

汾河流域新型城镇化与生态韧性耦合协调时空演变及协调影响力研究
|
刘海龙(1983- ),男,甘肃正宁人,博士,副教授,主要从事区域生态安全与可持续发展研究。E-mail: liuhailong5117@163.com |
收稿日期: 2023-04-17
修回日期: 2023-11-13
网络出版日期: 2024-03-12
基金资助
山西省哲学社会科学规划课题(2022YY061)
Spatio-temporal evolution and coordination influence of coupling coordination between new urbanization and ecological resilience in Fenhe River Basin
Received date: 2023-04-17
Revised date: 2023-11-13
Online published: 2024-03-12
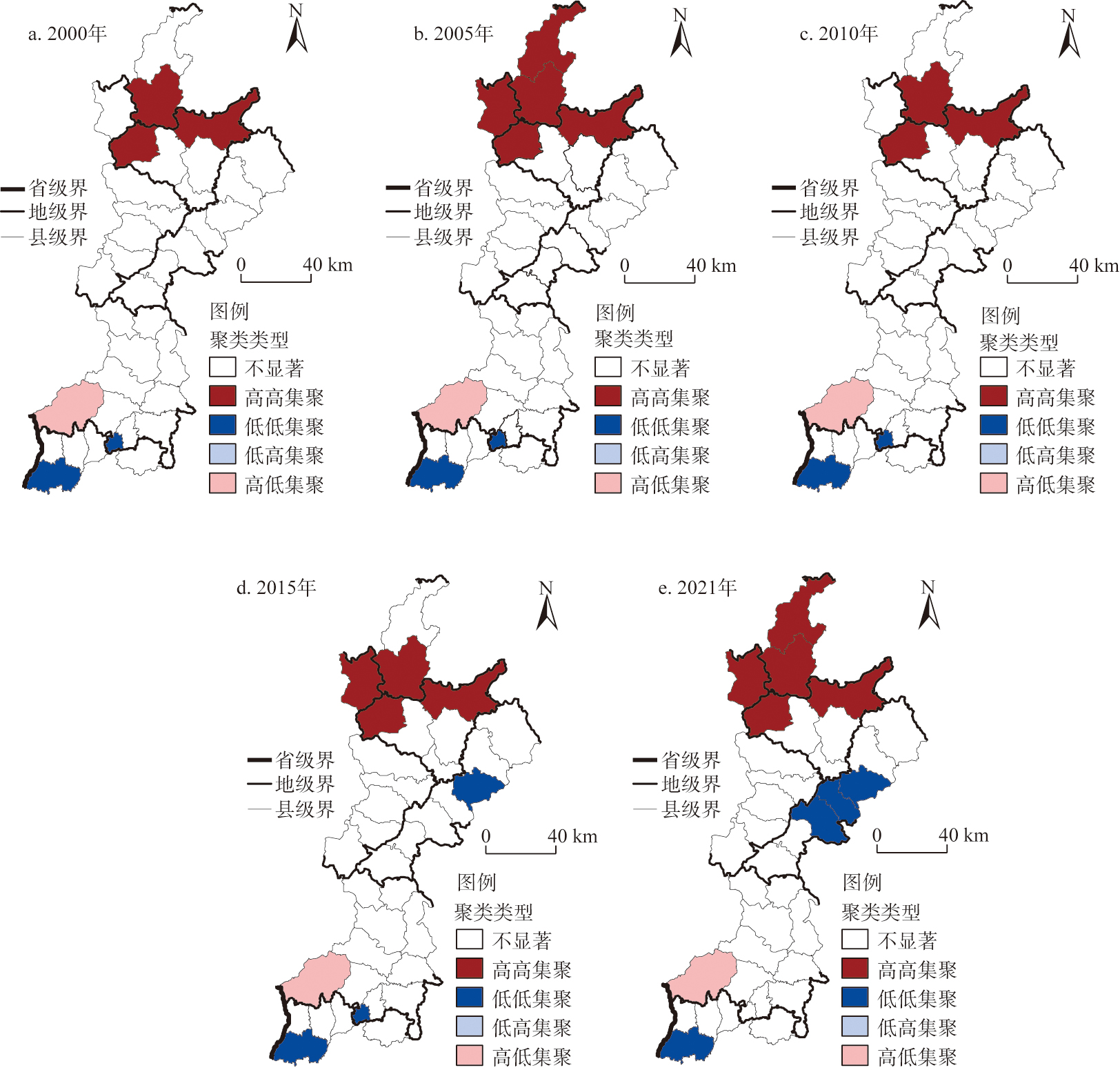
构建基于“规模—密度—形态”的三维流域生态韧性分析框架,运用耦合协调模型测算并分析2000—2021年汾河流域县域新型城镇化与生态韧性的耦合协调时空演变特征,采用空间自相关模型揭示耦合协调的空间集聚特征,引入协调影响力指数表征各子系统对整体耦合协调度的作用力及作用程度。结果表明:(1)2000—2021年汾河流域各县域新型城镇化水平总体缓慢提升,“核心—边缘”空间格局显著,生态韧性综合指数持续降低,空间格局上高值区呈“S”型分布,低值区集中于中部谷地。(2)耦合协调度呈现由“轻度协调”向“轻度失调”下滑的发展特征,受区位优势和生态禀赋因素影响,耦合协调度空间分布呈现由核心向边缘逐级提升的“环状”分布格局,空间集聚趋势显著。(3)新型城镇化中人口、空间、社会、绿色子系统对综合耦合协调度起反向阻滞作用,经济城镇化对综合耦合协调度的影响先阻滞后推动,生态韧性子系统对综合耦合协调度均起反向阻滞作用,规模、密度韧性阻滞力增强,形态韧性阻滞程度减弱。(4)新型城镇化水平不均衡发展的“马太效应”更加明显,生态韧性受制于生态资源本底,空间演变存在路径依赖现象,汾河流域兼具城镇化推进对生态产生负效应的流域普遍性特征和资源发展型县域产业转型缓慢、生态建设较城镇化显著滞后的特殊性。
刘海龙 , 王改艳 , 张鹏航 , 王争磊 , 张丽萍 . 汾河流域新型城镇化与生态韧性耦合协调时空演变及协调影响力研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2024 , 39(3) : 640 -667 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20240309
This paper constructs a "Size-Density-Morphology" basin ecological resilience evaluation system, using the coupled coordination model to estimate and analyze the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of coupled coordination between new urbanization and ecological resilience in counties of the Fenhe River Basin from 2000 to 2021, and the spatial autocorrelation model is used to reveal the spatial clustering characteristics of coupled coordination. The coordination influence index is introduced to characterize the effect and the degree of role of each subsystem on the overall coupling coordination degree. The results show that: (1) From 2000 to 2021, the level of new urbanization in counties of the Fenhe River Basin had been improved slowly, the "core-edge" spatial pattern was significant, and the comprehensive index of ecological resilience had been decreasing continuously. The high-value areas in the spatial pattern are distributed in an "S" shape, and the low-value areas are concentrated in the central valley. (2) The coupling coordination degree is characterized by a downward trend from "mild coordination" to "mild imbalance". Affected by the location advantages and ecological endowment factors, the spatial distribution of the coupling coordination degree showed a "ring" distribution pattern of increasing from the core to the edge, and the spatial agglomeration trend is significant. (3) In the new urbanization, the population, space, society and green subsystems have a reverse blocking effect on the integrated coupling coordination degree, while the influence of economic urbanization on the comprehensive coupling coordination is first blocked and then promoted, and the ecological resilience subsystem has a reverse blocking effect on the integrated coupling coordination degree, with the scale and density toughness blocking increased and the morphological toughness blocking degree weakened. (4) The "Matthew effect" of the unbalanced development of new urbanization level is more obvious, and the external supply of energy in resource-based counties forces the density toughness to drop significantly. The ecological resilience is restricted by ecological resources, and the spatial evolution is path-dependent. The Fenhe River Basin has both the universal characteristics of urbanization, which has negative effects on the ecology, and the particularity of slow industrial transformation in resource-developing counties, and the significant lag of ecological construction compared with urbanization.

表1 新型城镇化综合水平测度指标体系Table 1 The comprehensive index system of new urbanization |
| 准则层 | 指标层 | 表征意义 | 客观权重 | 主观权重 | 综合权重 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 人口城镇化 | 常住人口城镇化率/% | 城镇化发展水平 | 0.0283 | 0.1282 | 0.0669 | 正 |
| 城镇人口密度/(人/km2) | 人口空间分布疏密程度 | 0.0855 | 0.0388 | 0.0640 | 正 | |
| 乡村从业人员占比/% | 乡村实际从业状况 | 0.0121 | 0.0706 | 0.0325 | 负 | |
| 空间城镇化 | 人均建成区面积/(人/km2) | 人均城市化区域大小 | 0.0489 | 0.0968 | 0.0764 | 正 |
| 路网密度/(km/km2) | 城市道路网发展规模 | 0.0361 | 0.0533 | 0.0487 | 正 | |
| 城市建设用地面积比例/% | 城市土地利用强度 | 0.0842 | 0.0293 | 0.0552 | 正 | |
| 经济城镇化 | 人均GDP/元 | 经济发展状况 | 0.0973 | 0.1515 | 0.1349 | 正 |
| 经济密度/(万元/km2) | 单位面积经济效益水平 | 0.1804 | 0.0437 | 0.0986 | 正 | |
| 二三产业比例/% | 产业结构 | 0.0136 | 0.0691 | 0.0340 | 正 | |
| 人均规模以上工业总产值/(万元/人) | 工业生产规模 | 0.1026 | 0.0981 | 0.1114 | 正 | |
| 社会城镇化 | 人均社会消费品零售额/(万元/人) | 居民生活水平状况 | 0.0771 | 0.0678 | 0.0803 | 正 |
| 每十万人中中小学人数/人 | 教育事业发展规模 | 0.0351 | 0.0373 | 0.0402 | 正 | |
| 每万人拥有医疗机构床位数/张 | 医疗保障设施水平 | 0.0410 | 0.0205 | 0.0322 | 正 | |
| 绿色城镇化 | 森林覆盖率% | 森林资源和绿化水平 | 0.0379 | 0.0428 | 0.0448 | 正 |
| 人均公共绿地面积/(人/km2) | 绿地空间生态水平 | 0.0934 | 0.0248 | 0.0535 | 正 | |
| CO2排放量/Mt | 平均温室气体排放量 | 0.0037 | 0.0160 | 0.0085 | 负 | |
| PM2.5均值/(μg/m³) | 颗粒物污染状况 | 0.0228 | 0.0113 | 0.0178 | 负 |
表2 生态韧性综合水平测度指标体系Table 2 The comprehensive index system of ecological resilience |
| 准则层 | 客观权重 | 主观权重 | 综合权重 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 规模韧性 | 0.3452 | 0.4934 | 0.4178 | 正 |
| 密度韧性 | 0.3652 | 0.3108 | 0.3411 | 正 |
| 形态韧性 | 0.2896 | 0.1958 | 0.2411 | 正 |
表3 用于生态足迹计算的均衡因子与产量因子Table 3 Equivalence factors and yield factors for ecological footprint calculation |
| 土地类型 | 中国均衡因子 | 汾河流域均衡因子 | 中国产量因子 | 汾河流域产量因子 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 | 1.74 | 0.85 | 1.74 | 0.48 |
| 草地 | 1.41 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.56 |
| 林地 | 0.44 | 0.63 | 0.51 | 1.40 |
| 水域 | 0.35 | 0.50 | 0.74 | 1.40 |
| 化石燃料用地 | 1.74 | 0.85 | 1.74 | 0.48 |
| 建筑用地 | 1.41 | 0.81 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
表3 2000—2021年汾河流域新型城镇化与生态韧性耦合协调性全局Moran's I指数统计值Table 3 The Global Moran's I index statistics of coupling coordination degree of new urbanization and ecological resilience at county level in the Fenhe River Basin from 2000 to 2021 |
| 指标 | 2000年 | 2005年 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2021年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran's I | 0.283 | 0.338 | 0.290 | 0.353 | 0.377 |
| Z统计量 | 2.788 | 3.264 | 2.852 | 3.387 | 3.580 |
| P值 | 0.009 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.004 |
图10 2000年汾河流域新型城镇化与生态韧性子系统协调影响力Fig. 10 Coordinated influence of of new urbanization subsystem and ecological resilience subsystem at county level in the Fenhe River Basin in 2000 |
图11 2005年汾河流域新型城镇化与生态韧性子系统协调影响力Fig. 11 Coordinated influence of of new urbanization subsystem and ecological resilience subsystem at county level in the Fenhe River Basin from in 2005 |
图12 2010年汾河流域新型城镇化与生态韧性子系统协调影响力Fig. 12 Coordinated influence of new urbanization subsystem and ecological resilience subsystem at county level in the Fenhe River Basin in 2010 |
图13 2015年汾河流域新型城镇化与生态韧性子系统协调影响力Fig. 13 Coordinated influence of new urbanization subsystem and ecological resilience subsystem at county level in the Fenhe River Basin in 2015 |
| [1] |
邵佳, 冷婧. 湖南武陵山片区新型城镇化与生态环境耦合协调发展. 经济地理, 2022, 42(9): 87-95.
[
|
| [2] |
王少剑, 崔子恬, 林靖杰, 等. 珠三角地区城镇化与生态韧性的耦合协调研究. 地理学报, 2021, 76(4): 973-991.
[
|
| [3] |
曾凡盛, 冯兴华, 唐燕, 等. 鄱阳湖流域县域生态韧性空间格局演变研究. 地理与地理信息科学, 2022, 38(6): 29-35.
[
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
孙阳, 张落成, 姚士谋. 基于社会生态系统视角的长三角地级城市韧性度评价. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2017, 27(8): 151-158.
[
|
| [14] |
白立敏, 修春亮, 冯兴华, 等. 中国城市韧性综合评估及其时空分异特征. 世界地理研究, 2019, 28(6): 77-87.
[
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
朱媛媛, 汪紫薇, 顾江, 等. 基于“乡土—生态”系统韧性的红色旅游资源利用空间格局优化研究: 以大别山革命老区为例. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(7): 1700-1717.
[
|
| [17] |
黄晶, 佘靖雯, 袁晓梅, 等. 基于系统动力学的城市洪涝韧性仿真研究: 以南京市为例. 长江流域资源与环境, 2020, 29(11): 2519-2529.
[
|
| [18] |
杨宜男, 李敬, 王立, 等. 长三角地区城市化对典型生态系统服务供需的影响. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(6): 1555-1571.
[
|
| [19] |
聂名萱, 黄思华, 濮励杰, 等. 快速城镇化地区生态系统服务的时空动态及权衡与协同分析: 以苏锡常地区为例. 长江流域资源与环境, 2021, 30(5): 1088-1099.
[
|
| [20] |
陈晓红, 吴广斌, 万鲁河. 基于BP的城市化与生态环境耦合脆弱性与协调性动态模拟研究: 以黑龙江省东部煤电化基地为例. 地理科学, 2014, 34(11): 1337-1343.
[
|
| [21] |
赵建吉, 刘岩, 朱亚坤, 等. 黄河流域新型城镇化与生态环境耦合的时空格局及影响因素. 资源科学, 2020, 42(1): 159-171.
[
|
| [22] |
贵立德. 兰州市城镇化水平与其生态用地的供求关系. 水土保持通报, 2012, 32(4): 298-302.
[
|
| [23] |
韩秀丽, 胡烨君, 马志云. 乡村振兴、新型城镇化与生态环境的耦合协调发展: 基于黄河流域的实证. 统计与决策, 2023, 39(11): 122-127.
[
|
| [24] |
夏楚瑜, 国淏, 赵晶, 等. 京津冀地区生态系统服务对城镇化的多空间尺度动态响应. 生态学报, 2023, 43(7): 2756-2769.
[
|
| [25] |
熊建新, 王鑫滨, 赵迪, 等. 城镇化进程中生态承载力系统耦合时空格局及影响因素: 以洞庭湖区为例. 经济地理, 2022, 42(10): 83-91.
[
|
| [26] |
李翅, 马鑫雨, 夏晴. 国内外韧性城市的研究对黄河滩区空间规划的启示. 城市发展研究, 2020, 27(2): 54-61.
[
|
| [27] |
李嘉艺, 孙璁, 郑曦. 基于适应性循环理论的区域生态风险时空演变评估: 以长江三角洲城市群为例. 生态学报, 2021, 41(7): 2609-2621.
[
|
| [28] |
王少剑, 刘志涛, 张婷婷, 等. 服务业与多维城镇化的耦合协调研究: 以广州市为例. 热带地理, 2019, 39(3): 450-460.
[
|
| [29] |
刘海龙, 王炜桥, 王跃飞, 等. 汾河流域生态敏感性综合评价及时空演变特征. 生态学报, 2021, 41(10): 3952-3964.
[
|
| [30] |
史利江, 刘敏, 李艳萍, 等. 汾河流域县域经济差异的时空格局演变及驱动因素. 地理研究, 2020, 39(10): 2361-2378.
[
|
| [31] |
李敏纳, 蔡舒, 覃成林. 黄河流域经济空间分异态势分析. 经济地理, 2011, 31(3): 379-383, 419.
[
|
| [32] |
苏迎庆, 张恩月, 刘源, 等. 汾河流域土地利用变化及生态环境效应. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(3): 968-977.
[
|
| [33] |
冯雨雪, 李广东. 青藏高原城镇化与生态环境交互影响关系分析. 地理学报, 2020, 75(7): 1386-1405.
[
|
| [34] |
邓宗兵, 宗树伟, 苏聪文, 等. 长江经济带生态文明建设与新型城镇化耦合协调发展及动力因素研究. 经济地理, 2019, 39(10): 78-86.
[
|
| [35] |
修春亮, 魏冶, 王绮. 基于“规模—密度—形态”的大连市城市韧性评估. 地理学报, 2018, 73(12): 2315-2328.
[
|
| [36] |
马琪, 刘康, 刘文宗, 等. 干旱半干旱区生态保护红线划分研究: 以“多规合一”试点榆林市为例. 地理研究, 2018, 37(1): 158-170.
[
|
| [37] |
俞孔坚, 李博, 李迪华. 自然与文化遗产区域保护的生态基础设施途径: 以福建武夷山为例. 城市规划, 2008, (10): 88-91, 96.
[
|
| [38] |
赵震宇, 宋冬林. 中国化石能源使用可持续性评估: 基于1990—2006年数据. 地理科学, 2010, 30(1): 75-79.
[
|
| [39] |
刘某承, 李文华. 基于净初级生产力的中国生态足迹均衡因子测算. 自然资源学报, 2009, 24(9): 1550-1559.
[
|
| [40] |
陈义忠, 乔友凤, 郝灿, 等. 长江中游城市群生态足迹指标与社会经济发展的适配性. 资源科学, 2022, 44(10): 2137-2152.
[
|
| [41] |
刘某承, 李文华, 谢高地. 基于净初级生产力的中国生态足迹产量因子测算. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(3): 592-597.
[
|
| [42] |
杨亮洁, 张小鸿, 潘竟虎, 等. 成渝城市群城镇化与生态环境耦合协调及交互影响. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(3): 993-1004.
[
|
| [43] |
林建鹏. 中国医疗资源配置与服务利用协调发展的时空演化: 基于机构分层分析框架. 地理科学, 2022, 42(2): 284-292.
[
|
| [44] |
刘海龙, 张丽萍, 王炜桥, 等. 中国省际边界区县域城镇化空间格局及影响因素. 地理学报, 2023, 78(6): 1408-1426.
[
|
| [45] |
付扬军, 师学义, 和娟. 汾河流域景观破碎化时空演变特征. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(8): 1606-1619.
[
|
| [46] |
张佰发, 李晶晶, 胡志强, 等. 自然禀赋与政区类型对中国县域经济发展的影响. 地理研究, 2021, 40(9): 2508-2525.
[
|
| [47] |
姜海宁, 张文忠, 余建辉, 等. 山西资源型城市创新环境与产业结构转型空间耦合. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(2): 269-283.
[
|
| [48] |
张洁, 李同昇, 王武科. 渭河流域人地关系地域系统耦合状态分析. 地理科学进展, 2010, 29(6): 733-739.
[
|
| [49] |
胡振鹏, 黄晓杏, 傅春, 等. 环鄱阳湖地区旅游产业—城镇化—生态环境交互耦合的定量比较及演化分析. 长江流域资源与环境, 2015, 24(12): 2012-2020.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |