党的“十九大”召开标志着中国特色社会主义进入新时代,这是习近平总书记对党和国家事业发展的科学判断,也是对中国发展新的历史方位的郑重宣示。方位决定方略,人与自然和谐共生是新时代的基本方略之一。人与自然和谐共生,需要按照生态文明的发展理念,以尊重自然、顺应自然、保护自然为前提,以资源承载与环境约束为基础,通过底线管控、用途管制、生态修复等措施,擘画高质量的国土空间新格局[1,2]。国土空间是人类生存与发展的环境总成,也是区域人地关系及其相互耦合的容器[3,4]。国土空间规划是对国土空间有序开发与有效保护的整体性谋划,是国家空间发展的指南与可持续发展的空间蓝图,是各类开发保护活动的基本依据[5]。随着城镇化与工业化的快速蔓延与持续渗透,国土空间开发与保护面临城乡土地结构失衡、国土空间开发失序、地域主体功能失调等诸多问题[6⇓-8],这给新时代国土空间治理带来巨大压力和挑战。新时代国土空间治理要求转变传统的“单一”规划路径与“单向”增量思维[5],基于整体综合视角聚焦国土空间系统的过程耦合与空间集成[9],强化资源环境的底线约束并通过用途管制实现全国主体功能区划与地方空间规划[10,11]。因此,如何建立新时代国土空间治理的科学认知与理论框架,是国土空间治理体系与治理能力现代化建设需要着力破解的理论和现实难题。
国土空间功能定位、区划与优化作为国土空间规划的重要内容,是新时代国土空间治理体系与治理能力现代化建设的关键命题。国土空间功能是在特定的地域空间范围内与人地关系交互作用下,以满足人类需求或增进人类福祉为目的,依据国土空间规划确定的方案对空间进行开发、保护与治理,从而直接或间接地为人类社会提供各类产品和服务的效用[12]。国际上对国土空间功能研究主要以生态系统功能、农业功能、景观功能等内容为主[13⇓-15],侧重从单一的城市系统、乡村系统、农业系统探索其时空格局、演化机理、调控路径等内容[16⇓⇓-19]。中国学者则依托当前国土空间规划编制工作实践,充分开展主体功能区划、“三生功能”分类、“三区三线”划定、国土空间分区管制等理论与实证探索[6,11,20],极大地丰富了国土空间功能研究的框架体系。然而,国土空间系统是一个交织着人文与自然因素的复杂动态系统,国土空间功能的呈现是多元子系统及其构成要素动态演化的结果,对单一地域功能或空间系统的理论认知并不能反映国土空间系统的整体性原理。因此,本文基于当前重大战略决策的理论与现实诉求,辨析国土空间功能的理论演进,构建国土空间功能理论认知模型,探讨国土空间功能研究的基本框架,旨在充实国土空间功能研究的理论体系并为国土空间规划实践提供指导。
1 国土空间功能的理论演进
1.1 地域功能是衍生国土空间功能概念的逻辑起点
地域功能理论萌芽于19世纪西方区域研究和区划实践,尤其得益于20世纪以后西方国家广泛开展的国土空间规划实践,地域功能理论获得了迅速的发展。地域功能不是单一系统或单一单元所承担的功能,而是人地关系在可持续发展过程中所承担的综合功能,这一理论本质与国土空间功能的内涵不谋而合。从世界各国的空间规划实践过程来看,虽然自然环境与人文要素千差万别,但基于地域功能划分国土空间功能类型区已成共识。然而,从系统论的角度来看,地域功能侧重于表达特定地域自然系统和人文系统的耦合功能,着重体现功能的空间性并具有区域性、现势性、物质性等特点;而国土空间功能偏向于表达在地域功能基础上叠加规划意识形态后所形成的功能,主要强调空间的功能性并具有全局性、战略性、前瞻性等特点。由此可见,地域功能是衍生国土空间功能概念的逻辑起点,而国土空间功能是地域功能演进的高级形态。国土空间规划功能分区必须充分把握地域空间分异的客观规律,以“区内功能相同或相似、区外功能相异或相斥”为主要准则[21],识别诸多具有明确功能标识的地域单元,典型如“主体功能”“三生功能”“三区功能”等。不同功能的地域单元是规划引导与空间治理的政策单元,在指导各类空间规划、统筹区域发展、协调人地关系等方面发挥着重要作用。
1.2 人地关系地域系统理论是构建国土空间功能理论体系的内核
人地关系地域系统是以地球表层一定地域为基础的人地关系系统,是由人类社会和地理环境两个子系统在特定的地域中交错构成的一种动态结构[22]。这一理论由吴传钧先生于1991年正式提出,并由黄秉维、陈述彭、陆大道等地理学者发展与完善,现已成为综合研究地理格局形成与演变规律的理论基石[23]。人地关系在21世纪受到持续关注,为表明人类活动对地球造成的巨大变化,国际地圈生物圈计划(IGBP)提出“人类世”(Anthropocene)的概念,用以标识地球历史已经进入一个新的地质年代[24]。与此同时,刘彦随[25]指出现代人类活动强烈作用于地球表层人地系统,形成了人地系统耦合与交互作用的地表圈层——“人地圈”(Human-earth sphere)。国土空间是“人地圈”的尺度表达与“人类世”的行动场域,是一个国家或地区地表系统构成要素与人类经济社会活动的场所,是人地关系及其系统演化在地域空间的活动范围。国土空间系统以人地关系地域系统为核心,国土空间功能的形成体现了自然系统对人类活动的承载功能和反馈机制,以及人类活动对自然系统的空间占用和适应依赖[23]。国土空间功能的理论贡献在于指导国土空间区划与优化,为此需要在尊重自然、顺应自然、保护自然的前提下,协调人与人、人与环境、环境与环境等关系,这决定了国土空间功能理论建构必须以人地关系地域系统理论为内核。
1.3 空间整合是国土空间功能理论体系演进的重要向度
随着“逆城市化”“乡村后生产主义”等新问题与新现象的涌现,学术界意识到传统的国土空间功能分区理念已经不能从根本上解决当前国土空间规划存在的复杂问题[26]。为此,国土空间功能理论体系的丰富和发展需要突破既有研究对单一地域功能或空间系统的理论认知,从整体性视角探索系统融合、要素耦合、功能复合、尺度叠合等问题。从地域系统来看,国土空间规划不仅打破了传统的城乡分界,而且也增进了陆海联系,使得不同结构的地域系统互动关联更加频繁和复杂,基于系统融合建立全域国土空间认识观是理解这一动态过程的前提。从要素构成来看,国土空间系统融合了生态子系统、社会子系统与经济子系统,并且包含物质空间、社会空间、虚拟空间等多元空间,尤其是系统要素的耦合与内聚决定了国土空间功能的类型[27]。因此基于要素视角探索国土空间的系统耦合机理、空间嵌套逻辑以及要素作用机制,是揭示国土空间结构演替与功能分异的重要内容。从功能类型来看,国土空间功能表现为利益相关者对地域空间的需求状态,并且需求多样性引致的功能在有限空间叠加,识别并厘清各项功能的复合关系是构建国土空间功能理论体系的基础。从空间尺度来看,尺度依赖是识别国土空间功能的前置条件,为此需要建立一个从全球到局部的等级刻度,从尺度叠合的视角构建理解国土空间功能动态性与等级性的理论框架。
2 新时代国土空间功能的科学认知
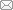
中国是全球面积最大且人口最多的发展中国家,在积极响应经济增长、消除饥饿、气候行动等可持续发展目标(SDGs)的同时,经济增速放缓、城乡差距扩大、生态环境退化等问题日渐突出。可持续发展作为世界主要经济体协调经济、社会与环境发展共同遵守的基本法则,亦是破解上述问题的“金钥匙”。党的“十八大”以来,在可持续发展理念的指引下以生态文明建设、国土空间规划体系建立、乡村振兴战略、高质量发展、美丽中国建设、“双碳”目标为宏伟蓝图的重大战略决策的提出,为推进新时代国土空间治理体系与治理能力现代化注入了新活力。国土空间规划作为落实新时代国土空间治理的政策工具和关键举措,主要任务之一是开展国土空间功能的定位、区划与优化。为此,本文立基于当前重大战略决策的理论与现实诉求,构建了国土空间功能理论认知模型(雪花模型),以辨析新时代国土空间功能研究的科学价值(图1)。
图1
图1
国土空间功能理论认知模型(雪花模型)
Fig. 1
Theoretical cognitive model of territorial space function (snowflake model)
2.1 战略决策是引领国土空间功能区划的政策导向
近年来,中国政府基于国际经验与本土实践提出了一系列以生态文明建设为核心的重大战略决策,要求树立尊重自然、顺应自然、保护自然的生态文明理念,建立全国统一、责权清晰、科学高效的国土空间规划体系,促进经济由高速增长阶段向高质量发展阶段转变,着力补齐乡村发展的短板,全面实现农业强、农村美与农民富,建设人与自然和谐共生的美丽中国。在区域发展上,持续推进西部大开发、东北振兴、中部崛起、东部率先、京津冀协同发展、长江经济带发展、粤港澳大湾区建设、长三角一体化发展、黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展等九大区域发展战略,推动成渝地区双城经济圈建设,促进革命老区、民族地区、边疆地区、贫困地区加快发展,以及发展海洋经济[28]。在资源利用上,国家推行“双碳”战略目标、黑土地保护、三江源保护、退耕还林(草/湖/沙)等一系列重大工程,极大地改变了自然资源的开发利用方式,进而引导区域国土空间功能定位与区划。总之,通过这一系列重大战略决策与区域发展战略的逐步推进,规范国土空间开发秩序与形成合理的国土空间开发结构,引导不同地域国土空间功能的形成、集聚与优化,可见国家重大战略决策是引领国土空间功能区划的政策导向。
2.2 主体功能是刻画国土空间功能格局的总体方案
随着全球化、城镇化与工业化的不断深入,人类干扰活动的增强使得地域空间功能的属性和状态在有限空间出现挤占、集聚、重叠与转化,甚至演化为激烈的矛盾与冲突[29],因此如何协调不同地域空间功能的矛盾与冲突以促进区域可持续发展,是未来国土空间格局优化需要着力解决的重要内容。为此,中国人文与经济地理学者主张按照主体功能区划实现国土开发保护的有序性与可持续性。主体功能区是基于不同区域的资源环境承载能力、现有开发密度和发展潜力等,将特定区域确定为具有生产、生活、生态等特定主体功能类型的一种空间单元[6]。《全国主体功能区规划》按开发方式将国土空间划分为优化开发、重点开发、限制开发和禁止开发,刻画了未来国土空间开发与保护格局的规划蓝图,体现了国土空间功能区划的顶层设计和制度安排[6]。国家以下各级行政单位通过国土空间规划划定“三区三线”,合理布局生产、生活与生态空间,依据特定区域乡村地域系统的结构与格局,进行地域系统主体功能分区、主导类型分类、主要用途分级,确立区域国土空间规划体系及其优化调整方案[30],体现了国土空间功能在宏观尺度对主体功能区划方案的承接与在微观尺度对国土空间开发利用和保护的落实。
2.3 底线管控是落实国土空间功能分区的基本前提
国土空间系统是由自然生态系统与社会经济系统组成的复合系统,系统内任一空间单元都具有特定的本底功能和发展需求[31],这是国土空间规划中底线管控思维的出发点。以“三区三线”划定为主要内容的空间管制规则,是新时代国土空间治理落实底线思维的直观体现。“双评价”作为构建国土空间格局的基本战略与实施功能分区的科学基础,为“三区三线”划定提供了充足的理论证据与实践手段。习近平总书记以及中央政策文件多次要求在“双评价”基础上,科学有序统筹布局和划定“三区三线”,建立以“双评价”和“三区三线”为主要内容的底线管控思维,形成以底线管控引领国土空间开发保护格局的新理念[10,32]。底线管控中的“底线”不是国土空间资源开发与保护的最低下限,而是推进城镇化、调整经济结构、确保生态安全格局不可逾越的红线[33],是协调发展与保护矛盾以及调和国土空间功能冲突的平衡线。不仅如此,底线管控表征了一个国家或地区维护经济安全、粮食安全与生态安全的状态和能力,体现了国土空间功能分区对上位规划的衔接与下位规划的约束。由此表明,底线管控是编制国土空间规划的基础,是指导国土空间功能分区与土地利用的基本前提。
2.4 用途管制是强化国土空间功能格局的制度保障
党的“十八届三中全会”以来,以“国家治理体系与治理能力现代化”为目标导向、《生态文明体制改革总体方案》印发为内容导向、“国土空间用途管制司”成立为行政导向的国土空间用途管制体系逐步建立,标志着用途管制将实现由单要素管理到生命共同体管制,由注重资源性向注重资源、资产、权利综合性转变[34]。这一转变也促使用途管制对象从土地利用向国土空间转变,国土空间用途管制注重单一地类保护向空间统筹转型、地类管制向空间管控转型、指标传导为主向指标与分区相结合转型、底线约束向约束与引导并重转型[11]。传统的用途管制经验及当前的规划实践均表明,国土空间管制中的“空间”理论上是功能空间[35,36]。国土空间功能定位与区划是体现国土空间规划的重要内容,也是落实国土空间用途管制的基本单元[26]。面对新时代国土空间治理理念的转变,国土空间开发、利用与保护必须符合国土空间用途管制确定的区域、边界、用途和使用条件等,国土空间功能定位与区划既要体现国家主体功能区划要求,还要尊重地方自然资源与社会结构的本底差异,增强用途管制与空间功能发挥的关联逻辑,以此明确“以用途定功能,以功能促用途”的治理路径。
2.5 分区管治是引导国土空间功能转型的有效途径
国土空间功能既囿于自然资源本底、社会经济状况、制度管理水平等地域差异,也体现了国家行政意识与公民自发行为的互动关系。依据地域功能—结构的空间组织规律与人地系统耦合关系探析地域空间功能的分区管治策略,是优化国土空间功能的有效途径[37]。全球尺度上,面对逆全球化、“一带一路”倡议、(后)疫情时代等新形势,中国应积极主动谋划如何建立粮食、能源、生态、科技、政治等领域的国土空间安全格局,以应对全球变暖、资源枯竭、生态恶化、贸易封锁、地缘冲突等潜在危机,探索国土空间分区优化的“外治”之道;国家尺度上,通过明确城镇空间、农业空间和生态空间以及划定城镇开发边界、永久基本农田保护红线与生态保护红线,构建以新型城镇化、粮食安全和生态安全为重点的“三区三线”管控体系;县级尺度上,《市县国土空间规划分区与用途分类指南》将县级国土空间按照保护与保留、开发与利用的原则划分为生态保护区、自然保留区、永久基本农田集中区,以及城镇发展区、农业农村发展区、海洋发展区,制定国土空间分区优化的“内治”之策。通过“内外兼修”“上下融通”“纵横交错”等策略,构建新时代国土空间功能的分区管治体系并引导功能转型。
2.6 空间协同是表征国土空间功能优化的根本目标
国土空间单元可能同时包含多种功能,各项功能在要素的非均衡集聚与扩散作用下呈现出明显的空间异质性和时间变异性,加之利益相关主体的偏向性选择导致各项功能之间的相互关系复杂化[29]。国土空间功能优化调控需要理清各项功能之间的空间结构与组织联系,以此引导区域资源开发并逐步实现空间协同。空间协同是国土空间功能优化调控的一种目标状态,该状态下空间要素的组合与配置最优,利益主体的空间权益得以充分保障,人与自然能够和谐共生。为此,空间协同需要满足要素协同、利益协同与人地协同三个要求。首先,国土空间系统是由多要素组成的多功能系统,要素协同是国土空间功能优化调控的基础,要素非均衡配置则可能引发资源过度开采、空间秩序混乱、生态系统退化等区域性乃至全球性问题;其次,国土空间功能类型多样、空间分布不均衡且受人类决策支配,加之系统构成要素的变动及人类需求的改变,使得国土空间功能优化调控需要协调相关利益主体的各项需求;再者,国土空间资源开发利用的过程也是人类通过各种手段调整人地关系的过程,而国土空间功能是地域人地关系的映射,因此人地协同是表征国土空间功能优化调控的重要刻度。
3 新时代国土空间功能的研究框架
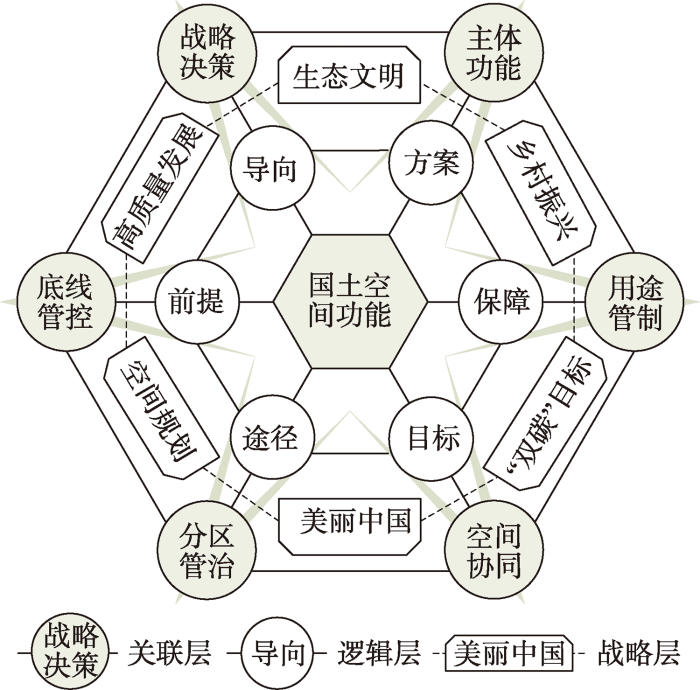
国土空间功能的概念雏形虽可追溯至古罗马时代,但直到20世纪初西方国家国土空间规划实践的大量开展,才逐渐完善了国土空间功能研究的框架体系。中国的国土空间功能研究始于21世纪初,尤其是第三轮国土空间规划编制的主要任务之一在于划定不同类型的功能区。在此背景下,本文面向服务国家重要战略决策、优化国土空间开发格局与可持续发展的战略需求,从学理认知、分类识别、演化机制、动态权衡提出国土空间功能研究的基本问题及其研究框架(图2)。该框架既有助于贯彻落实优化国土空间开发格局的发展理念,又有助于为国家重大战略决策实施提供理论指导。
图2
3.1 国土空间功能的学理认知
规划作为人类利用与管控空间的政策工具,虽然其理论体系和技术方法不断调整变化,但国土空间作为规划的客体赓续至今。国土空间功能定位与区划是体现国土空间规划基础性、综合性和战略性作用的重要内容。国外真正具备现代规划学意义的国土空间功能概念直到20初期才在英美等国家出现。这一阶段产生的诸多空间规划理论成为国土空间功能研究的重要理论源泉,如霍华德的田园城市理论、柯布西耶的“光辉城市”理论、沙里宁的有机疏散理论等。随后,西方国家一百多年的国土空间规划实践探索逐渐完善了国土空间功能的理论框架,尤其是《雅典宪章》提出的功能分区理论有效指导了当时欧美城市建设。当前中国国土空间规划编制的主要任务之一在于划定不同类型的功能区,为此开展了主体功能区划、“三生功能”分类、“三区三线”划定、国土空间分区管制等诸多应用探索。虽然如此,国土空间功能这一概念却较少被学界所“提及”,对国土空间功能及其所涉及的学理问题缺乏系统阐释,实践操作层面国土空间功能分类、评价与优化仍然以土地利用为对象。国土空间功能是国土空间系统构成要素作用的结果,国土空间系统以人地关系地域系统为核心。社会经济发展促使人地关系在地域空间上不断重组,同时地域空间功能也呈现不断循环往复与推陈出新的演化状态,由此决定国土空间功能的优化调控必须以协调人地关系和权衡地域功能为基础与前提。因此,援引并吸取中西方空间规划理论、人地关系地域系统理论、地域功能理论等理论养分,借鉴国外国土空间规划经验及依托本土国土空间规划实践,建立并完善国土空间功能理论体系,厘清国土空间功能的内涵本质及学理价值,可为国土空间规划实践提供重要的理论支撑。
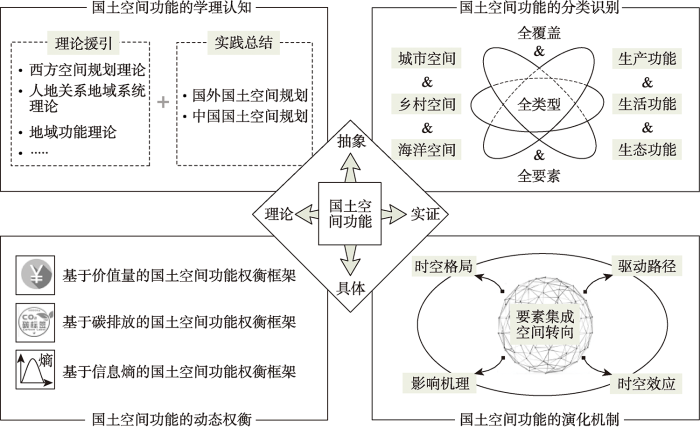
3.2 国土空间功能的分类识别
分类识别是开展国土空间功能研究的基础。由于国土空间功能具有系统差异性、功能复合性、时空异质性等多重特性[38,39],其分类识别必须解决如下问题。一是国土空间功能分类识别要覆盖全部地域。国土空间是由城市、乡村与海域组成的笛卡尔三维空间,并且同一空间单元在不同尺度下的功能状态与属性具有不一致性,这要求国土空间功能分类识别必须融合不同地域系统的空间差异,为此需要以可持续发展目标为指引,将三大空间分别解构为生产功能、生活功能与生态功能。二是国土空间功能分类识别要包含所有功能类型。社会经济发展过程中,由于资源的有限性和竞争性以及主观认识与客观属性的差异,导致国土空间功能被认可、保护与利用的机会不均等,如耕地的生态功能被忽视。为此,国土空间功能分类不仅要识别各类空间的主要功能,还要识别复合在该类空间上的非主要功能。三是国土空间功能分类识别要综合考虑全部要素。国土空间功能是系统构成要素在内部与外部的联系与关系中表现出来的特征和能力,这要求国土空间功能分类识别既要体现系统构成要素的异质结构,还要合理识别因人类需求叠加或进阶而涌现的系统新功能。为此,需要分别以产品属性、社会属性、生态属性等为分类标志细化“三生”功能,并遴选适当数据类型或观测指标量化表征。综上,国土空间功能分类识别应充分利用多源、多时相与多尺度数据并结合实地调查,确保数据的精准性、功能分类的真实性以及与用地分类的衔接性,以此建立一套全覆盖、全类型、全要素的国土空间功能分类体系(图3)。
图3
图3
国土空间功能分类识别框架
Fig. 3
Classification and identification framework of territorial space functions
3.3 国土空间功能的演化机制
国土空间系统是一个交织着人文与自然因素的复杂动态系统,系统内部各要素及其相互之间均存在非线性竞合关系,国土空间功能演化既是系统构成要素与外部环境相互联系与相互作用的结果,更是地域人地关系在自然和人文地理格局及演变过程的响应。一方面,国土空间系统是一个由生态系统、社会系统与经济系统组成的复合系统,系统及其要素的扰动决定了国土空间的“本底功能”,并且人类需求的变化与社会经济活动的干扰引导国土空间的“需求功能”在时间维度与空间尺度上不断演化;另一方面,当前“未来地球”计划以及可持续性科学都着重强调自然与人文要素的综合集成,尤其是在地理学“文化转向”和社会学“空间转向”的深刻背景下,空间生产及其公平正义问题进入了空间研究的领域[40],其不仅契合了新时代生态文明建设坚持人地和谐共生的理论整合要求,也符合国土空间规划功能分区的发展诉求,更有可能为复杂的国土空间功能“耦合—嵌套”关系提供一个全新的解释思路。综上,国土空间功能时空格局演化是系统内外合力作用的结果,为此厘清国土空间系统从要素空间到系统空间、从简单系统空间到复杂系统空间、从环境系统空间到过程系统空间再到耦合系统空间的转变过程与作用机理,集成自然与人文因素解析国土空间涌现的新内涵、新结构和新功能,阐述国土空间功能演化的过程、路径、机理与效应,对构建可持续国土空间开发保护格局具有重要意义。
3.4 国土空间功能的动态权衡
国土空间系统构成要素的异质组合与人类需求的适时变动赋予了国土空间多种功能,而社会经济转型发展导致各项功能相互作用与相互影响,表现为此消彼长的权衡关系或互相增益的协同关系[41]。国土空间功能的权衡关系,指一种功能变化会引起另一种功能的反向变化,即表现为竞争、冲突关系;协同关系,指一种功能的变化会引起另一种功能的同向变化,即表现为协调、共生关系。此外,国土空间功能还存在兼容关系,即一种功能变化不会或较小影响另一种功能变化,即表现为兼受、容纳关系。管控冲突、促进共生是国土空间功能动态权衡的目标导向,也是实现人类与自然和谐共融的重要前提,这首先需要制定科学的功能判别规则。本文提供三种思路:一是构建基于功能价值量的国土空间功能权衡框架,充分利用多源数据以及综合运用多种方法,测算一定时期内人们在国土空间开发利用过程中所获取的各类产品与服务的价值量[42],并以此作为判别规则量化不同功能之间的权衡/协同关系;二是构建基于碳排放的国土空间功能权衡框架,由于国土空间功能演化是对地表覆盖变化与人类活动干扰的响应,而这一过程会导致碳排放的变化[43],因此建立土地利用与人类活动碳排放核算清单,以此权衡国土空间功能演化与碳排放的关系,可为国土空间规划助力国家实现“双碳”目标提供参考;三是构建基于信息熵的国土空间功能权衡机制,国土空间系统是一个具有典型耗散结构特征的开放系统,而信息熵作为度量耗散结构系统有序性的一种方式已经被广泛证实和认可[44],国土空间功能演化是系统内部及其与外部系统间进行物质、能量和信息交换的表征或结果,依据熵定律系统演化伴随着熵增与熵减,探析国土空间功能演化与信息熵之间的量化关系及其演化机制,可为国土空间系统的优化调控和可持续发展提供理论指导。
4 结论与讨论
4.1 结论
(1)当前国土空间规划的主要任务之一在于遵循地域功能的空间结构与组织特征将国土空间划分为不同类型的功能区,而根植于西方区域规划实践的地域功能理论正是指导国土空间功能分区的理论基础,也是衍生国土空间功能概念的逻辑起点。国土空间功能理论体系的构建须以人地关系地域系统理论为内核,并着力突破既有研究对单一地域功能或空间系统的理论认知,从整体性视角建立系统融合、要素耦合、功能复合、尺度叠合等问题的理论分析框架。
(2)国土空间功能是架构国土空间规划理论体系与实践框架的重要内容。本文从战略决策、主体功能、底线管控、用途管制、分区管治、空间协同等六个方面构建了国土空间功能理论认知模型(雪花模型),其中战略决策是引领国土空间功能区划的政策导向,主体功能是刻画国土空间功能格局的总体方案,底线管控是落实国土空间功能分区的基本前提,用途管制是强化国土空间功能格局的制度保障,分区管治是引导国土空间功能转型的有效途径,空间协同则是表征国土空间功能优化调控的根本目标。
(3)国土空间功能研究还需面向优化国土空间开发格局与可持续发展的战略需求,吸取中西方相关理论养分与空间规划经验以拓展国土空间功能研究的理论体系和框架范式,基于全覆盖、全类型与全要素视角构建兼具实用性和可操作性的国土空间功能分类体系,集成自然与人文因素解析国土空间涌现的新内涵、新结构和新功能,阐述国土空间功能演化的过程、路径、机理与效应,探索建立基于功能价值、碳排放、信息熵等准则的国土空间功能权衡机制。
4.2 讨论
党的“十九大”以来,以可持续发展理念为指引的一系列重大战略决策的提出,标志着中国特色社会主义进入新时代。国土空间规划作为落实新时代国土空间治理的政策工具和关键举措,主要任务之一在于依据地域分异特征开展国土空间功能定位、区划与优化。然而,受困于长期以来的“单一”规划思维以及国土空间规划仍处于探索阶段,国土空间功能内涵及其理论体系尚未系统阐释,由此导致现有的理论体系无法有效指导国土空间开发与利用实践。因此,一方面有必要借鉴伯吉斯的同心圆理论、霍伊特的扇形理论、哈里斯和乌尔曼的多核心理论等城市区划理论精髓,以及汲取法国“农村振兴计划”、韩国“新农村运动”、德国“巴伐利亚试验”等乡村运动养分,逐步建立本土化的国土空间功能研究的理论框架;另一方面,有必要融合拓展国土空间功能研究内容,在国土空间功能定位、区划与优化实践过程中关注绿色基础设施(green infrastructure)的空间配置及生态社会效应[45]、国土空间治理(spatial governance)的差异化调适机制[46]、国土空间系统韧弹性(resilience)的概念框架与提升路径[47]等新技术、新问题和新命题;再者,有必要立基于当前重大战略决策与理论研究成果,基于系统、流域、网格等尺度探索国土空间多功能的协同融合机制[48],立足于新型全球化视野构建“一带一路”沿线国家空间规划体系与国土空间安全格局[49],整合大数据、云计算、人工智能等新兴技术以丰富国土空间功能研究的技术方法体系[50]。新时代国土空间功能理论体系的构建要以服务生态文明建设、国土空间规划体系建立、乡村振兴战略、美丽中国建设、“双碳”战略目标等重大战略为出发点,着力解决新时代背景下国土空间治理提出的新命题,充分借鉴城市功能分区理论、乡村地域多体系统学说、土地利用规划原理、景观生态学方法等研究成果,融合高质量发展、生命共同体、“两山”理论等思想精髓,揭示国土空间系统的要素构成及其作用机制,阐释国土空间多功能的耦合协同演化机制,明确不同空间尺度下国土空间功能的优化调控路径,以此丰富和发展国土空间功能理论体系与实践框架。
参考文献
国土空间生态修复亟待把握的几个要点
Several key points in territorial ecological restoration
美丽中国与国土空间用途管制
Beautiful China and the land space use control
基于人地耦合系统的国土空间重塑
Geogovernance of national land use based on coupled human and natural systems
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20191003 URL [本文引用: 1]
Territory spatial planning and national governance system in China
中国主体功能区划方案
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502002
[本文引用: 4]

中国主体功能区划方案是刻画未来中国国土空间开发与保护格局的规划蓝图,主体功能区规划已上升为主体功能区战略和主体功能区制度。2004-2014年,笔者组织系列研究项目,配合国家编制主体功能区规划,研究地域功能基础理论和功能区划技术流程,提出国家和省区尺度进行空间管制的地域功能区域类型为城市化区域、粮食安全区域、生态安全区域、文化和自然遗产区域等4类,在此基础上转化为以县级行政区划为单元的优化开发、重点开发、限制开发和禁止开发4类主体功能区。研制了由水资源、土地资源,生态重要性、生态脆弱性、环境容量、灾害危险性、经济发展水平、人口集聚度和交通优势度等9类可定量指标及战略选择为1项定性指标构成的地域功能识别指标体系,进行了单项指标评价,开发并运用地域功能适宜程度综合评价指数进行了综合评价,测算了各省区保护类区域下限、开发类区域上限以及开发强度等关键参数;研讨了以规划为应用指向的主体功能区划分方法,形成中国首部主体功能区划方案,按照全国主体功能区规划口径,2020年与2010年相比,全国国土空间开发强度从3.48%增加到3.91%;按照省区集成的主体功能区规划口径,优化、重点、限制开发区域的土地面积比重分别为1.48%、13.60%、84.92%,城市化、粮食安全、生态安全区域的土地面积比重分别为15.08%、26.11%、58.81%。结合区域发展水平、资源环境承载状态、民生质量等相关分析,给出了主体功能区的主要特征。通过区划方案校验,国家和省区分两级采用笔者主持制定的《主体功能区划技术规程》互动完成的全国主体功能区划方案,同预判的吻合程度多为80%以上。
Draft of major function oriented zoning of China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502002
[本文引用: 4]

Major Function Oriented Zoning (MFOZ) is the blueprint for the future developmnt and protection pattern of China's territory, and has been raised to from major function zones planning to major function zoning strategy and major function zoning institution. From 2004 to 2014, the author organized a series of research projects to compose MFOZ for the country, studied basic theory of regional function and MFOZ technical process, and proposed that space controlling zones of national and provincial scales can be divided into four types: urbanized zones, foodstuff-security zones, ecological safety zones, cultural and natural heritage zones. On this basis, major function zones of county scale should be transferred to optimized, prioritized, restricted, and prohibited zones. In this paper, a regional function identification index system comprising nine quantitative indicators (including water resources, land resources, ecological importance, ecological fragility, environment capacity, disaster risk, economic development level, population concentration and transport superiority) and one qualitative indicator of strategic choice is developed. Based on the single index evaluation, comprehensive evaluation using regional function suitability evaluation index is conducted, aiming at testing several key parameters including lower limit of protection zones and upper limit of development zones at the provincial level. In addition, a planning-oriented zoning method of major function zones is also discussed, which has brought the first MFOZ planning in China. According to the MFOZ caliber, it is forecasted that national spatial development intensity will rise from 3.48% in 2010 to 3.91% in 2020. Furthermore, according to caliber of the provincial integrated MFOZ planning, the area of optimized, prioritized and restricted zones accounts for 1.48%, 13.60% and 84.92%, respectively, and that of urbanized, foodstuff-security and ecological safety zones accounts for 15.08%, 26.11% and 58.81%, respectively. In combination of analyses of development level, resources and environmental carrying status and quality of the people's livelihood, the main characteristics of MFOZ were identified. Through verification, MFOZ draft of national and provincial scales, which is interactively accomplished with "MFOZ Technical Process" put forward by the author, is mostly above 80% identical with what have been forecasted.
中国乡村振兴规划的基础理论与方法论
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006002
[本文引用: 1]

农业农村现代化是实施乡村振兴战略的总目标,科学编制乡村振兴规划事关国家乡村振兴战略的推进及实施成效。《全国乡村振兴战略规划(2018—2022)》提出以来,如何建立符合中国乡村发展基本特点与规律的乡村振兴规划基础理论,研制县域乡村振兴规划方法与方案,成为当前学术研究及政府决策的重要课题和重点任务。基于乡村地域多体系统理论,构建了乡村振兴规划理论模式,提出了“三主三分”乡村振兴规划方法。“三主三分”的基本原理是依据特定区域乡村地域系统结构与格局,进行地域系统主体功能分区、主导类型分类、主要用途分级,确立乡村振兴规划空间体系及其优化调整方案。该体系运用于宁夏回族自治区盐池县乡村振兴总体规划,制定了坚持生态优先、因地制宜、产业支撑、城乡融合的乡村振兴规划原则,提出应重点发展乡村专业合作组织和村镇混合制经济,加快建设以滩羊、黄花、小杂粮产业化为特色、生态文化旅游智慧化为亮点的优势产业体系;在空间上突出中心城镇地位,形成以县城和3个重点镇为中心、“三产”融合发展的村镇有机体、居业协同体。本研究是对创建中国乡村振兴规划体系的有益尝试,可为全国县级乡村振兴规划与乡村发展决策提供参考依据。
The basic theory and methodology of rural revitalization planning in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006002
[本文引用: 1]

Agricultural and rural modernization is the general goal of the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy. The scientific formulation of the rural revitalization planning is related to the implementation effect of the national rural revitalization strategy. How to establish the basic theory of rural revitalization and develop the methods of rural revitalization planning have become important tasks of academic research and government decision-making. This paper constructed the theoretical model and method system of rural revitalization planning, tried to carry out the main function-oriented zoning, dominant type classification and principal purpose classification of rural regional system, and established the spatial system of rural revitalization planning and its optimal adjustment scheme. This system was applied to the overall rural revitalization planning in Yanchi County of Ningxia. By establishing the principle of rural revitalization planning that sticks to ecological priority, adaptation to local condition, industrial support and urban-rural integration, it put forward that the priority should be given to the development of rural professional cooperation organizations and the mixed economy of villages and towns, and the acceleration of the construction of advantageous industrial system characterized by the industrialization of tan-sheep, day lily, and minor cereals, and highlighted by the wisdom of eco-cultural tourism. Moreover, it was encouraged to give prominence to the position of the central town in space, and form the village organism and housing industry coordination body with the county seat and three key towns as the center of integrated industry development. The typical case study of Yanchi County has shown that the main contents and technical points of rural revitalization planning were embodied in the following four aspects: (1) determining the overall orientation of rural revitalization planning, and clarifying the phased development mode, key areas; (2) developing the county area based on the main function-oriented zoning, leading type classification and main purpose classification system, and exploring the territorial pattern and differentiation rules; (3) establishing the county development mode and industrial system, formulating coordination schemes of different main function-oriented zones, and revealing the spatial configuration and structural relationship of different dominant types; (4) exploring the local association and hierarchical system of each dominant type in its scale and level. The main task of implementing the rural revitalization planning is to promote the formation of a new pattern of urban-rural development with factors gathering, reasonable structure and orderly space in accordance with the objective requirements of "industrial prosperity, ecological livability, rural civilization, effective governance and prosperous life". China is facing great differences in rural development and many problems in transformation. Regional disparities and urban-rural differences determine the complexity, diversity and differences of rural governance and rural revitalization planning. China's rural transformation-urban and rural integration-rural revitalization-high quality development will become the major development logic and new normal in the future. The research on rural revitalization planning in the new era should focus on the overall situation of regional coordination and urban-rural integration, and solve the practical problems of "rural disease", so as to serve the national rural revitalization planning and scientific decision-making.
基于土地系统科学的土地利用转型与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 1]

土地系统科学的研究视角可为促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型研究提供参考借鉴。本文在梳理国际上土地系统科学发展历程基础上,基于土地系统科学研究视角探讨了土地利用转型影响城乡融合发展的理论框架、方式与路径以及促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控途径与措施。土地系统科学致力于监测土地变化,解释驱动因素和反馈机制,理解发生于土地上的人类—环境相互作用,实现将对土地系统的科学发现转化为可持续土地利用解决方案。土地系统运行以土地可持续利用与人类福祉为准绳,显化为土地利用的多维效应。通过科学管控土地利用转型实现土地系统的良好运行能够影响城乡融合发展进程。土地利用转型通过效率提升、价值显化、要素流通与结构优化4大渠道,在“强整体”效应与“补短板”效应的作用下助推城乡融合发展。基于土地系统科学视域下促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控需要重塑土地权能体系,推进国土空间综合整治,健全土地利用转型管控体系。
Urban-rural integrated development and land use transitions: A perspective of land system science
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 1]

The research perspective of land system science can provide a reference for the study of urban-rural integrated development promoted by land use transitions. Based on the review of the development of land system science, this paper discusses the theoretical framework concerning land use transitions affecting urban-rural integrated development guided by land system science, the influential ways and paths of land use transitions on urban-rural integrated development, and the measures of promoting urban-rural integrated development via adjusting and controlling land use transitions. Land system science is committed to monitoring land use change, explaining the driving forces and feedback mechanism, understanding the human-environment interactions occurring on land, and translating scientific findings on land system into solutions for sustainable land use. The operating of land system takes sustainable land use and human well-being as the criterions, and manifests as multi-dimensional effects of land use. Operating well the land system via scientifically adjusting and controlling land use transitions can affect the process of urban-rural integrated development. Land use transitions promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas under the effects of strengthening the whole and reinforcing weak links through four channels, i.e., efficiency improvement, value embodiment, development elements circulation and structure optimization. In order to promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas from the perspective of land system science, the adjustment and control of land use transitions need to reshape the land use rights system, to promote the integrated consolidation of territorial space, and to improve the management and control system of land use transitions.
过程耦合与空间集成: 国土空间生态修复的景观生态学认知
Processes coupling and spatial integration: Characterizing ecological restoration of territorial space in view of landscape ecology
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200102 URL [本文引用: 1]
生态文明视角下的国土空间底线管控: “双评价”与国土空间规划监测评估预警
Territorial space baseline control from the perspective of ecological civilization: "Double evaluation" and monitoring-evaluation-warning
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20201009 URL [本文引用: 2]
国土空间用途管制的改革逻辑及其规划响应路径
Reform logic of territorial space use regulation and the response path of land spatial planning
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200601 URL [本文引用: 3]
Multifunctional landscapes identification and associated development zoning in mountainous area
DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.023 URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatial identification of land use functions and their tradeoffs/synergies in China: Implications for sustainable land management
Towards multifunctional land use in an agricultural landscape: A trade-off and synergy analysis in the Lower Fraser Valley, Canada
DOI:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.12.013 URL [本文引用: 1]
Climate-land-use interactions shape tropical mountain biodiversity and ecosystem functions
DOI:10.1038/s41586-019-1048-z URL [本文引用: 1]
Global estimates of the value of ecosystems and their services in monetary units
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoser.2012.07.005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Classification of the heterogeneous structure of urban landscapes (STURLA) as an indicator of landscape function applied to surface temperature in New York city
面向国土空间规划的乡村空间治理机制与路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106008
[本文引用: 1]

城乡国土空间统一用途管制背景下,乡村空间治理成为国土空间治理体系的重要组成部分。从乡村空间治理的理论内涵出发,构建了乡村空间治理理论分析框架,探讨了乡村空间治理作用于国土空间规划的内在机制和可行路径。结论如下:① 乡村空间治理是以乡村空间为治理对象,通过规划和协商等方式,实现乡村空间用途有效管制,空间权利有序配置,凸显多元主体参与的“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的综合治理过程;② 通过“举措—效能—目标”体系,构建了刚性与弹性结合、物质空间与空间关系交互、空间权属与空间组织叠加的乡村空间“物质—组织—权属”综合治理分析框架;③ 多级尺度互联互通(区域—村域—地块)的乡村空间治理特征有利于完善乡村空间治理体系;④ 乡村空间治理通过多种手段并施、多元主体参与、多重价值共享,完善国土空间规划体系,推进多规融合,细化国土空间用途管制,促进乡村善治和生态治理;⑤ 乡村空间治理通过“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的动员和行动策略,构建新型村庄运营模式和组织机制,为落实实用性村庄规划和乡村振兴战略创造条件。
Rural spatial governance for territorial spatial planning in China: Mechanisms and path
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106008
[本文引用: 1]

Under the background of unified management of urban and rural space, rural spatial governance has become an important part of the spatial governance system. Conducting in-depth theoretical and practical research on rural spatial governance and analyzing the mechanisms and path of rural spatial governance in national spatial planning will be conducive to improving the planning and control system of rural space. Starting from the connotation rural spatial governance, this paper constructs a theoretical analysis framework of rural spatial governance based on the comprehensive perspective of spatial governance, discusses the internal mechanism and feasible paths of rural spatial governance in territorial spatial planning, and then realizes the theoretical and practical research of rural spatial governance. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Rural spatial governance starts from the coordination theory of human-land relations in the rural regional system. Through planning and negotiation, it realizes effective control of rural space usage, and orderly allocation of space rights. Rural spatial governance highlights the comprehensive governance process that combines "top-down" and "bottom-up" participation by multiple subjects. (2) Through the "action-efficiency-target" system, the comprehensive governance analysis framework of "matter-organization-ownership" in rural space provides an effective scheme for the construction of multiple rural spatial governance that combines rigidity and flexibility, interaction between material space and space relationship, and superposition of spatial ownership and spatial organization. (3) The rural spatial governance features of interconnecting various scales (region-village-plot) are conducive to improving the rural spatial governance system. (4) The multiple governance means, participation modes and value-sharing mechanisms of rural spatial governance are conducive to enriching the territorial spatial planning system, promoting the integration of multiple regulations, refining the control of territorial space use, and ensuring good rural governance and ecological governance. (5) Rural spatial governance uses mobilization strategies of "top-down" and "bottom-up", and creates conditions for the implementation of practical village planning and revitalization strategies through the construction of new village operation models and reconstruction of organizational mechanisms.
转型发展期“多规合一”理论认知与技术方法
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.05.001
[本文引用: 1]

中国工业化、城镇化已进入转型发展新阶段,创新驱动发展与体制机制约束的矛盾加剧,资源短缺性及其配置低效性日益凸显,“多规合一”受到各级政府和学术界的广泛关注。推进“多规合一”,创新区域规划理论与技术方法,构建中国特色的国土空间规划体系成为当前全面深化改革的重要议题之一。本文深入分析了中国“多规不一”现实问题,总结了“多规”矛盾的本质特征,探讨了“多规合一”的战略定位,构建了“三主三分”的“多规合一”基本理论框架,提出了“三步走”多规逐步调适的技术途径及其长效机制。“多规合一”的核心在于从区域空间优化的战略高度统筹协调各项规划,科学引导城乡土地优化配置,实现“多规”在空间上的同一性、在功能上的融合性、在发展过程中的协同性。“多规合一”的重点是推进形成一个总分有序、层级清晰、职能精准的区域规划体系。
Theoretical analysis and technical methods of "multiple planning integration" in the rural to urban transition period in China
国土空间规划背景下的新疆国土空间综合发展区划
Comprehensive development regionalization of territorial space in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region under the background of territorial spatial planning
论地理学的研究核心: 人地关系地域系统
The core of study of geography: Man-land relationship areal system
DOI:10.2307/140646 URL [本文引用: 1]
“人地关系地域系统”是综合研究地理格局形成与演变规律的理论基石
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
[本文引用: 2]

同近年国外人文地理学呈现人文化趋势相比,中国人文与经济地理学秉承吴传钧先生关于人文与经济地理学是研究自然圈与人文圈相互作用下、人类活动分布格局形成和演变规律的一门交叉学科的定位,形成了以不同空间尺度的地域、重要的生产生活领域、以及典型的地域空间类型的可持续发展时空规律作为研究指向的中国人文与经济地理学主流学派。吴先生提出的“人地关系地域系统”理论不仅为人文与经济地理学,而且是为整个地理学的综合研究提供了重要的理论基石。地域功能性、系统结构化、时空变异有序过程、以及人地系统效应的差异性及可调控性,是该理论的精髓,这与“未来地球”研究计划的前沿思想完全契合。近10年来,以城镇化科学模式、主体功能区划、一带一路路线图、京津冀城市群、农村空心化和精准扶贫、东北振兴与资源型城市转型、行政区划优化等为研究对象,发展了人文与经济地理重要的可持续过程、地域功能形成和综合地理格局有序化规律、城市群形成演化机理及其资源环境效应、问题地区可持续生命周期与振兴路径、地缘政治地缘经济和区域间相互作用关系、人文界线对可持续发展的影响等理论方法。人文与经济地理学科建设取得重要进展,应用成果对近年来中国生态文明建设和可持续发展产生了重要影响。中国人文与经济地理学在全球范围内发展态势最佳、总体水平领先,以此告慰吴传钧先生,并以此纪念吴传钧先生百年诞辰。
"Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction": A theoretical cornerstone for comprehensive research on formation and evolution of the geographical pattern
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
[本文引用: 2]

Compared with the increasingly obvious humanistic tendency in foreign human geography, China's human and economic geography still follows Academician Wu Chuanjun's theory, with human and economic geography as an interdisciplinary subject which is the study of the formation and evolution of the distribution pattern of human activities under the interaction of natural circle and human circle. And China's mainstream school on human and economic geography has been formed with studies on spatio-temporal rule of sustainable development on territories with different space scales, territories with important production and living, and territories with typical geospatial patterns as the main research points. "Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction", developed by Academician Wu Chuanjun, is the important theoretical foundation not only for human and economic geography, but also for the comprehensive research on geography. The essence of the theory, which includes territorial functional, system structured, orderly process for spatio-temporal variation, and the difference and controllability of human-environment interaction system effect, is entirely harmonious with the forefront of thought of the "Future Earth" studies program. In recent decade, with scientific mode of urbanization, major function oriented zoning, road map for the Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, rural hollowing and targeted poverty alleviation, revitalization of Northeast China and transformation of resource-based cities, and administrative area optimization as the main research objects, theoretical methods have been developed in the aspects of important sustainable process of human and economic geography, territorial function formation and ordering rules for comprehensive geographical pattern, formation and evolution mechanism of urban agglomeration and its resources and environmental effects, sustainable life cycle and the revitalization of the path for problem areas, the interaction between geopolitics, geo-economy and regions, and effect of cultural boundaries on sustainable development. China's human and economic geography has made great progress in discipline development, and the application results have produced profound influences on the ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in recent years. With decades of hard work, China's human and economic geography has reached a world-class advanced level, so as to console the soul and spirit of Wu Chuanjun on the occasion of commemoration of the centenary of his birth.
现代人地关系与人地系统科学
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

人地关系地域系统理论系统提出30 a来,对促进地理学综合研究、学科建设和服务国家重大战略决策发挥了重要的科学支撑与导向作用。深入解析了人地关系地域系统理论的科学内涵及时代价值,诠释了现代人地系统的类型与环境,提出了“人地圈”与人地系统科学研究的主要内容和前沿领域。初步研究表明:① 现代人地系统具有复杂性、地域性和动态性特征,人?地交互作用过程、格局及其综合效应正在发生深刻变化,地球表层人地系统成为现代地学综合研究的核心内容和重要主题。② 科学认知和有效协调人地关系,亟需深入探究人地系统耦合格局与机理,探明人地关系地域系统类型、结构及其动力机制。依据城乡关系将人地关系地域类型划分为城市地域系统、城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统。乡村地域系统可细分为农业系统、村庄系统、乡域系统、城镇系统等子系统,分别对应于作土关系、人居关系、居业关系、产城关系。③ 现代人类活动强烈地作用于地球表层人地系统,形成了人地系统耦合与交互作用的地表圈层——“人地圈”,其实质是现代人类活动与地表环境相互联系、耦合渗透而形成的自然–经济–技术综合体或人地协同体。④ 人地系统科学或人地科学是研究人地系统耦合机理、演变过程及其复杂交互效应的新型交叉学科。它是现代地理科学与地球系统科学的深度交叉和聚焦,以现代人地圈系统为对象,致力于探究人类活动改造和影响地表环境系统的状态,以及人地系统交互作用与耦合规律、人地协同体形成机理与演化过程。人地系统耦合与可持续发展是人地系统科学的研究核心。传承创新人地关系地域系统理论和发展人地系统科学,更能凸显地球表层人类的主体性、人地协同的过程性和可持续发展的战略性,为人地系统协调与可持续发展决策提供科学指导。
Modern human-earth relationship and human-earth system science
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

In the past 30 years, the theory of human-earth areal system has played an important support and guidance role in promoting the comprehensive research, disciplinary development and serving national strategic decision of geography. This study analyzes the scientific connotation and era value of human-earth areal system, explores the types and environment of modern human-earth system, and puts forward 'human-earth sphere' and the main contents and frontier fields of human-earth system science. The results show that: 1) The modern human-earth system is characterized by complexity, regionalism and dynamicity. The processes, pattern and comprehensive effect of human-earth interaction are undergoing profound changes, and the human-earth system on the surface of the earth has become the critical content and important theme of modern geosciences. 2) To scientifically understand and effectively coordinate the human-earth relationship, it is urgent to explore the coupling pattern and mechanism of human-earth relationship and to analyze the type, structure and dynamic mechanism of human-earth areal system. Based on the urban-rural relationship, the human-earth areal system can be divided into urban regional system, urban-rural integration system and rural regional system. Furthermore, the rural regional system is subdivided into agricultural system, village system, rural system and township system. 3) Modern human activities strongly affect the human-earth system on the surface of the earth, forming a new surface with the coupling and interaction between human and earth. In essence, it is a natural-economic-technological synthesis or human-earth coordination. They are also the main contents of deepening the researches on the coupling of human-earth system and supporting decision-making for coordinated development of human-earth system. 4) Human-earth system science or human-earth science is a new interdisciplinary subject which studies the coupling mechanism, evolution process and complex interaction effect of man earth system. It is the deep intersection and focus of modern geographic science and earth system science. Taking the modern human-earth sphere system as the research object, it is committed to exploring the state of human activities transforming and affecting the surface environment system, the interaction and coupling law of human-earth system, the formation mechanism and evolution process of human-earth coordination.Human-earth system coupling and sustainable development is the core of human-earth system science. Inheriting and innovating the theory of human-earth areal system and developing the human-earth system science will highlight the subjectivity of human on the earth surface, the process of human-earth coordination and the strategy of sustainable development, thus providing scientific guidance for the coordination of human-earth system and sustainable development decision-making.
基于要素视角的耕地“三生”功能理论建构与实证研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200400
[本文引用: 1]

基于要素视角考察耕地功能还处于探索阶段,并且已有的耕地功能分类体系与国家乡村振兴战略及国土空间规划体系衔接性较弱。论文通过对耕地构成要素的系统分析,界定了耕地、耕地功能及耕地生产-生活-生态功能的内涵,理论上建构了耕地“三生”功能的测评框架及分区概念模型。实证表明,南安市80%的耕地生产与生活功能以及60%的耕地生态功能为中等及以上,说明耕地利用功能强度较高。耕地生产、生活与生态功能分别在自然生产潜力与地理区位条件、耕作可达水平与耕地依赖程度、生态基底条件与生态保护政策等因素的影响下,表现出较为明显的地域趋同性。南安市耕地多功能利用水平较低且耕地开发已经危及区域生态安全,为此需要依据耕地功能分区的空间分布、组合结构及功能强度采取差异化的利用、保护与管理策略。
Theory building and empirical research of production-living-ecological function of cultivated land based on the elements
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200400
[本文引用: 1]

The rapid social and economic development led to the gradual emergence of the multi-functionality of cultivated land. However, existing studies mainly evaluate the function of cultivated land from the perspective of a single function, while the comprehensive investigation of the production-living-ecological function of cultivated land based on elements still remained in the exploratory stage. Therefore, the connotations of cultivated land, cultivated land function, and cultivated land production-living-ecological function were defined based on the systematic analysis of the cultivated land system as well as its elements, and the evaluation framework and the zoning conceptual model of the production-living-ecological function of cultivated land were theoretically constructed. The empirical results showed that the production and living functions of more than 80% of cultivated land and the ecological function of more than 60% of cultivated land were medium or above, which indicated that the degree of development and utilization of cultivated land in Nan′an City was at a high level, and there might be overlap, occupation, and agglomeration between different functions. Under the influence of natural production potential and geographical location conditions, arable land reach level and cultivated land dependence, ecological base condition and ecological protection policy, the production-living-ecological function of cultivated land showed evident regional convergence. About 50% of the cultivated land in Nan′an City had a single function, indicating that the comprehensive level of cultivated land function was still low. The area proportions of function combination models indicated that although cultivated land still provided important food security and social security, the development of cultivated land had been endangering regional ecological security. Therefore, it is necessary to take differentiated utilization, protection, and management strategies according to the spatial distribution, combination pattern, and function intensity of cultivated land functional zoning. Our study could provide theoretical and methodological support for the multifunctional utilization and management of cultivated land under the background of rural revitalization strategy and national spatial planning system construction.
(现场实录)政府工作报告
www.xinhuanet.com/politics/2020lh/2020-05/22/c_1126018545.htm . 2020-05-22.
On-site Record Government Work Report
www.xinhuanet.com/politics/2020lh/2020-05/22/c_1126018545.htm , 2020-05-22.]
An analysis of land use conflict potentials based on ecological-production-living function in the southeast coastal area of China
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 1]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the New Era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 1]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
From land cover change to land function dynamics: A major challenge to improve land characterization
DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.08.005
PMID:18809242
[本文引用: 1]

Land cover change has always had a central role in land change science. This central role is largely the result of the possibilities to map and characterize land cover based on observations and remote sensing. This paper argues that more attention should be given to land use and land functions and linkages between these. Consideration of land functions that provide a wide range of goods and services makes more integrated assessments of land change possible. The increasing attention to multifunctional land use is another incentive to develop methods to assess changes in land functions. A number of methods to quantify and map the spatial extent of land use and land functions are discussed and the implications for modeling are identified based on recent model approaches in land change science. The mixed use of land cover, land use and land function in maps and models leads to inconsistencies in land change assessments. Explicit attention to the non-linear relations between land cover, land use and land function is essential to consistently address land change. New methods to map and quantify land function dynamics will enhance our ability to understand and model land system change and adequately inform policies and planning.
基于“双评价”集成的国土空间地域功能优化分区
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190327
[本文引用: 1]

“双评价”(资源环境承载能力和国土空间开发适宜性评价)作为构建国土空间的基本战略格局、实施功能分区的科学基础,为主体功能区降尺度传导、国土空间结构优化、国土开发强度管制等提供了一系列重要参数。以地域功能理论为基础,从人地关系演化出发,探索“双评价”的理论内涵,建立“双评价”到地域功能优化分区的科学逻辑,指出“双评价”集成实现综合效益最大化时所形成的主体功能分区方案为地域功能优化分区的最优方案。以福建省、六盘水市为案例,将人类生产生活的合理需求转化为用地需求参数,通过降尺度的参数分解与测算,结合上位规划及政府与专家系统研判,确定总量控制、结构化控制、空间结构或战略格局控制等目标参数,并在“双评价”基础上,通过不断调整指标、参数及阈值,逐步进行格网单元地域功能优化。着重考虑相邻区域功能冲突与协调、差异化的主体功能定位、土地利用现状及规划、区域发展战略格局以及海陆统筹等区域特征,不断校核与优化。从数据的可获取性、数据集满足理论模型及评估方法的适应程度、可使用的分析方法及模型的不确定性以及尺度效应等方面,探讨功能分区方案不确定性及其解决途径,增强优化结果的鲁棒性,以此作为“三区三线”划定等国土空间规划的科学基础。
Territorial function optimization regionalization based on the integration of "Double Evaluation"
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190327
[本文引用: 1]

As the scientific basis for constructing the basic strategic structures of territorial land space and implementing functional zoning, the "Double Evaluation" (i.e. resources and environmental carrying capacity and territorial development suitability evaluation) provides a series of important parameters for the downscaling of the major function zoning, the optimization of the spatial structure, and the intensity control of the land development. Based on territorial function theory, this paper explores the theoretical connotation of "Double Evaluation" from the evolution of human-land relationship, establishes the scientific logic of "Double Evaluation" to territorial function optimization, and points out that the major function regionalization scheme from "Double Evaluation" comprehensive integration that realizes the comprehensive benefit maximization is the optimal result of territorial function optimization. Taking Fujian province and Liupanshui city as two cases, we transform the rational demand of human production and living activities into the demand control parameters of land use. Combined with the superior planning and the government and expert system, we determine the critical target parameters, including the total control parameters, structural control parameters, spatial structure or strategic pattern control parameters, through the parameter decomposition and measurement of downscaling. By adjusting the indicators, parameters and thresholds, the gird cell territorial function optimization is continuously carried out, and the grid cell territorial function optimization regionalization schemes under different scenarios is obtained. Then continuous evaluation, check and optimization are carried out by the comparison with the planning of major function zones, land use status, neighboring areas, the construction needs of regional development and spatial strategy, as well as the relationship between land and sea. Given the influence of the uncertainty of available data, the adaptability of the data set to the theoretical model, the uncertainty of a usable analytical model and the scale effect, the uncertainty of the major function regionalization scheme and its solution are discussed to enhance the robustness of the optimization results as the scientific basis for territorial planning such as the "Three Zones and Three Lines" (Three Zones represent ecological space, agricultural space, and urban space; Three Lines represent ecological conservation redline, permanent capital farmland, and urban development boundary).
国土空间规划中的承载力反思: 概念、理论与实践
Carrying capacity reconsidered in spatial planning: Concepts, methods and applications
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20191005 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国国土空间用途管制的基础性问题思考
Rethinking on the basic issues of territorial and spatial use control in China
天水市国土空间功能区划与未来空间发展格局: 基于主体功能区划框架
The functional zoning of territorial space and the developmental pattern of future space: Based on the framework of the major function-oriented zoning
Urban encroachment, forest regrowth and land-use institutions: Does zoning matter
?.DOI:10.1016/j.landusepol.2009.06.007 URL [本文引用: 1]
地域功能—结构的空间组织途径: 对国土空间规划实施主体功能区战略的讨论
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190865
[本文引用: 1]

地域功能-结构的空间组织规律是人地系统耦合研究的基本理论问题,也是开展国土空间规划、塑造可持续地理格局的基础理论。从地理学对地理过程的重复、预测、调控、优化的讨论入手,阐释了空间治理体系是现代地理学用于调控和优化可持续地理过程与格局的重要途径。采用生态-生活-生产等三生空间构成的地域功能空间结构呈现的时空演变特征,表达了地域功能-结构的空间有序性法则,阐释了地域功能与自然地理环境相协调、同一地域单元各类功能及不同单元之间冲突最小化、地域功能在不同空间尺度有效传导、以及长时间尺度综合效益最大化等空间组织目标。从可持续性出发,建立自然要素的资源、环境、生态和灾害四大属性的概念,并通过四大属性集成构成自然承载力,分析承载力的原值、余量和潜力在空间规划中的作用,形成自下而上解析空间组织的基本方法。从新空间均衡出发,基于承载力、融入位置和空间结构参量后构成的地域功能适宜性,形成自上而下解析空间组织的基本方法。进而讨论了集成两种方法形成的主体功能区具备的对空间组织与规划的基础价值和战略价值,提出主体功能区的区划、战略、制度和规划用途分离及相互关联的新思路。以实施主体功能区战略为主线、以空间降尺度传导主体功能为核心科学问题、以关键约束参数为空间结构控制性指标,讨论了数据库与地域功能谱系、功能和尺度依赖的承载力评价方法与模型库、“三区三线”的建构框架,论证了空间规划实施主体功能区战略的途径,提出地理学应着力加强大、中空间尺度(区域性)国土空间规划基础理论和方法、强化技术等科技支撑体系建设的建议。
Spatial organization pathway for territorial function-structure: Discussion on implementation of major function zoning strategy in territorial spatial planning
中国县级“三生用地”分类体系的理论构建与实证分析
A classification systems of production-living-ecological land on the county level: Theory building and empirical research
城乡规划编制中的“三生空间”划定思考
Reflections on delimiting the three basic spaces in the compilation of urban and rural plans
空间生产视角下的旅游地空间研究范式转型: 基于空间涌现性的空间研究新范式
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2015.01.47
[本文引用: 1]

面对中国经济、社会转型的实践背景和地理学“文化转向”、社会学“空间转向”的理论背景,空间生产为旅游地空间研究提供了新的重要视角,推动着旅游地空间研究范式的转型。在认识旅游地空间系统性的基础上,界定了空间涌现性的概念,提出了空间生产视角下的旅游地空间研究新范式。这一新范式主要表现在:① 新的空间研究视角,厘清旅游地空间生产研究的理论逻辑和学科理路;② 新的空间观,树立以内涵复杂性、尺度嵌套性、过程非守恒性为核心特征的新的旅游地涌现空间观,实现空间认识从要素到系统、从简单环境系统到过程系统再到复杂耦合系统的转变;③ 新的空间研究路径,更加注重社会空间、微观解构、尺度转换;④ 新的空间研究框架,遵循“过程-格局-机制”的研究路线,建立复杂系统涌现空间研究框架,开展多尺度、多类型旅游地空间生产的系统研究。空间生产视角下的旅游地空间研究范式转型,将有助于拓展旅游地理学研究视角和范式,增强旅游地理学对中国旅游发展实践的响应和指导。
The paradigm transformation of space in tourism destination from perspective of production of space: A new paradigm of space based on emergence of space
生态系统服务权衡与集成方法
DOI:10.18402/resci.2016.01.01
[本文引用: 1]

生态系统服务是人类从生态系统中所获得的各种的惠益,自20世纪90年代提出后在国际上迅速成为生态学、地理学和环境科学等领域的研究前沿热点。联合国大会于2012年正式批准生物多样性与生态系统服务政府间科学政策平台(IPBES)建设,制定概念框架,确定近期研究主要任务包括三项快速的评估和两项政策决策性的评估。本文探索了生态系统服务权衡及区域集成方法,并以黄土高原地区为例进行了应用。研究结果表明,土地利用变化与土壤保持、碳固定具有正效应,与产水量间存在负效应;粮食生产能力与农业生产条件改善、人工投入增加和技术进步密切相关。生态系统服务之间的消长和权衡具有尺度依赖性,植被恢复的区域适宜性评价及水分效应方面还需要进一步研究。
Trade-off analyses and synthetic integrated method of multiple ecosystem services
DOI:10.18402/resci.2016.01.01
[本文引用: 1]

:Ecosystem services are the benefits that people obtain from ecosystems. Research on ecosystem services has been a hotpot in the fields of ecology, geography and environmental sciences since 1990s. Towards a better understanding of ecosystem services and a strengthened linkage between science and policy, Intergovernmental Platform for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) was established officially by the United Nations General Assembly in 2012. To date, IPBES has built a conceptual framework for assessment of ecosystem services, and determined the main tasks, including three rapid assessments and two assessments for policy decision. To provide insights into the main tasks, we synthesized trade-off analyses and synthetic integrated method of multiple ecosystem services, and took the Loess Plateau as a case to identify the potential and effectiveness of the above method. The results showed that there was a positive relationship between land use and soil conservation, carbon sequestration, while there was a negative relationship between land use and water yield. In addition, the grain productive capacity was closely related to agricultural production condition, artificial input and technical progress. As trade-off and synergy among the multiple ecosystem services are scale-dependent, more research should be carried out in the aspects of regional suitability assessment of vegetation restoration and water effect.
Quantitative identification and spatial analysis of land use ecological-production-living functions in rural areas on China's southeast coast
中国土地利用碳排放的研究误区和未来趋向
Misunderstandings and future trends of researches on land use carbon emissions in China
基于耗散结构系统熵模型的乡村生产空间系统有序性研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020170933
[本文引用: 1]

通过分析乡村生产空间系统的耗散结构特征,建立系统熵模型,运用关联熵和运行熵,从系统的主体(多元主体)、客体(地)和环境三要素入手构建指标体系,讨论系统内部结构和运行状态的有序性,并以重庆市合川区龙市镇为研究区予以实证,研究表明:研究区乡村生产空间系统关联熵先增后减,系统内部结构有序性呈现阶段性特征,2008—2011年主要受城市化无序扩张和土地利用方式低效粗放等因素影响,系统内部结构趋于混乱无序,2011—2015年主要因财政支农力度增强、农业投入产出水平提高、生态修复力度加大等因素刺激,系统内部结构逐渐趋于有序化;2008—2015年,乡村生产空间系统运行熵逐年减小,在农业综合开发投入大幅增加引起的生产条件改善、产业结构调整与提档升级等驱动下,呈现出持续有序化的发展态势;围绕乡村生产空间系统的内部结构及运行状态的演化规律,从优化土地利用结构、构建现代农业产业体系、编制和完善相关规划、培育新产业新业态入手,提出相关策略,以促进乡村生产空间系统有序健康发展。
Research on the order of rural production space system based on a system entropy model in the dissipative structure
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020170933
[本文引用: 1]

By analyzing the dissipative structure characteristics of rural production space system, and establishing system entropy model using correlation entropy and running entropy, this study establishes an index system following three elements: the subjects of rural production space system (the multiple subjects), the objects (the land), and the environment. Then, taking Longshi Town in Hechuan district in Chongqing as an example, this study discusses the order of internal structure and the order of running state of rural production space system. The results show the following aspects. The correlation entropy of the rural production space system of the study area increased first and then decreased, with its internal structure presenting a periodic characteristic from disordering to ordering. From 2008 to 2011, the system internal structure tended to be chaotic and disordered, resulting in irregular urban expansion and extensive land use. From 2011 to 2015, driven by the strengthened financial support to agriculture, the improvement of agricultural input-output level, the enhancement of ecological restoration and so on, the system internal structure gradually entered the stage of orderly development. From 2008 to 2015, the running entropy of rural production space system decreased year by year, which showed a law of continuous ordering. This phenomenon is attributed to the industrial structure adjustment as well as the production conditions improvement brought by the substantially increased investment of comprehensive agricultural development. Therefore, centering on the evolution law of the internal structure and running state of rural production space system, this study puts forward strategies from the land use structure optimization, the modern agricultural industry system construction, the planning preparing and perfection, and the rise of new industries and new types of business. Hereby, rural production space system is expected to develop towards orderly and healthy way.
Urban green infrastructure and ecosystem services in sub-Saharan Africa
DOI:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.06.001 URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatial governance and planning systems in the public control of spatial development: A European typology
DOI:10.1080/09654313.2020.1726295 URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatial planning for multifunctional green infrastructure: Growing resilience in Detroit
DOI:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.10.005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Tradeoffs between agricultural production and ecosystem services: A case study in Zhangye, Northwest China
The Belt and Road Initiative: A Pathway Towards Inclusive Globalization
基于位置大数据的村域尺度多功能性评价: 以苏州市为例
Evaluation of multifunctionality on village scale using location-based big data: A case study of Suzhou
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210311 URL [本文引用: 1]