逐渐形成“公共服务设施—传统居住区和现代居住区—商业区—农业区和工业区”的圈层式布局模式。③ 乡村物质空间的多元分化动力主要源于新产业介入和主导产业的更替转变。内生的土地流转方式和外生的城市资本共同推动乡村工业化进程,市场力推动了产业发展向服务业转型。④ 乡村工业化驱动了村社组织对历史建筑功能的置换,改变了乡村以宗族血缘和地缘为主的社会关系,产生了由外来务工人员和城市低收入阶层组成的业缘关系,乡村社会关系逐渐多元化。⑤ 城郊乡村空间多元分化遵循着资本和土地利益博弈逻辑。本地村民、代耕农民、经济合作社、工业经营主体和服务业经营主体等行为主体对空间进行争夺和利益博弈,村社组织起着关键的中介作用。
Spatial differentiation and mechanisms of typical rural areas in the suburbs of a metropolis: A case study of Beicun village, Baiyun district, Guangzhou
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908010
[本文引用: 1]

The reforms of global production modes and social systems have accelerated the process of urbanization, and the urban-rural flow speeds up spatial differentiation in the rural suburbs. Based on spatial production theory and game theory, this paper analyzes the spatial differentiation and its influence mechanism in Beicun in the suburbs of Guangzhou. The results are as follows: (1) Since the 1980s, Beicun has experienced three stages: agricultural development, industrial development, and service industry development. The industry has changed from single to diversified, and the transformation from agricultural decentralization to rural community has been realized. (2) In the transformation of rural economic development, the land use type and structure of Beicun tended to be diversified, and the spatial relationship of various types of land use was complicated, emerging in new characteristics of land for mixed commercial and residential use, and mixed industrial and commercial use, gradually forming a circle-type spatial layout structure model of "public service facilities-traditional and modern residential areas-commercial areas-agricultural and industrial areas". (3)The diversification of the rural material space was mainly due to the intervention of new industries and the transformation of leading industries. Both endogenous land-transferring mechanisms and exogenous urban capital promoted the industrialization process, and market power promoted the transformation of manufacturing industry into a service industry. (4) The industrialization process promoted the functional replacement of historical buildings by village organizations; changed the social relationship of the village to the blood clan and made it more geographically oriented; and produced an occupational relationship between migrant workers and urban low-income groups. (5) The multi-differentiation of suburban rural space followed the game logic of capital and land interests. The rural community played a key mediation role in the competition for space and in the game interests among local villagers, farmers, cooperative economy, industrial operators, and service owners.
收缩乡村的空废成因与精明收缩规划策略: 基于豫东典型乡村的田野调查
Vacant mechanism and smart shrinkage strategies for shrinking village: Based on field studies in rural areas of Eastern Henan
论乡村数字化与乡村空间转型
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202302012
[本文引用: 1]

数字技术向乡村地域的延伸与渗透深刻影响着乡村经济、社会和政治的组织方式与结构,推动城乡发展网络化视域下乡村地域系统的转型与重组。本文在界定乡村数字化概念内涵的基础上,探讨了乡村数字化与乡村空间转型的耦合关系,深度剖析了乡村数字化与乡村空间转型的作用机制,并构建面向乡村数字化发展转型的研究内容体系。主要结论为:① 乡村数字化是伴随数字技术广泛应用于广大乡村地域,重塑乡村物质环境、经济形态、社会网络及空间组织的过程,促使乡村经济社会形态和空间组织结构发生数字化转型,包括数字技术作用于乡村地域空间的过程、作用和效应等。② 乡村数字化背景下乡村空间转型趋于综合复杂,物质、经济、社会和文化等多重空间叠合转型,并在数字信息连通下衍生出赛博空间及网络文化形态。③ 数字基础设施建设与乡村物质空间转型的逻辑、数字经济发展与乡村经济形态转变的机制、数字技术应用与乡村社会空间重组的关系、数字治理模式与乡村空间组织重构的作用共同构成乡村数字化与乡村空间转型的多维内嵌机制。④ 在城乡融合发展与乡村振兴的重大战略指向下,在强化学科贡献的基础上探寻数字化下乡村发展前沿领域与创新维度,聚焦智慧乡村应用场景、研制乡村规划建设体系与工程技术标准和规范,服务于乡村可持续发展、信息化和现代化发展转型。
Rural digitalization and rural spatial transformation
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202302012
[本文引用: 1]

The extension and penetration of digital technology into rural areas profoundly affects the organization and structure of rural economy, society and politics, and promotes the transformation and reorganization of rural territorial system from the perspective of urban-rural development network. Based on defining the concept of rural digitalization, this paper discusses the coupling relationship between rural digitalization and rural spatial transformation, deeply analyzes the mechanism of rural digitalization and rural spatial transformation, and builds a research framework for rural digitalization development and transformation. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) Rural digitalization is a process of reshaping the physical environment, economic form, social network and spatial organization of rural areas with the wide application of digital technology in vast rural areas. It promotes the digital transformation of rural economic and social forms and spatial organizational structure, including the process, role and effect of digital technology on rural regional space. (2) Under the background of rural digitalization, the transformation of rural space tends to be comprehensive and complex, and multiple spaces such as material, economy, society and culture are superimposed and transformed, and cyberspace and network culture forms are derived under the connection of digital information. (3) The multi-dimensional embedded mechanism of rural digitalization and rural spatial transformation includes the logic of digital infrastructure construction and rural physical environment transformation, the mechanism of digital economic development and rural economic transformation, the relationship between digital technology application and rural social network restructuring, digital governance models and the role of rural spatial organization reconstruction. (4) Under the major strategic direction of urban-rural integrated development and rural revitalization, future research needs to explore frontier fields and innovative dimensions of rural development based on digitalization for strengthening disciplinary contributions. It includes focusing on smart rural application scenarios, developing rural planning and construction systems and engineering technical specifications, and serving the rural sustainable development, informatization and modernization of rural development.
空间治理背景下乡村发展路径的转型与创新
Transformation and innovation of rural development path under the background of spatial governance
乡村自主性空间治理: 一个综合分析框架
Autonomous rural spatial governance: A comprehensive analysis framework
Engaging the global countryside: Globalization, hybridity and the reconstitution of rural place
DOI:10.1177/0309132507079503
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This article applies Massey's (2005) call for a relational understanding of space that can challenge aspatial readings of globalization to the study of globalization in a rural context. Critiquing existing rural research for tending towards studies of global commodity chains and overarching processes of globalization, it argues for more place-based studies of globalization as experienced in rural localities. The concept of the `global countryside' is introduced as a hypothetical space that represents the ultimate outcome of globalizing processes, yet it is noted that the characteristics of the `global countryside' find only partial articulation in particular rural spaces. Understanding this differentiated geography of rural globalization, it is argued, requires a closer understanding of how globalization remakes rural places, for which Massey's thesis provides a guide. The article thus examines the reconstitution of rural places under globalization, highlighting the interaction of local and global actors, and of human and non-human actants, to produce new hybrid forms and relations. As such, it is argued, the politics of globalization cannot be reduced to domination or subordination, but are instead a politics of negotiation and configuration.
Rural geography: Blurring boundaries and making connections
DOI:10.1177/0309132508105001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

A number of commentaries and articles have been published in recent years reflecting on the nature, history and practice of rural geography. The introspective mood follows a period in which rural geography has been widely considered to have been resurgent, but indicates concerns about the unevenness of progress in rural geography, and about the readiness of the subdiscipline to address new challenges. This article, the first of three progress reports on rural geography, focuses on attempts within these interventions to rethink the boundaries of rural geography and its connections with other fields of study. First, it examines renewed debates on the definition and delimitation of the rural, including efforts to rematerialize the rural. Second, it considers the rejuvenation of work on rural—urban linkages, including concepts of city regions, exurbanization and rurbanity. Third, it discusses the interdisciplinary engagement of rural geographers, including collaboration with physical and natural scientists.
西方国家乡村空间转型研究及其启示
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.08.003
[本文引用: 3]

西方国家对乡村空间的认识经历物质、意象再到三元综合体的深化,后者作为西方学界理解乡村空间的系统性理论框架,为研究从生产主义到后生产主义的转型过程提供全新视角。西方国家的乡村分化表明,乡村空间转型的功能与价值重塑,在全球乡村视角下有一般规律性,对中国乡村空间转型研究有重要启示。当前中国正处于城乡空间加速重构的关键时期,加强乡村空间及其转型在多维度认知、多功能趋势和多主体机制等方面的研究,形成具有中国特色的乡村地理学研究范式,响应乡村振兴的时代主题。
Rural space transition in western countries and its inspiration
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.08.003
[本文引用: 3]

Recognition of rural space in western countries has undergone a profound turn from material and ideational space to the three-fold model of rural space proposed by Halfacree. Fundamentally influenced by “the production of space” and widely accepted as the systematic theoretical framework of rural space in western world, this model provides a whole new perspective on the transition of rural space in western countries from productivism to post-productivism. Differentiated rural space in western countries manifest that affected by interwoven forces of globalization, urbanization and modernization, dynamics and patterns of rural space transition development has been regenerated by combination and reorganization of essential productive factors, as well as its functions and values. Process of rural space transition in western countries reflects general rules in the view of “global countryside” proposed by Woods, which offers a great and significant enlightenment for studies in China. Based on the situation that urban and rural space is going through a critical period of accelerated reconstruction, theoretical guidance is urgently needed for newly emerging problems, patterns and forces, especially more studies on multi-dimensional cognition, multi-functional trend and multi-agent mechanism of rural space and its transition. In the end, this paper calls for establishing research paradigm of rural geography with Chinese characteristics, so as to better respond to the theme of the times on rural revitalization
国际农村空间多元化研究的知识图谱分析
International rural space diversification based on knowledge mapping analysis using CiteSpace
Trial by space for a 'radical rural': Introducing alternative localities, representations and lives
DOI:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2006.10.002 URL [本文引用: 2]
空间生产视角下的城中村物质空间与社会变迁: 南京市江东村的实证研究
The physical space change and social variation in urban village from the perspective of space production: A case study of Jiangdong village in Nanjing
旅游影响下传统社区空间变迁的理论探讨: 基于空间生产理论的反思
Traditional community space change under the influence of tourism: A reflective study based on space production theory
乡村旅游社区可持续发展研究: 基于空间生产理论三元辩证法视角的分析
Sustainable development of rural tourism community: Based on the analysis from the perspective of ternary dialectics on production of space
基于空间三元辩证法的迁村并点型乡村公共空间生产研究: 以西安地区石砭峪新村为例
Study on the rural public space production research of the relocation and combination-oriented rural based on spatial trialetics: A case study of Shibianyu village in Xi'an area
理性、流动与家庭: 村民日常生活语境下的乡村性转型
Rationality, mobility and family: Transformation of rurality in villagers' daily lives
乡村生活空间网络结构特征与优化: 以江汉平原典型乡建片区为例
Structural characteristics and optimization strategies of the rural living space network: A case study of typical rural construction area in Jianghan Plain
乡村地域多功能的内涵及其政策启示
Connotations of rural regional multifunction and its policy implications in China
A new measure of accessibility based on perceived opportunities
DOI:10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.10.598 URL [本文引用: 1]
Accessibility of rural life space on the Jianghan plain, China: The role of livelihood
This article aims to contribute to the relationship between accessibility of rural life space and rural livelihood capital and transitions in rural central China. Employing data produced from a household survey, we developed a composite index for accessibility of rural life space incorporating spatial and temporal attributes of a household’s daily activities and then explored the mediation effect of rural livelihood capital and transitions on accessibility. Results revealed a pattern of diversification in terms of life space accessibility undertaken for daily activities across households. Both livelihood capital and transitions had significant mediation effects on the relationship between socio-economic characteristics of rural households and accessibility of rural life space. The effects of livelihood capital on livelihood transitions also influenced the path on rural households’ accessibility of rural life space. One of the implications of this article is to link rural transformation to the context of urbanization and rural access issues from a perspective of daily activity, and then to figure out the best method for rural development policy and service planning.
Motility: Mobility as capital
DOI:10.1111/ijur.2004.28.issue-4 URL [本文引用: 1]
Changing patterns of rural life space: A perspective of mobilities
DOI:10.1080/17450101.2022.2071631 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于力学平衡模型的长三角港口物流发展协调性研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.11.003
[本文引用: 1]

基于港口物流协调发展理论分析框架,构建相应的综合评价指标体系和协调性判别模型,对长三角13个港口物流发展协调性进行综合评判。结果表明:长三角已形成较为明显的以上海港为核心,宁波-舟山港、苏州港和南京港为副中心,其余港口为重要补充的多层次港口物流规模等级结构;港口物流协调发展层次总体偏低,以低水平协调型为主,且港口物流发展协调度与综合发展度间存在紧密联系,呈现明显的“U”型曲线特征;港口物流协调发展偏离方向集中化特征不明显,制约不同港口物流协调发展的主要因素存在较大区别,同时就物流运营发展滞后型、城市支撑发展滞后型和基础设施发展滞后型港口分别提出改进方向。
Coordination of port logistics development based on mechanical model: A case of the Yangtze River Delta port system
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.11.003
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the idea of systems theory, one new theoretical analytical framework for port logistics coordinated development is proposed by the authors. The framework consists of three subsystems, including port infrastructure, logistics operation, and city support. On the basis of it, one comprehensive index system of port logistics coordinated development is established in this research. It contains 3 second grade indexes and 14 third grade indexes. This article abstracts the coupling relationship, between the three subsystems, into vector relation of three forces with different direction in Cartesian coordinate system. Then, the authors construct the coupling coordination discriminate model of port logistics development, by combing the comprehensive evaluation index system with the mechanical model. Furthermore, by using the natural and social economic statistic data from 13 container ports in the Yangtze River Delta in 2013, the comprehensive development level, the coordinated development state and the main restrictive factors of port logistics development are estimated and quantified. The results show that: 1) There are some significant differences in the comprehensive development degree of port logistics among the Yangtze River Delta port system, and it has formed a multi-level port logistics hierarchical structure. Shanghai is the center, Ningbo-Zhoushan, Suzhou and Nanjing are the sub-centers, and the rest of the ports is the supplement. 2) There are some obvious differences in the coordination degree of port logistics in the Yangtze River Delta post system. The overall level of coordination is obviously low. The Yangtze River Delta post system includes five kinds of coordination development types, of which the low-level coordination type is the main types, and it covers 7 ports, accounting for 53.85% of the total ports. In particular, the comprehensive development degree is closely linked with the coordination degree of port logistics, and the relation is in line with the ‘U-shaped’ curve. 3) The concentration characteristic of the deviated direction of the coordination degree is not obvious. The quantity of ports in the lag type of the port infrastructure, logistics operation and city support subsystems is approximately the same. Finally, how to promote the coordinated development of the Yangtze River Delta port logistics has carried on the preliminary discussion.
基于力学平衡模型的耕地多功能演变及其协调性分析: 以珠江三角洲为例
The coordination and evolution of farmland multifunctionality based on a mechanical model: A case study of the Pearl River Delta
大城市郊区乡村转型与重构的典型模式分析: 以天津东丽区华明镇为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180976
[本文引用: 1]

城市和乡村是连续统一体,乡村地域系统在城市化和工业化的带动下不断发生着转型与重构。探索乡村转型发展路径,总结成功经验模式,对促进乡村可持续发展乃至实现乡村振兴具有重要意义。城市郊区地处城乡交错带,相比农村腹地,乡村转型具有独特优势。本研究以华明镇为例,详细阐述了以城镇化整理路径实现乡村转型发展的典型模式。研究发现,华明镇乡村转型以“三整合”为标志,通过实施宅基地换房,建设现代农业产业园和工业园区,改革集体经济,创新金融服务,整合社区服务组织,实现了生产要素的优化配置,促进了村庄“人-地-业”协调发展。但是,以城镇化整理为主导的乡村转型模式,会造成传统乡村聚落的消失,需要强大的财政支持与政策体系支撑,仅适应于非农化水平较高的乡村地区,应审慎对待,不能盲目推进。
Typical model of rural transformation and restructure in suburban areas: A case study of Huaming township in Dongli district, Tianjin city
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180976
[本文引用: 1]

Rural and urban areas are continuous space. Under the influence of urbanization and industrialization, rural areas have been experiencing constant transformation and restructuring. It is important to understand what kind of transition has happened in rural areas and how the rural areas have been changed. Consequently, we need to explore the process of rural transformation and summarize some typical models. In this way, we can provide some successful experience to promote rural transformation and revitalization. Suburban areas are located in the fringe of city and countryside, where the urbanization and rurality are intersected with each other. Compared with the rural hinterland, suburban areas have more advantages to realize rural transformation due to its special position. In order to figure out the process of rural transformation in suburban areas, we take a case study of Huaming Township to clarify its development path to realize urban-rural integration. Our research shows that the rural transformation of Huaming Township could be summarized as “Three Integration Models”, including space restructuring, industrial restructuring and organization restructuring. Firstly, the government purchased the rural construction land and implemented land reclamation, and local villagers moved into relocated buildings with decent compensation. Then the agricultural park and industrial park were constructed to develop facility agriculture and equipment manufacturing industry. In addition, some innovations occurred in the economic sector. For example, the rural collective economy was transformed into stocking system economy, villagers assembled their spare capital and initiated a village bank, so that farmers can acquire more profits and earn more money. The industrial park also abandoned some traditional dirty industry and introduced some advanced environmental industry in order to promote the local industrial structure. As for the social management, the government reformed the household registration system and grassroots organizations, transforming village committee into neighborhood committee and providing the same social insurance for villagers as citizens. Furthermore, the township integrated all law enforcement agencies into one team, so villagers can enjoy more convenient public service. With the adjustment of economic structure and relocation of rural space, Huaming Township has achieved coordinated development. However, this kind of development path like Huaming Township resulted in disappearance of traditional rural settlements, and it also needs strong financial and political foundation. Therefore, the Huaming model is only appropriate for those villages where residents are more inclined to nonagricultural employment and urban lifestyle.
国家重点生态功能区乡村人居环境演变及影响机制: 以湖北省利川市为例
Research on evolution and influential mechanism for rural human settlement in national key ecological function areas: A case of Lichuan
基于结构方程模型的城镇化农民可持续非农生计分析: 以晋西北朔州市为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201411003
[本文引用: 1]

晋西北属于国家级和省级限制开发区,其先天脆弱的自然生态系统导致土地沙漠化、水土流失以及农民贫困问题。2000年后晋西北生态脆弱区农民城镇化现象呈规模性增长趋势,通过形成“城镇化农民生计非农化—农地流转—农地规模经营—农村居民收入提高—生态恢复保护”互动关系链,可以为降低晋西北生态脆弱区土地人口压力和恢复其生态环境开辟新途径,而这条关系链存在的关键则是城镇化农民的可持续非农生计。借鉴国际上应用范围最广的可持续生计SL框架——DFID模型,选取晋西北地区大城市朔州市为实证研究对象,基于结构方程模型定量测定了脆弱性背景—生计资本—生计策略—生计结果相互之间复杂的影响机制。研究表明:① 脆弱性背景对生计策略产生显著的负向影响,且通过影响生计策略间接对生计结果产生负向影响。② 人力资本、物质资本、金融资本均对继续留城务工的生计策略产生正向影响;生计资本中只有物质资本对就业性质有影响力。③ 人力资本对职业层次和娱乐生活丰富度均有显著的正向影响;社会资本对职业层次没有显示出显著影响力,但却对进城务工后的收入增加显示出正向影响力;金融资本对娱乐生活丰富度有显著正向作用力。④ 继续留城务工的生计策略对娱乐生活的丰富度有正向影响,就业性质则对收入增加有正向影响力。
Analysis of sustainable non-agricultural livelihoods of urbanized farmers based on Structural Equation Model: A case study of Shuozhou city in Northwestern Shanxi province
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201411003
[本文引用: 1]

Belonging to restricted development zones at both national and provincial level, northwestern Shanxi province has inherent vulnerability of natural ecosystems which have caused land desertification, water and soil loss, and farmers' poverty. Since 2000, the urbanization of farmers in ecological fragile region of northwestern Shanxi has been growing rapidly. Forming an interaction chain of “transformation from agricultural to non-agricultural livelihoods of urbanized farmers—farmland transfer—scale management of farmland—improvement of rural residents' income—ecological restoration and protection” could provide a new way of reducing population pressure on land and restoring ecological environment in the study area. The key point of this interaction chain is the sustainable non-agricultural livelihoods of urbanized farmers. Using DFID model—a sustainable livelihoods (SL) framework which is the most widely applied all over the world as reference, and taking Shuozhou—a big city in northwestern Shanxi for an empirical study, this paper quantitatively measures the complicated influencing mechanism between vulnerability context, livelihoods capitals, livelihoods strategies, and livelihoods outcomes. The results show that: (1) the vulnerability context has a significant negative impact on livelihoods strategies, and it negatively influences livelihoods outcomes indirectly through livelihoods strategies as well. (2) Human capital, physical capital, and financial capital have a positive impact on livelihoods strategies of non-agricultural labor remaining in the city. In livelihoods capitals, only physical capital has impact on the nature of employment. (3) Human capital has a significant positive impact on both career level and richness of entertainment life. Social capital has not exerted significant impact on career level, but has positive impact on the income increase after the farmers moved into the cities. Financial capital shows a significant positive impact on the richness of entertainment life. (4) The livelihoods strategies of non-agricultural labor remaining in the city have a positive impact on the richness of entertainment life. Besides, the nature of employment displays a positive impact on income increase.
乡村转型发展格局与驱动机制的区域性分析
The spatial disparity of rural transition development and regional characteristics of its driving forces
从本土到全球网络化的人地关系思维范式转型
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110001
[本文引用: 1]

早期地理学关于人地关系的研究多基于本土思维,秉持“一方水土养育一方人”的理念。在严重依赖自然资源的传统农业社会,这一理念及其指导下的区域地理研究和区域管理实践,对于促进人与自然的协调发展起到积极作用。随着系统开放程度的增加,规模不等、层级不同的地域系统形成了一个相互依赖、相互耦合的地理网络。每个地域都是这个网络上的节点,地域问题的产生与解决与网络上其他节点有密切关联、与地域系统内外因素紧密相关,地域外因素有时甚至起主导作用。虚拟水、生态足迹、贸易隐含碳排放、资源纽带关系及人地关系远程耦合等概念和方法的提出,标志着人地关系研究范式从本土思维向全球网络化思维转型。依照新的理念和研究范式,传统的本土思维范式及建立在此范式上的相关研究主题(如区域承载力)应该受到重新审视。
Paradigm transformation in the study of man-land relations: From local thinking to global network thinking modes
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110001
[本文引用: 1]

The early studies on the relationships between man and land in geography mostly focused on local regions and held the idea that "the land and water resources in a region feed the person in the region". In the traditional agricultural society, which relies heavily on natural resources, the idea, and regional geographic research and management practice under its guidance play a positive role in promoting the development between man and nature, and sustainable resource use. With the continuous increase in openness of man and land system resulted from development of science and technology and transport improvement, regional systems on different scales and at different economic development levels have formed an interdependent and coupled geographic network. Every region becomes a node in this network, and the formation and solution of regional problems are closely related to other nodes in the network, and are related to internal and external factors of the regional system. In some cases, external factors even play a more important role. The introduction of some concepts and methods marks the paradigm transformation of man-land relationship research from local thinking paradigm to global networked thinking paradigm, such as virtual water, ecological footprint, carbon emissions due to goods trade, resource link and tele-coupling of man-land relationship. This study discusses the paradigm transformation from three aspects: the evolution characteristics of man-land system, the changes of thinking paradigm and study methods in man-land relationships, and the realization paths and practical significances of the transformation of thinking paradigm in man-land relationship research. According to new ideas and thinking paradigms, traditional local thinking modes and related research themes such as regional carrying capacity can not fully express the new characteristics of man-land relationships. At present, studies related to regional carrying capacity have become an important issue in land use planning and urban planning in China. In the development of land use planning at different levels, "evaluation of resource and environmental carrying capacity" has become the premise and basis of planning. In the implementation of this concept, we usually simply uses population size as the control index. In the context of an increasingly open system, studies in the carrying capacity of resources and environment may be re-examined. This is especially necessary in smaller scale regional systems (e.g., at a county level).
中国区域农村发展动力机制及其发展模式
Dynamic mechanism and models of regional rural development in China
DOI:10.11821/xb200802001
[本文引用: 1]

The agriculture, rural and farmer development are the principal and radical problems in the recent economic and social process in China. Nowadays, aiming at building a moderately prosperous society in all respects and modernizing the country, the project of new socialist countryside construction was advanced at the Fifth Plenary Session of the 16th Central Committee of the Party, which means advanced production, improved livelihood, a civilized social atmosphere, clean and tidy villages and efficient management. Though many researches have been conducted on the new socialist countryside construction and given some suggestions, there have been relatively few studies on the research of rural development theory. It is an original approach to the analysis of the elements and configuration of the whole rural development system to provide theoretical basis for choosing rural development models based on the view of system theory. The results are as the follows: (1) The regional system is a urban-rural integration, so it is very necessary to study rural development problem in the general framework of the whole regional system. (2) Regional rural development system is a complicated synthesis, including regional rural development core system and regional rural development exterior system. The former is composed of rural natural system, rural economic system, rural social system and rural ecological system, and the latter consists of regional development policies, international trade circumstance, etc. The essence of rural development is the process of mutual coupling and coordination of the two sub-systems. (3) The regional rural comprehensive ability lies on two aspects including the rural development inner ability and the exterior drive of urbanization and industrialization. The interaction mechanism obeys parallelogram principle in physics. The evolvement characteristics of rural development system are different in the different combinations of the inner and exterior driving forces. (4) According to the difference of rural development driving forces, rural development models are classified into two types, namely the dominant type of rural self-development and the dominant type of the exterior drive of industrialization and urbanization, and six sub-types at the second level, which are industry driving, villages and towns construction driving, labor force transfer driving, characteristic industry driving, eco-tourism development and specialized market organization driving. In conclusion, it is a scientific approach to the exploration of regional rural sustainable development models, based on the analysis of elements, construction, and function of regional rural development system and characteristics.
地域主体功能导向的江汉平原乡村发展能力时空变化
Spatio-temporal evolution of rural development capacity of Jianghan Plain from the perspective of regional major function
中国重点农区乡村地域功能演变及其影响机理: 以江汉平原为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.01.006
[本文引用: 1]

乡村振兴战略的实施亟需提炼不同乡村地域类型的发展路径。论文构建了乡村地域生产、生活、生态功能测度指标体系,刻画江汉平原乡村地域功能演化特征;基于空间计量模型探析了江汉平原乡村地域功能演变的影响因素及作用机理。研究结果发现:① 江汉平原各县域乡村地域功能指数均呈现出不同程度的增长趋势,生产、生活、生态功能指数分别增长78.26%、34.25%、9.68%;生产功能增长主导和生活功能增长主导是乡村地域综合功能提升的主要类型。② 江汉平原乡村地域功能存在显著的空间非均衡分布格局,生态功能主导型县域主要分布于北部边缘地区,生活功能主导型县域集中分布于中部和南部地区,生产功能主导型县域分布相对零散;生态功能和生活功能主导江汉平原乡村地域功能的空间变化。③ 外源驱动对江汉平原乡村地域功能变化主要表现为负向作用,内生响应主要表现为正向作用;乡村生产功能受外源驱动和内生响应的影响程度最高,乡村地域综合功能被影响程度次于乡村生产和生活功能;乡村地域综合功能和生产、生活功能具有正向的空间溢出效应。探寻农产品主产区乡村地域功能演变的影响因素及作用机理,有助于识别差异化的乡村发展路径,为乡村振兴战略实施提供参考依据。
Change and mechanism of influence of rural territorial functions in major agricultural areas of China: A case study of the Jianghan Plain
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.01.006
[本文引用: 1]

The identification of rural territorial functions of major agricultural areas can provide an important support for rural revitalization and food security. The Jianghan Plain is one of the main agricultural areas in China and is undergoing a rapid rural transformation and reconstruction. From the perspective of ecological, production, and living spaces, this study constructed an indicator system for the assessment of production, living, and ecological functions of rural areas. Using the entropy weight method to determine the weights of indicators, we examined the pattern of change of rural territorial functions in the rural areas of the Jianghan Plain from 2000 to 2015. The influencing mechanism of change was analyzed by applying spatial econometric models. The results show that: 1) The total index value of rural territorial functions of the rural area in the Jianghan Plain increased notably. Values of the three sub-index of production, living, and ecological functions increased by 78.26%, 34.25%, and 9.69%. Growths in the production function and living function were the two main ways of rural function improvement in the Jianghan Plain. 2) The rural function index values of the Jianghan Plain showed prominent spatial differentiation, with an overall east-west divide. Specifically, counties dominated by ecological function mostly aggregated on the northern fringe of the Jianghan Plain, while those dominated by living function aggregated on the central and southern part of the Jianghan Plain, and those dominated by production function showed a random spatial distribution. Ecological function and living function played a major part in the change of rural functions in the Jianghan Plain. 3) We argue that the factors that affect rural development can be divided into two types, namely exogenous driving forces and endogenous responses. The results of the spatial econometric models indicate that both types have an impact on the change in rural territorial functions in the Jianghan Plain. More specifically, the exogenous factors showed a positive influence on the change of rural function in the Jianghan Plain, while the endogenous factors showed a negative effect. The greatest impacts of both the exogenous and the endogenous factors were on production function, followed by living function and total function. The marketization response had spatial spillover effects on the change of rural territorial functions of the Jianghan Plain. Our findings indicate that developing multifunctional agriculture in the Jianghan Plain is a rational choice. In practice, exploring change and influencing mechanism of rural territorial functions for major agricultural areas, on the one hand will be helpful for identifying different patterns of rural development and providing guidance for the implementation of rural revitalization. On the other hand, research on functional types of rural areas could have a broad impact on rural development and urban and rural coordination. Due to the differences in major territorial functions and external conditions, we suggest that the applicability of the evaluation index system and influencing mechanism should vary along with the territorial types.
从“地方空间”“流动空间”到“行动者网络空间”: ANT视角
"Space of places", "space of flows" and "space of actor-networks": From the perspective of ANT.
基于行动者网络理论的逢简村传统村落空间转型机制解析
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.11.009
[本文引用: 1]

基于行动者网络理论,对顺德区杏坛镇“逢简水乡”的空间重构过程与机制进行分析。结果表明:① 逢简村的空间转型过程分为旅游型美丽乡村的建设和运营2个阶段。② 美丽乡村建设阶段是以地方政府为关键行动者,形成了以权力为核心的自上而下征召的行动者网络,实现了乡村环境的综合整治,为运营阶段做准备。③ 运营阶段的行动者网络发生了转变,村集体、村民和其他下层行动者逐渐拥有更多的话语权,强化村民自治经营能力,增加了村内的公共空间建设并推进功能性空间的转化,进入了社区营造和经营阶段。④ 乡村转型发展的过程中,行动者网络的结构处于时时动态调整的状态,乡村空间转型与重组呈现出一个持续的过程。随着关键行动者目的转变、社区营造机制的引入(征召方式的改变),网络中的行动者角色发生变化,促成行动者网络转变,进而对乡村空间转型与重构产生作用。
Mechanism of rural space transformation in Fengjian acient village of Shunde district, Foshan based on the actor network
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.11.009
[本文引用: 1]

With China’s rural transformation development, the rural space is facing a significant reconstruction. This article analyzes the process and mechanism of spatial reconstruction of "Fengjian" in Xingtan Town, Shunde District, Foshan City by using the theory of actor network. The results shown that this village had experienced two stages: the construction phase of the tourism-type beautiful countryside and the operation phase of cultural tourism-type village. With the local government acting as the key actor, the actor network of the construction is authority-based and realized the reconstruction of the ecology, living and production space. The operation phase of the network has changed, with the village committee, villagers and other lower-level actors gradually gaining more right to speak, which increased the public space and promoted the transformation of functional space. The mechanism of the actor's network transformation is mainly due to the change of the key actor's purpose, the adoption of the community empowerment (changing the way of enrolment), and the change of the actor's role in the network. As the actor network is in a dynamic process, rural spatial reconstruction is also a continuous process. The reconstruction of the rural space caused the dissolution of rurality. But under protection of the government and the villagers with high awareness of the reserving rural nature, a good demonstration of balancing the villagers’ interest and rurality was present.
行动者网络理论与农村空间商品化: 以北京市麻峪房村乡村旅游为例
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201708006
[本文引用: 1]

乡村旅游作为农村空间商品化的表现形式之一,在增加农民收入、阻止农村衰退、振兴农村经济方面发挥着重要作用。为此本文以北京市昌平区麻峪房村的乡村旅游为例,借助行动者网络理论分析农村空间商品化的形成与演变,并讨论农户在此过程中的参与。麻峪房村在从农民生活空间转变为城市居民消费空间的过程中,形成了以区旅游局、乡旅游公司为关键行动者,并吸纳了多个人类和非人类行动者所构成的行动者网络。在网络形成的过程中农户参与乡村旅游的程度逐渐提高,由此推动了麻峪房村农村空间商品化的发展。麻峪房村演变为城市居民消费空间后,由于行动者网络发生变化使农村空间商品化发生变化,导致麻峪房村农村空间商品化程度降低。同时新的行动者网络中的各行动者的不对等性明显,各行动者之间存在很多异议,使该网络趋于僵化、丧失活力,不足以支撑麻峪房村乡村旅游继续发展。在麻峪房村农村空间商品化的形成过程中,农户的院落区位、年龄与原有工作等对农户参与乡村旅游的意愿产生不同的影响。当农村地区行动者网络中的关键行动者与行动者利益共通且紧密联系时,其空间商品化就得到强化,反之亦然。
Actor network theory and commodification in rural space: A case study of Mayufang village in Beijing
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201708006
[本文引用: 1]

Along with the development of facility agriculture, horticultural agriculture and leisure agriculture, nowadays, the functions of agricultural production in rural areas have been weakened but the functions of consumption have been increased in Beijing. This shows that the commodification of rural space in Beijing has been developed in recent years. Rural tourism, as one of the important forms of the commodification of rural space, has played an important role in increasing farmers' income, preventing rural decline and revitalizing rural economy. Therefore, this paper selects rural tourism as the representative of the commodification to examine the formation and evolution of spatial commodification of rural space in Mayufang village as well as to explore farmers' participation in this process based on the actor network theory. In the process of the transformation, the rural areas being the farmers' producing and living spaces have changed to the urban residents' leisure and consumption spaces in Mayufang village and formed a heterogeneous actor-network, in which Tourism Bureau of Changping District and Changling Travel Company and other human actors and non-human actors have played a focal role. Major actors used the policy and the financial support to enroll farmers and other actors by the top-down executive network. Along with development of promotion, training, supervision and infrastructure, some local farmers started to create the physical and non-physical environments for the urban residents' consumption activities. Thus more and more farmers have been engaged in rural tourism, and the commodification of rural spaces in Mayufang village has been developed. As Mayufang village became the consumption space to the urban residents, the commodification of rural space in Mayufang village started its transformation of actor network. However, with the quit of non-human actors, which is Duijiuyu Natural Beauty and reduction of incentives launched by the original major actors, the representative of market has become the focal actor in the new actor network. More and more farmers, who were against the common purpose of the actor network were excluded, quitted the former actor network, thus commodification in rural space in Mayufang village declined. In the process of the formation of commodification of rural space in Mayufang village, the farmers who had the advantages of location, age and profession have much stronger desire to be involved in rural tourism, unemployed farmers prefer to be involved in rural tourism than farmers who make a living on agriculture. The farmers who worked in township enterprises are more willing to participate in rural tourism than self-employed business persons; villagers employed in the government units have less possibility to take part in rural tourism. While commodification of rural space in Mayufang village has declined, farmers began to transfer the labor force to other professions from rural tourism. When interests of major actors are commonly and inextricably linked with actors in actor network in rural areas, its commodification in rural space is strengthened, and vice versa.
面向国土空间规划的乡村空间治理机制与路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106008
[本文引用: 1]

城乡国土空间统一用途管制背景下,乡村空间治理成为国土空间治理体系的重要组成部分。从乡村空间治理的理论内涵出发,构建了乡村空间治理理论分析框架,探讨了乡村空间治理作用于国土空间规划的内在机制和可行路径。结论如下:① 乡村空间治理是以乡村空间为治理对象,通过规划和协商等方式,实现乡村空间用途有效管制,空间权利有序配置,凸显多元主体参与的“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的综合治理过程;② 通过“举措—效能—目标”体系,构建了刚性与弹性结合、物质空间与空间关系交互、空间权属与空间组织叠加的乡村空间“物质—组织—权属”综合治理分析框架;③ 多级尺度互联互通(区域—村域—地块)的乡村空间治理特征有利于完善乡村空间治理体系;④ 乡村空间治理通过多种手段并施、多元主体参与、多重价值共享,完善国土空间规划体系,推进多规融合,细化国土空间用途管制,促进乡村善治和生态治理;⑤ 乡村空间治理通过“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的动员和行动策略,构建新型村庄运营模式和组织机制,为落实实用性村庄规划和乡村振兴战略创造条件。
Rural spatial governance for territorial spatial planning in China: Mechanisms and path
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106008
[本文引用: 1]

Under the background of unified management of urban and rural space, rural spatial governance has become an important part of the spatial governance system. Conducting in-depth theoretical and practical research on rural spatial governance and analyzing the mechanisms and path of rural spatial governance in national spatial planning will be conducive to improving the planning and control system of rural space. Starting from the connotation rural spatial governance, this paper constructs a theoretical analysis framework of rural spatial governance based on the comprehensive perspective of spatial governance, discusses the internal mechanism and feasible paths of rural spatial governance in territorial spatial planning, and then realizes the theoretical and practical research of rural spatial governance. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Rural spatial governance starts from the coordination theory of human-land relations in the rural regional system. Through planning and negotiation, it realizes effective control of rural space usage, and orderly allocation of space rights. Rural spatial governance highlights the comprehensive governance process that combines "top-down" and "bottom-up" participation by multiple subjects. (2) Through the "action-efficiency-target" system, the comprehensive governance analysis framework of "matter-organization-ownership" in rural space provides an effective scheme for the construction of multiple rural spatial governance that combines rigidity and flexibility, interaction between material space and space relationship, and superposition of spatial ownership and spatial organization. (3) The rural spatial governance features of interconnecting various scales (region-village-plot) are conducive to improving the rural spatial governance system. (4) The multiple governance means, participation modes and value-sharing mechanisms of rural spatial governance are conducive to enriching the territorial spatial planning system, promoting the integration of multiple regulations, refining the control of territorial space use, and ensuring good rural governance and ecological governance. (5) Rural spatial governance uses mobilization strategies of "top-down" and "bottom-up", and creates conditions for the implementation of practical village planning and revitalization strategies through the construction of new village operation models and reconstruction of organizational mechanisms.