自然资源是地球系统过程与全球变化的重要组分,同时是社会经济发展的主要生产要素[1]。生态文明、高质量发展、国家治理与国家安全的新时代特征对自然资源管理提出新要求[2],要从技术创新与制度创新两方面不断加强对国家资源战略的保障能力,自然资源研究理论与创新是其关键基础[3]。2018年党中央国务院以原国土资源部为主体组建了自然资源部,从实质上推动了资源由分类管理向综合管理转变。同年9月,土地科学首次纳入香山科学研讨会,会上达成土地科学香山共识,建议将土地科技创新纳入国家科技计划重点研究。在自然资源专业学科建设上,中国自然资源学会等一直致力推动构建本科—硕士—博士完整的资源科学人才培养体系,推动形成以资源利用保护为核心的多学科交叉融合研究领域,初步划分了其学科体系,同时新时代自然资源管理重大变革为科学研究带来新发展机会[1,4],学科专业综合建设蓄势待发。国家自然科学基金是中国基础研究资助的主渠道,服务国家重大战略需求与支撑学科建设是国家自然科学基金的使命之一[5]。鉴于上述自然资源管理的重大实践与研究变革,在国家自然科学基金委员会(以下简称“基金委”)新一轮改革战略指导下,地理科学学科深入落实地球科学部“四梁八柱”战略布局,深刻把握国家重大战略需求与学科交叉融合的科学创新趋势,审时度势,在广泛调研征求科学家意见基础上,于2020年对学科布局进行优化调整。新一版申请代码取消了三级代码,按自然地理学、人文地理学与信息地理学三个分支学科设置了17个二级代码,减少代码层次,增加管理幅度,通过扁平化方式打通相近学科壁垒。其中,地理科学学科整合了2019版申请代码中D010401水资源与流域管理、D010402土地资源与土地系统、D010403自然资源评价和D010404自然资源利用与规划4个与自然资源管理有关的三级代码,统一为新版的二级申请代码“D0111土地科学和自然资源管理”[6]。
国家自然科学基金代表该领域的基础研究前沿,是申请者学术创新的集聚输出,是学术前沿风向标,在科学界有较高声誉,极受科研工作者关注。“D0111土地科学和自然资源管理”申请代码的设置顺应了交叉融合的科学创新趋势,体现了地理科学服务国家自然资源管理战略的担当。该申请代码强调地理科学的前沿发展和国家需求,将“土地科学”和“自然资源管理”并重,重点支持土地要素结构与功能时空变化、土地系统运行规律与调控、人地关系地域系统中自然要素与人文要素耦合过程机理,以及土地资源、水资源、生物资源、矿产资源与各类能源的评价、利用与规划,交叉融合特征明显。该申请代码设立两年来,已对该领域发展起到了引领作用。为帮助申请者进一步了解申请代码设置初衷、申报资助状况和研究主题热点,本文分析2019年以来D0111申请代码下项目申报与资助状况,分析项目申报与资助格局,阐述不同研究方向热点,旨在基于研究现状提出该申请代码的战略发展方向,更好地服务于国家社会经济与科技战略需求。
1 研究方向划分
作为典型交叉领域,国家自然科学基金D0111申请代码下研究内容多样,涉及自然科学、工程技术与社会经济等不同学科。如,以耕地为对象的研究,内容既可以耕地的理化属性等自然要素为主,又可以耕地产权与治理政策等人文要素为主,而要素属性不同,研究方法与范式差别极大。为进一步整体梳理认知该申请代码领域的具体内容,本文考虑了自然资源的多样性及研究性质差异,按照研究对象和研究要素性质两个维度(表1)细化分析研究方向。
表1 土地科学和自然资源管理领域研究方向划分
Table 1
| 研究对象 | 研究要素性质 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然要素为主N | 自然人文要素交叉C | 人文要素为主S | ||
| 生态资源E | 生态过程与环境效应E-N | 生态评价与权衡优化E-C | 价值核算与社会治理E-S | |
| 土地资源L | 土壤LS | 土壤组分与功能效应LS-N | 质量因素与过程管理LS-C | —— |
| 农用地LA | 农用地系统生态效应LA-N | 利用转型与结构布局LA-C | 土地流转与农户生计LA-S | |
| 建设用地LU | 生态扰动与污染修复LU-N | 时空变化与转型优化LU-C | 市场效率与政策制度LU-S | |
| 土地系统LY | 生态扰动与环境效应LY-N | 系统转型与优化调控LY-C | 运行效率与空间治理LY-S | |
| 水资源W | 资源质量与水文过程W-N | 预测评价与优化配置W-C | 主体行为与水权制度W-S | |
| 矿产和能源资源M | 矿物与能源形成机理M-N | 矿产能源评价与优化M-C | 资源管理与资源政策M-S | |
| 生物资源B | 生物量测算生态效应B-N | 资源分布与价值评价B-C | 产权治理与政策创新B-S | |
分类是自然资源管理的根本前提,但由于涉及学理、法理与管理多个层面,自然资源标准分类体系未形成[7,8],虽然有自然资源部、中国自然资源学会等,出版了《中国资源科学百科全书》等,但自然资源标准分类体系需继续整合创新。在国家自然科学基金D0111申请代码论证设立时,科学家对研究对象进行初步划分。综合上述不同方面,本文把D0111申请代码研究对象划分为生态资源(E)、土地资源(L)、水资源(W)、矿产和能源资源(M)、生物资源(B),其中土地资源(L)可细化为土壤(LS)、农用地(LA)、建设用地(LU)和土地利用系统(LY)。研究要素性质主要涉及自然要素为主(N)、自然人文要素交叉(C)和人文要素为主(S)三方面。研究性质上分为三类:自然要素体现对资源本底研究,自然人文要素交叉主要涉及对资源评价、规划与保护等利用活动研究,人文要素主要包括对资源管理的研究。因此,表1横行可以分类统计该申请代码下不同研究对象的项目申报资助数量,通过纵列可分析该领域研究是以交叉为主,或偏向人文要素抑或偏向自然要素研究,两两交叉得到不同研究方向细类,这种分类兼顾了研究对象与要素性质,对透视申报资助状况提供框架基础,可以全面审视该领域研究项目格局。要说明的是对象为土壤资源时,其本身属于自然要素,不存在其人文属性治理研究,关于测土配方施肥与土壤变化社会经济因素等则归并为交叉类研究。
2 申报资助格局与研究热点
2.1 申报格局分析
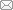
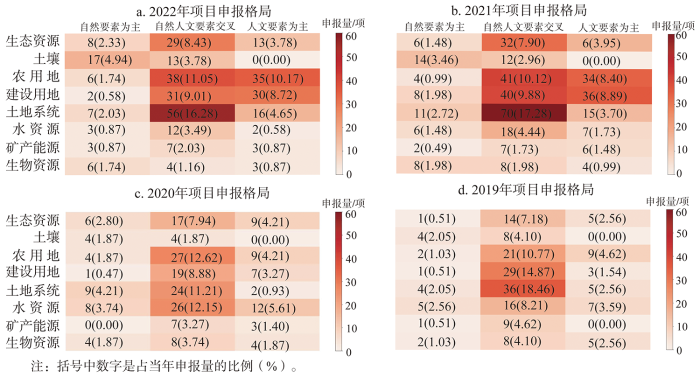
基于以上分类框架,对2019—2020年D010401-D010404和2021—2022年D0111申请代码下面上项目、青年科学基金项目与地区科学基金项目(以下简称“面青地”项目)进行统计(图1)。从申报数量来看,2019—2022年面青地项目申报数量分别为195项、214项、405项与344项。从研究要素属性来看,自然人文要素交叉类研究项目占50%以上,表明该申请代码交叉融合特征显著,是地理科学自然与人文要素研究的重要交汇领域和交叉融合创新的主要方向[9]。此外,2021年与2022年中,人文要素为主研究的申报项目占比分别为29.14%与29.65%,而自然要素为主的项目占比仅约为14%~15%。从研究性质上看,该申请代码虽以交叉融合研究为主,但更偏向人文要素,因此基金委在地理学科三大分支学科框架下把其划为人文地理学分支学科[10]。其中,2021年以土地资源为研究对象的项目占70.37%,生态资源研究占14.53%,其他自然资源研究占比未超过10%;2022年以土地资源为研究对象的申报项目占比进一步提升,达到72.97%,表明当前该申请代码下土地科学研究占主要部分,与当初“土地科学与自然资源管理并重”[10]的初衷理念有一定差距。
图1
图1
2019—2022年D0111申请代码不同研究方向申报格局
Fig. 1
The distributed pattern of projects application of different research interests within the code of D0111 in 2019-2022
2022年,以土地资源为研究对象的项目中,土壤类30项,占总数的8.72%,其中以自然要素为主的17项,自然人文综合项目13项,因为土壤本身属于自然要素,多以自然与交叉研究为主;农用地研究79项,占比最高,为22.97%,且以交叉与人文社科研究为主,为38项。农业是基础产业,农用地与全局土地利用变化密切相关,关系着中国的粮食安全与生态环境权衡。乡村振兴战略背景下,国家对农业与农用地极为重视,在基金申请层面,耕地保护与种植结构调整项目申报数量增加明显。建设用地是社会经济发展载体,是土地利用变化最为突出的用地类型,是土地系统优化调控的关键。建设用地扩张不仅对地球地表层运行产生扰动,影响关键生态与水文过程[11],且在社会经济领域,农村宅基地改革与建设用地指标配置是资源管理核心,其优化配置更决定区域发展公平性[12],因此一直是研究与申报重点。以建设用地为对象的研究中,交叉类研究占9.01%,人文要素为主类的研究占8.72%,占比相对较高,而自然要素为主的研究占比仅为0.58%,其人文社科属性较突出。土地利用变化作为一个整体,不同用地类型间是此消彼长关系。学术界历来重视土地系统、土地利用变化与国土空间优化等主题研究,国土空间规划、土地调查评价、土地冲突权衡等都属于该领域核心议题,以土地系统为对象的研究保持较高占比,一直是申报重点。在具体研究中,主要以自然和人文要素的交叉研究为主,即土地系统模拟优化、土地利用变化的综合效应等,而单纯涉及自然环境效应或国土空间治理研究的项目申报相对少。研究对象为生态资源的申报项目占14.54%,资源问题与环境问题密不可分,资源开发往往带来环境问题,加之生态资源具有“点多面广”的特点,交叉类研究方向最多,占8.43%,而以自然要素为主和与人文要素为主的研究分别占2.33%和3.78%。以水资源为对象的研究占比为4.94%。水资源是关键的自然资源,而自然资源是一个泛称概念,D0111申请代码中把水资源纳入自然资源范畴,强调水资源的管理调控。此外,矿产能源方面研究仅占3%~4%,生物资源占3%~4%,其自然属性类研究相对突出。
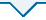
2021年申请代码调整以来,“D0111土地科学和自然资源管理”申请代码下,以土地资源为主题的研究约占70%,显著高于申请代码调整之前50%~60%的比例,可见,申请代码设立使土地资源类申报项目占比提升10多个百分点。对比前后,农用地、建设用地与水资源领域的申报情况变化较大。其中,农用地由2019年的16.41%增长到2022年的22.97%,这与现阶段国内外新形势下,粮食与农业现代化问题突出,农业与耕地重要性日益凸显有关。建设用地研究由2019年的16.92%增加至2022年的18.31%,增长幅度虽不大,但深刻改变了其研究性质,2019年建设用地的以人文要素为主的研究仅占1.54%,而2022年这一方向为8.72%,表明更多建设用地研究开始转向人文要素视角,或其他经济管理学科相关研究逐渐进入该申请代码。水资源研究则由14.36%减少至4.94%,水资源研究专业性较强,由于专门资源类型有其自身申报代码,部分资源管理相关研究都转投各自相应申请代码,如有些申报了D0102水文学和气候学代码。除此之外其他研究方向申报格局改变不大。可见,新申请代码汇聚了原来分散在其他学科与部门的相关申报项目,通过交叉融合改变了研究方向格局,进而塑造学科内力。
2.2 资助格局分析
2021年与2022年D0111申请代码下共资助面青地项目74项与66项,资助率为18.3%与19.19%。由于样本数有限,不同研究方向资助率有一些不确定性,但总体存在一些普遍性规律(表2、表3)。首先,土地资源研究类项目资助数量最多,2021年与2022年分别为55与56项,占比为74%与85%,这说明该申请代码不管从申报还是资助格局上,都以土地科学占主导,其他自然资源申报量在减少,且资助率不稳定,这不利于研究的多样性和创新性,更不符合当初设定初衷,比如2022年水资源研究仅资助1项,而生物资源0项。其次,从学科代码改革后,该申请代码下人文要素研究占比在增加,人文类资助率随申报量增加而在增加,2021年自然要素为主的研究资助率为25.42%,人文要素为主的研究资助率为14.41%,而到2022年出现反转。再次,土地资源中农用地、建设用地与土地系统项目资助数量占比高,资助数量与资助率比较稳定,其中2022年农用地研究项目占36.4%,而申报项目只占总数的30%。
表2 2021年D0111申请代码下不同研究方向资助格局
Table 2
| 研究对象 | 研究要素性质 | 合计 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然要素为主 | 自然人文要素交叉 | 人文要素为主 | ||
| 生态资源 | 1(16.67) | 6(18.75) | 1(6.25) | 8(14.81) |
| 土壤 | 4(28.57) | 3(25) | — | 7(26.92) |
| 农用地 | 1(25) | 9(21.95) | 6(17.65) | 16(20.25) |
| 建设用地 | 3(37.5) | 5(12.5) | 4(11.11) | 12(14.29) |
| 土地系统 | 1(9.09) | 17(24.29) | 2(13.33) | 20(20.83) |
| 水资源 | 1(16.67) | 2(11.11) | 1(14.29) | 4(12.9) |
| 矿产能源 | 1(50) | 0(0) | 2(33.33) | 3(20) |
| 生物资源 | 3(37.5) | 0(0) | 1(25) | 4(20) |
| 合计 | 15(25.42) | 42(18.42) | 17(14.41) | 74(18.27) |
注:括号中为资助率(%),下同。
表3 2022年D0111申请代码下不同研究方向资助格局
Table 3
| 研究对象 | 研究要素性质 | 合计 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然要素为主 | 自然人文要素交叉 | 人文要素为主 | ||
| 生态资源 | 1(12.5) | 3(10.34) | 2(15.38) | 6(12) |
| 土壤 | 4(23.53) | 1(7.69) | — | 5(16.67) |
| 农用地 | 3(50) | 13(34.21) | 8(22.86) | 24(30.38) |
| 建设用地 | 0(0) | 7(22.58) | 7(23.33) | 14(22.22) |
| 土地系统 | 0(0) | 10(17.86) | 3(18.75) | 13(16.46) |
| 水资源 | 0(0) | 1(8.33) | 0(0) | 1(5.88) |
| 矿产能源 | 0(0) | 2(28.57) | 1(33.33) | 3(23.08) |
| 生物资源 | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) |
| 合计 | 8(15.38) | 37(19.47) | 21(20.59) | 66(19.19) |
D0111申请代码有效汇聚有关自然资源管理领域研究者,已凝聚合力推动研究进步,服务了国家自然管理需求与支撑学科建设。但由于申请代码设置时间短,目前以数量融合为主,且该申请代码下的项目来自于不同学科领域,研究范式与方法相互之间差别较大,缺乏根基理论与主导学科支持,需要进一步融合释放创新潜力。此外,该领域服务国家社会需求的应用研究与国家自然科学基金支持的基础研究之间差异需要更好的切入点来破解,如何基于需求问题导向凝练背后科学问题,促进基础研究走向应用亟需重视。通过分析发现,该申请代码下土地科学项目无论申报量还是资助量都占绝对主导,其他自然资源管理研究很少,与当初设定初衷有一定偏差,这可能因为土地科学在教育部目录有相应学科支持,已培育一定科研力量且能有效聚集,而自然资源由于其本身综合性与研究对象分散独立性,不能有效汇聚各类自然资源研究,因此如何构建地理学视角下自然资源管理学科框架,阐明科学内涵,确立研究边界与研究范式,以汇聚各类自然资源管理研究项目,使在该申请代码下土地科学和自然资源管理研究相得益彰,齐头并进,是期待解决的问题。
2.3 研究热点透视
研究热点是指申报项目比较热衷的主题,透视研究热点可以把握各领域研究现状。要明确的是研究热点并不直接对应研究前沿,研究热点除遵循学术逻辑外,还受国家自然资源管理政策等影响。根据2019—2022年“D0111土地科学和自然资源管理”申请代码下1158项面青地申报项目统计,具体方向和主要热点如下:
(1)研究对象是生态资源时,以自然要素为主的研究关注气候变化影响下关键生态过程的变化与响应,方法上以自然观测与实验为主,偏向传统生态学研究,研究热点包括放牧、采矿与基础设施建设等人类活动对生态系统碳氮循环、水文过程、极端气候与其他方面的生态扰动效应;自然人文交叉的研究包括生态系统功能评价、生态安全风险评价与优化调控等,尺度主要集中在中宏观尺度,是典型的自然要素与人文要素的耦合研究。研究热点是生态系统服务的权衡与优化、生态风险与安全评价、恢复力评价、景观格局优化等;以人文要素为主的研究则多关注生态社会化治理,比如多主体治理与价值评估等,把生态作为公共物品寻求治理路径模式,研究热点是生态产品价值实现、自然资本核算与各类保护地治理等。
(2)研究对象是土壤时,以自然要素为主的研究探讨土地利用活动对土壤微生物、有机质与土壤污染等土壤理化属性和空间分异的影响,与土壤学、生态学有深度交叉,方法以田野采样加实验分析为主,研究热点是土壤碳排放、土壤有机质等土壤理化性质与功能;自然人文交叉的研究主要从土壤视角研究耕地质量,比如耕地质量检测与评价、耕地健康诊断等,涉及土壤组分与社会经济能力需求等因素,热点是以土壤为主导因素的耕地质量监测与时空变化,要素交叉性明显。
(3)研究对象是农用地时,以自然要素为主的研究主要包括农用地系统关键元素循环、气候变化与水土效应,偏向农业资源与环境领域,实验观测是其主要研究方法,热点是农业种植的生态环境效应,比如对土壤环境、水文过程与主要元素循环的影响;自然人文交叉的研究方向主要有两方面,一是耕地资源数量、质量与功能转型机制、过程与相应生态社会经济效应,手段主要是基于自然信息与社会经济数据的综合应用。二是研究种植结构地域分布与变化,揭示农地系统要素结构变化规律,从大农业系统视角揭示转型期不同用地的变化,交叉特色明显。研究热点是耕地多功能转型机理与权衡、自然与社会经济条件对耕地可持续利用影响机制、耕地非粮化格局机制效应与监测,种植结构变化的影响因素、农用地系统生态保护与粮食安全权衡、农地系统要素结构与运行机制等;以人文要素为主的研究以耕地政策与产权流转为主,此外还包括农业农村政策,如基于农业主体的农业生态系统治理与农户生计转型等,研究范式上与经济学和管理学相近,研究热点包括农用地流转、农户生计变化的环境效应、非粮化管制与耕地保护政策等。
(4)研究对象是建设用地时,以自然要素为主的研究主要在一手观测数据支撑下,探究建设用地的生态环境扰动与污染治理等,偏向自然科学与工程技术。热点为城市污染土地修复与城市热效应模拟;自然人文交叉的研究则涵盖城镇扩张与更新、建设用地结构变化与农村宅基地的时空变化、转型机理与优化调控等,需要社会经济数据与空间数据,注重空间分析,热点是宅基地转型与乡村重构、基于空间网络的城市群土地利用模拟与效应、城市更新,相比于城市扩张,更注重城市内部用地细类研究,比如工业用地、城市绿地与城市空地等;以人文要素为主的研究主要探索城乡建设用地制度政策,比如土地财政与宅基地流转等,热点是宅基地流转与制度创新、城乡建设用地市场、多尺度城市土地资源错配与纠错机制。
(5)研究对象是土地系统整体时,以自然要素为主的研究主要涉及土地利用系统变化的生态环境效应与关键过程扰动,方法上偏向实验观测与高精度大数据信息监测,热点为典型区域土地利用变化的关键生态效应,如沙地土地利用变化对地下水影响,流域土地利用对水质影响等;自然人文交叉的研究是对土地利用系统中数量与空间变化的分析与优化调控,土地功能权衡、冲突处理、空间规划等都归属该类研究,要素同样有自然和人文综合属性,方法上尤其需要信息地理技术的支持,热点是多功能与国土空间优化配置,尤其关注三生空间、生态文明与高质量发展导向下的国土空间优化研究;以人文要素为主的研究主要包括国土空间治理体系、效率与公平性,是经济与社会理论在土地系统治理中的创新应用,热点是研究资源配置视角下的空间治理机制与路径,聚焦空间治理。
(6)研究对象是水资源时,以自然要素为主的研究主要剖析灌溉信息、水文过程与水质特征,偏向水文学与水资源学领域,方法以实验观测为主,热点是资源利用的水文过程与效应;自然人文交叉的研究主要包括水资源供需评价与优化调控,如农业、工业与生活用水预测,水—土—能—粮耦合研究等,既涉及水资源自然禀赋与时空变化,也涵盖社会经济技术约束下的水资源利用供需评价等,热点是水土资源匹配耦合、不同部门用地预测、水资源规划评价、优化配置研究;以人文要素为主的研究则主要探讨水资源的多主体治理、水资源评价与政策,热点是资源政策绩效评价、水资源多主体治理等。但由于该方向申报量小,透视热点代表性有限。
(7)研究对象是矿产与能源资源时,以自然要素为主的研究主要是矿产与能源产生机制与环境效应,科学问题偏向微观,热点是矿产资源成矿机理与生物质能源的资源环境效应;自然人文交叉的研究主要是各类矿产与能源,如风能、水电等的空间分异、效率测度与优化配置,为资源管理提供直接依据,其自然与社会科学属性交叉明显,热点是基于供需视角的风能、电能等新能源的空间优化配置;而以人文要素为主的研究主要针对矿产能源的地理空间交易与战略政策,探究矿产能源国家主体性下的宏观政策。
(8)研究对象是生物资源时,以自然要素为主的研究主要讨论林草动植物资源与关键生态过程的互馈影响,偏向植物学与林学,热点是生物资源的生态效应,比如森林碳氮效应;自然人文交叉的研究主要是资源的空间适宜性评价与价值评价并解释其时空演变规律,热点是动植物资源空间适宜性评价;而以人文要素为主的研究涉及动植物资源的产权、社区共管等治理政策研究,热点是草地治理。
3 自然资源管理领域发展展望
国家自然科学基金是科学工作者、基金管理者与评审专家构建共同体的载体,需要共同体群策群力[13],才能使基金事业行稳致远,其中申请代码领域的研究方向、范式等要共同体集思广益,共同推动研究领域发展。基于对D0111领域申报资助格局与研究热点分析,为使该研究领域发展壮大,占领科学高地,应从自身角色出发在以下几方面加强建设。
(1)指出基础研究是整个科学体系源头,是所有技术问题的总机关,加强基础研究是科技自立自强的必然要求。《国家自然科学基金条例》规定,支持基础研究是国家自然科学基金的任务使命,这是国家对国家自然科学基金的战略定位,并非支持全部类型研究。目前,国家自然科学基金实行板块管理架构,把9大学部划分为4大板块,即基础科学板块、技术科学板块、生命与医学板块和交叉融合板块[14]。其中,地球科学部归属基础科学板块。地理科学学科下属的“D0111土地科学和自然资源管理”领域,有较强应用性,旨在服务国家重大需求与经济主战场,但其选题要体现问题背后的基础科学属性与地理科学本性,从地理科学视角出发,以基础科学问题为导向继承创新地理科学研究范式,基于交叉素材提出新理论,丰富地理科学的研究内容,对地理科学发展建设做出时代贡献[15]。如果该申请代码下各领域相关研究简单杂糅混合,缺乏学科指引,不挖掘现实需求背后的科学问题,则不能形成合力,更可能弱化地理科学色彩。
(2)坚持申请代码设置的科学初衷内涵。研究多样性是学科发展的生命力,尤其对“D0111土地科学和自然资源管理”这样一个以交叉融合创新而设置的申请代码,其不仅支持土地科学问题,同样支持自然资源管理方面研究,应特别重视两方面研究协同并进,相互支持,持续发展。经上述分析发现,现有申请中土地科学项目已经超过70%,自然资源管理相关项目持续减少。目前,土地研究在正式学科目录中已有对应学科,而资源管理学科尚在论证阶段,尚未形成凝聚力。自然资源是个综合概念,如果没有正式学科统一凝聚,其研究势必不能深入。而自然资源管理系统化、专业化、复杂化的内在性质又迫切需要学科专业提供服务支持,因此,建议本学科领军人才和团队积极推动自然资源学科建设,明确其基础理论、研究对象与研究范式,整合人才队伍,服务于新时代国家自然资源管理的重大需求[16]。此外,还要防止该申请代码研究格局出现“马太效应”,某几个研究方向越做越大,其他研究方向逐渐失去信心而退出,这样会导致研究多样性损失,不利于融合创新。
(3)高质量交叉融合促进学科创新发展。交叉融合是大科学时代科学研究的重要特征,是科技创新重要来源,是推进科技创新治理体系的路径之一[17]。2021年,基金委成立交叉科学学部,国务院学位委员会设立第14个学科门类——交叉学科,全国各类高校和科研院所陆续成立交叉研究院,制度体系日臻完善。但交叉融合不是简单机械叠加,而是来自科学研究的内生需求。自然资源是典型交叉研究领域[18],作为最具交叉属性的分支代码,D0111肩负着探索地理科学高质量交叉融合的重任,需要界定自然要素与社会经济要素的交叉关系,判别其是天然形成还是人为交叉,主要通过多学科内容、模式与路径的深度探索,回答两个问题:一是科学问题是否具有交叉性,自然资源的可持续利用是开发、使用、保护与管理的全链条问题。人地系统理论认为社会经济发展通过调控对资源环境进行优化配置,而资源环境利用变化深受社会经济影响,两者密不可分[19]。二是问题解决方式是否有交叉性,要判别研究视角与方式是否有交叉性,比如地理信息技术在历史资源保护应用,基于生物行为的城市扩张边界模拟等。
(4)创新研究范式服务地理科学学科建设。研究范式变革是自然科学基金改革的主要抓手,每个学科都存在不同范式。从近现代地理学150年左右的发展历史看,地理科学既要守正又要创新,服务现实需求,拥抱时代主流。区域分析是地理科学安身立命、不同于其他学科的研究范式。20世纪五十年代以来,计量革命从科学性层面加速了地理科学与主流科学研究范式接轨,进入后现代主义时期,人本主义、马克思主义等各类地理学流派相继出现[20]。地理科学与时俱进,在坚持自我与融入现代科学过程中形成“格局—过程—机制”成熟范式[21]。进入数据驱动与交叉融合的大科学时代后,地理科学研究范式的创新使命更为艰巨。D0111申请代码以交叉类研究为主,但又包涵纯自然与人文要素研究,同时对地理信息技术要求高,因此是开拓地理科学范式创新的理想素材。该申请代码下研究可从以下三方面进一步提升:首先,在研究对象上,以地理科学为主凝聚相关学科,坚持“格局—过程—机制”范式,吸纳其他学科研究特色,博采众长;其次,在研究方法上,发挥信息地理学优势,拥抱数据驱动模式,从数据处理延伸到人工智能;第三,在研究内容上,由静态到动态,由局部到系统,从追求细节发展到尺度关联,从多层次的分科知识演变到探索共性原理[22]。
土地科学和自然资源管理代码领域设立是新时代国家自然资源管理重大变革关于基础研究的内在需求,是基金委优化学科布局改革的重要体现。本文分析了该领域各研究方向的申请资助格局,透视了研究热点,并提出发展展望,回应了申请者对该代码领域的主要关切。本文透视传递该研究领域的热点前沿,加快前沿知识有效传播,有利于在此基础上推动土地科学和自然资源管理面向科学前沿进一步发展;通过剖析研究格局背后的学科因素,可进一步支撑土地科学学科发展与资源科学学科建设,并不断深化地理科学内涵,促进学科高质量建设。该领域基础研究发展可为新时代自然资源管理提供技术与制度创新动力,从而通过底层科学问题解决根本上服务于国家自然资源重大战略需求。
参考文献
中国自然资源研究的发展历程及展望
The development history and prospect of natural resources research in China
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200801 URL [本文引用: 2]
中国新时代自然资源治理体系的理论构想
On China's governance system for natural resources in the New Era
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200804 URL [本文引用: 1]
新时代中国自然资源研究的机遇与挑战
Opportunities and challenges of natural resources research of China in the New Era
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200802 URL [本文引用: 1]
资源科学的学科建设与人才培养模式的实践与思考
Practice and reflections of discipline construction and talent cultivation mode for resources science
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200805 URL [本文引用: 1]
地理科学的学科体系构建与内涵
The construction of discipline system of science of geography and its significance
自然资源分类: 从理论到实践、从学理到管理
DOI:10.18402/resci.2021.11.01
[本文引用: 1]

自然资源分类对自然资源管理和资源科学学科体系建设与发展具有重要科学价值与现实意义。基于自然资源的科学内涵,通过追踪公开发表的中英文文献,从理论到实践,系统梳理与对比分析了自然资源的传统与经典、学理与属性、法理与管理等分类特征及其发展。综述表明:自然资源分类聚焦于学理、法理和管理三方面,在学理分类上国内外保持相对一致性,但法理与管理分类上差异较大;现行分类存在体系繁多、边界重叠、交叉重复等问题。国际上,20世纪初期以前单门类或特定区域资源分类研究已相当深入,自然资源分类成为资源科学研究的主要内容之一;1960年代以来,日臻完善的资源科学学科体系推动自然资源分类研究进入新的发展时期,地理学、资源学、生态学、经济学、环境科学等分类思想“群星荟萃”,尽管迄今仍未形成统一的自然资源分类体系,但已构成自然资源学理分类的思想基础。在中国,自然资源分类研究大抵以20世纪50—60年代开展的自然资源综合科学考察为分水岭,单门类资源分类研究发展较快、综合分类体系初见端倪;系统性、综合性的分类研究始于20世纪末期,以中国自然资源学会成立及《中国资源科学百科全书》问世为重要标志,尤以自然资源属性和用途的多级分类方法应用广泛。目前国内总体处于统一自然资源分类探索阶段,在政策层面已得到自然资源部等部门的高度重视。鉴于此,有必要科学认识和厘清不同自然资源分类的特征与作用,以期对自然资源分类标准化和自然资源管理现代化有所裨益。
Classification of natural resources: From theory to practice and from principle to management
DOI:10.18402/resci.2021.11.01
[本文引用: 1]

The unification of classification standards of natural resources is of great significance for the integrated management of natural resources and development of Resources Science. Based on the scientific connotation of natural resources, this article compared and summarized the tradition and classics, theories and attributes, and jurisprudence and management of natural resources classifications and their evolution process. This preliminary review typically relied on the currently available historical English literature (including published papers, books, and reports) and some literature in Chinese. The review showed that the classification of natural resources mainly focuses on three aspects of theories, principles, and management. Compared with the first aspect, the latter two of classifications showed larger differences in China and internationally. In particular, the existing natural resources classification cannot well avoid the overlap of natural resource management and the classification standards are not uniform. Internationally, many scholars have conducted in-depth studies and analyses on single category or specific region of resources classification in the early 1990s. Then new developments were achieved in Geography, Ecology, Resources Science, Economics, and Environmental Science in the 1960s. Overall, international methodologies provide a basis for the classification of natural resources in China, although there is still a lack of a standard set of classification theories. In China, the massive comprehensive surveys of natural resources (1950s-1960s) are a turning point in the study on the classification of natural resources. Thereafter, research on single category natural resources classification (e.g., land resources and water resources) has developed rapidly, while comprehensive classification remains sparse, sporadic, and scattered. It was not until the late 1990s that the establishment of the China Society of Natural Resources (1983) and the publication of China Encyclopedia of Resources Science (2000) symbolized the born of systematic and comprehensive classification of natural resources in China. In particular, the multilevel classification method based on the uses and attributes of natural resources is widely used. At present, studies related to the integrated classification of natural resources in China are at their developing stage, and the unified classification system has gained much attention from national decision-making departments of the Ministry of Natural Resources the People’s Republic of China. In view of the situation, it is necessary to recognize and clarify the characteristics and functions of different classifications of natural resources for standardization and modernization of management and classification of natural resources.
自然资源分类相关问题探讨及新分类方案构建
DOI:10.18402/resci.2021.11.02
[本文引用: 1]

对自然资源进行统一的科学分类是开展自然资源调查评价、履行其管理职责、编制国土空间规划、实施山水林田湖草的整体保护、系统修复和综合治理、实现自然资源治理能力现代化等重大战略任务的最基础性前期工作。针对学术界、管理层和实际工作者对自然资源分类的不同意见和分歧,本文创新性地从空间、属性、用途、管理等视角提出了一个含有3个一级大类、11种二级门类、62种三级类别的新分类框架和分类方案。该方案不仅区分了自然资源的地理空间,便于分类管理和实际操作,而且区分了自然资源的不同用途与属性,很好地反映了作为物质或能量的自然资源与作为环境条件的自然要素之间类型上的差异性。研究成果为推进自然资源分类体系的完善,并与国际接轨、提升自然资源治理现代化能力,以及推动自然资源管理部门与生态环境、农田水利、国土空间规划、城乡建设等部门在自然资源、国土空间、生态修复等重大任务和目标上的有机衔接,具有重要应用价值和现实意义。
Discussion on the classification of natural resources and a new classification framework and scheme
DOI:10.18402/resci.2021.11.02
[本文引用: 1]

The scientific classification of natural resources is the most basic preliminary work for carrying out the investigation and evaluation of natural resources, fulfilling its management responsibilities, preparing spatial planning, implementing the overall protection of landscape, forest, land, lake, and grass (Shan-Shui-Lin-Tian-Hu-Cao, in Chinese) and systematic restoration and comprehensive management, and realizing the modernization of natural resources governance. In view of the different opinions and differences of academic researchers, management authority, and practitioners on natural resources classification, this article creatively proposes a new classification framework and classification scheme with three primary categories, 11 secondary categories, and 62 third-level categories from the perspective of space, attribute, use, and management of natural resources. The scheme not only distinguishes the geographical space of natural resources, facilitates differentiated management and practical operation, but also distinguishes different uses and attributes of natural resources, which well reflects the difference between natural resources as matter or energy and natural elements as environmental conditions. The results of this research have application value and practical significance for promoting the improvement of natural resources classification system and international integration, enhancing the modernization of natural resources management, and promoting the intrinsic connection between natural resources management departments and ecological environment, farmland and water conservancy, spatial planning, and urban and rural construction departments with regard to the key tasks and objectives for natural resources, territorial space, and ecological restoration.
国家自然科学基金视角下地理科学融合发展路径探索
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202208001
[本文引用: 1]

随着整体科学的进步和国家社会的发展,地理科学已迈入跨学科交叉融合发展的新阶段。通过学科间和领域间的深度融合寻求新发展路径,完善知识体系,充分发挥服务国家社会之功能,是当前地理科学发展的当务之急。本文基于自然科学基金视角,分析了中国地理科学融合发展的现状与问题,认为其与国际前沿未充分接轨,研究的全球政治、经济、文化影响力有待加强,认为地理科学融合国家重大需求进行理论与技术创新的能力有待提升,认为学科内部体系要根据知识融合需求进一步优化。在此基础上,提出了资助政策引导下地理科学面向世界科技前沿的学科交叉融合、面向国家重大战略的多领域交叉融合和面向申请代码优化布局的分支学科交叉三大融合发展路径与相应政策工具。未来国家自然科学基金委员会将立足于保持学科发展的持续性和稳定性,通过政策创新来激励地理科学与其它学科、领域的交叉融合,以建设更具有活力与创新性的学术生态系统。
Exploring the integrative development paths of geographic sciences from the perspective of National Natural Science Foundation of China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202208001
[本文引用: 1]

With the progress of holistic science and human society, development of geographical sciences has entered a new stage of interdisciplinary integration. Under this context, geographical sciences urgently needs to seek new paths through the deep integration of disciplines to better improve the knowledge system and contribute to the country and society development effectively. Based on the perspective of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), this paper firstly deeply analyzes the current status and problems of the integration and development of geographical sciences in China, and points out that it is not fully integrated with the frontier of international geographical sciences, and the global political, economic and cultural influence of geographical research in China needs to be strengthened; considers that the ability of Geographic Sciences integrating national major practical needs for theoretical and technological innovation should be improved; suggests that the internal discipline system of geographical sciences in China should be further optimized according to the needs of knowledge integration. Then, this paper proposes three paths for the integrated development of geographical sciences under the guidance of funding policies, that is, the interdisciplinary integration facing the frontiers of science and technology in the world, the multiple fields integration facing the major national development strategies, and inner-discipline integration facing the optimized application codes of NSFC. In future, based on maintaining the continuity and stability of the development of disciplines, the NSFC will encourage the integration of geographical sciences with other disciplines and fields through the improvement and innovation, so as to promote and build a healthier and more innovative system.
国家自然科学基金地理科学申请代码的调整优化
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202011001
[本文引用: 2]

学科申请代码调整优化是国家自然科学基金委员会“科学基金学科布局改革”任务的重要组成部分和切入点。本文回顾了地理学科申请代码的历史沿革,系统梳理了当前版本地理学科申请代码存在的问题,论述了新版(2021版)申请代码体系的架构理念、遵循原则、形成过程,着重阐释了新申请代码的历史沿革、科学内涵与学科定位。新版申请代码体系较以往版本有以下4个显著特征:① 逻辑更自洽,一级代码名称由“地理学(D01)”改为“地理科学(D01)”;② 学科更融合,取消三级申请代码,仅设二级申请代码,更能体现学科的交叉融合;③ 领域更全面,针对学科发展趋势及经济社会发展需求,增加了“灾害地理”“土地科学”“地理大数据与空间智能”等新兴学科、领域的代码;④ 技术更重视,增设“地理观测与模拟技术”,鼓励面向地理科学问题研究所需关键工具、仪器的研制。
Adjustment and optimization of geographical sciences application code of NSFC
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202011001
[本文引用: 2]

The adjustment and optimization of discipline application code is an important part and breakthrough point of the task of "science foundation discipline layout reform" of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC). This paper reviewed the historical evolution of the application code of geography discipline, systematically sorted out the problems existing in the current version of the application code for geography discipline, discussed the framework concept, principles and formation process of the new version (2021 Edition) application code system, and emphatically explained the historical evolution, scientific connotation and discipline orientation of the new application code. Compared with the previous versions, the new version of the application code system has the following four unique features: (1) The logic of the system is more reasonable; the first level code name has been changed from "Geography (D01)" to "Geographical Science (D01)". (2) The disciplines are more integrated by setting the second-level application code instead of the three-level application code, which can better reflect the interdisciplinary integration. (3) The fields are more comprehensive; according to the development trend of disciplines and the needs of economic and social development, codes of emerging disciplines and fields such as "disaster geography", "land science", and "geographic big data and spatial intelligence" have been added to the list. (4) More attention has been given to technology, namely, "geographic observation and simulation tools" are identified to encourage the development of key tools and instruments for the research of geographical issues.
20世纪80年代末以来中国土地利用变化的基本特征与空间格局
Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns and causes of land use changes in China since the late 1980s
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201401001
[本文引用: 1]

Land-Use/land Cover Changes (LUCC) are a direct consequence of human and nature interactions. China's Land Use/cover Datasets (CLUD) were updated regularly at five-year intervals from the late 1980s to the year of 2010 with standard procedures based on Landsat TM/ETM + images. A dynamic zoning method was proposed to analyze major land-use conversions. The spatiotemporal characteristics, differences, and causes of land-use changes at a national scale were then examined. The main findings are summarized as follows: Land-Use Changes (LUC) across China indicated a significant variation in spatial and temporal characteristics in the past 20 years between the 20th and 21st centuries. The amount of cropland change decreased in the south and increased in the north, but the total area remained almost unchanged. The reclaimed cropland was shifted from northeast to northwest. The built-up lands were expanded rapidly, which were mainly distributed in the east and gradually spread out to the midwest. Woodland decreased first and then increased, but desert area was inverted. Grassland continued decreasing. Different spatial patterns of LUC in China were found between the late 20th century and the early 21st century. The original 13 LUC zones were replaced by 15 units with changes of boundaries in some zones. The main spatial characteristics of these changes included (1) an accelerated expansion of built-up land in the Huang-Huai-Hai region, the coastal areas of southeastern China, the midstream area of the Yangtze River, and the Sichuan Basin; (2) the shifted land reclamation in the north from Northeast China and eastern Inner Mongolia to the oasis agricultural areas in Northwest China; (3) the continuous transform from rain-fed farmlands in Northeast China to paddy fields; and (4) the effectiveness of the “Grain-for-Green” project in the southern agricultural-pastoral ecotones of Inner Mongolia, the Loess Plateau, and mountainous areas of southwestern China. In recent two decades, although climate change in the north impacted the change in cropland, policy regulation and economic driving forces were still the primary causes of LUC across China. During the first decade of the 21st century, the anthropogenic factors that drove variations in land-use patterns have shifted the emphasis from one-way land development to both development and conservation. The "dynamic zoning method" was used to analyze changes in the spatial patterns of zoning boundaries, the internal characteristics of zones, and the growth and decrease of units. The results revealed "the pattern of the change process," namely the process of LUC and regional differences in characteristics at different stages. The growth and decrease of zones during this dynamic LUC zoning, variations in unit boundaries, and the characteristics of change intensities between the former and latter decades were examined. The patterns of alternative transformation between the "pattern" and "process" of land use and the reasons for changes in different types and different regions of land use were explored.
我国土地管理政策: 理论命题与机制转变
Land management policy in China: Theoretical proposition and mechanism transformation
基于科学基金共同体视角的科学基金制度规范体系探析
Science fund rules and regulatory system based on scientific fund community perspective
基于板块的国家自然科学基金资源配置机制改革与思考
Reform and reflection on the resource allocation of National Natural Science Foundation of China based on the four sections
国际地理学新发展: 尊重差异、包容多样—国际地理联合会2018年区域会议述评
2018年8月6-10日,国际地理联合会2018年区域会议在加拿大魁北克城召开。会议围绕“尊重差异、包容多样”的主题展开,吸引了全球1500余名专家学者汇聚魁北克城,研讨国际地理学的最新进展。当前国际地理学的发展倡导尊重差异的地理教育理念,强调在变化与差异中实现社会—自然系统的耦合,注重地理信息科学的创新学术价值,聚焦全球化与区域性的融合发展。对中国学者的启示主要为:把握地理学多样化的发展趋势;发展基于学科交叉的综合性理论和方法;创新地理教育以推动全球差异化、多元化的发展。作为国际地理联合会执委会和委员代表工作会议的重要成果,选举产生了新的执委成员,傅伯杰院士正式任职国际地理联合会副主席。
New developments in international geography: Appreciating differences: A review of the 2018 International Geographical Union Regional Conference
The 2018 International Geographical Union Regional Conference was held on August 6 to 10, in Quebec City, Canada. "Appreciating Difference" is the theme of the conference. This session is the largest conference in Canada's geography-related conferences, attracting more than 1,500 experts and scholars around the world to gather in Quebec City to discuss the latest developments in geography. The current development of international geography advocates the concept of geography education that respects differences, emphasizes the coupling of social-natural systems in change and difference, pays attention to the innovative academic value of geographic information science, and focuses on the integration of globalization and regional development. The enlightenment to Chinese scholars is mainly reflected in: Grasping the development trend of geographical diversity; developing comprehensive theories and methods based on interdisciplinary research; reshaping geography education to promote global differentiation and diversification. As an important result of the working meeting of the International Geographical Union and its members' representatives, a new member of the executive committee was elected, and academician Bojie Fu? was formally appointed vice chairman of the International Geographical Union.
自然资源与环境安全研究进展
Research progress in natural resources and environmental security
是什么决定学科交叉研究成败
What determines the success or failure of interdisciplinary research
地理学与资源科学研究的交叉与融合
The interdisciplinary study and integration of disciplines for geography and resources science
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200806 URL [本文引用: 1]
地理科学的价值与地理学者的情怀
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201510001
[本文引用: 1]

本文强调了前辈地理学家提出的关于地理学是介于自然科学和社会科学之间的交叉学科的观点。从中国国家需求及当代国际地理学的发展趋势,从理论与实践的结合上论述了地理科学的学科对象、学科性质及区域性、综合性、知识结构等方面的特点,特别突出地阐述了地理科学与纯自然科学或纯社会科学的诸多不同点。提倡地理学家要十分关注中国的环境变化及带来的严重的可持续发展问题,并发挥综合和交叉研究的优势。此外还指出中国地理学面临着重要的发展机遇,也出现了深刻的危机。
The value of geographical science and the feelings of geographers
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201510001
[本文引用: 1]

This paper focuses on the viewpoint proposed by predecessors of geography and they believed that geography is interdiscipline subject between natural science and social science. From the perspective of national demand and development trend of international geography, this paper explains the objects and nature of geographical science and characters of region as well as comprehensive characteristics and knowledge structure. Besides, it elaborates the differences among geography, natural science and social science and advocates that geographers should concentrate on the China's environmental changes and the issues of sustainable development and further fulfil the advantages of interdiscipline and comprehensive subject. Finally, this paper proposes that China's geographical science is faced with the significant opportunities and some deep-seated crises.
地理学方法论演变与价值判断
The geographical methodology between subjectivity and objectivity
DOI:10.11821/yj2010050019
[本文引用: 1]

The subjectivity and objectivity are an important pair of category of the geographical methodology, and the problem about them focuses on whether scholars should introduce their values into the process of scientific study. This paper defines the values and purposes of geographers as subjective things, and the external scientific or philosophical theories as objective things for geography. According to analysis of the category of objectivity, we firstly show that there is a kind of features cross-paralleled on specialization and interdisciplination in the course of scientific development. Secondly, the theoretical pluralism of the scientific philosophy have strongly influenced the geographical methodology: the frequent interdisciplinary researches after World War II have helped us to expand the scope of the geographical thoughts and contents; and with the theoretical evolvement of the scientific philosophy from Kuhn's Paradigm to Lakatos's Research Programs to Feyerabend's theory of "Anything goes", the geographical methodology has undergone the process from a single paradigm to the pluralism. Finally, the theories of sociology of scientific knowledge make many geographers feel that geographical knowledge often develops under the special social and cultural context so that there is not methodological consensus, and geography is reshaped by rhetoric and discourse. According to analysis of the category of subjectivity, we intend to indicate that the researchers can not break away from and get rid of his value judgments, and their value can not be "neutral" in the study. For the value judgments in the course of research, scholars should be wary of it and hold the principle of strict and integrated logic. As for the teleology, the destination of the whole study lies in "return to self" like humanism, that is from the subject back to the awareness for us. In short, in combination of subjectivity with objectivity, the methodology, including geographical methodology, is the product of interaction between the general rule of scientific and philosophical development and the values and purposes of the scholar himself or herself.
地理学: 从知识、科学到决策
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 1]

地理学是研究地理要素或者地理综合体空间分布规律、时间演变过程和区域特征的一门学科,是自然科学与人文科学的交叉,具有综合性、交叉性和区域性的特点。随着地理信息技术发展与研究方法变革,新时期的地理学正在向地理科学进行华丽转身,研究主题更加强调陆地表层系统的综合研究,研究范式经历着从地理学知识描述、格局与过程耦合,向复杂人地系统的模拟和预测转变。在服务国内重大需求和国际全球战略过程中,地理学正在扮演愈发重要的角色,在新型城镇化、生态环境保护、水土资源管理、地缘政治等领域拥有广阔发展前景。中国地理学正面临前所未有的机遇,需要紧紧围绕国家重大需求,创新发展综合性的理论、方法和技术,逐步形成具有鲜明中国特色、深远国际影响的地理科学体系,为中国和全球的可持续发展服务。
Geography: From knowledge, science to decision making support
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
Paradigm shift in science with tackling global challenges
DOI:10.1093/nsr/nwz155 [本文引用: 1]