

南水北调工程通水对受水区农业用水的影响
|
徐章星(1991- ),男,江苏苏州人,博士,讲师,硕士生导师,主要从事水利经济学研究。E-mail: xuzhangxing@hhu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2023-09-04
修回日期: 2024-02-19
网络出版日期: 2024-05-11
基金资助
江苏省社会科学基金青年项目(22EYC011)
江苏高校哲学社会科学研究一般项目(2022SJYB0032)
中央高校基本科研业务经费项目(B230207027)
江苏省创新支撑计划(软科学研究)专项资助(BR2023021-2)
The influence of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on agricultural water use in the water-receiving areas
Received date: 2023-09-04
Revised date: 2024-02-19
Online published: 2024-05-11
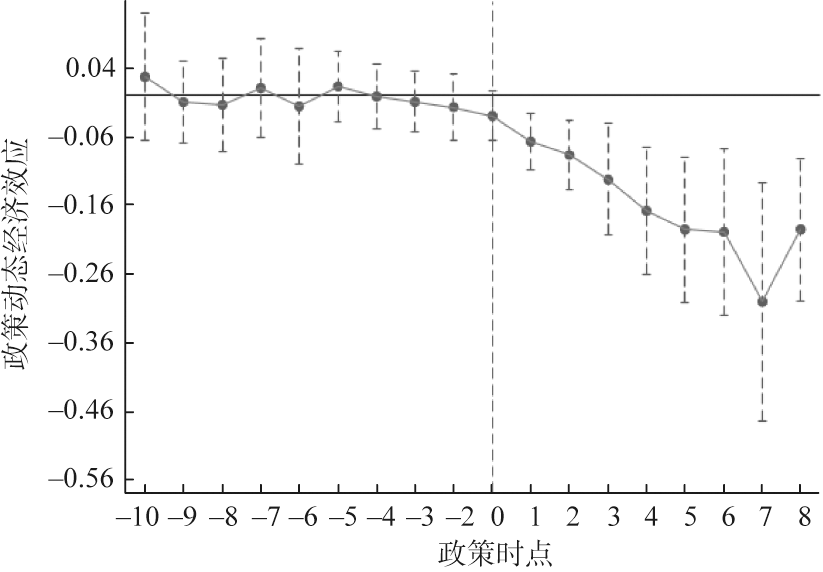
利用中国31个省(自治区、直辖市)2004—2021年面板数据,构建渐进双重差分模型,基于规模和结构双重视角,考察了南水北调工程通水对于受水区农业用水的影响。结果表明:(1)南水北调工程通水降低了受水区农业用水规模和农业用水占比,其中的作用机制为经济作物种植面积和比例的减少,以及粮食作物种植比例的增加;(2)相较于东线而言,南水北调工程通水对于受水区农业用水的负向影响在中线地区更为严重;(3)南水北调工程“通水间接返还农业用水”的效应存在,但现阶段被工程对受水区农业用水的直接效应所遮掩。因此,需要从战略高度清晰认识到南水北调工程通水对于受水区农业用水的影响,强化农业用水支撑,保障国家粮食安全,推动南水北调后续工程高质量发展。
徐章星 , 邱晓楠 , 田贵良 , 李祎雯 . 南水北调工程通水对受水区农业用水的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 2024 , 39(5) : 1222 -1240 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20240515
Based on the panel data of 31 provincial-level regions in China from 2004 to 2021, this paper constructs a Time-varying DID model from dual perspectives of scale and structure to examine the impact of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project (hereafter the Project) on agricultural water use in the water-receiving areas. The results show that: (1) The water supply of the project has reduced the scale and proportion of agricultural water use in the receiving areas, and the mechanism analysis of the result is the reduction of the planting area and proportion of economic crops, and the increase of the proportion of grain crops. (2) Compared with the eastern route, the negative impact of the Project on the agricultural water use in the receiving areas is more serious in the middle route areas. (3) There is an effect of "indirect return of agricultural water through water supply" of the Project, but at this stage it is neglected by the direct impact of the Project on agricultural water use in the water-receiving areas. Therefore, it is necessary to clearly understand the impact of the Project on the agricultural water use of the water-receiving areas from a strategic perspective, to strengthen the support of agricultural water use to ensure national food security, and to promote the high-quality development of follow-up projects of the Project.

表1 变量描述性统计Table 1 Descriptive statistics of variables |
| 变量 | 单位 | 样本量/个 | 均值 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 中位数 | 最大值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农业用水规模 | 亿m3,取自然对数 | 558 | 4.395 | 0.987 | 1.030 | 4.595 | 6.331 |
| 农业用水结构 | 无 | 558 | 0.611 | 0.181 | 0.069 | 0.620 | 0.952 |
| 工程通水 | 无 | 558 | 0.093 | 0.291 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 播种面积 | 千hm2,取自然对数 | 558 | 8.103 | 1.190 | 4.484 | 8.479 | 9.620 |
| 一产就业 | 万人,取自然对数 | 558 | 6.291 | 1.131 | 3.219 | 6.554 | 8.085 |
| 灌溉条件 | 无 | 558 | 0.433 | 0.187 | 0.148 | 0.379 | 1.234 |
| 农村居民用电量 | 亿kW·h/万人 | 558 | 0.166 | 0.440 | 0.003 | 0.053 | 4.087 |
| 农业产值 | 亿元,取自然对数 | 558 | 6.790 | 1.191 | 3.238 | 7.055 | 8.789 |
| 涉农固定资产 | 亿元,取自然对数 | 558 | 5.425 | 1.451 | 0.473 | 5.541 | 8.404 |
| 水资源禀赋 | 亿m3,取自然对数 | 558 | 4.952 | 0.845 | 3.094 | 5.188 | 6.428 |
表2 基准回归结果Table 2 Benchmark regression results |
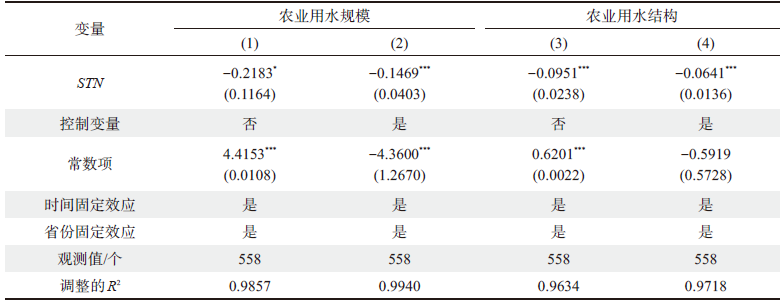 |
注:括号内为聚类到省份的标准误,*、***分别表示10%、1%的显著性水平,下同。 |
表3 稳健性检验:排除同期政策和加入前定变量Table 3 Robustness test: Excluding contemporaneous policies and incorporating prefixed variables |
 |
注:**表示5%的显著性水平,下同。 |
表4 稳健性检验:PSM-DID和CSDID估计Table 4 Robustness testing: PSM-DID and CSDID estimates |
 |
表5 机制检验Table 5 Mechanism verification |
| 变量 | 粮食作物面积 (1) | 经济作物面积 (2) | 粮食作物比例 (3) | 经济作物比例 (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STN | 0.0891 (0.0839) | -0.1852*** (0.0526) | 0.0419*** (0.0151) | -0.0498*** (0.0163) |
| 控制变量 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 常数项 | 5.1333** (2.3548) | 6.8263*** (2.3067) | 0.6723* (0.3604) | 0.3261 (0.4153) |
| 时间固定效应 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 省份固定效应 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 观测值/个 | 558 | 558 | 558 | 558 |
| 调整的R2 | 0.9887 | 0.9871 | 0.9819 | 0.9373 |
表6 区域异质性分析Table 6 Regional heterogeneity analysis |
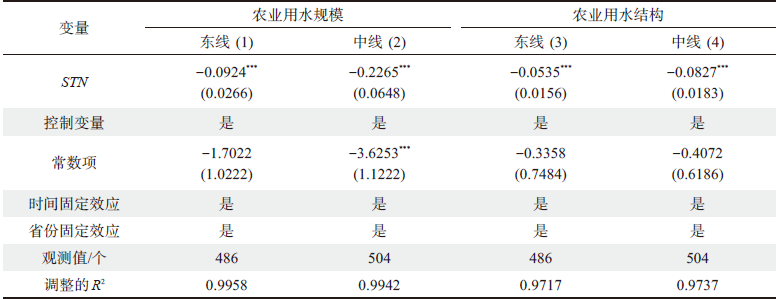 |
表7 调水返还农业用水:基于农业用水规模视角Table 7 Water diversion and return of agricultural water: From the perspective of agricultural water use scale |
 |
表8 调水返还农业用水:基于农业用水结构视角Table 8 Water diversion and return of agricultural water: From the perspective of agricultural water use structure |
 |
表9 南水北调工程通水对受水区分类用水的影响Table 9 The impact of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on the classification of water use in receiving areas |
 |
表10 南水北调工程通水对受水区地表水和地下水的影响Table 10 The impact of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on surface water and groundwater in the receiving areas |
 |
表11 南水北调工程通水对受水区农业用水变动的影响Table 11 The impact of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on changes in agricultural water use in receiving areas |
| 变量 | 规模变动 (1) | 结构变动 (2) |
|---|---|---|
| STN | -4.2375** (1.5668) | -0.0107*** (0.0032) |
| 控制变量 | 是 | 是 |
| 常数项 | 1.0704 (50.6925) | -0.1192 (0.1219) |
| 省份固定效应 | 是 | 是 |
| 时间固定效应 | 是 | 是 |
| 观测值/个 | 527 | 527 |
| 调整的R2 | 0.0714 | 0.1504 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
谢晗进, 谭熙. 南水北调东、中线全面通水对农业水足迹的脱钩: 基于76个沿线城市的准自然实验. 生态经济, 2023, 39(1): 137-147.
[
|
| [3] |
樊旭, 徐惠亮, 周洁. 京杭运河扬州段沿运灌区用水情况分析及管理建议. 中国水利, 2015, (2): 24-26, 32.
[
|
| [4] |
席海洋, 陈克恭, 鱼腾飞, 等. 南水北调西线一期工程调水新增水资源利用. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 158-166.
[
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
肖挺. “南水北调”工程对第一产业影响效果评估: 合成控制法下中线工程沿线及汉水地区的分析. 南开经济研究, 2022, (2): 35-50.
[
|
| [8] |
杨富茂. “南水北调”对农业生产的损益分析: 基于湖北、河南两省14个村庄1222位农民的调查. 绿色科技, 2019, (8): 247-249, 252.
[
|
| [9] |
邓志刚, 郭培震, 乔从恒. 德州市南水北调供水存在问题及对策建议. 海河水利, 2022, (1): 5-8.
[
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
尹新明. 南水北调受水区某工业新城取水水源与水资源配置分析. 陕西水利, 2023, (3): 33-35.
[
|
| [12] |
韩雁, 张士锋, 吕爱锋. 外调水对京津冀水资源承载力影响研究. 资源科学, 2018, 40(11): 2236-2246.
[
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
李佳, 张荣, 毛豪林, 等. 河南省南水北调工程供水效益分析. 河南水利与南水北调, 2019, 48(12): 78-80.
[
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
杨丽, 朱启林, 孙静, 等. 北京市南水北调中线工程供水效益评估. 人民长江, 2017, 48(10): 44-46, 78.
[
|
| [17] |
刘辉, 狄乾斌. 南水北调东线“一期”工程对京杭大运河沿线城市经济发展的影响分析: 基于合成控制法的实证. 资源开发与市场, 2020, 36(11): 1185-1191.
[
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
刘远书, 籍国东, 罗忠新, 等. 南水北调东线治污对山东段的环境与经济影响: 基于EKC曲线理论的实证分析. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2020, 30(10): 73-81.
[
|
| [20] |
程扬, 张雪花, 冯婧. 南水北调工程受水区生态环境效应研究. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2016, 26(s2): 183-186.
[
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
赵晶, 毕彦杰, 韩宇平, 等. 南水北调中线工程河南段社会经济效益研究. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 49(6): 855-866.
[
|
| [24] |
秦欢欢, 孙占学, 高柏. 农业节水和南水北调对华北平原可持续水管理的影响. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(7): 1716-1724.
[
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
周晓坤, 王哲. 南水北调工程对阳谷县农业灌排影响分析. 山东水利, 2014, (12): 44-45.
[
|
| [27] |
方国华, 赵文萃, 李鑫, 等. 南水北调东线江苏境内受水区节水潜力分析. 水利经济, 2022, 40(4): 1-5, 27, 91.
[
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
张超正, 杨钢桥. 农地整治何以促进农户收入增加: 基于整治模式和地貌类型的异质分析. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(12): 3114-3130.
[
|
| [33] |
段存儒, 曾贤刚. 中国资源型城市转型对劳动力需求的影响. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(3): 606-617.
[
|
| [34] |
秦腾, 佟金萍, 支彦玲. 水权交易机制对农业用水效率的影响及效应分析. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(12): 3282-3296.
[
|
| [35] |
刘昌明. 南水北调: 在节水的基础上实施缓解北方水危机. 科学对社会的影响, 2003, (3): 26-31.
[
|
| [36] |
刘予, 孙颖, 殷琨. 南水北调引水进京后北京市地下水环境预测. 水文地质工程地质, 2005, (5): 93-96.
[
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
冯忠伦, 张振成, 焦裕飞, 等. 南水北调输水对梁济运河区域地下水位的影响. 灌溉排水学报, 2016, 35(5): 97-102.
[
|
| [39] |
田贵良, 赵秋雅, 吴正. 乡村振兴下水权改革的节水效应及对用水效率的影响. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2022, 32(12): 193-204.
[
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
江艇. 因果推断经验研究中的中介效应与调节效应. 中国工业经济, 2022, (5): 100-120.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |