

面向居民福祉的国土空间规划监测评估预警模型体系研究——基于可行能力理论
|
焦林申(1991- ),男,河南商丘人,博士,助理研究员,研究方向为建成环境与居民福祉、大数据与人工智能应用。E-mail: jiaolinshen@hzcu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2024-04-07
修回日期: 2024-10-18
网络出版日期: 2025-02-21
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42271230)
国家自然科学基金项目(42330510)
Research on the well-being-oriented model system of monitoring-evaluation-warning for territorial spatial planning: Based on the capability approach
Received date: 2024-04-07
Revised date: 2024-10-18
Online published: 2025-02-21
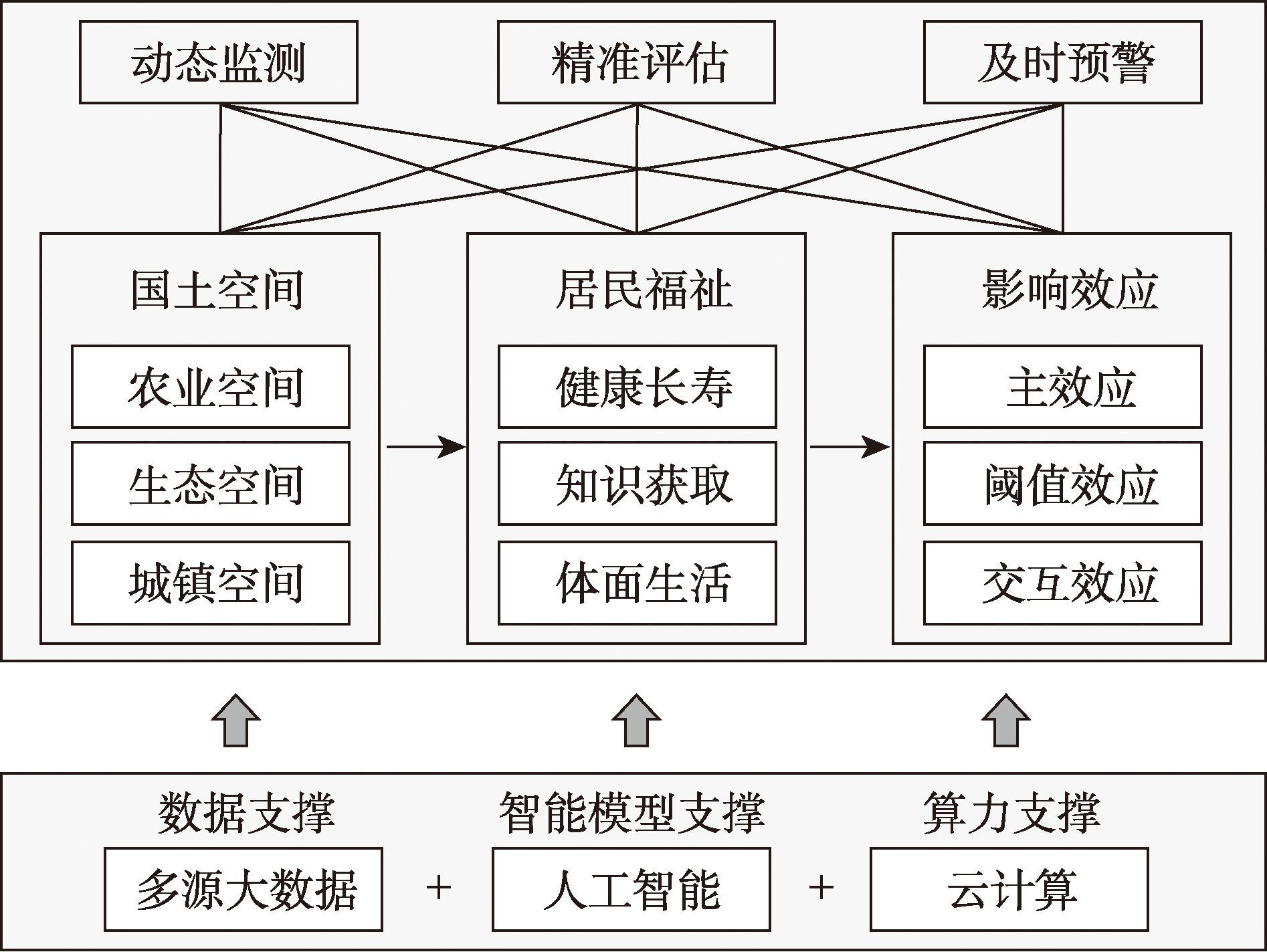
国土空间规划监测评估预警不仅是全国国土空间规划实施监测网络(CSPON)建设的重点内容,也是落实以民生福祉为发展根本目的的福祉发展观的重要抓手;然而现有研究侧重于空间要素和技术方法,对人的关怀不足,存在“见地不见人”的问题。基于对理解发展和福祉产生重大影响的可行能力理论,构建面向居民福祉的国土空间规划监测评估预警概念模型;在此基础上形成以居民福祉为价值标准,以动态监测、精准评估和及时预警为主要内容,以大数据、人工智能和云计算为关键技术支撑的智能模型体系;并以常熟市为例构建应用情景,展示模型体系在落实福祉发展观、推动智慧规划转型方面的应用价值。研究可为CSPON建设和实施监督体系提供理论借鉴和方法支撑。
焦林申 , 张敏 , 甄峰 , 张姗琪 , 秦萧 . 面向居民福祉的国土空间规划监测评估预警模型体系研究——基于可行能力理论[J]. 自然资源学报, 2025 , 40(3) : 584 -599 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20250302
The monitoring-evaluation-warning of territorial spatial planning is not only the key content of China Spatial Planning Observation Network (CSPON) but also an important mean to implement the people-centered development thought. However, existing studies predominantly emphasize spatial elements while overlooking resident well-being. The Capability Approach (CA) has been a powerful and more widely used evaluative framework for individual well-being and public policy. From the view of the CA, well-being is defined as capabilities and is the end for the human-oriented development. Inspired by the CA, this paper constructed an innovative conceptual model for well-being-oriented monitoring-evaluation-warning of territorial spatial planning. In this conceptual model, well-being is the final target instead of the spatial results, as well as a people-centered development ideology. The model is composed of three core elements: dynamic monitoring, accurate evaluation, and timely early warning. It is technologically underpinned by big data, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing, which together offer robust analytical capabilities. Compared to existing research, our monitoring, evaluation, and warning system not only focuses on territorial space and