国土空间生态修复作为提升生态功能、改善生态环境质量的人类活动[1],是缓解人地矛盾、保障人类福祉的重要途径[2,3]。党的“十八大”以来,中国高度重视生态文明建设,实施一系列生态保护修复政策和重大工程,生态保护修复制度体系也日趋完善,国土空间治理能力显著增强。“十四五”规划和2035年远景目标纲要强调,“守住自然生态安全边界,促进自然生态系统质量整体改善”。党的“二十大”报告将“促进人与自然和谐共生”确立为中国式现代化的本质要求,并再次强调“坚持山水林田湖草沙一体化保护和系统治理”,把生态系统的完整性作为生态系统发挥生态功能、实现自然修复的前提条件,对国土空间生态修复的系统性与协调性提出更高要求。
作为具有完整生态结构的自然地理单元,流域包括了河流、湖泊、丘陵、森林、荒漠、农田、城镇等多种生态系统,流域国土空间生态修复理论上具备更高的修复效益[4,5]。流域生态修复起源于河流治理,经历了从河流水质单目标治理到全流域综合修复的发展历程。20世纪中期,欧洲多国为了解决工业污染问题,联合启动莱茵河治理计划,形成了国际河流保护与修复示范经验[6]。21世纪初期,《欧洲水框架指令》(EU Water Framework Directive)将水生态修复的重点从河流转向了完整的流域生态系统,为流域系统修复提供了行动框架[7]。国内流域系统化治理虽然起步较晚,但成果丰硕。自20世纪50年代开始,中国陆续开展七大流域综合规划编制与修订,逐步完善了江河治理体系。2016年,中国全面推行以河长制、湖长制为代表的流域综合管理方案,为提升流域生态环境质量奠定了基础[8]。面向一体化保护需求,中国又进一步作出长江经济带建设、黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展两项宏观战略部署,就统筹流域尺度系统治理做出了重大探索[9]。总体而言,提升生态系统完整性是当前国际社会的共同关注,开展流域生态系统保护修复是其中一项研究热点。综合考虑流域生态保护和经济发展目标,探索流域国土空间保护与修复的规划路径,是对中国国土空间生态修复规划体系的重要补充,也是新时期生态文明建设的重要方向[10,11]。然而,流域国土空间生态修复仍然存在着理论指导科学性不足、实践方案可用性不强等现实问题[12,13],亟需进一步凝练流域生态保护修复的科学认知与规划要点。
因此,本文基于“一个核心—两个维度—三对关系”的基本逻辑梳理流域国土空间生态修复的理论认知,进一步提出定量刻画人水关系、明确时空尺度衔接、开展分区分类治理、强化自然持续保障四大规划要点,以期促进理论指导和规划实践的辩证统一,为新时期国土空间生态质量整体提升提供科学支撑。
1 流域国土空间生态修复理论认知
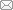
流域国土空间生态修复的对象是由自然生态、社会经济因素共同驱动的复杂开放系统,需要综合运用景观生态学、流域生态学、恢复生态学以及地理学人地关系论等学科观点,对流域内社会—生态要素进行系统梳理与优化配置。深入理解流域系统中的要素关联、过程耦合与空间集成是支撑国土空间生态修复的科学前提[14]。按照“一个核心—两个维度—三对关系”的逻辑主线厘清流域国土空间生态修复的理论内涵(图1):一是以水作为统筹流域山水林田湖草沙全要素的核心,深化对流域生态修复对象的理解;二是从空间与时间两个维度,厘清整体与局部、长期与短期之间的关系,提升流域生态修复的可持续性;三是立足人与自然的关系,协同生态保护与社会发展目标,统筹自然边界与行政界线,协调自然恢复与人工修复共同“做功”,从目标、范围和途径三个层次保障流域国土空间生态修复的系统性。
图1
图1
流域国土空间生态修复理论认知
Fig. 1
Theoretical cognition of watershed-based territorial ecological restoration
1.1 “一个核心”——准确识别以“水”为核心的关键要素
流域一方面面临着水资源短缺、植被退化、土壤流失、自然灾害威胁等生态风险,另一方面也存在着区域发展失衡、产业结构低效等社会经济发展问题。传统的单要素线性治理模式违背了自然发展规律,忽视了生态系统构成要素之间的耦合关联,导致生态保护修复工作难以达到预期的整体效益[18]。因此,流域国土空间生态修复的重点是识别“水”与其他自然生态要素的相互作用关系和动态变化特征,在此基础上构建山水林田湖草沙全自然要素和以“人”为核心的社会经济要素的耦合联系,基于流域水资源生态承载能力优化要素分配,规避生产、生活、生态用水竞争[19],立足生命共同体的高度系统谋划全域全要素综合治理。例如,云南抚仙湖流域山水林田湖系统治理项目,即是利用关键要素“湖”与“水”的生态过程串联山、林、田等要素,根据问题导向和目标指引原则部署生态保护修复工程,满足区域社会、经济、生态可持续发展的需求[20,21]。
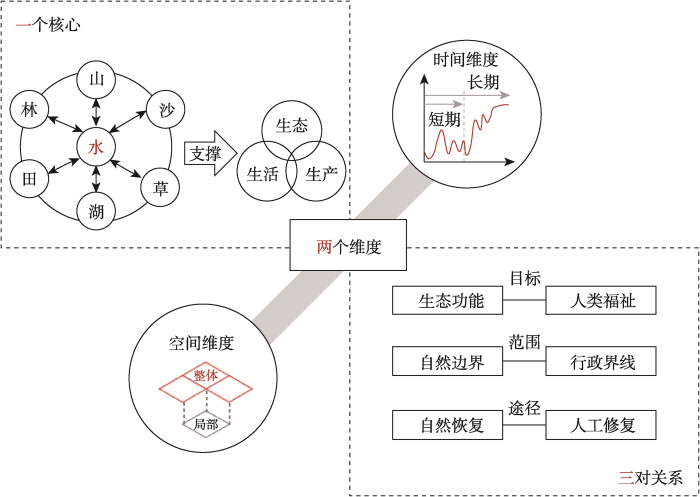
1.2 “两个维度”——深入把握时间和空间两大维度
流域国土空间生态修复是一项长期性、系统性战略目标,需要从时间和空间两个维度出发明确生态保护修复工作的尺度依赖,确保工程措施的稳健有效。
(1)时间尺度重在长短兼顾、动态适应。生态系统兼具复杂性与动态性,伴随着人类活动干扰下的生态系统演替过程,生态系统状态也会相应发生变化,需要根据实际情况对修复方案进行动态调整,确保生态系统质量在长时序范围稳定提升[22]。特别是在气候变化背景下,流域开发保护同时面临陆地储水量失衡与发展用水需求日益增加的双重压力[23]。因此,流域国土空间生态修复需要立足当下,解决流域生态系统核心生态问题(如水源涵养、防洪防灾、水质提升等),通过严格自然保护地监管、退耕还林、河岸带综合整治等措施,为进一步提高生态系统质量奠定基础。面向长期的远景规划,则需要从单一系统优化转向生态网络构建,同时结合生态修复需求的动态变化开展生态修复模式的适应性调整。例如,内蒙古乌梁素海流域初期的主要矛盾是湖区面积急剧减少、生态功能严重退化,后期主要目标则是在提升自然要素协同性的基础上,进一步促进“人、地、业”要素整体优化布局,当地经过分时、分区、分步部署生态修复项目,完成了从保护湖区到保护完整生态系统,从解决生态问题到促进社会—生态协调发展的转型[24,25]。
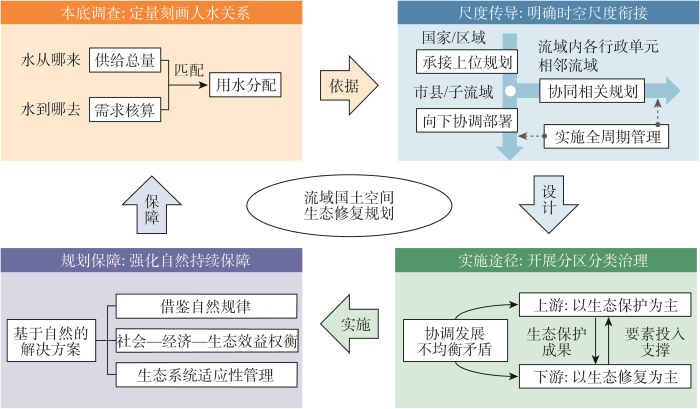
1.3 “三对关系”——从目标、范围、途径三个层次实现人与自然和谐共生
不断加剧的人类活动正在深刻影响着自然生态系统的结构与功能。以人类为主体的社会经济系统与自然生态系统之间的耦合关系越发密切,“社会—生态”复合系统已成为当前生态保护修复的基本视角[28]。流域是人与自然共存的空间载体,开展生态保护修复工作需要在把握生态修复系统性、长期性的基础上,进一步协调好人与自然的关系。
(1)协同生态功能与人类福祉的关系。从国际生态修复的理念发展来看,21世纪以来人们对于“社会—生态”复合系统的关注度显著提升,兼顾人类福祉提升与生态系统健康成为了首要目标,需要在明确各要素相互影响路径和机理的基础上,开展山水林田湖草沙一体化保护修复。流域生态系统涵盖了水循环、养分运移、水沙输移等多个完整的生态过程[29,30],为人类提供了水源涵养、土壤保持、洪水调蓄、产品供给、休闲游憩等多重生态系统服务[31⇓-33],是人类社会保持生产生活稳定的基本保障。生态系统服务与人类福祉存在复杂联系[34],人类福祉的实现过程不可避免会对流域生态过程造成干扰[35],进而导致自然生态系统脆弱性加剧[36],损害生态系统贡献人类福祉的能力。提升生态系统结构与功能的多样性,进而提高生态系统抗干扰能力是保护与修复的直接目标。面向社会—生态复杂系统可持续发展需求,还需要在提高生态环境承载能力的同时转变生产方式与发展理念,积极实现人类福祉与生态功能的双重提升。
(3)协调自然恢复与人工修复的关系。工业文明以来,人类生产力水平(亦即对自然的影响能力)逐渐提升,可以依赖人工技术手段进行生态保护与治理,如水坝、河堤等硬质基础设施能够有效应对洪水灾害,但也带来了河流生境破碎化的风险[41]。以自然恢复为主的生态修复方针是开展流域国土空间生态修复的更优途径,也是正确处理人地关系、人水关系的基础。按照自然恢复与人工修复强度的比例差异,通常可以将生态保护与修复途径区分为利用(更好地利用现有自然生态系统)、恢复(调整现有生态系统的解决方案)、重建(创建和管理新生态系统的解决方案)三大层次[42]。由于流域水系之间的自然本底条件、生态系统退化机制与受损程度存在明显的时空分异特征,需要针对不同水系空间的主导问题,因地制宜确定治理模式。对于轻微退化的系统仅需适当的人工引导系统自然恢复,而退化严重的生态系统则应通过生态重建来适时遏制退化趋势[43]。
2 流域国土空间生态修复规划要点
国土空间生态修复规划是一项服务于生态文明建设和高质量发展的专项规划,既要深化各级国土空间规划中生态修复和国土综合整治的目标,同时也要细化生态保护和修复的实施途径,对各类保护修复项目作出统筹安排[44]。专项规划一般在国家、省和市县层级编制,或针对特定的区域或流域尺度展开。区域是一种客观存在、主观划分的地域形式,多以行政单元作为空间基础(例如京津冀地区、长三角地区、粤港澳大湾区等等),区域规划为地方政府跨区域生态治理协同联动提供了支撑。流域是按照自然边界划分的特殊地理单元,河流水文作用使得自然与社会要素之间的联系更为紧密。流域规划同样关注协调跨行政区域的生态问题,但在方案制定过程中更为尊重自然生态系统的发展规律,基于系统思维解决流域内部复杂的人水矛盾。总体而言,流域与区域是基于不同地理认知与发展需求所确定的空间规划具体边界,二者相辅相成,在生态文明建设中均发挥着重要作用。当前区域国土空间生态修复规划编制方案已经基本成熟,而流域国土空间生态修复规划将成为下一步协调跨区域生态保护修复问题的重要抓手,有必要梳理规划编制重点,服务国土空间规划体系建设。
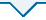
相较而言,流域国土空间生态修复规划突破了行政单元的限制,在区域国土空间生态修复规划编制内容的基础上,还需在本底调查、尺度传导、实施途径以及规划保障四个层面进一步明确工作要点(图2)。其中,本底调查需特别强调人水关系的定量刻画,基于供需确定各项规划目标的用水安排;尺度传导则需以本底调查结果为基本依据,在空间尺度下明确流域规划与其他相关规划的关系,在时间尺度上开展全周期实施监测确保规划有序落实;实施途径层面重在分区分类管理,需要结合不同尺度下的观测和分析开展系统设计,基于规划手段确保流域上下游、左右岸协同发展;规划保障的关键在于吸纳国际前沿的生态恢复理念,为规划方案实施提供可持续保障。
图2
图2
流域国土空间生态修复规划要点
Fig. 2
Key planning issues of watershed-based territorial ecological restoration
2.1 定量刻画人水关系
流域生态修复的重点在于调节流域人水关系,缓解国土空间开发与保护矛盾。其中,“人”是干扰活动的实施主体,以“水”为核心的自然要素是抵抗干扰的主体,二者之间的关系决定了生态系统的健康水平[45]。流域尺度开展的国土空间生态修复仍然遵循生态保护修复专项规划的任务要求,但需要在规划导向与任务安排等方面进一步突出以水为核心的规划特色,统筹水资源约束、水生态基底、水环境容量、水灾害规避作用,基于社会—生态过程串联各项自然生态与社会经济要素,协调经济、社会、生态三方面发展目标对水资源利用的现实矛盾,提出流域多目标协同优化方案,推动全面绿色转型发展。在规划编制前期阶段,需要开展科学的本底调查工作,明确水资源供给与需求的关系,即回答“水从哪儿来,水到哪儿去”两方面密切关联的问题:一方面需要对地表生态过程进行定量刻画,明确流域内天然径流量、地下水位等水文特征年际变化趋势,科学计算流域内可支配的水资源供给总量,突出水资源对生态保护修复以及社会经济发展的刚性约束;另一方面则需要测算生态保护、工业发展以及农业灌溉等方面的水资源利用系数,统筹保障流域内生态安全、粮食安全以及能源安全的用水需求,依据水资源生态承载力协调生态用水指标。科学的量化结果不仅能够协调自然生态过程和社会经济过程,为生态保护与社会发展提供综合水资源保障,还能够杜绝生态工程项目过度取水等问题,避免对生态环境造成二次破坏[46]。
2.2 明确时空尺度衔接
流域国土空间生态修复规划是对现行国土空间规划体系的重要补充,有必要进一步明确流域尺度规划编制在国土空间规划体系中的职能作用。从空间尺度上看,流域国土空间生态修复规划具有明显的层次性特征,纵向视角上需要承接上位规划(包括国家级重大战略规划、区域国土空间规划等)的生态保护格局、生态修复目标任务,也需要针对市县级或子流域尺度具体生态保护修复实践开展协调性部署,实现从宏观总体目标制定到中微观具体保护修复措施遴选的有效衔接。流域作为完整的自然地理单元,其规划范围往往呈现尺度大、跨行政区域的特点,从横向视角来看需要遵循全域修复的系统思想,协调流域内外关系:对内建立统一规划平台,一方面统筹流域内各行政单元形成规划合力,另一方面需要配合各类专项规划,协同构建生态保护、农业生产以及城镇开发格局,确保规划核心目标一致、空间布局统一;对外关注与相邻流域之间的溢出效应、协同效应,统筹解决跨流域生态安全问题。与此同时,在时间尺度上则需要做好流域国土空间生态修复规划的全周期管理,开展适应性调节:规划方案应首先明确各类生态保护修复工程项目的建设时序,中后期则需要通过定期体检与评估识别规划实施瓶颈,及时调整规划方案以适应新发展需求。
2.3 开展分区分类治理
流域国土空间生态修复规划编制既要尊重自然规律,更要协调社会经济发展需求,统筹实施分区分类管理。流域上下游区位不同,经济发展水平之间的差异客观存在,规划编制的难点在于如何落实整体保护、系统修复的规划理念,协调上下游发展不均衡的矛盾。流域国土空间生态修复规划应从自然地理格局的空间异质性入手,针对上下游的不同阶段发展特点按需施策,提出协同治理的有效路径[47⇓-49]。一般而言,流域上游地区的生态系统健康状况关系流域整体的生态安全,应以生态保护作为主要导向,重构自然保护地体系以增强生态系统稳定性与生物多样性。流域下游地区往往是社会经济发展的重要承载地,应重点开展生态保护和修复工程,提高生态环境承载能力,支撑区域可持续发展。规划还应同时考虑到上下游生态补偿政策的顶层设计,基于生态系统服务付费等政策补偿工具提升上下游地区协同治理的积极性,确保全流域居民都能够切实享受到生态修复带来的惠益[50,51]。在流域分区基础上,可以按照开展修复的适宜性与可行性,划分保护、恢复、重建等生态修复类型,作为项目落地实施的基本依据。总体来看,分区从较为宏观的角度剖析自然资源本底特征与生态系统功能的空间格局,分类则是基于系统要素组合特征,在中微观尺度上划分不同的保护修复措施。
2.4 强化自然持续保障
流域生态保护与修复工作既要立足中国国情,也要兼具全球视野。基于自然的解决方案(Nature-based Solutions,NbS)集成了国际前沿生态系统管理方法,不仅将自然作为生态保护修复的对象,同时也将其视作解决社会问题的有效途径,倡导借助小规模人工修复提升大尺度自然保护与恢复成效,增强生态保护修复可持续性。NbS是保护、可持续利用和修复自然的或被改造的生态系统的行动[52],以景观作为主要研究尺度[53]。从修复途径来说,NbS强调人工与自然方法集成的系统化途径,强调尊重并运用自然规律应对社会挑战[54];从修复目标来看,NbS不是仅追求生态治理,而是倡导社会—生态协同发展[55];从修复手段来看,NbS并非一成不变的解决方案,而是更强调根据生态系统动态变化,实施适应性管理[56]。因此,NbS与流域一体化保护修复理念高度契合,能够有效保障规划可持续性[57]。NbS涵盖从方案规划、工程设计以及项目管理的全过程[58]:在规划设计初期,NbS强调借鉴自然规律,通过关键生态过程识别,从源头规避生态退化,实现一体化修复;在中期的工程设计阶段,NbS倡导统筹生态供给与社会需求,权衡社会—经济—生态三方面的效益,促进多目标协同实现;在规划设计后期阶段,生态系统适应性管理是项目实施的重点保障,需要结合自然生态系统状态、社会经济发展水平及其变化趋势,以及工程实施效果适时调整保护修复目标与策略,结合管理与控制手段引导系统韧性提升[59]。NbS所蕴涵的借鉴自然规律、多目标效益权衡以及生态系统适应性管理等规划理念能够为可持续推进流域国土空间开发与保护协同提供核心支撑。
3 结论
流域国土空间生态修复立足完整生态单元,是新时期实现国土空间整体保护、系统修复的关键途径。如何凝练流域国土空间生态修复的系统认知,进而指导规划实践仍然是当前亟待解决的关键问题[60]。“一个核心—两个维度—三对关系”的认知逻辑,从修复对象、修复尺度以及修复模式三个方面深化流域国土空间生态修复的理论内涵,为促进流域可持续发展提供了认知基础。受限于流域生态系统的异质性、复杂性,本文仅对流域国土空间生态修复基本逻辑做出一般性探讨,未能完全覆盖所有要素关联与过程耦合,流域生态修复的理论方法仍有待进一步深入探索。研究所提出的流域国土空间生态修复规划四项要点,为新时期有序推进流域生态保护与修复工作提供了有效工作指引,但尚未形成完整的规划路径。下一步研究中应当聚焦典型流域特质分析,探讨因地制宜的流域生态保护与修复规划方案编制技术要点。
参考文献
国土空间生态修复: 概念思辨与理论认知
Ecological restoration for territorial space: Basic concepts and foundations
论国土空间生态修复基本逻辑
Basic logic of territorial ecological restoration
国土空间生态保护和修复研究路径: 科学到决策
Research framework for territorial ecological conservation and restoration: From scientific research to decision making
生态修复背景下流域国土空间韧性研究思路
Research path on the resilience of watershed territorial space under the background of ecological restoration
Relationship between ecological condition and ecosystem services in European rivers, lakes and coastal waters
DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.155 URL [本文引用: 1]
Climate change risk management in transnational river basins: The Rhine
DOI:10.1007/s11269-011-9891-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
The EU Water Framework Directive: From great expectations to problems with implementation
DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.228 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国地方政府环境治理的政策效应: 基于“河长制”演进的研究
The policy effects of local governments' environmental governance in China: A study based on the evolution of the "River-Director" system
以流域为单元的山水林田湖草沙一体化保护修复
Protection and restoration for the integration of mountains, rivers, forests, fields, lakes, grasslands and sands based on watershed
基于自然的解决方案的流域生态修复路径: 以长江经济带为例
Application of nature-based solutions in ecological restoration of watershed: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt
Integrating top-down and bottom-up approaches improves practicality and efficiency of large-scale ecological restoration planning: Insights from a social-ecological system
我国流域国土空间规划制度构建的若干探讨: 基于国际经验的启示
On the institutional construction for territorial planning of China's river basin: The enlightenment from international experience
Freshwater biodiversity conservation through source water protection: Quantifying the potential and addressing the challenges
DOI:10.1002/aqc.v29.7 URL [本文引用: 1]
过程耦合与空间集成: 国土空间生态修复的景观生态学认知
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200102
[本文引用: 1]

新时期国土空间生态修复的核心是整体保护与系统治理,强调生态保护修复与社会经济发展耦合关联的系统性、协同性。景观生态学以景观为研究对象,基于整体综合视角聚焦景观结构与功能演变及其与人类社会相互作用机理,重点关注过程耦合与空间集成。面向国土空间生态修复的战略需求,景观生态学“格局与过程耦合—时空尺度—生态系统服务—景观可持续性”的研究路径能够为国土空间生态修复提供重要学科支撑;依据格局—过程互馈机理识别退化、受损的山水林田湖草生命共同体,基于景观多功能性权衡协调社会—生态需求并确定修复目标,应用生态安全格局优化多层级修复网络体系,建立面向景观可持续性的多尺度级联福祉保障。
Processes coupling and spatial integration: Characterizing ecological restoration of territorial space in view of landscape ecology
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200102
[本文引用: 1]

The core of ecological restoration of territorial space is the holistic protection and systematic governance in the new period. It emphasizes the synergies between ecological conservation and socio-economic development. Landscape ecology focuses on the dynamics of landscape structure and function, and the interactive mechanism between them and human society from a comprehensive perspective, especially paying attention to processes coupling and spatial integration. The approach of "coupling patterns and processes-spatial and temporal scale-ecosystem services-landscape sustainability" in landscape ecology can provide significant disciplinary support for ecological restoration of territorial space. In the practice of ecological restoration of territorial space, pattern-process coupling theory should be employed to identify degraded or damaged life community of mountains, rivers, forests, farmlands, lakes and grasslands. Ecosystem services tradeoffs of multifunctional landscape for balancing social, economic and ecological demands are used to determine ecological restoration targets. For systematic restoration, the ecological security pattern is an effective way to optimize a multi-level restoration network, and the multi-scale cascade framework for human well-being safeguard can be built based on landscape sustainability.
“双碳”目标下的流域生态环境保护规划: 理念更新与措施调适
Watershed ecological and environmental protection planning under the 'dual carbon' goals: Concept renewal and measure adjustment
Simulation and measurement of soil conservation service flow in the Loess Plateau: A case study for the Jinghe River Basin, Northwestern China
Revegetation in China's Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits
DOI:10.1038/nclimate3092 [本文引用: 1]
山水林田湖草生态保护修复思路与实践
Design of implementation path of ecological engineering for ecological protection and restoration of multi ecological elements
Balance of water supply and consumption during ecological restoration in arid regions of Inner Mongolia, China
山水林田湖草生态保护修复的系统性认知
Systematic cognition of ecological protection and restoration of mountains-rivers-forests-farmlands-lakesgrasslands
抚仙湖流域山水林田湖草生态保护修复思路与实践
Ideas and practice of ecological protection and restoration of mountain-river-forest-farmland-lake-grassland system in Lake Fuxian Basin
An assessment framework for climate-proof nature-based solutions
DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.341 URL [本文引用: 1]
Climate change threatens terrestrial water storage over the Tibetan Plateau
DOI:10.1038/s41558-022-01443-0 [本文引用: 1]
基于生态系统评价的山水林田湖草生态保护与修复体系构建研究: 以乌梁素海流域为例
Ecological protection and restoration of forest, wetland, grassland and cropland based on the perspective of ecosystem assessment: A case study in Wuliangsuhai Watershed
山水林田湖草生态保护修复试点工程布局及技术策略
Distribution and technical strategies of ecological protection and restoration projects for mountains-rivers-forests-farmlands-lakes-grasslands
Nature-based solutions as enablers of circularity in water systems: A review on assessment methodologies, tools and indicators
试论国土空间整体保护、系统修复与综合治理
Overall protection, systematic restoration and comprehensive management of land space
社会—经济—自然复合生态系统与可持续发展
Social-economic-natural complex ecosystem and sustainability
流域输沙量变化归因分析方法综述
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.12.013
[本文引用: 1]

流域输沙量变化是水文过程的一个重要环节,同时与区域水资源、土壤管理、甚至生态系统的健康运行紧密联系,因而如何量化气候变化和人类活动对输沙量变化的相对贡献率成为水文学研究的热点问题。论文主要系统总结了流域输沙量变化归因分析的9种方法:简单线性回归分析、双累积曲线法、泥沙归因诊断分析法、库坝拦沙量法、SEDD模型、SWAT模型、弹性系数法、相似天气条件法和水保法,阐述了各方法的计算过程及其适用性,并对各种方法进行评价,同时对未来的流域输沙量变化归因分析方法进行展望:① 尝试新方法的应用,以探索更为适当的输沙量预测新方法;② 考虑流域内极端降雨事件对输沙变化的定量影响,进一步提高结果的准确度;③ 明晰各归因分析方法的局限性和差异性,进行科学的结合与相互验证。研究结果可为流域内生态水文综合治理和土地资源优化管理提供科学依据。
Review on the methods to separate the impacts of climate and human activities on sediment discharge
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.12.013
[本文引用: 1]

As an important part of hydrological process, sediment transport is closely related to regional water resources, soil management, and even the healthy operation of ecosystem. Therefore, quantifying the relative contribution rate of climate change and human activities to sediment transport variation has become a hot issue in hydrology research. In this study, nine methods of attribution analysis of sediment discharge change, including simple linear regression analysis, double cumulative curve method, sediment attribution diagnosis analysis method, dam-sedimentation based method, sediment delivery distributed (SEDD) model, soil & water assessment tool (SWAT) model, elastic coefficient method, similar weather conditions method, and soil and water conservation method were systematically summarized. The calculation process and applicability of each method were elaborated, and the attribution analysis of sediment discharge change in the future was also discussed. Specifically, future work should try to enhance the application of new methods to explore a more appropriate new method for sediment discharge prediction. The impact of extreme rainfall events on sediment transport changes should be considered as well so that the accuracy of the results can be improved. Additionally, the limitations and differences of each attribution analysis method should be clarified, and hence the integration of existing evaluation methods and their mutual verification can improve the precision of the prediction. The results from this study can provide a scientific basis for the comprehensive management of ecological hydrology and land resources management in watersheds.
城市化对流域生态水文过程的影响研究综述
Impacts of urbanization on watershed ecohydrological processes: Progresses and perspectives
基于生态系统服务视角的山水林田湖草生态保护与修复: 以洞庭湖流域为例
Ecological protection and restoration of forest, wetland, grassland and cropland based on the perspective of ecosystem services: A case study in Dongting Lake Watershed
黄河源区气候—植被—水文协同演变及成因辨析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202207011
[本文引用: 1]

全球变化下黄河源区水文过程的演变影响流域生态系统的水源涵养功能,流域植被改变也影响水循环。本文基于气候、植被信息和VIP分布式生态水文模型,开展黄河源区水碳循环要素变化的集成模拟,分析了气候—植被—水文要素的协同演变机制。结果表明,2000年以来黄河源区气候呈暖湿化趋势;植被绿度明显提高,2010—2019年比2000—2009年平均增加了4.5%;生长季延长了至少10 d;植被生产力(GPP)显著上升,倾向率为4.57 gC m<sup>-2</sup> a<sup>-1</sup>;植被恢复措施对GPP变化的贡献约为23%,气候变化和大气CO<sub>2</sub>升高的施肥效应的贡献为77%。源区植被蒸散量(ET)呈增加趋势,倾向率为2.54 mm a<sup>-1</sup>,水分利用效率(WUE)亦提高,平均相对上升率为5.1% a<sup>-1</sup>。GPP、ET和WUE年总量及其变化率在海拔4200 m以下随高度上升而减小,之后变化趋缓。源区植被绿度和径流系数与当年和前一年降水呈显著正相关,反映降水蓄存于植物根层土壤的遗留效应。蒸散增强在一定程度上有利于源区地表—大气之间的水分再循环,帮助缓解生态恢复引起的产水能力下降,促进降水—植被—径流之间的良性互馈关系的形成。揭示水文对气候变化和植被恢复的响应和互馈机制,可为生态恢复措施对源区水源涵养功能的影响及效应的定量评估提供科学依据。
Co-evolution of climate-vegetation-hydrology and its mechanisms in the source region of Yellow River
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202207011
[本文引用: 1]

Vegetation recovery under global change and its consequent evolution of eco-hydrological processes have modulated the water resources conservative capacity in the source region of the Yellow River (YRSR). Based on climatological data, remotely sensed vegetation index and geographical information, the integrated simulations of water and carbon cycles in the YRSR are presented, with the vegetation interface processes (VIP) distributed eco-hydrological dynamic model. Then the co-evolving mechanisms of hydrological and vegetation dynamics are investigated. Results show that warming and wetting climate in the YRSR has improved the vegetation growing condition and extended the growing period for more than 10 days in recent decades. Averaged NDVI from 2010 to 2020 increased by 4.5% relative to that from 2000 to 2009. Vegetation gross primary productivity (GPP) shows a significant uptrend with a rate of 4.57 gC m-2 a-1, 77% of which is contributed by climate change and elevated atmosphere CO2 fertilization, and the rest 23% is by vegetation greening. Evapotranspiration (ET) is increasing at a rate of 2.54 mm a-1 and vegetation water use efficiency (WUE, expressed as GPP/ET) is also improving at a relative rate of 5.1% a-1. Generally, annual ET, GPP and WUE and their trends are decreasing along the elevation below 4200 m. At basin scale, there are significant positive correlations between the vegetation greenness and the runoff coefficient with precipitation in the current and previous years, demonstrating a legacy effect of precipitation for vegetation recovery on water conservation capacity. The increased ET might be a benefit to the water recycle between land surface and atmosphere, which will alleviate the reduced potential of water yield owing to ecological restoration and establish trades-off and synergies among precipitation, vegetation and water yield. Conclusively, exploring the mechanisms of hydrological responses to climate change and vegetation recovery and its feedback will provide scientific support to the assessment of ecological engineering programs in the source regions.
中国内陆河流域城市景观过程对涉水生态系统服务的影响评价研究进展
Research progress of evaluation on the impacts of urban landscape dynamics on water-related ecosystem services in inland river basin, China
Ecosystem services-human wellbeing relationships vary with spatial scales and indicators: The case of China
Regionalization of water environmental carrying capacity for supporting the sustainable water resources management and development in China
DOI:10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.03.030 URL [本文引用: 1]
Ecological restoration is not sufficient for reconciling the trade-off between soil retention and water yield: A contrasting study from catchment governance perspective
国土空间生态修复亟待把握的几个要点
Several key points in territorial ecological restoration
省级“双评价”的理论思考与实践方案: 以浙江省为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20201003
[本文引用: 1]

资源环境承载能力与国土空间开发适宜性评价(“双评价”)在国土空间规划体系中发挥着重要的基础性作用,是空间决策科学性和空间治理有效性的基本保障。从省级国土空间规划的定位出发,剖析省级国土空间规划对“双评价”科学支撑和简单适用的基本要求,总结当前省级“双评价”面临理论与实践的挑战。在此基础上,构建了一套“三维内涵—一对关系—两种尺度—四个层面”的省级“双评价”方案,深入挖掘资源环境承载的能力、压力、潜力三维内涵,立足于承载力与适宜性之间的逻辑联系,以浙江省为案例,从县级行政区和栅格单元两种尺度开展了“双评价”实践,并从优势短板识别、要素空间统筹、开发时序安排及空间格局优化四个层面支撑省级国土空间规划的编制。旨在为省级“双评价”提供一种可行、科学、实用的评价框架,为国土空间规划中布局优化、结构调整、指标分解等实践提供支撑。
Theoretical thinking and practical scheme of "double evaluations" at provincial level: A case study of Zhejiang province
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20201003 URL [本文引用: 1]
黄河流域协同治理: 现实要求、实现路径与立法保障
Collaborative governance of the Yellow River Basin: Realistic requirements, realization approaches and legislative emphases
流域府际生态协同治理优于属地治理的证成与实现: 基于动态演化博弈模型
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20230514
[本文引用: 1]

府际协同治理是推进流域生态治理体系和治理能力现代化的重要手段,但其优于传统属地治理模式的证成逻辑并不明晰,这使得地方政府对生态协同治理效能的信心不足,流域府际生态协同治理机制的实行面临法制规范缺失、治理主体缺位和内生动力缺乏的问题。以成本—收益为驱动分析框架,分别构建生态属地治理模式与府际生态协同治理模式的博弈模型,可厘清地方政府在流域生态治理中的行为逻辑与影响因素。研究发现:中央政府是推动流域府际生态协同治理模式实施的有效领导力量;府际协同创造的生态治理加成效益证明了生态协同治理模式能够提升流域整体生态质量水平;生态治理利益的最大化实现与公平化分配应当并重,以此作为流域生态治理的二元目标。
The justification of inter-government ecological collaborative governance in the river basin better than territorial governance and its realization path: Based on the dynamic evolutionary game model
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20230514 URL [本文引用: 1]
More than one million barriers fragment Europe's rivers
DOI:10.1038/s41586-020-3005-2 [本文引用: 1]
Nature-based solutions: New influence for environmental management and research in Europe nature-based solutions, an emerging term
DOI:10.14512/gaia.24.4.9
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Greening roofs or walls to cool down city areas during summer, to capture storm water, to abate pollution, and to increase human well-being while enhancing biodiversity: nature-based solutions (NBS) refer to the sustainable management and use of nature for tackling societal challenges.\n Building on and comple- menting traditional biodiversity conservation and management strategies, NBS integrate science, policy, and practice and create biodiversity benefits in terms of diverse, well-managed ecosystems.
人工如何支持引导生态系统自然修复
How does artificiality support and guide the natural restoration of ecosystems
省级国土空间生态修复规划编制的思路与方法:以广东省为例
The thought and methodology of ecological restoration planning of national land space at the provincial level: A case study of Guangdong province
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003357
[本文引用: 1]

Unlike previous ecological restoration programs, the main focus of ecological restoration of national land space has changed from a single element in the natural ecology to the whole social-ecological system. The approach of this ecological restoration has changed from applying the pipe-end treatment to a single process to employing system restoration of the community of life consisting of mountains, rivers, forests, fields, lakes, and seas. Additionally, the aim has evolved from improving the health and stability of the ecological system to building a complex system in which humans and nature can coexist and develop a harmonious relationship. As the research on ecological restoration of national land space is developing a systemic and comprehensive view, it urgently requires support from multidisciplinary theories and methodologies. Ecological restoration planning of national land space at the provincial level is an action guide and programmatic document for provinces to further promote the construction of ecological civilization in this new era. This is a new but arduous and complex strategic task that allows extensive discussion on its research theories and methods. Accordingly, multidisciplinary theories and methods and participation from different parties and places are required. This study begins with the analysis of the scientific connotation and theoretical basis of ecological restoration planning of national land space, uses the man-land relationship theoretical framework as the guidance, integrates landscape ecology and nature-based solutions, and considers the local practice of ecological restoration planning of national land space in Guangdong Province. This paper presents the ideas and methods of provincial-level ecological restoration planning of national land space by focusing on the key points and difficulties, such as targets, indicators, major patterns, regional layout, and engineering systems. This is summarized as follows: the overall thinking of "six steps," the target system of "four dimensions," the zoning task of "three spaces," the spatial layout of "three levels," and the engineering system of "three scales." The study enriches the research on the method of ecological restoration planning of national land space by refining thoughts and methods and providing a reference for the ongoing ecological restoration planning of provincial-level national land space in China.
国土空间生态修复布局研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.11.011
[本文引用: 1]

实施国土空间生态修复是新时期生态文明建设的重要途径。国土空间生态保护与修复的布局影响着保护实施力度、工程修复成效以及社会资源分配,是科学开展生态修复工作的前置条件和基础环节。论文在辨析生态修复相关概念关联的基础上,从区域识别和时序判别2个层面出发,结合文献计量学分析整理了国际生态修复布局研究现状,梳理了景观“格局—过程—服务—可持续”理论范式在国土空间生态修复布局研究中的应用。论文提出了支撑可持续发展的生态保护修复目标构建、以社会满意度为导向的生态修复时空需求权衡、面向多重成本的生态修复成本科学评估、在生态刚性约束背景下的基于自然解决方案、恢复力思想下生态保护和人工修复决策阈值、基于时空模拟的生态保护与修复工程选址决策6项重要研究趋向,从而架构了耦合社会—生态目标的国土空间生态修复布局研究路径,以期为国土空间生态修复相关研究和实践提供参考。
Research progress on the arrangement of territorial ecological restoration
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.11.011
[本文引用: 1]

The implementation of ecological restoration of territorial space is an important way to construct ecological civilization in the new era. The arrangement of ecological protection and restoration is the precondition and basic link for scientifically carrying out ecological restoration, which affects the protection implementation, the effectiveness of engineering restoration, and the allocation of social resources. Based on the analyses of the relationship of the concepts related to ecological restoration, and from the perspectives of region identification and temporal sequence identification, this study used bibliographic analysis to examine the current research status of the ecological restoration arrangement internationally, and reviewed the application of the theoretical paradigm of landscape "pattern-process-service-sustainability" in the study of the arrangement of terrestrial ecological restoration. This article identified six important research trends, including the construction of ecological protection and restoration goals that support sustainable development, the balance of spatial and temporal needs for ecological restoration based on social satisfaction, opportunity cost-oriented ecological restoration cost evaluation, natural solutions based on ecological rigid constraints, decision-making threshold of ecological protection and artificial restoration under the concept of resilience, and location decisions for ecological protection and restoration projects based on spatial and temporal simulation, to construct a terrestrial ecological restoration arrangement research system coupled with social-ecological goals. It may provide a reference for the research and practice of ecological restoration of territorial space.
Global priority areas for ecosystem restoration
DOI:10.1038/s41586-020-2784-9 [本文引用: 1]
基于系统保护规划的黄河流域湿地优先保护格局
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.201809.040
[本文引用: 1]

黄河流域湿地为我国生物多样性维持提供了重要生境.本研究基于黄河流域气候分区、地貌单元及湿地遥感数据,构建黄河流域生态地理综合湿地分类系统.在系统保护规划理论框架下,将湿地气候-地貌分类单元作为生态系统层次保护对象,结合黄河流域鸟类分布范围作为物种层次的保护对象,设定30%湿地优化目标,将公路、铁路、城镇、农村居民点、水坝等作为度量因子创建黄河流域保护代价图层,并利用系统保护规划工具——Marxan软件构建黄河流域湿地保护优化格局,识别湿地保护空缺.结果表明: 黄河流域大部分沼泽湿地集中在黄河上游区域,目前源区保护区覆盖面积大,在内蒙古、甘肃及四川部分区域一些稀有湿地类型游离在保护体系外;黄河中游湿地类型以河道和河滩湿地类型为主,保护覆盖率极低,保护空缺严重,经优化保护网络体系后,保护成效可分别得到29.1%、37.6%的提升.黄河下游湿地主要集中在黄河三角洲区域,目前保护体系完整,保护空缺面积极小.总体上,黄河流域中游河流湿地的保护空缺比例最高,亟需重视.本研究基于湿地保护格局优化结果分区分析黄河流域湿地保护模式,为黄河流域湿地的保护规划管理提供了科学性建议,从宏观层面上为黄河流域水生态保护奠定了基石.
Priority conservation pattern of wetlands in the Yellow River Basin based on systematic conservation planning
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.201809.040
[本文引用: 1]

Yellow River basin is a significant habitat for biodiversity conservation in China. Here, we established a integrated classification system of wetlands based on climate types and geomorphological units, with which as the coarse-filter surrogates of biodiversity elements to complement the fine-filter surrogates of distribution of focal bird species. Then, we applied the theoretical framework of systematic conservation planning (SCP), with those two biodiversity surrogates as protection objects and watershed as planning units. We calculated social and economic costs (including roads, railroads, towns, rural settlements, dams) and set targets of 30% to input Marxan to figure out the optimal set of planning units, which met the protection target with the minimum of social economy cost and land resources. We identified a conservation priority pattern by calculating the irreplaceability of each unit by Marxan. Then, we compared the priority pattern with the existing reserve system to analyze conservation gap in the Yellow River basin. The results showed that most marsh wetlands were concentrated in the upper reaches of the Yellow River. The coverage of reserves in the source area was large. Some rare wetland types in Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Sichuan were separated from the protection system. The main wetland types in the middle reaches of the Yellow River were riverine wetlands, with low protection coverage rate and large conservation gaps. After protection network system being optimized, the protection effect was improved by29.1%-37.6%. The wetland in the lower reaches of the Yellow River was mainly concentrated in the Yellow River Delta area. The protection system was good and the conservation gaps was small. Overall, riverine wetlands in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin had the highest area proportion of conservation gaps which needed more attention. Based on the priority conservation pattern, our results provided scientific suggestions for the protection planning and management of wetlands in the Yellow River basin, which would lay a foundation for the water ecological protection of the Yellow River basin from the macro scale.
流域生态空间与生态保护红线规划方法: 以长江流域为例
A method for evaluating ecological space and ecological conservation redlines in river basins: A case of the Yangtze River Basin
基于小流域尺度的县域国土空间生态修复分区: 以山西汾河上游为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20230508
[本文引用: 1]

县域国土空间生态修复是生态修复规划体系的重要一环,也是生态修复工程项目实施的直接上位指导性规划,基于小流域尺度的生态修复分区研究可以为黄土高原地区县域生态修复分区的理论和实践提供有益参考。以汾河上游为例,首先,基于数字高程模型提取地形特征的方法确定了89个小流域单元,进而定量评估水源涵养、水土保持、生物多样性、食物供给四种典型生态系统服务,综合识别区域主导生态功能,据此划定5个生态功能分区;然后,以生态功能分区内生态群落为基础,通过对不同生态群落的生态功能统计比较,划分12个生态修复分区;最后,将小流域合并得到沟域生态系统单元,进而划分了25个生态修复工程分区统筹后期工程项目实施,并提出相应的生态修复策略。本文提出新的生态修复分区思路,以期为县域国土空间生态修复规划的编制提供指引。
Ecological restoration zoning of county-level territorial space based on small watershed scale: A case study of the upper Fenhe River in Shanxi
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20230508 URL [本文引用: 1]
不同类型生态补偿在山水林田湖草生态保护与修复中的作用
Role of various types of eco-compensation in ecological protection and restoration of mountains-rivers-forests-farmlands-lakesgrasslands
国土空间生态修复若干重大问题研究
DOI:10.13745/j.esf.sf.2021.6.20
[本文引用: 1]

国土空间生态保护与修复是实现美丽中国、关系中华民族永续发展的根本大计。本文采用文献资料综合分析法、系统回顾法、实证分析法、类比分析法、趋势外推法、政策环评等相结合的方法开展了一系列工作:从国家方略、顶层设计两个方面,梳理了国土空间生态保护与修复的脉络;从国土空间生态修复规划、技术路经与方法、野外台站和科研样地等角度,阐明了国土空间生态保护与修复研究的方法论;举例辨析了国土空间生态保护与修复的若干“伪生态”和“假技术问题”;指出了国土空间生态保护与修复发展的战略方针、战略目标、战略方向、战略原则、战略重点、战略对策;从生态保护与修复的重大科学问题和热点、语境分析、分区分类、差异化、生态补偿机制等5个方面,提出了助推中国国土空间生态保护与修复需要的科技支撑;讨论了“两屏三带”、科学推进生态修复,以及管理逻辑与技术逻辑融合问题。研究结果为破解国土空间“整体保护、系统修复与综合治理”过程中生态要素的综合性与管理事权的部门化、生态空间的连续性与区域的政区化、生态工程的长期性与行政管理的届次化三大矛盾,提供了科学依据。
The major issues in ecological restoration of China's territorial space
Ensuring that nature-based solutions for climate mitigation address multiple global challenges
DOI:10.1016/j.oneear.2022.04.010 URL [本文引用: 1]
Core principles for successfully implementing and upscaling nature-based solutions
基于自然的解决方案: 一个容易被误解的新术语
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0232.2019.03.040
[本文引用: 1]

随着基于自然的解决方案受到越来越广泛的研究与实践,不同利益群体对其定义的探讨也逐渐增多。但概念的内涵却因研究者们所处的立场不同,而具有众多开放的解读,从而带来了一系列认知的分歧与误区。因此,为了避免基于自然的解决方案因概念泛化而失去核心价值,将通过解释普遍的认识分歧与误区,澄清基于自然的解决方案既不是倡导对原始自然的回归,也不是新兴人工技术叠加的生态治理策略,进而阐明基于自然的解决方案区别于其他生态管理策略的核心价值在于,它是运用科技力量重新了解自然系统并利用自然自身,采用自然力量取代人工技术,作为解决方案中真正做功的核心部分。最后,探讨作为应对可持续发展挑战的综合途径,基于自然的解决方案所具有的核心价值对中国生态建设的启发:在生态建设的过程中,应通过生态设计,合理结合自然与人工的力量,建设具有综合生态系统服务功效的新型生态系统,以应对“经济—社会—环境”三者耦合的可持续发展挑战。
Nature-based solutions: A new term that is easily misunderstood
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0232.2019.03.040
[本文引用: 1]

As Nature-based Solutions are studied and practiced more widely, the range of definitions used by different groups has gradually increased. However, the connotations of the concept have many potential interpretations as different researchers have different viewpoints, which brings with it a series of cognitive differences and misunderstandings. Therefore, by explaining the common differences and misunderstandings, this article clarifies that Nature-based Solutions are neither advocating the return to primitive nature nor ecological management strategies that are superimposed by emerging artificial technologies. Rather, it aims to advocate that Nature-based Solutions are different from other ecological management strategies. The core value lies in that the power of science is used to re-interpret the natural system, and people should replace artificial technology with natural forces as the core part of the solution. Finally, based on the core values of Nature-based Solutions, the author derives inspiration from China's ecological construction: in the process of ecological restoration, we should build a new ecological system with integrated ecosystem services through ecological design and the rational integration of natural and artificial forces. We aim to address the sustainability challenges through systematic design.<br><div> <br></div>
A framework for assessing and implementing the co-benefits of nature-based solutions in urban area
DOI:10.1016/j.envsci.2017.07.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于自然解决方案的研究视角综述及中国应用启示
A review of nature-based solutions research perspectives and enlightenments thereof to the application in China
Planning nature-based solutions: Principles, steps, and insights
DOI:10.1007/s13280-020-01365-1
[本文引用: 1]

Nature-based solutions (NBS) find increasing attention as actions to address societal challenges through harnessing ecological processes, yet knowledge gaps exist regarding approaches to landscape planning with NBS. This paper aims to provide suggestions of how planning NBS can be conceptualized and applied in practice. We develop a framework for planning NBS by merging insights from literature and a case study in the Lahn river landscape, Germany. Our framework relates to three key criteria that define NBS, and consists of six steps of planning: Co-define setting, Understand challenges, Create visions and scenarios, Assess potential impacts, Develop solution strategies, and Realize and monitor. Its implementation is guided by five principles, namely Place-specificity, Evidence base, Integration, Equity, and Transdisciplinarity. Drawing on the empirical insights from the case study, we suggest suitable methods and a checklist of supportive procedures for applying the framework in practice. Taken together, our framework can facilitate planning NBS and provides further steps towards mainstreaming.
Towards an operationalisation of nature-based solutions for natural hazards
Environmental and climate policy integration: Targeted strategies for overcoming barriers to nature-based solutions and climate change adaptation