黄河流域作为一个特殊的地理单元,跨越了中国三大阶梯和东中西部三大经济地带,既构成中国重要的生态屏障,也是中国打赢脱贫攻坚战的重要区域。大面积集中连片的耕地、丰富的土地资源和能源供应、鲜明独特的文化资源等是其高质量发展的有利条件。黄河流域是中国典型的生态脆弱区和贫困区,其流经的黄土高原是世界上水土流失面积最大的区域,中上游地区贫困现象普遍且人口众多[1]。生态本底脆弱、自然资源禀赋限制明显和水资源严重短缺等问题是黄河流域发展面临的重要短板,长期经济发展需求与粗放发展模式下的人地矛盾是黄河流域发展问题的本质[2]。生态退耕政策的推行和实施,缓解了黄河流域的水土流失,但对经济却产生了一定程度的负面影响[3]。随着中国西部大开发和中部崛起等国家战略的实施,黄河流域工业发展迅速增长,经济得到快速发展[4],但随之产生的是资源耗竭、生态破坏和环境污染等问题[5]。当前,随着人口激增、经济活动不断扩大和城市化快速发展,黄河流域人口、资源、环境与经济发展失衡,可持续减贫和高质量发展成为黄河流域亟待解决的重大挑战[6],黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展因而上升为国家重大战略。
人地关系的协调与否直接关系黄河流域发展质量与趋向[7]。黄河流域脆弱的自然生态在长期开发建设活动影响下更为敏感,草地退化导致了上游地区水源涵养功能的下降,中游地区依然存在着较为严重的水土流失问题,下游地区生态治理与居民生活和经济发展之间的矛盾也日益严峻。国土空间作为承载国民生存和发展的空间,其有序开发和宜居环境的营造是实现区域可持续发展和建设生态文明的客观需要[8]。科学合理的国土开发和利用策略是高质量发展的重要导向,只有在资源环境承载力的范围内开发利用国土空间,才能实现绿色可持续发展[9,10]。当前研究已经探讨了单一地类的利用策略[11]和单一视角下的土地利用策略[12],以及生态系统服务之间关系和驱动力视角下土地利用建议和管理重点[13]。黄河流域作为一个在边界范围内逐步发展而成的自然—社会—经济复合系统[5],其国土空间利用策略要从多视角多维度进行综合考虑和系统协调。同时,其不同区段在地理环境、资源禀赋和社会经济发展及文化传统等方面都存在显著的空间差异和发展不均衡[5],高质量发展策略要明确其上中下游的治理需求差异,针对不同区域的自然和人文特征制订不同的发展方向和策略。
生态系统保护是黄河流域高质量发展的基础与前提,黄河流域的复杂系统特征决定了其生态保护不能单就水论水,而是要与整体国土空间利用和产业发展相互配合。学术界有关黄河流域自然资源和生态系统保护以及人地关系协调方面的探讨,已经从关注流域突出的水资源问题如水资源演化[14,15]和水资源承载力[16⇓-18]、土地利用格局及驱动力[19⇓-21]、产业发展和经济发展[22,23]等,扩展到流域生态系统服务和驱动力[24,25]与生态系统服务供需核算[26],以及流域综合治理[27]和主体功能优化[28]等方面。随着黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展上升为国家重大战略,许多学者进一步对黄河流域的高质量发展与生态保护[29,30]及其关键和路径[7,31,32]等开展研究,揭示了黄河流域的发展态势。但是,高质量发展下的生态系统保护和国土空间可持续利用涉及多学科知识,深入揭示人与自然相互作用关系等科学问题需要综合集成和多学科交叉研究。从多学科综合维度深入剖析黄河流域发展现状和问题,在揭示人类活动对流域生态系统的影响机制的基础上提出流域生态保护与国土空间利用策略,亟待进一步深入。
面临国家生态文明建设战略和高质量发展需求,本文从地理学、生态学、区域经济学等维度科学认知黄河流域现状和资源环境限制,构建黄河流域生态保护与国土空间利用策略研究框架;基于理论研究框架,分析黄河流域国土空间格局时空演变规律,探讨黄河流域城镇化、土地开垦、生态退耕等人类活动对生态系统的影响,诊断和识别黄河流域国土空间利用和生态系统保护问题;分析黄河流域国土空间开发利用的水资源限制、地质环境限制及资源环境承载力,明确黄河流域不同地区的发展限制,提出面向黄河流域高质量发展的生态系统保护与国土空间开发利用策略和政策建议。以丰富横跨中国不同经济地带大型流域人与自然相互作用关系的科学问题研究,为推动黄河流域高质量发展提供理论支撑和决策依据,亦对推进黄河流域生态文明建设和促进全国区域平衡发展具有重要现实意义。
1 研究方法与数据来源
1.1 研究区概况
图1
图1
黄河流域所涉及的县域范围及基本概况
Fig. 1
The scope and basic overview of counties involved in the Yellow River Basin
1.2 数据来源与处理
根据Wang等[33]的研究,将不同土地利用类型依次归类为生态空间、农业空间、城镇空间。2000年和2018年分县域城镇用地、农村居民点用地、有林地和天然草地、耕地等土地利用数据来源于原国土资源部土地利用年度变更调查,由此计算各类土地利用类型占行政单元总面积的比例;黄河流域新增耕地数据来自参考文献 [26]。植被归一化指数(NDVI)数据由Landsat 8遥感数据计算获取;降水和农业生产潜力数据来源于中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心(
1.3 研究方法
1.3.1 研究框架
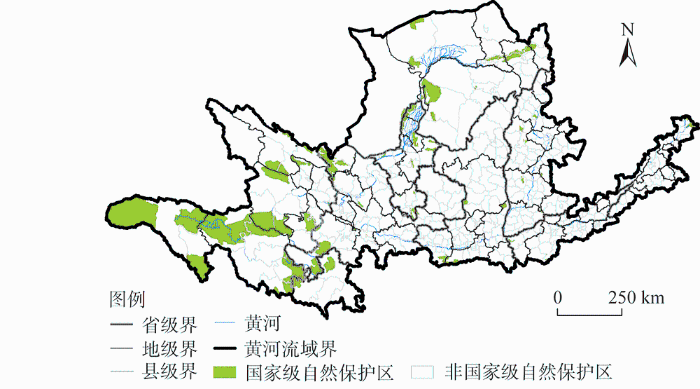
高质量发展的核心即把握好生态环境保护和经济发展的关系,生态系统保护是黄河流域高质量发展的基础与前提,人地关系协调直接关系到黄河流域发展质量。为了满足生存和发展需要,人类各种开发活动对生态系统造成干扰和破坏,资源环境承载能力的空间差异及其变化反过来影响生态系统状况和人类行动决策;人类进而通过制定发展策略和政策来响应压力并影响人类行动,以降低和补救由压力造成的环境破坏与损失,最终构成了“压力—状态—响应”的循环关系。
黄河流域高质量发展策略研究即科学认知黄河流域的发展现状和压力,分析不同压力影响下的国土空间格局演变和生态系统状况,诊断和识别黄河流域发展问题,以此提出合理的应对解决策略和政策建议。黄河流域高质量发展的生态保护与国土空间利用策略研究框架见图2。在分析黄河流域城镇化发展等压力导致的土地开发和生态建设等行动的基础上,综合考虑国土空间开发利用的水资源限制、地质环境限制等资源环境限制,以及大气环境、生境风险等环境影响风险,结合生态系统服务供给等生态支撑条件,科学认知黄河流域生态系统的本底条件,定量测度区域发展限制性因子和资源环境承载能力。同时,针对黄河流域生态空间、农业空间和城镇空间演变特征和生态系统保护现状,分析城镇化发展、土地开发、生态建设等压力和人类活动对国土空间格局和生态系统的影响,揭示人类活动对流域生态系统保护的影响机制,科学诊断识别国土空间利用和生态系统保护的问题。基于上述研究,针对不同类型问题,从农业空间利用与保护、城镇空间优化与发展以及生态空间保护三个方面,提出面向黄河流域高质量发展的生态系统保护与国土空间开发利用策略和政策建议。
图2
图2
黄河流域高质量发展的生态保护与国土空间利用策略研究理论框架
Fig. 2
A theoretical framework of the strategies of ecosystem protection and territory spatial utilization for high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin
1.3.2 空间相关性分析
本文借助双变量局部Moran's I指数[35]来分析新增耕地面积与其带来的生产潜力变化和NDVI变化之间的空间关系,以及农业空间占比与生产潜力之间的空间相关性,把握它们之间的集聚与分异特征。
1.3.3 核密度分析
核密度分析能有效测度局部密度变化和探索空间热点,较好地反映地理现象在空间上的距离衰减,通常采用Rosenblatt-Parzen核估计[36]。在ArcGIS 10.4中选取默认带宽,对黄河流域土地开发强度进行核密度分析,以直观获取其聚集或离散等空间分布特征。
1.3.4 生态系统服务供给与生境风险指数测算
1.3.5 资源环境承载力评价
表1 资源环境综合限制性指数测算指标
Table 1
| 目标层 | 准则层 | 指标名称 |
|---|---|---|
| 资源环境禀赋 | 水资源限制性 | 三级流域地表水资源分布、地下水资源分布 |
| 地质灾害限制性 | 地面沉降、地质灾害易发程度区划 | |
| 环境影响风险 | 大气环境生态系统风险 | 单位GDP的大气PM2.5环境容量生境风险指数 |
| 生态系统支撑条件 | 生态系统服务供给 | 生态系统服务供给指数 |
1.3.6 生态基础设施网络体系构建
基于团队相关研究[38],采用InVSET的生境质量模型(Habitat Quality Model)计算黄河流域生境质量指数。综合生境质量指数和生境风险指数,识别生态源地,构建包含显性阻力面和隐性阻力面的综合生态阻力面,基于生态源地与生态阻力面,借助Circuitscape插件中的Linkage-Mapper模块构建生态廊道,并构建黄河流域生态基础设施网络体系。
2 结果分析
2.1 黄河流域国土空间格局与资源环境限制性
2.1.1 黄河流域城镇化发展与国土空间格局时空演变
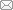
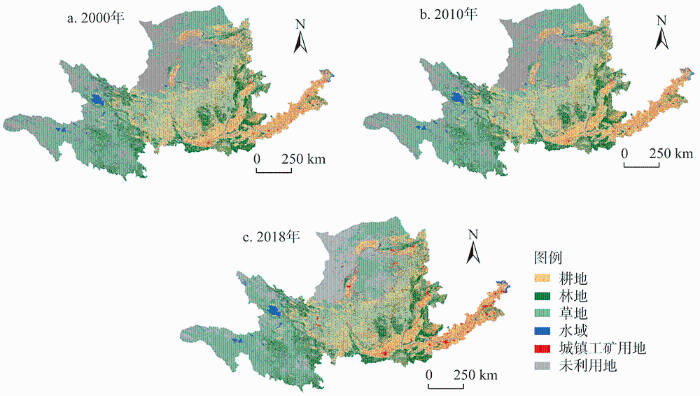
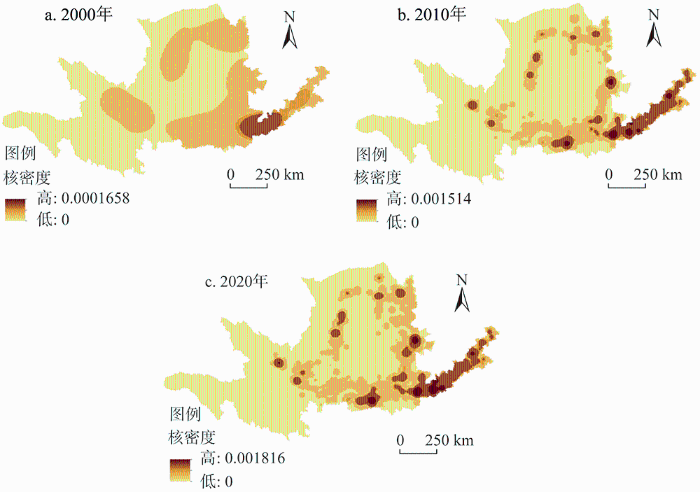
受自然条件影响,黄河流域社会经济沿河发展,沿河县域占流域14.13%的土地承载了39%的人口和38%的GDP,城镇空间呈沿河走向的条带状分布(图3)。夜间灯光数据反映人类活动的强度,黄河流域人类活动强度和城镇发展与人口密度、经济密度、土地开发强度以及基础设施和公共服务的空间分布一致(图4)。随着中国西部大开发和中部崛起等国家战略实施,国土空间开发向中西部倾斜,黄河流域土地开发强度由2000年下游的单核心发展为2010年和2018年的多核心,且均呈现沿河分布特征(图5),这就决定了其国土空间开发应当通过点状开发,以核心城市群带动周边区域发展。而且,黄河上游是中国重要的生态屏障带,分布有56个国家级自然保护区,涉及县域面积占流域土地总面积的61%,但仅承载20%左右的人口和GDP,生态脆弱性和重要性决定了生态保护在黄河流域国土空间开发和利用中的重要意义。此外,截至2019年黄河流域仍有62个贫困县未脱贫,占全流域面积的55%,且集中分布于自然保护区范围,发展水平和质量亟需提升,探索生态保护与经济建设协调的发展路径是黄河流域高质量发展的关键。
图3
图3
2000年、2010年和2018年黄河流域土地利用
Fig. 3
Land use of the Yellow River Basin in 2000, 2010 and 2018
图4
图5
图5
2000年、2010年和2018年黄河流域土地开发强度核密度
Fig. 5
The kernel density estimation of land development intensity in the Yellow River Basin in 2000, 2010 and 2018
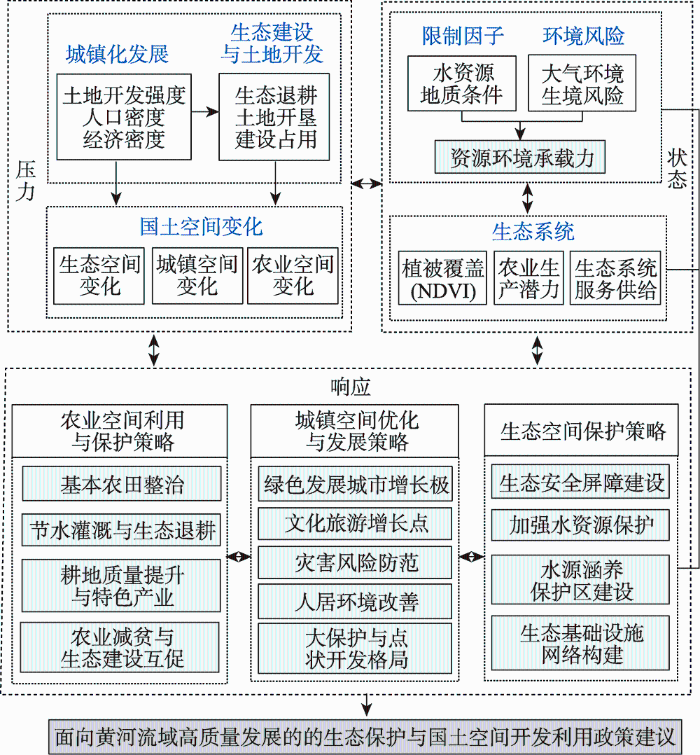
快速城镇化发展导致黄河流域国土空间格局变化剧烈,2000—2018年耕地整体减少,下游及沿河地区建设用地增加明显。2000—2018年黄河流域城镇用地比例从0.27%增加到1.02%,面积增长89.35万hm2,农村居民点比例由1.89%上升到2.07%;林地和草地是黄河流域主要的生态空间,林地集中分布于中下游的太行山脉、汾河和渭河流域等地,天然草地广泛分布于三江源地区、内蒙古高原和黄土高原,2000—2018年有林地增加了171.14万hm2,天然草地减少1317.87万hm2;耕地是黄河流域主要的农业空间,主要分布中上游南部和下游地区,与城镇发展趋势一致,反映了黄河流域作为中国农业经济开发地区的特征,2000—2018年耕地面积净减少80.2万hm2。从不同区域来看(表2),沿河区域的城镇用地比例和居民点用地比例高于流域平均水平且增幅明显,是流域城镇用地和农村居民点主要的增加来源;自然保护区所在县域2000—2018年天然草地比例从58.17%下降到48.46%,草地生态系统退化严重,有林地的增速较慢;沿河自然保护区县域和沿河县域耕地比例减幅最大,以建设占用和生态退耕为主。黄河流域建设用地快速扩张和耕地及生态用地的减少与退化很大程度上威胁着流域的可持续发展,国土空间利用格局亟需优化。
表2 2000—2018年黄河流域不同区域城镇用地、农村居民点、耕地、有林地和天然草地比例变化
Table 2
| 分区 | 流域 占比 | 城镇用地比例 | 农村居民点比例 | 耕地比例 | 有林地比例 | 天然草地比例 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000年 | 2018年 | 变化 量 | 2000年 | 2018年 | 变化 量 | 2000年 | 2018年 | 变化量 | 2000年 | 2018年 | 变化 量 | 2000年 | 2018年 | 变化 量 | ||||||
| 沿河县域 | 14.13 | 0.79 | 2.98 | 2.19 | 4.69 | 5.29 | 0.60 | 35.52 | 32.81 | -2.71 | 6.90 | 10.21 | 3.31 | 18.32 | 11.40 | -6.92 | ||||
| 沿河自然保 护区县域 | 4.41 | 0.47 | 2.25 | 1.78 | 2.89 | 3.26 | 0.37 | 22.82 | 18.75 | -4.07 | 11.8 | 6.69 | -5.11 | 25.91 | 22.98 | -2.93 | ||||
| 自然保护区 县域 | 42.91 | 0.13 | 0.60 | 0.47 | 0.85 | 1.04 | 0.19 | 8.29 | 8.03 | -0.26 | 5.70 | 6.86 | 1.16 | 58.17 | 48.46 | -9.71 | ||||
| 其他县域 | 43.35 | 0.26 | 0.94 | 0.68 | 2.14 | 2.29 | 0.15 | 20.65 | 18.08 | -2.57 | 9.20 | 11.26 | 2.06 | 40.37 | 33.01 | -7.36 | ||||
| 黄河流域 | 100.00 | 0.27 | 1.02 | 0.75 | 1.89 | 2.07 | 0.18 | 16.23 | 15.21 | -1.02 | 7.33 | 9.08 | 1.75 | 45.70 | 37.59 | -8.11 | ||||
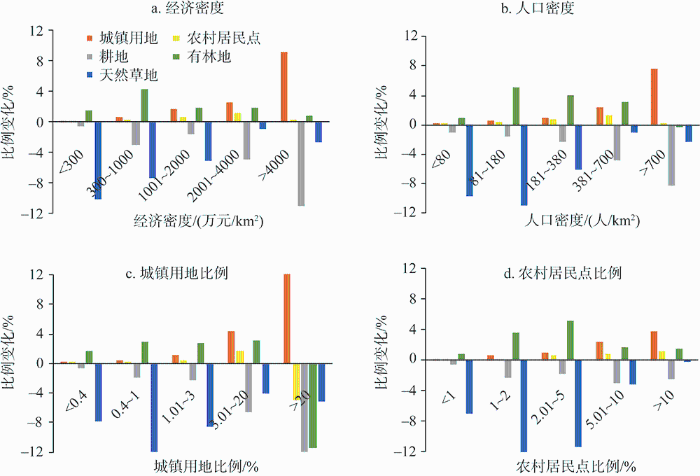
从主要地类变化与社会经济的关系来看(图6),黄河流域的社会经济发展影响着耕地变化,2000—2018年经济密度、人口密度、城镇用地比例和农村居民点比例高值区的耕地比例增幅最大。同时,城镇用地比例高值区的有林地比例和天然草地比例的大幅减少,城镇扩张是黄河流域生态空间减少的重要原因;有林地比例增幅最大区域为经济密度、人口密度和城镇用地比例较低区域,而非最低区域,与具有一定水平农村居民点区域保持一致,可能与此区域坡耕地退耕还林实施有关;天然草地减幅最大区域为人口密度、城镇用地和农村居民点用地比例较低区域,可能与耕地开垦和天然草地退化相关。根据以上分析,可以确定黄河流域国土空间利用与经济发展密切相关,且经济发展与生态保护严重失调。
图6
图6
2018年黄河流域不同经济密度、人口密度、城镇用地和农村居民点比例下的各类用地比例变化
Fig. 6
Changes in the proportion of various land types under different economic densities, population densities, the proportion of urban land and rural residential areas in the Yellow River Basin in 2018
2.1.2 黄河流域生态建设与土地开发效应
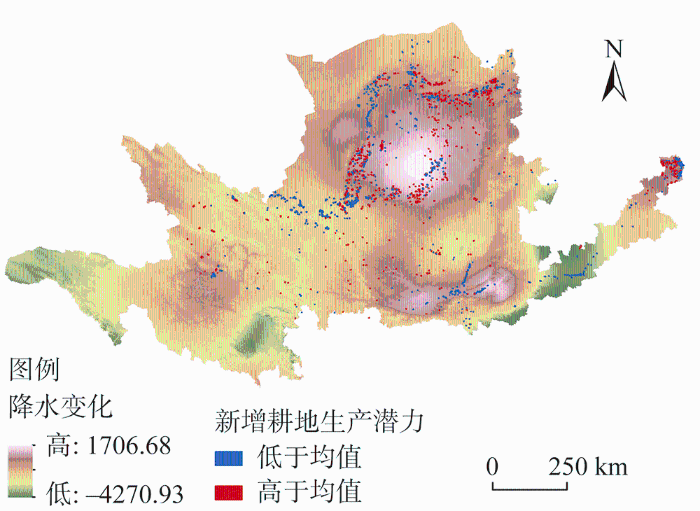
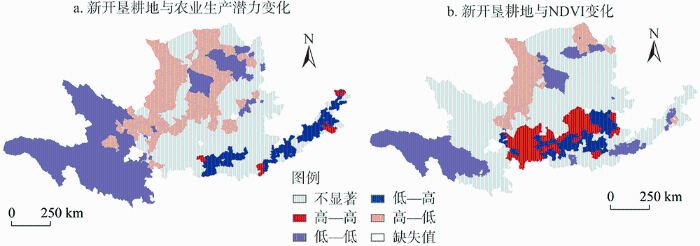
黄河流域生态系统脆弱,土地开垦长期受到关注。20世纪80年代中期随着土地家庭承包制度的完善,黄河流域草地开垦为新的沙漠化留下隐患。随着国家对北方地区防沙治沙、水土流失治理生态建设工程的实施,天然草地保护和不合理土地开垦控制取得成效。2000—2018年黄河流域新开垦耕地主要分布在降水增加地区,主要来源于未利用地和草地,带来的耕地增加占耕地总面积1.52%,但仅15%的农业生产潜力高于区域平均水平,且主要分布在沿河县域(图7)。新开垦耕地与生产潜力在下游地区呈现大面积低—高集聚和小面积的高—高集聚;中游鄂尔多斯高原地区主要为高—低集聚,自然条件限制使得该地区耕地开垦带来的生产潜力增加十分有限;上游地区由于自然气候和生态保护限制,主要是低—低集聚(图8a)。2000—2018年新开垦耕地区域的NDVI增加了0.12,生态系统服务供给指数增加了2.51(表3),开垦面积与NDVI变化在降水稍多的黄土高原南部和秦岭北坡等地呈现高—高集聚和高—低集聚分布(图8b),说明开垦耕地在该区对植被覆盖的改善作用明显。总体来看,水资源对黄河流域农业发展的限制十分明显,靠开垦耕地增加粮食生产潜力对大部分地区的作用不大。
图7
图7
2000—2018年黄河流域新开垦耕地的农业
生产潜力与降水变化空间分布
Fig. 7
The spatial distribution of agricultural production potential and precipitation changes of reclaimed cultivated land in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2018
图8
图8
2000—2018年黄河流域新开垦耕地与农业生产潜力变化和NDVI变化的LISA分布
Fig. 8
LISA cluster map of reclaimed cultivated land and changes in agricultural production potential and NDVI in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2018
表3 2000—2018年黄河流域不同区域NDVI和生态系统服务供给变化
Table 3
| 分区 | NDVI | 生态系统服务供给 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变化量 | 年增长率/% | 变化量 | 年增长率/% | ||
| 退耕还林还草区 | 0.10 | 1.37 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |
| 新开垦耕地区 | 0.12 | 1.80 | 2.51 | 0.61 | |
| 新增建设用地区 | -0.06 | -0.95 | -1.89 | -0.42 | |
| 全域 | 0.05 | 0.66 | -3.88 | -0.82 | |
生态退耕导致的耕地减少占耕地总面积的1.8%,退耕还林还草使得黄河流域中部黄土高原地区以及上游自然保护区所在贫困县域的新增林地和草地占比高于其他区域,分别占区域土地总面积的6.95%和17.98%,NDVI增加了0.10,生态系统服务供给指数也有所提高。但其人口和经济密度增加均有限,退耕还林还草的经济效果有待提升。此外,退耕还林还草虽然导致耕地减少,但耕地生产潜力却增加了1.7万t,这是由于生态退耕主要针对质量较差耕地,退耕有效地恢复植被的同时,也增强了土壤侵蚀抵抗力。对比土地开垦对生产潜力的影响,可以看出提高耕地质量的重要性。
建设占用是黄河流域尤其是下游地区耕地和生态用地减少的重要原因,城市扩张造成的耕地减少达43.3万hm2,占城市扩张来源总面积的59%,这也是导致2000—2018年下游农业生产潜力下降重要原因。同时,城镇扩张很大程度上导致了生态空间的减少,威胁生态系统健康,2000—2018年城镇空间增长率高的地区与NDVI和生态系统服务供给减少区域在空间分布上一致。中上游地区建设用地增加导致了部分重点生态功能区和自然保护区天然草地大幅减少,水源涵养功能降低,珍稀濒危野生动植物栖息地破碎;下游地区过度开发建设导致水生态系统退化,带来洪水泛滥、湖泊湿地萎缩、生物多样性下降等问题。城镇空间扩张导致的土地利用剧烈变化,进一步加剧了生态功能退化和生态与经济发展的失调。
2.1.3 黄河流域资源环境限制与承载能力
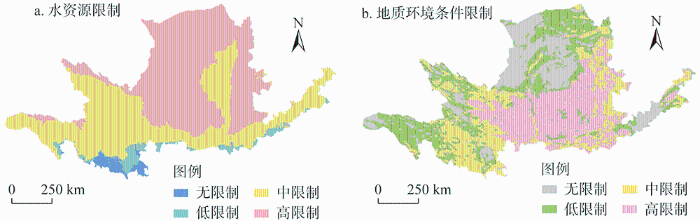
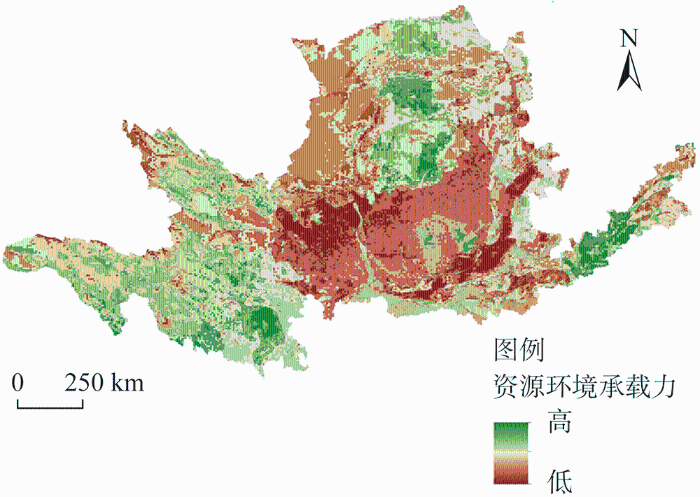
水资源是黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展的核心要素。黄河流域水资源匮乏,地表水和地下水资源在全国均属于较缺乏和严重缺乏区域,整个流域的水资源开发利用主要为高限制和中限制,仅南部小范围为低限制和无限制(图9a)。黄土高原作为中国最大的生态脆弱地区和全球最严重的水土流失区域之一,地质环境条件以高限制为主(图9b),且资源环境承载能力低(图10),是黄河流域高质量发展需重点关注的区域。黄河流域生态系统服务供给整体水平较低[34],供需局部失衡,尤其是自然保护区所在县域,虽然其生态系统服务供给水平较高,但是由于国土空间开发限制使得经济发展水平较低[26]。而生态系统服务需求较高的下游和一些沿河县域,随着经济快速发展,城镇发展规模和空间布局与自然环境承载能力之间矛盾越来越突出。识别出黄河流域的发展限制,进而因地制宜地选择发展方式和生活方式,是缓解经济发展和生态保护矛盾关系的重要一步。
图9
图9
黄河流域国土空间开发利用水资源限制和地质环境条件限制
Fig. 9
Water resources restriction and geological environment condition restriction in the development and utilization of territorial space in the Yellow River Basin
图10
图10
黄河流域资源环境承载力评价
Fig. 10
Evaluation of resource and environmental carrying capacity of the Yellow River Basin
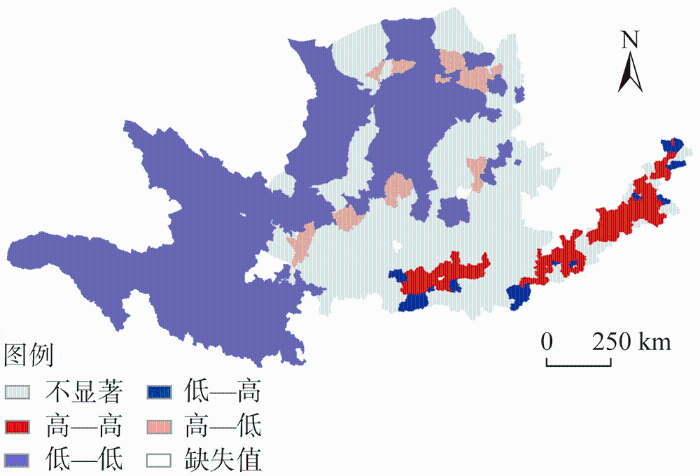
作为中国传统的农区,黄河流域种植业和畜牧业规模庞大,但现代化程度不高且区域差异明显。黄河流域的降水对农业生产潜力具有极大影响,农业生产潜力较高的区域与农业空间比例、人口密度分布具有较强的空间一致性(图11)。下游华北平原气候与地理条件优越,农业空间占比与农业生产潜力呈现高—高集聚分布,是重要的粮食生产基地;中上游地区主要以低—低集聚分布为主,自然条件限制了农业发展,但是畜牧业较发达,农牧产品优势突出,生产和发展潜力巨大。到目前为止,黄河流域的耕地依然以发挥其基本的粮食生产功能为主。作为黄河流域的优势资源,耕地的多功能性和农牧业的巨大潜力应当得到充分发挥。认清黄河流域耕地利用和农牧业发展存在的问题并加以改善和优化,对黄河流域的高质量发展和全国的粮食安全意义重大。
图11
图11
黄河流域农业空间占比与农业生产潜力LISA分布
Fig. 11
LISA cluster of agricultural land space proportion and production potential in the Yellow River Basin
黄河流域能源丰富,如上游的水能和风能、中游的煤炭以及下游的天然气和石油资源。但目前其能矿资源的开发还是以资源开采与初级加工为主,发展规模和污染控制都有待提高,中游晋陕蒙地区的矿山地质环境问题影响着人居环境和城市发展,工矿废弃地和采煤沉陷区都有待治理。流域目前产业结构以能源重化工为主,经济发展对资源型产业的依赖过高,严重制约了经济发展质量并威胁着流域生态安全。此外,黄河沿线的陕西、山西等是中华民族及华夏文化的重要发源地和多民族融合的主要区域,孕育着中华文明,在文化传承和文明进步方面发挥着重要作用,但目前其人文景观和文化资源优势发挥并不明显。摒弃靠资源开发和建设扩张的发展道路,充分发挥其人文资源优势,确立绿色发展路径和新的支撑点才是黄河流域未来的发展方向。
2.2 面向黄河流域高质量发展的生态保护与国土空间开发利用策略
针对黄河流域水资源限制、生态系统保护和建设薄弱、城镇空间发展定位有待优化、农业空间利用效率不高等问题,提出面向黄河流域高质量发展的生态保护与国土空间开发利用策略。
2.2.1 黄河流域城镇空间优化与发展策略
黄河流域高质量发展不仅要关注生态效益,也需要加强对社会和经济效益的关注,实现自然资源保护与经济建设协同发展。针对发展质量不高、城镇空间扩张过快等问题,首先要加强建设用地节约集约利用,严格控制建设用地扩张。其次,摒弃过去城市发展的梯度转移路径和高耗能、高污染产业的规模发展模式,加快产业结构调整和优化,推动形成绿色发展方式和生活方式。还要突出其独特自然—人文优势,以中原城市群为核心增长极,以兰西、呼包鄂榆等城市群为新兴增长极,传承区域本土历史文化名城名镇名村和传统村落保护,融合发展生态旅游、文化旅游、红色旅游与文化创意等,完善旅游服务设施,打造黄河流域生态文化旅游增长点。同时,针对黄土高原发展限制大和资源环境承载低等问题,加强黄土高原水土流失与地质灾害防治,以水定城、以水定人,统筹推进山水林田湖草系统治理、环境整治与美丽城乡建设,促进灾害风险防范与人居环境改善,形成大保护与点状开发格局。
2.2.2 黄河流域生态空间保护策略
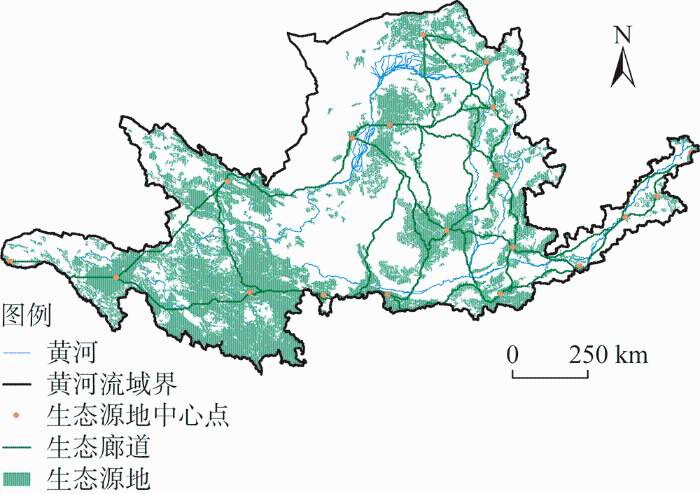
黄河流域生态退耕生态成效明显,但水资源匮乏,存在局部地区天然草地减少和生态系统退化等问题。通过强化三江源草原草甸湿地生态功能区、甘南黄河重要水源补给生态功能区、黄土高原丘陵沟壑水土保持生态功能区等国家重要生态功能区及黄河水系保护和生态修复,科学合理调控水资源和水沙关系;实施水资源与生态安全屏障保护和修复工程建设,恢复长城沿线防风固沙林草植被,提升森林、草原、湿地等水源涵养和水土保持功能;稳步推进中上游尤其是黄土高原地区的生态退耕工程,控制无序开荒增地,加大力度防治天然草地荒漠化;严格保护黄河流域集中分布的56个国家自然保护区,将国家自然保护区和生态系统完整性和原真性高、代表性强的自然地理区域作为生态源地和生态廊道,以黄河支流次支流等为骨架,构建黄河流域生态基础设施网络(图12),形成以水资源保护为核心、以生态基础设施保护修复为主体的可持续生态系统管理模式。
图12
图12
黄河流域生态基础设施网络体系
Fig. 12
Ecological infrastructure network system of the Yellow River Basin
2.2.3 黄河流域农业空间利用与保护策略
黄河流域耕地生产潜力整体较低且建设占用耕地严重,存在农业空间利用效率不高且耕地利用功能单一等问题。在推行生态退耕政策的同时,要兼顾耕地保护和质量提高。通过基本农田整治改善农业生产条件,提高农业生产能力,促进农业多功能利用,在保障粮食安全的同时,提高农业空间的生态调节功能。当前黄河流域脱贫攻坚战虽已取得全面胜利,但农民人均收入仍较低[39],加快欠发达地区的发展是促进黄河流域高质量发展的难点[40]。重点优化农业空间布局,强化下游盐碱地与中低产田改造,充分发挥耕地资源和农业基础优势,通过布局特色农业产业和大力发展节水高效农业、生态农牧业农业,将生态产品优势转化为经济产品优势,形成区域特色产业链,充分挖掘黄河流域农产品和畜产品生产和发展潜力。同时,配套实施特色产业扶贫、旅游扶贫,改善贫困乡村生产生活条件,以农业产业发展促生态建设和扶贫减贫。
3 结论与建议
3.1 结论
本文基于“压力—状态—响应”关系建立了黄河流域高质量发展的生态保护与国土空间利用策略研究框架,诊断和识别出黄河流域在资源环境利用方面,存在地质环境和水资源限制程度高、文化资源优势未能发挥等问题;在城镇空间发展方面,局部地区城镇化发展快速但生态保护和建设不足,流域经济发展不平衡和生态环境脆弱导致部分地区生态系统服务供需失衡;在生态空间保护方面,生态退耕效益明显,但草地生态系统退化严重,自然保护区和生态功能重要区需加强保护;在农业空间利用方面,存在农业生产潜力和现代化程度不高,且耕地多功能利用不足等问题,农业减贫及生态调节功能有待加强。针对以上问题,从三类空间利用角度提出了相应的优化和保护策略。
3.2 建议
在黄河流域各类空间保护和优化策略的基础上,应当科学制订黄河流域国土空间规划,与国家、区域相关规划有机衔接,突出规划先行和引领作用。进一步实施黄河流域“水资源保护—绿色发展—文化传承”建设协同发展战略,发挥区域独特的自然—人文优势特色,将水资源保护和生态屏障建设与绿色产业发展、特色文化传承、美丽乡村建设有机结合。同时,构建循环型产业体系,推动产业绿色低碳发展,实现生态保护优先绿色发展模式,实施符合区域特色的农林产业扶贫、旅游扶贫、电商扶贫、科技扶贫、生态保护建设扶贫、转移就业脱贫、教育扶贫等脱贫扶贫工程。最后还要启动制订黄河流域绿色产业扶持政策与保障措施,以及黄河流域上下游之间水资源保护和生态保护的区际利益生态补偿差异化政策,形成资金分配与水资源保护和生态保护成效挂钩机制,为黄河流域高质量发展提供支撑保障。
参考文献
黄河流域农区贫困特征及其影响因素
DOI:10.18402/resci.2020.01.18
[本文引用: 1]

中国创造性地实施精准扶贫政策以来,减贫人口和减贫效果均较显著,在世界反贫困史上取得了举世瞩目的成就。黄河流域作为中国贫困人口众多的典型区域,开展整体性、系统性解析具有重要意义。本文利用ArcGIS、地理探测器等工具,以356个贫困空间单元为基础,通过研究发现:①黄河流域上游、中游农区呈现出贫困人口多、贫困程度深,且具有明显的空间集聚特征;②黄河流域贫困具有明显的空间异质性,流域整体和上、中、下游各地区所受影响因素的作用强度不同,经济因素对贫困解释力较强,部分因子交互作用呈现“1+1>2”的互补增强效应;③黄河流域农区致贫因子各异,且作用强度不同,呈现出自然贫困→经济贫困→社会贫困的变化态势,而社会贫困难以改善自然贫困,最终形成“贫困循环怪圈”,其中自然因素是贫困发生的基础性因素,经济因素是贫困发展的主导性因素,社会因素则是解决贫困的关键性因素。
Spatial characteristics and influencing factors of rural poverty in the Yellow River Basin
DOI:10.18402/resci.2020.01.18
[本文引用: 1]

China creatively implemented the precision poverty alleviation policy in 2014 and has made significant achievements in reducing population in poverty and poverty reduction, which is remarkable in the anti-poverty history of the world. As the key area of poverty in China, the Yellow River Basin is in urgent need of an overall and systematic analysis of its poverty status and poverty alleviation situation. Based on the data of 356 county-level administrative units and using ArcGIS and geographical detector tools, this study found that: (1) Rural areas in the upper and middle reaches of the Yellow River Basin showed typical characteristics of poor population, deep poverty, and spatial agglomeration of population in poverty. (2) Poverty distribution of the rural Yellow River Basin showed clear spatial heterogeneity; the intensity of the influencing factors basin-wide and in the upper, middle, and lower reaches of the basin was different; and the explanatory power of the economic factors to poverty was stronger than other factors. The interaction between some factors showed a synergetic effect of 1+1> 2. (3) Environmental poverty led to economic poverty, which in turn caused social poverty, and social factors are not conducive to improving the environmental poverty, and thus a “poverty loop” was formed in the rural areas of the Yellow River Basin. Environmental factors were the basic causal factors of poverty, economic factors were the leading factors of poverty development, and social factors were the key factors for solving the problem of rural poverty.
黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展战略立法的策略
Strategy of the legislation of Yellow River Basin ecological protection and high-quality development
Exploring impacts of the Grain for Green program on Chinese economic growth
DOI:10.1007/s10668-020-00810-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
黄河流域经济社会发展指标分析
Study on the economic and social development indicators in the Yellow River Basin
中国矿产资源开发利用的环境影响
Environmental impacts caused by the development and utilization of mineral resources in China
发展地理学视角下欠发达地区贫困的地方分异与治理
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910011
[本文引用: 1]

在梳理发展地理学的发展过程、基本理论、分析模式和方法的基础上,结合中国解决区域性整体贫困目标和可持续发展本地化与减贫的学术探索,构建了欠发达地区贫困的发展地理学分析框架,建立了由经济地理资本、社会地理资本、文化地理资本、生态地理资本和政治地理资本构成的“五位一体”地理资本指标体系,提出了数据处理集成方法和技术流程,系统分析欠发达地区贫困的地方分异与治理方案。实证研究显示:① 地理探测可以确定作用地方贫困的主导地理资本,各主导地理资本对贫困发生率的决定力L<sub>A</sub><sub>, </sub><sub>P</sub> ≥ 0.15;② 在不同主导地理资本作用下,5个单维地理资本指数及其合成的区域地理资本指数地方分异明显,存在阻隔和时滞特征;③ 贫困的地方分异可分为经济地理资本约束型、经济—社会地理资本约束型、经济—社会—生态地理资本约束型、经济—社会—文化—生态地理资本约束型4大类共7小类;④ 立足发展特征,挖掘地方动力,提出不同贫困分异类型的地方治理对策和模式。乡村振兴和2020年的减贫转向,应重视欠发达地区贫困的空间分异与空间扩散、空间整合的综合研究,为可持续发展本地化与减贫提供发展地理学解决方案。
Local differentiation and alleviation of poverty in underdeveloped areas based on development geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910011
[本文引用: 1]

The development of development geography stems from the study of underdeve-lopment and poverty. On the basis of combing the development process, basic theories, analytical models and methods of development geography, and combined with China's academic exploration of regional overall poverty alleviation and localization and poverty reduction of sustainable development, this paper constructs an analytical framework of development geography of poverty in underdeveloped areas, and establishes the "five-in-one" geographical capital index system composed of economic geographical capital, social geographic capital, cultural geographic capital, ecological geographic capital and political geographic capital. The integration method and technical flow of data processing are put forward to analyze the local differentiation of poverty in underdeveloped areas. The results show that: (1) Geographical detection determined the leading geographic capital that plays a role in poverty, and the determinative force of each leading geographic capital on the poverty incidence LA,P ≥ 0.15; (2) Under the action of different dominant geographical capitals, the five single-dimensional geographic capital indexes and their synthetic regional geographic capital indices have obvious local differentiation, and have the characteristics of barrier and time delay; (3) The poor local differentiation can be divided into four types: economic geographical capital constraint, economic-social geographical capital constraint, economic-social-ecological geographical capital constraint, and economic-social-cultural-ecological geographical capital constraint; (4) Based on the characteristics of development, we tap the local dynamics and put forward the targeted countermeasures and models of different types to alleviate local poverty. Under the background of rural vitalization and the 2020 poverty alleviation shift, it is necessary to focus on the comprehensive research on spatial differentiation, spatial diffusion and spatial integration of poverty in less developed areas, so as to provide development geographical solutions for localization and poverty reduction of sustainable development.
黄河流域高质量发展: 人地协调与空间协调
High-quality development of the Yellow River Basin from a perspective of economic geography: Man-land and spatial coordination
DOI:10.2307/142170 URL [本文引用: 2]
基于“三生”空间的传统村落人居环境演变及驱动机制: 以湖南江永县兰溪村为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.011
[本文引用: 1]

在快速城市化与乡村旅游开发背景下,从“三生”空间视角探索乡村人居环境演变特征和发展机理,可在一定程度上反映出中国传统村落发展的一般规律。本文以湖南省江永县兰溪村为例,基于参与性农村调查与评估(PRA)、GIS空间分析等方法,研究了其“三生”空间演变的过程、格局与机制,结果如下:①从“三生”空间视角,分析了传统村落人居环境与“三生”空间的系统耦合特征。认为传统村落人居环境在空间上要实现生活空间宜居、生产功能协调和生态空间优美,这与“三生”空间系统目标和特征非常契合;②从“三生”空间演变特征来看,兰溪村生活空间由血缘集聚向外围扩散转换,生产空间由农业功能向旅游功能转型,生态空间由外部整体收缩向内部斑块化发展。“三生”空间演变过程是一个相互交织、相互渗透的过程,“三生”空间逐渐由传统的人居空间向新型复合空间转变;③传统村落“三生”空间格局的演变过程,是在旅游市场需求、政府政策引导、空间行为转变和自组织反应力的内外双重驱动作用下的结果,内力驱动主要集中在农户生活空间结构特征上的延续与转化,外力驱动主要体现在生产和生态空间结构的转型与更替。
Change of human settlement environment and driving mechanism in traditional villages based on living-production-ecological space: A case study of Lanxi village, Jiangyong county, Hunan povince
高质量发展的目标要求和战略路径
The goals and strategy path of high-quality development
中国空间治理体系现代化在“十九大”后的新态势
Rural restructuring at village level under rapid urbanization in metropolitan suburbs of China and its implications for innovations in land use policy
DOI:10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.12.001 URL [本文引用: 1]
黄河流域水循环演变若干问题的研究
Study of some problems in water cycle changes of the Yellow River Basin
人类活动影响下的黄河流域水资源演化规律初探
Evolutionary laws of the Yellow River Basin's water resources under the impact of human activities
基于极大熵原理的黄河流域水资源承载力研究: 以山西段为例
水资源承载力是度量水资源安全的一个重要手段,是探讨用水对策的重要依据,也是近年来水科学领域研究的热点问题。该文在灰色系统理论理论基础上,根据信息论中Jaynes 最大信息熵原理,提出了一种水资源承载力评价模型;将其应用到山西省黄河流域水资源承载力评价中,并将评价结果与模糊综合评判结果进行对比分析,说明了该模型结果的分辨率、灵敏度以及评价的可靠性都有一定程度提高,从而为水资源承载力研究提供了新的思路与方法。
Water resource carrying capacity in Yellow River Watershed based on the theory of maximum entropy: A case of Shanxi part
黄河流域水资源承载力评价
Water resources carrying capacity evaluation of the Yellow River Basin
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190815 URL [本文引用: 1]
Assessing regional sustainability: The case of land use and land cover change in the Middle Yiluo catchment of the Yellow River Basin, China
DOI:10.1016/S0143-6228(00)00020-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
黄河流域三生空间的演变与区域差异: 基于资源型与非资源型城市的对比
DOI:10.18402/resci.2020.12.03
[本文引用: 1]

黄河流域是中国生态脆弱性较典型的国土空间范围,流域内资源型与非资源型城市经济发展方式差异大,研究两者三生空间的演变与区域差异,对认知黄河流域国土空间开发利用状况很重要。在三生空间分类的基础上,采用空间自相关、泰尔指数,测度了流域内两类城市三生空间的区域差异。研究表明:①两类城市三生空间均变化较大,生活空间上升显著,资源型城市生态空间被生活、生产空间挤压的时段更长;非资源型城市生产空间被生活、生态空间挤压的时段更长。②两类城市三生空间具有空间聚集特征,三生空间的高密度区和低密度区较稳定。③对于影响两类城市三生空间区域差异的要素(经济和人口)而言,经济发展更易扰动三生空间变化。在经济和人口要素的影响下,非资源型城市三生空间的区域差异较大,而资源型城市的区域差异较小,其可能的原因与非资源型城市经济发展方式多样而资源型城市相对单一有关。黄河流域所有城市三生空间的总体差异主要来自两类城市内部。资源型城市生产、生态空间的区域差异,以及非资源型城市生活空间的区域差异,对黄河流域所有城市三生空间的区域差异产生主要影响。本文提出相关对策建议,以期为黄河流域国土空间管控与治理提供参考。
Change and regional differences of production-living-ecological space in the Yellow River Basin: Based on comparative analysis of resource-based and non-resource-based cities
DOI:10.18402/resci.2020.12.03
[本文引用: 1]

It is known that the ecological vulnerability is rather prominent in the Yellow River Basin (YRB); there are great differences in economic development mode between resource-based and non-resource-based cities in this basin. Studying the evolution and regional differences of the production-living-ecological space (PLES) of two types of cities in the basin, which is particularly important to understand the development and utilization of land-space in the YRB. Based on the PLES classification, this study measured the regional differences of PLES in the two types of cities by employing spatial auto-correlation and Theil index. It was found that: (1) PLES of the two types of cities changed dramatically, living space had increased significantly; the ecological space of resource-based cities was squeezed by living and production space for a longer time; while the production space of non-resource-based cities was squeezed by living and ecological space for a longer time. (2) PLES of the two types of cities showed the characteristics of spatial aggregation, and the high-density area and low-density area of PLES of each type was relatively stable. (3) For factors (economy and population) affecting the regional difference of PLES of the two types of cities, economic development was more likely to cause the change of PLES. Influenced by economic development and population, the regional difference of the PLES of non-resource-based cities was obvious, while that of resource-based cities was comparatively small. Possible reasons for the differences may be the diverse modes of economic development in non-resource-based cities and the lack of diversity in resource-based cities. The overall regional differences of PLES of all cities in the Yellow River Basin mainly depend on the internal differences of the two types of cities. The regional differences of production and ecological spaces from the resource-based cities and the regional differences of living space from the non-resource-based cities had major impact on the regional differences of PLES of all cities in the Yellow River Basin. This paper puts forward relevant countermeasures and suggestions, which is of significance for the management of land-space in the YRB.
黄河流域土地利用时空格局演变及驱动力
DOI:10.18402/resci.2020.03.05
[本文引用: 1]

土地利用时空格局是人类与自然相互作用状况的重要表征。研究黄河流域土地利用时空格局及其驱动因素,厘清土地利用类型转换及粮食保障用地、生态保育用地、城乡建设用地的时空变化特征,可为黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展国家重大战略的规划制定与实施提供参考。本文基于土地利用类型转移矩阵和空间自相关,从城市群、省、市、县多尺度入手,利用7期土地利用数据对黄河流域1970—2015年土地利用状况及变化进行探究。结果表明:①黄河流域生态保育用地和耕地占比多年平均值分别为79.04%和18.64%,表明生态保护和粮食生产是其两大主体功能;②城乡建设用地占比逐年提高,城市群地区是建设用地扩张的主体空间;③黄河流域耕地、生态保育用地和城乡建设用地各节点年份Moran’s I均大于0.75,表明3种功能类型用地具有强空间正向集聚效应,呈现出“凹”字型分布格局;④城乡建设用地扩张以牺牲耕地为代价,同时部分农村居民点用地逐渐转化为城镇用地;⑤人口规模和经济发展是促进土地利用变化的核心因素,驱动力因素存在区域差异,在黄河下游的山东、河南,经济水平达到一定规模后,伴随经济再发展不会出现大规模城乡建设用地扩张。
Spatiotemporal changes and driving forces of land use in the Yellow River Basin
DOI:10.18402/resci.2020.03.05
[本文引用: 1]

The spatiotemporal pattern of land use is an important representation of the interaction between human and nature. Study on the spatial-temporal pattern of land use and its driving factors in the Yellow River Basin and to clarify land-use conversion as well as the spatial-temporal variation of cultivated land, ecological land and urban-rural construction land, which can provide some reference for the planning and implementation of the national strategy of ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. Based on the transfer matrix of land use types and spatial autocorrelation, the study explored the land use in the Yellow River Basin provinces from 1970 to 2015 by using land use data of seven periods from multiple scales of city cluster, province, city, and county. The results show that: (1) The proportion of ecological land and arable land in the Yellow River Basin is 79.04% and 18.64% respectively on average, indicating that ecological protection and food production are two main functions there; (2) The urban-rural construction land proportion increases year by year, and urban agglomeration region is the main space of construction land expansion; (3) Moran’s I of arable, ecological, urban-rural construction land of the Yellow River Basin provinces was more than 0.75 in different years and showed a strong positive spatial agglomeration effect and a pattern of concave type distribution ; (4) The expansion of urban-rural construction land is at the expense of arable land, and at the same time, part of rural land is gradually transformed into urban land, and the imbalance between human and land is increasingly prominent. (5) Population size and economic development are the core factors to promote land use change, and the performance of different spatial driving factors is inconsistent. There will not appear large-scale expansion of urban and rural construction land with the economic development in Shandong and Henan provinces located in the lower reaches of the Yellow River.
黄河流域县域经济密度测算及空间分异研究
A study on estimates and spatial differentiation of economic density at county level in Yellow River Basin
黄河流域产业发展对生态环境的胁迫诊断与优化路径识别
DOI:10.18402/resci.2020.01.13
[本文引用: 1]

黄河流域是中国区域发展战略格局的重要支撑区以及国土生态安全的关键区域,也是国家重要的能源安全支撑区和粮食安全基地。但受区位条件、自然地理环境和资源禀赋等因素影响,该地区经济基础相对薄弱,以能源重化工为主的单一化产业体系加重了地区生态环境负担。本文在辨析黄河流域生态保护与高质量发展主要限制因素的基础上,分析了地区产业发展对生态环境本底、大气环境、水资源与水环境、生态功能的胁迫特征,总结了地区产业发展与生态环境保护的主要矛盾及需要把握的关系;提出实现黄河流域生态保护与高质量发展目标,必须处理好产业开发布局与流域生态环境安全格局稳定、重点区域产业发展与资源环境承载能力、重点突破与系统统筹的关系。为此,建议该地区应优化产业发展路径,积极推进以绿色循环为核心的新型工业化,提升产业发展层次;以地区资源环境约束促进能源基础原材料产业规模控制和效率提升;以资源环境承载力为基础优化产业空间布局,确定适宜的产业发展空间和生态保护红线,推进重点能源化工基地建设和城市群产业集聚区建设;加强能矿资源开发的生态空间管控与生态修复,实施一批区域性生态环境治理和修复工程。
Environmental stress and optimized path of industrial development in the Yellow River Basin
DOI:10.18402/resci.2020.01.13
[本文引用: 1]

The Yellow River Basin is a key area for China’s regional development strategy and national ecological security. However, affected by the location, physical environment, and resource endowments, the economic foundation of the region is relatively weak. It has formed an industrial system dominated by energy and heavy chemical industries, which greatly increased the regional ecological burden. The Yellow River Basin is facing the predicaments of weak economic foundation and weak development ability, the pressures of accelerating social and economic development and transformation of development mode, the contradictions between resource use and ecological protection and between industrial development and environmental carrying capacity, and the challenges of deteriorating local living environment. The core contents of ecological environment protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin is to balance the relationship between resource use and environmental protection, the scale of development and the carrying capacity of resources and the environment, and the development of key areas and the protection of the total ecological security to ensure energy security, ecological security, food security, watershed security, and the health of human settlements. We suggest that the region should optimize the industrial development path, actively promote the new industrialization with green industrial development as its core, and improve the level of industrial development and resource and environmental efficiency; optimize the industrial space based on the resource and environmental carrying capacity, determine suitable industrial development space and ecological protection red line, promote the construction of key energy and chemical bases and the construction of industrial clusters in urban agglomerations, implement strict environmental access policies, and improve environmental control standards for industrial development; strengthen spatial control and ecological restoration of energy and mining development projects, and implement a series of regional ecological environment governance and restoration projects.
Factors influencing ecosystem services in the Pearl River Delta, China: Spatiotemporal differentiation and varying importance
黄河流域县域尺度生态系统服务供给和需求核算及时空变异
The relationship between supply and demand of ecosystem services and its spatio-temporal variation in the Yellow River Basin
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210110 URL [本文引用: 4]
黄河流域的综合治理与可持续发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912001
[本文引用: 1]

黄河流域与黄河所经地区在国家发展中具有极为重要的战略地位。2019年9月习近平总书记在郑州主持召开黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展座谈会上发表了重要讲话,具有重大战略意义。本文对黄河流域的综合治理与可持续发展形成了初步认识,指出新时代黄河流域全面深刻转型发展的任务仍然艰巨,需转变理念,持续推进能源清洁高效利用,因地制宜重点推进产业发展,不搞粗放式大开发,搞好资源耕地保护等方面应是推进黄河流域综合治理及保障可持续发展的重要举措,认为“黄河经济带”在全国经济层面上不存在,目前不适宜将“黄河三角洲”确定为国家战略。
Development and management tasks of the Yellow River Basin: A preliminary understanding and suggestion
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912001
[本文引用: 1]

The Yellow River Basin and the areas along the Yellow River play an important strategic role in national development. Xi Jinping, General Secretary of the CPC, delivered an important speech at the symposium on ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin in Zhengzhou, which is of great strategic significance. This paper gives a preliminary understanding of the comprehensive governance and the sustainable development of the Yellow River Basin. It points out that the task of the comprehensive and profound transformation and development of the Yellow River Basin in the new era is still arduous, and change of concept is required. Continuing to promote the clean and efficient use of energy, promoting industrial development in accordance with local conditions, preventing extensive development and protecting cultivated land resources should be regarded as important measures to strengthen the comprehensive management and guarantee the sustainable development of the Yellow River Basin. It is believed that the "Yellow River Economic Belt" does not exist at the national economic level, and it is not appropriate to identify "the Yellow River Delta" as a national strategy.
流域主体功能优化与黄河水资源再分配
Optimization of main functions of river basin and redistribution of water resources in the Yellow River
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210116 URL [本文引用: 1]
黄河流域生态保护与高质量发展的耦合关系及交互响应
Coupling relationship and interactive response between ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210112 URL [本文引用: 1]
黄河流域生态环境与高质量发展测度及时空耦合特征
Level measures and temporal and spatial coupling analysis of ecological environment and high quality development in the Yellow River Basin
黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展的关键: 人地系统的优化
The key to ecological protection and high quality development in the Yellow River Basin: Optimization of human-land systems. Journal of North China university of water resources and electric power
黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展: 框架、路径与对策
Ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin: Framework, path, and countermeasure
in China: Land policies and regional social-economical drivers
Spatial imbalance and changes in supply and demand of ecosystem services in China
DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.080 URL [本文引用: 3]
Local indicators of spatial association: LISA
DOI:10.1111/j.1538-4632.1995.tb00338.x URL [本文引用: 1]
利用核密度与空间自相关进行城市设施兴趣点分布热点探测
Detecting "Hot Spots" of facility POIs based on kernel density estimation and spatial autocorrelation technique
面向可持续城市生态系统管理的资源环境承载力评价方法与实践应用: 以烟台市为例
Evaluation method and application for resources-environment carrying capacity towards sustainable urban ecosystem management: A case study of Yantai city
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20201006 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于生态安全格局的国土空间生态保护修复关键区域诊断与识别: 以烟台市为例
Determining and identifying key areas of ecosystem preservation and restoration for territorial spatial planning based on ecological security patterns: A case study of Yantai city
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200116 URL [本文引用: 1]
着力构建黄河流域脱贫攻坚长效机制
Efforts to build a long-term mechanism for poverty alleviation in the Yellow River Basin
基于地理单元的区域高质量发展研究: 兼论黄河流域同长江流域发展的条件差异及重点
High quality regional development research based on geographical units: Discuss on the difference in development conditions and priorities of the Yellow River Basin compared to the Yangtze River Basin
DOI:10.2307/142170 URL [本文引用: 1]