key technologies but also encompasses the well-being of residents and the relationship between territorial space and resident well-being. Thus, we extend the scope of traditional studies by integrating well-being into the implementation and supervision of the territorial spatial planning, ensuring a more holistic and inclusive assessment of the planning's impact. To support the evolution of smart planning, we proposed three smart model systems for dynamic monitoring, accurate evaluation, and timely early warning respectively. The results of the practical application in the built environment show the promise of applying the model system to CSPON. This paper enriches existing literature by incorporating the CA and well-being, offering a novel perspective on how to reconceptualize the monitoring, evaluation and warning of territorial spatial planning. This paper also illustrates the pathways on how to implement the well-being thought in the monitoring-evaluation-warning of territorial spatial planning and providing theoretical reference and method support for CSPON construction.

表1 面向国土空间规划监测评估预警的居民福祉指标体系Table 1 Indicators of well-being for monitoring-evaluation-warning for territorial spatial planning |
| 维度 | 指标 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| 健康长寿 | 平均寿命/年 | 居住地一定范围内,近5年已故人口的平均寿命,表征获取长寿的可行能力 |
| 平均疾病负担/种 | 居住地一定范围内,近5年已故人口的平均死因疾病数量,通过正向化处理,表征生存质量方面的可行能力 | |
| 残疾*(是/否) | 对有残疾的样本的其他两个指标赋予折减权重,将其设置为0.5,表征健康长寿维度中的福祉剥夺程度 | |
| 知识获取 | 受教育年限/年 | 基于受教育水平折算后的受教育年限,表征获取知识的可行能力 |
| 职业、技能资格证书等级/年 | 获取相应等级证书所需年限,表征在知识获取维度中的高级可行能力 | |
| 体面生活 | 住房成本/(元/月) | 房价或租金,表征与收入和住房相关的可行能力 |
| 低保家庭人均实际月收入* /(元/月) | 加入低保补贴后的人均实际月收入;将其与案例地人均月收入的比值作为折减系数,表征在体面生活维度中的福祉剥夺程度 |
注:带“*”标注的为剥夺指标,仅根据布尔值和实际值确定同纬度其他指标的折减系数。 |
图5 福祉指数和空间分布模式LISA图注:a图中,x轴为归一化后的福祉指数,0代表福祉最低,1代表福祉最高,黑色短横线长短代表标准差,多维福祉指数为聚合后的综合福祉,其余为特定维度内的福祉指数。b图为多维福祉指数在市域范围内的局部空间模式空间尺度为250 m的六边形网格,无六边形格网覆盖区域为无数据区域,下同。 Fig. 5 Well-being index and the spatial pattern presented by LISA diagram |
图7 居民福祉的群体差异注:人群按纵轴分为左右两类人群,水平柱体的出现位置表明该群体的福祉水平低于对标群体,数值为差异程度,具体指与对标群体的福祉指数差值与自身福祉指数的比值;柱体颜色表示该群体内部的更小亚群,有助于呈现福祉群体差异在更小亚群中的微妙变化。 Fig. 7 Group differences of well-being |
| [1] |
苏红键. 中国地区福祉的比较研究. 社会科学战线, 2020, (10): 89-98.
[
|
| [2] |
陈明星, 周园, 汤青, 等. 新型城镇化、居民福祉与国土空间规划应对. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(6): 1273-1287.
[
|
| [3] |
庄少勤, 赵星烁, 李晨源. 国土空间规划的维度和温度. 城市规划, 2020, 44(1): 9-13, 23.
[
|
| [4] |
黄伊婧, 张姗琪, 林昀, 等. 城市级国土空间规划实施监测体系的构建思路与实践探索: 以宁波市为例. 自然资源学报, 2024, 39(4): 823-841.
[
|
| [5] |
曹春华, 卢涛, 李鹏, 等. 国土空间规划监测评估预警: 内涵、任务与技术框架. 城市规划学刊, 2022, (6): 88-94.
[
|
| [6] |
钟镇涛, 张鸿辉, 刘耿, 等. 面向国土空间规划实施监督的监测评估预警模型体系研究. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(11): 2946-2960.
[
|
| [7] |
田朝晖, 唐萍, 程潇菁. 省级国土空间规划监测评估预警机制框架建构与运用: 以湖南省为例. 国土资源导刊, 2023, 20(3): 54-60.
[
|
| [8] |
董云皓, 李长风, 高宇佳. 关于国土空间规划实施监督子系统建设方法的思考: 以上海市规划驾驶舱建设为例. 上海城市规划, 2022, (4): 43-48.
[
|
| [9] |
唐常春, 卢幸芷, 雷钧钧, 等. 新时期国土空间规划实施评估框架构建与方法创新: 以湖南省湘潭市为例. 规划师, 2021, 37(11): 48-54.
[
|
| [10] |
黄玫. 基于规划权博弈理论的国土空间规划实施监督体系构建路径. 规划师, 2019, 35(14): 53-57.
[
|
| [11] |
李明月, 周晓航, 周艺霖. 市县国土空间规划实施监测指标体系研究: 基于生命周期理论的广东省实例分析. 城市规划, 2022, 46(6): 57-67.
[
|
| [12] |
向晓琴, 高璟. 实施监测视角下的市级国土空间规划指标评析. 规划师, 2023, 39(12): 77-84.
[
|
| [13] |
刘禹麒, 钟镇涛, 周广明, 等. 国土空间规划监测评估预警关键技术研究及应用. 国土资源导刊, 2022, 19(4): 87-92.
[
|
| [14] |
游建标, 胡兆平. 国土空间规划体系下的动态监测评估系统关键技术研究. 北京测绘, 2022, 36(9): 1209-1214.
[
|
| [15] |
李媛, 王志锋, 赵守谅, 等. 以人为本的规划评估: 基于“城市人”理论人本逻辑下的S-CAD方法及应用. 城市规划, 2022, 46(12): 35-44.
[
|
| [16] |
甄峰, 张姗琪, 秦萧, 等. 从信息化赋能到综合赋能: 智慧国土空间规划思路探索. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(10): 2060-2072.
[
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
印阿马蒂亚·森著. 任赜,于真译. 以自由看待发展. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2012: 1-2.
[
|
| [19] |
王圣云, 翟晨阳, 罗颖, 等. 基于“功能—能力”框架的中国多维福祉测评及区域均衡分析. 地理科学, 2018, 38(12): 2031-2039.
[
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
UNDP.Human development report 2019: Beyond income, beyond averages, beyond today: Inequalities in human development in the 21st century. New York: United Nations Development Programme, 2019.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
田建国, 庄贵阳, 朱庄瑞. 新时代中国人类福祉的理论框架和测量. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2019, 29(12): 9-18.
[
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
姜凯凯. 空间资源配置视角下城市规划的转型策略研究: 基于我国市场经济实践的思考. 城市规划, 2021, 45(1): 30-38, 61.
[
|
| [27] |
刘雨婷, 覃盟琳, 欧阳慧婷, 等. 基于生态系统服务供需平衡的国土空间资源配置优化. 自然资源学报, 2024, 39(6): 1358-1383.
[
|
| [28] |
周昱辰, 尹丹, 黄庆旭, 等. 基于生态系统服务参与式制图的“三生”空间优化建议: 以白洋淀流域为例. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(8): 1988-2003.
[
|
| [29] |
MEA. Ecosystems and Human Well-being:A Framework for Assessment. Washington DC: Island Press 2005: 71-79.
|
| [30] |
董孝斌, 刘梦雪. 土地利用/覆盖变化—生态系统服务—人类福祉关系研究进展. 北京师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 58(3): 465-475.
[
|
| [31] |
何春阳, 张金茜, 刘志锋, 等. 1990—2018年土地利用/覆盖变化研究的特征和进展. 地理学报, 2021, 76(11): 2730-2748.
[
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
刘吉祥, 肖龙珠, 周江评, 等. 建成环境与青少年步行通学的非线性关系: 基于极限梯度提升模型的研究. 地理科学进展, 2022, 41(2): 251-263.
[
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
王伟, 柳泽, 林俞先, 等. 从国土空间规划 “一张图”到CSPON“一张网”学术笔谈. 北京规划建设, 2024, (1): 52-65.
[
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |