

国家级经济技术开发区建设对城市形态的影响——以长江三角洲地区为例
|
张潇(1994- ),男,山东寿光人,博士研究生,研究方向为城市地理与土地利用。E-mail: oozhangxiao@foxmail.com |
收稿日期: 2023-04-23
修回日期: 2023-11-03
网络出版日期: 2024-03-12
基金资助
国家社会科学基金项目(23BJL113)
The impact of the construction of national economic and technological development zones on urban form: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta Region
Received date: 2023-04-23
Revised date: 2023-11-03
Online published: 2024-03-12
国家级经济技术开发区是中国经济体制改革的开创性举措,对于推动区域经济发展和城市空间重构具有深远影响。基于长三角地区30 a土地利用数据,借助景观指数和多期双重差分模型等方法,多尺度检验国家级经济技术开发区建设对城市形态演化的影响。结果表明:(1)3 km与5 km缓冲区内均实现了从乡村地域到城市地域的转变,城市形态趋于规则化和紧凑化,并且具备一定空间分异特征;(2)国家级经济技术开发区的建设导致两种缓冲尺度内的形状指数下降,紧凑度指数上升,还致使5 km缓冲区内的规模指数显著降低;(3)国家级经济技术开发区对各类生产要素的集聚与约束效应,行政托管的管辖模式,以及企业超额用地等因素共同塑造了周边地区城市形态演化格局。
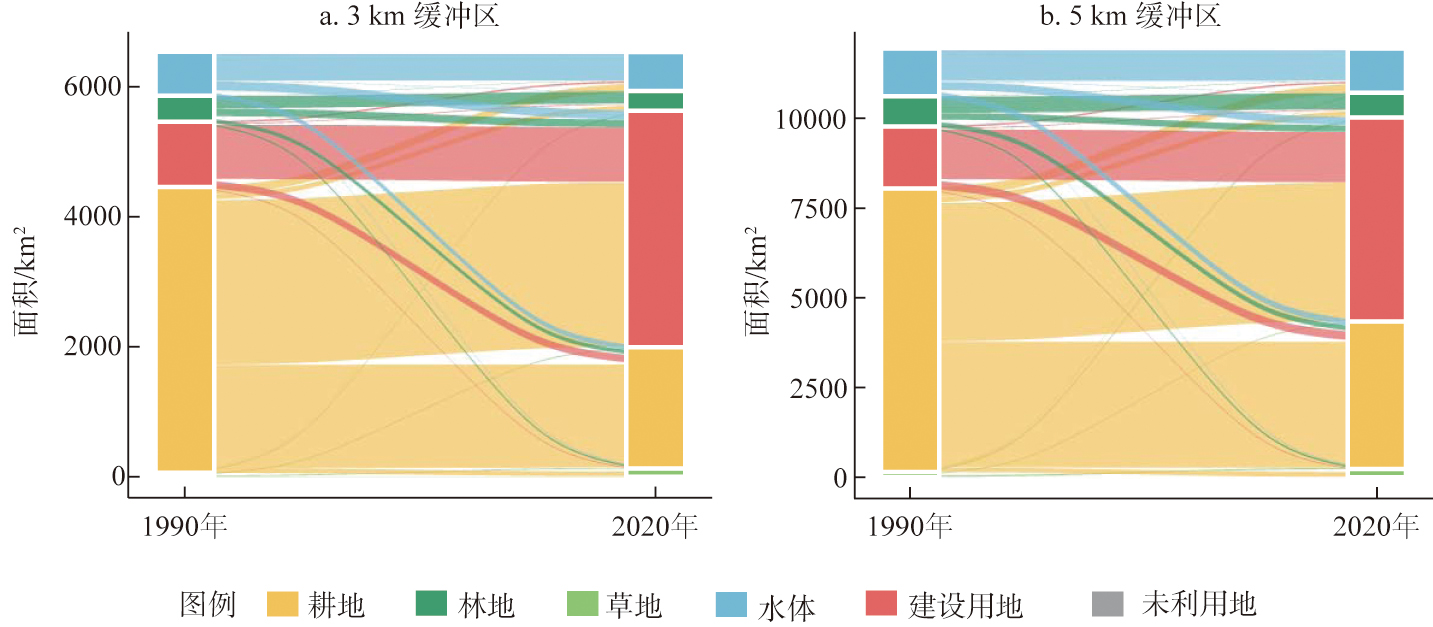
关键词: 城市形态; 土地利用; 双重差分模型; 国家级经济技术开发区; 长江三角洲地区
张潇 , 李冬花 , 张晓瑶 , 司月芳 , 谷人旭 . 国家级经济技术开发区建设对城市形态的影响——以长江三角洲地区为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2024 , 39(3) : 668 -681 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20240310
The establishment of national economic and technological development zones was a pioneering initiative in China's economic system reform, which has had a profound impact on promoting regional economic development and urban spatial restructuring. Based on land use data from the Yangtze River Delta Region over the past 30 years, the evolutionary characteristics of urban form, including its external contours and internal patterns, are comprehensively depicted from five dimensions: scale, form, compactness, fragmentation, and diversity, using landscape metrics. Methods such as buffer analysis and multi-period difference-in-differences model are employed to examine the effects and mechanisms of national economic and technological development zones on urban form evolution at multiple scales. The results indicate that: (1) Both the 3 km and 5 km buffer zones have undergone a transition from rural to urban areas, and the urban form has become more regular and compact, with some spatial differentiation characteristics. (2) The construction of national economic and technological development zones has led to a decrease in shape metrics and an increase in compactness metrics within the two buffer scales, as well as a significant reduction in the size metrics within the 5 km buffer zone. (3) Factors such as the agglomeration and restraint effects of national economic and technological development zones on various production factors, the jurisdiction mode of administrative trusteeship, and excessive land use by enterprises have jointly shaped the evolution pattern of urban form in surrounding areas. The "top-down" development model of national economic and technological development zones not only attracts numerous production factors but also formulates and implements various supporting policies and plans. This plays a crucial role in driving urban expansion, establishing development boundaries, and regulating land use order. It is the direct cause for inducing the regularization and compactness of urban form.

表1 城市形态测度指标Table 1 Urban form measuring index |
| 测量维度 | 测度指标 | 变量代码 | 含义 | 公式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 规模 | 最大斑块指数 | LPI | 衡量最大城市斑块的相对优势,体现城市单中心性 | 为i景观类型第j个斑块的面积(hm2); 为斑块ij的周长(m);g为景观类型像元之间的邻接数; 为景观类型i占据的面积比;m为景观类型总数(种);n为斑块总数(个);A为景观总面积(hm2);E为所有景观斑块总周长(m) | |
| 景观百分比 | PLAND | 反映城市用地的相对规模 | |||
| 形状 | 景观形状指数 | LSI | 反映城市斑块形状偏离规则结构的程度 | ||
| 平均分形维数 | MPFD | 体现城市形态的复杂性以及受人类干扰程度 | |||
| 紧凑性 | 集聚度 | AI | 度量城市斑块和宗地的空间配置 | ||
| 相似临近百分比 | PLADJ | 体现城市斑块之间彼此相邻的趋势 | |||
| 碎片化 | 斑块数量 | NP | 代表研究区间内建设用地斑块数量的变化 | ||
| 多样化 | 香农多样性指数 | SHDI | 反映不同土地利用类型的均匀分布程度 |
表2 开发区建设对3 km缓冲区内城市形态的影响Table 2 The impact of the construction of NETDZs on the urban form in the 3 km buffer zone |
| 变量 | LPI | PLAND | LSI | MPFD | AI | PLADJ | lnNP | SHDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DID | -2.642 | -2.183 | -1.459** | -0.00973** | 1.298*** | 1.234** | 0.0437 | -0.00288 |
| (-0.89) | (-1.02) | (-2.41) | (-2.12) | (2.70) | (2.54) | (0.28) | (-0.08) | |
| lnPOP | 7.479* | 5.612* | -1.772** | 0.000172 | 0.912 | 0.553 | -0.414* | -0.183*** |
| (1.78) | (1.84) | (-2.07) | (0.03) | (1.34) | (0.80) | (-1.85) | (-3.55) | |
| lnGDP | -0.0269 | -0.197 | 0.377 | -0.00768 | -0.115 | 0.175 | 0.256 | 0.0827** |
| (-0.01) | (-0.08) | (0.57) | (-1.54) | (-0.22) | (0.33) | (1.50) | (2.10) | |
| lnFDI | -0.560 | -0.778 | 0.524*** | 0.00313*** | -0.315** | -0.287** | 0.0565 | 0.0196** |
| (-0.72) | (-1.39) | (3.32) | (2.62) | (-2.50) | (-2.26) | (1.38) | (2.06) | |
| lnBUA | 11.77*** | 13.63*** | 1.549*** | 0.00234 | 0.184 | 0.397 | 0.251** | -0.0276 |
| (5.36) | (8.55) | (3.45) | (0.69) | (0.51) | (1.10) | (2.15) | (-1.02) | |
| lnPFE | 1.917 | 5.099** | -0.574 | 0.00612 | 1.368*** | 1.439*** | -0.269* | 0.0395 |
| (0.68) | (2.48) | (-0.99) | (1.39) | (2.97) | (3.09) | (-1.79) | (1.14) | |
| 常数项 | -205.9*** | -214.5*** | 21.17* | 1.014*** | 68.20*** | 68.83*** | 7.997** | 2.836*** |
| (-3.48) | (-4.99) | (1.75) | (11.05) | (7.08) | (7.07) | (2.54) | (3.90) | |
| 个体固定 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 时间固定 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 样本量/个 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 |
注:***、**、*分别表示在1%、5%、10%水平下显著,括号内数值为t值,下同。 |
表3 开发区建设对5 km缓冲区内城市形态的影响Table 3 The impact of the construction of NETDZs on the urban form in the 5 km buffer zone |
| 变量 | LPI | PLAND | LSI | MPFD | AI | PLADJ | lnNP | SHDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DID | -4.796* | -3.730** | -1.855** | -0.00340 | 1.231*** | 1.203** | 0.0437 | 0.0269 |
| (-1.96) | (-2.12) | (-2.39) | (-0.95) | (2.65) | (2.56) | (0.31) | (0.85) | |
| lnPOP | 7.569** | 8.139*** | -1.640 | 0.00198 | 0.851 | 0.795 | -0.442** | -0.0870** |
| (2.26) | (3.37) | (-1.54) | (0.41) | (1.34) | (1.24) | (-2.31) | (-2.01) | |
| lnGDP | -1.081 | -1.819 | 0.0892 | -0.00498 | -0.206 | -0.189 | 0.204 | 0.0529* |
| (-0.44) | (-1.03) | (0.12) | (-1.40) | (-0.45) | (-0.40) | (1.46) | (1.68) | |
| lnFDI | -0.0945 | -0.692 | 0.443** | 0.00316*** | -0.183 | -0.184 | 0.0252 | 0.0157** |
| (-0.16) | (-1.58) | (2.30) | (3.55) | (-1.58) | (-1.58) | (0.73) | (2.00) | |
| lnBUA | 8.654*** | 11.46*** | 2.596*** | 0.00116 | -0.195 | 0.0539 | 0.490*** | 0.000604 |
| (4.95) | (9.09) | (4.67) | (0.45) | (-0.59) | (0.16) | (4.90) | (0.03) | |
| lnPFE | 0.348 | 3.856** | -0.421 | 0.00246 | 1.218*** | 1.274*** | -0.119 | 0.0446 |
| (0.15) | (2.32) | (-0.57) | (0.73) | (2.78) | (2.88) | (-0.90) | (1.49) | |
| 常数项 | -166.6*** | -215.2*** | 13.57 | 1.020*** | 73.23*** | 70.81*** | 6.017** | 1.443** |
| (-3.56) | (-6.37) | (0.91) | (14.87) | (8.22) | (7.87) | (2.24) | (2.38) | |
| 个体固定 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 时间固定 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 样本量/个 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 | 352 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
杨山, 杨虹霓, 季增民, 等. 快速城镇化背景下乡村居民生活圈的重组机制: 以昆山群益社区为例. 地理研究, 2019, 38(1): 119-132.
[
|
| [3] |
张潇, 谷人旭. 土地利用冲突的时空格局刻画与多情景模拟研究: 以长江三角洲城市群为例. 地理研究, 2022, 41(5): 1311-1326.
[
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
潘竟虎, 戴维丽. 1990—2010年中国主要城市空间形态变化特征. 经济地理, 2015, 35(1): 44-52.
[
|
| [6] |
王慧芳, 周恺. 2003—2013年中国城市形态研究评述. 地理科学进展, 2014, 33(5): 689-701.
[
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
周滔, 王笛, 李帆. 多尺度下城市形态对空气质量的作用机制研究. 地理研究, 2022, 41(7): 1883-1897.
[
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
方颖, 白秀叶. 城市空间形态、公共服务空间均等化与居民满意度. 经济学(季刊), 2022, 22(4): 1405-1424.
[
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
刘志丹, 张纯, 宋彦. 促进城市的可持续发展: 多维度、多尺度的城市形态研究: 中美城市形态研究的综述及启示. 国际城市规划, 2012, 27(2): 47-53.
[
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
潘竟虎, 韩文超. 近20 a中国省会及以上城市空间形态演变. 自然资源学报, 2013, 28(3): 470-480.
[
|
| [17] |
徐银凤, 汪德根, 沙梦雨. 双维视角下苏州城市空间形态演变及影响机理. 经济地理, 2019, 39(4): 75-84.
[
|
| [18] |
海凯, 王思远, 马元旭, 等. “一带一路” 沿线地区城市扩张和形态变化分析. 地理学报, 2020, 75(10): 2092-2108.
[
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
武进. 中国城市形态:结构、特征及其演变. 南京: 江苏科学技术出版社, 1990.
[
|
| [21] |
李留通, 张森森, 赵新正, 等. 文化产业成长对城市空间形态演变的影响: 以西安市核心区为例. 地理研究, 2021, 40(2): 431-445.
[
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
蔡善柱, 陆林. 中国国家级经济技术开发区及其产业空间格局演化: 基于地级及以上市面板数据实证研究. 地理科学, 2019, 39(3): 415-423.
[
|
| [25] |
张若琰, 刘卫东, 宋周莺. 基于地理探测器的中国国家级开发区时空演化过程及其驱动力研究. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(10): 2672-2683.
[
|
| [26] |
黄晶, 薛东前, 董朝阳, 等. 干旱绿洲农业区土地利用转型生态环境效应及分异机制: 基于三生空间主导功能判别视角. 地理科学进展, 2022, 41(11): 2044-2060.
[
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
郑国, 周一星. 北京经济技术开发区对北京郊区化的影响研究. 城市规划学刊, 2005, (6): 23-26, 47.
[
|
| [35] |
张越, 叶高斌, 姚士谋. 开发区新城建设与城市空间扩展互动研究: 以上海、杭州、南京为例. 经济地理, 2015, 35(2): 84-91.
[
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
刘合林, 聂晶鑫. 2006—2018年中国省级以上开发区的空间分布特征变化. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(9): 2229-2240.
[
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
张海丹, 康若荷, 唐龙, 等. 新区建设后期控制性详细规划实施评估要点浅析: 以榆林市高新区北区为例. 城市发展研究, 2019, 26(s1): 47-52.
[
|
| [40] |
冯健, 叶竹. 基于个体生命历程视角的苏南城镇化路径转变与市民化进程. 地理科学进展, 2017, 36(2): 137-150.
[
|
| [41] |
杨凌凡, 罗小龙, 丁子尧. 资本与权力视角下开发区创新转型逻辑框架与政策建议. 规划师, 2022, 38(4): 50-57.
[
|
| [42] |
孔翔, 宋志贤. 内群体交往对开发区拆迁安置社区居民社区感的影响研究: 以昆山经济技术开发区周边X社区为例. 人文地理, 2019, 34(4): 47-53.
[
|
| [43] |
张景奇, 孙萍, 孙蕊. 城市蔓延理性与中国城市理性蔓延探究. 城市规划, 2014, (7): 31-36.
[
|
| [44] |
李凯, 王凯. 新区产业用地的更新困局与转型探索: 以北京经济技术开发区为例. 国际城市规划, 2022, 37(4): 74-82.
[
|
| [45] |
何芳, 龚芯欣. 工业区土地二次开发制度供求冲突与制度创新: 基于案例与城市政策实践分析. 中国房地产, 2013, (24): 48-55.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |