

中国锂资源综合风险动态演变及预警研究
|
成金华(1962- ),男,湖北黄冈人,博士,教授,研究方向为资源环境经济学、战略性关键矿产安全。E-mail: chengjinhua100@126.com |
收稿日期: 2023-09-04
修回日期: 2023-12-06
网络出版日期: 2024-03-12
基金资助
国家自然科学基金重大项目(71991482)
国家社会科学基金重点项目(23AZD072)
国家自然科学基金项目(72074198)
Toward the dynamic evolution and early warning of comprehensive risk in China's lithium resources
Received date: 2023-09-04
Revised date: 2023-12-06
Online published: 2024-03-12
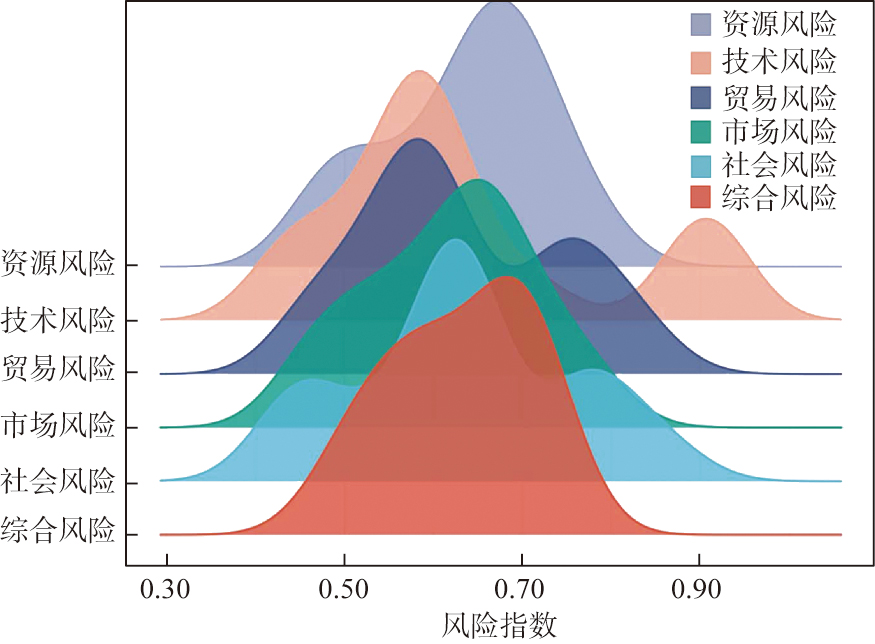
随着锂资源在电动汽车、储能等领域的广泛应用,锂资源的供需关系和市场格局愈加复杂,相关风险也逐步显现,这使得锂资源综合风险预警和科学管理变得迫切且必要。根据资源安全的五种基本含义对应地构建了涵盖“资源—技术—贸易—市场—社会”的中国锂资源综合风险评估框架。采用CRITIC权重结合灰色关联投影法对其进行了评估与预警,并采用通径分析厘清其影响路径。研究结果表明:(1)中国锂资源综合风险常年处于中风险及以上水平,以2015年为分水岭呈现双波峰变化状态,其中技术风险、贸易风险和社会风险呈现明显的多峰形态,两极分化现象较为突出;(2)中国锂资源综合风险未来将维持在“中警”状态;(3)风险之间存在显著的正向影响。
成金华 , 左芝鲤 , 詹成 , 郭海湘 . 中国锂资源综合风险动态演变及预警研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2024 , 39(3) : 528 -546 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20240303
Strategic critical minerals are crucial for the development of emerging industries and constitute a top priority for resource security. With the ongoing deepening of global multipolarity and economic globalization, the level of mutual connection and interdependence between nations has unprecedentedly increased. China not only has a sustained demand for mineral resources in economic growth but also experiences a growing need for various strategic critical mineral resources in emerging technologies, green energy, and other sectors. The widespread application of lithium resources in electric vehicles, energy storage, and other fields has led to an increasingly complex supply-demand relationship and market structure for lithium resources, with associated risks gradually becoming apparent. This underscores the urgency and necessity of early warning and scientific management of comprehensive risks related to lithium resources. This study constructed a comprehensive risk assessment framework for China's lithium resources, covering "resources-technology-trade-market-society," based on the five basic meanings of resource security. Five primary indicators and 22 secondary indicators were selected. The CRITIC weight, combined with the gray relational projection method, was employed to assess and warn about the comprehensive risk of lithium resources from 2008 to 2022. Path analysis was also conducted to clarify the pathways of influence. The study addresses three main research questions: "What is the current risk situation?", "What are the future risks?", and "How to avoid risks?". The results indicate that: (1) The comprehensive risk of China's lithium resources has consistently been at a medium-risk level or above, showing a dual-peak changing pattern since 2015. Among them, technology risk, trade risk, and social risk exhibit a typical multi-peak curve, with a prominent polarization phenomenon. (2) The early-stage comprehensive risk of China's lithium resources has been consistently in a "heavy warning" state and is expected to be maintained at a "medium warning" state in the future. Global events are often accompanied by abrupt changes in warning levels before and after their occurrence. Specifically, since 2017, there have been sudden changes in resource risk, technology risk, trade risk, market risk, and social risk, with their warning levels showing a phased growth pattern. In the future, market risk may continue to be in a "heavy warning" state. (3) There is a significant positive impact among the risks.

Key words: lithium resources; risk evolution; early warning; risk impact pathways; China
表1 中国锂资源综合风险评价指标体系Table 1 The comprehensive risk assessment indicator system for China's lithium resources |
| 一级指标 | 二级指标/单位 | 公式/来源 | 影响 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A)资源风险 | (A1)储量占比/% | 美国地质调查局 | - | [24] |
| (A2)产量占比/% | 美国地质调查局 | - | [24] | |
| (A3)储产比 | 根据公式计算 | - | [25,26] | |
| (A4)可替代性 | 欧盟委员会报告 | + | [27,28] | |
| (A5)报废回收率/% | 来自参考文献 | - | [29] | |
| (A6)产需平衡度 | 根据公式计算 | - | [30] | |
| (B)技术风险 | (B1)研发投入占比/% | 根据公式计算 | - | [31] |
| (B2)研发人员占比/% | 根据公式计算 | - | ||
| (C)贸易风险 | (C1)供给意愿指数 | 进出口数据来自于联合国商品贸易 统计数据库 | + | [19] |
| (C2)外部依赖度 | 根据公式计算 | + | [32] | |
| (C3)进口专业化程度 | 根据公式计算 | + | [33] | |
| (C4)供应中断概率 | 根据公式计算 | + | [20] | |
| (D)市场风险 | (D1)表观消费量增长率/% | 消费数据来自于有色金属工业协会 锂业分会 | + | [34] |
| (D2)价格波动率/% | 价格数据来自于Wind数据库 | + | [35,36] | |
| (D3)资源消耗强度 | 根据公式计算 | + | [37] | |
| (D4)经济贡献度 | 中国锂离子电池产业产值数据来自 于工信部 | + | [19] | |
| (E)社会风险 | (E1)矿业政策成熟度 | 加拿大Fraser Institute发布指数 | - | [27] |
| (E2)经济社会发展度 | 联合国开发计划署发布指数 | - | [38] | |
| (E3)政治稳定性 | 世界银行发布指数 | - | [39] | |
| (E4)经济自由度 | 华尔街日报和美国传统基金会联合 发布指数 | - | [19] | |
| (E5)环境政策严厉指数 | 经济合作组织发布 | - | [40] | |
| (E6)环境绩效指数 | 耶鲁大学发布 | - |
表2 A股锂矿板块主要上市公司Table 2 Major publicly listed companies in the A-share lithium mining sector in China |
| 公司名称 | 公司代码 | 公司名称 | 公司代码 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 赣锋锂业 | 002460 | 中矿资源 | 002738 |
| 天齐锂业 | 002466 | 江特电机 | 002176 |
| 盛新锂能 | 002240 | 西部矿业 | 601168 |
| 雅化集团 | 002497 | 盐湖股份 | 000792 |
| 臧格矿业 | 000408 | 科达制造 | 600499 |
| 西藏矿业 | 000762 | 紫金矿业 | 601899 |
表3 各指标CRITIC权重值Table 3 The CRITIC weights for each indicator |
| 指标 | 指标变异性 | 指标冲突性 | 信息量 | 权重/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A1)储量占比 | 0.408 | 24.387 | 9.948 | 7.35 |
| (A2)产量占比 | 0.275 | 23.282 | 6.405 | 4.73 |
| (A3)储产比 | 0.341 | 23.319 | 7.953 | 5.88 |
| (A4)可替代性 | 0.417 | 15.652 | 6.531 | 4.83 |
| (A5)报废回收率 | 0.399 | 15.793 | 6.308 | 4.66 |
| (A6)产需平衡度 | 0.286 | 27.518 | 7.877 | 5.82 |
| (B1)研发投入占比 | 0.351 | 17.490 | 6.138 | 4.54 |
| (B2)研发人员占比 | 0.465 | 15.671 | 7.280 | 5.38 |
| (C1)供给意愿指数 | 0.247 | 17.486 | 4.314 | 3.19 |
| (C2)外部依赖度 | 0.292 | 21.715 | 6.337 | 4.68 |
| (C3)进口专业化程度 | 0.271 | 23.546 | 6.379 | 4.71 |
| (C4)供应中断概率 | 0.269 | 24.204 | 6.502 | 4.81 |
| (D1)表观消费量增长率 | 0.318 | 16.991 | 5.404 | 3.99 |
| (D2)价格波动率 | 0.270 | 16.439 | 4.444 | 3.28 |
| (D3)资源消耗强度 | 0.270 | 19.065 | 5.154 | 3.81 |
| (D4)经济贡献度 | 0.313 | 15.422 | 4.831 | 3.57 |
| (E1)矿业政策成熟度 | 0.241 | 22.920 | 5.524 | 4.08 |
| (E2)经济社会发展度 | 0.337 | 15.485 | 5.217 | 3.86 |
| (E3)政治稳定性 | 0.298 | 18.022 | 5.379 | 3.98 |
| (E4)经济自由度 | 0.299 | 19.753 | 5.907 | 4.37 |
| (E5)环境绩效指数 | 0.279 | 20.970 | 5.852 | 4.33 |
| (E6)环境政策严厉指数 | 0.349 | 16.071 | 5.612 | 4.15 |
| [1] |
习近平. 高举中国特色社会主义伟大旗帜为全面建设社会主义现代化国家而团结奋斗. 在中国共产党第二十次全国代表大会上的报告, 2022.
[
|
| [2] |
成金华, 易佳慧, 吴巧生. 碳中和、战略性新兴产业发展与关键矿产资源管理. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2021, 31(9): 135-142.
[
|
| [3] |
侯增谦, 陈骏, 翟明国. 战略性关键矿产研究现状与科学前沿. 科学通报, 2020, 65(33): 3651-3652.
[
|
| [4] |
李鹏飞, 杨丹辉, 渠慎宁, 等. 稀有矿产资源的全球供应风险分析: 基于战略性新兴产业发展的视角. 世界经济研究, 2015, (2): 96-104, 129.
[
|
| [5] |
李鹏飞, 杨丹辉, 渠慎宁, 等. 稀有矿产资源的战略性评估: 基于战略性新兴产业发展的视角. 中国工业经济, 2014, (7): 44-57.
[
|
| [6] |
王安建, 高芯蕊. 中国能源与重要矿产资源需求展望. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(3): 338-344.
[
|
| [7] |
沈镭. 面向碳中和的中国自然资源安全保障与实现策略. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(12): 3037-3048.
[
|
| [8] |
张苏江, 崔立伟, 孔令湖, 等. 国内外锂矿资源及其分布概述. 有色金属工程, 2020, 10(10): 95-104.
[
|
| [9] |
郑人瑞, 唐金荣, 周平, 等. 我国锂资源供应风险评估. 中国矿业, 2016, 25(12): 30-37.
[
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
廖秋敏, 孙明浩. “逆全球化”背景下中国锂资源供应安全评价. 矿业研究与开发, 2022, 42(4): 179-186.
[
|
| [12] |
王安建, 王高尚, 陈其慎, 等. 矿产资源需求理论与模型预测. 地球学报, 2010, 31(2): 137-147.
[
|
| [13] |
王安建, 王高尚, 周凤英. 能源和矿产资源消费增长的极限与周期. 地球学报, 2017, 38(1): 3-10.
[
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
张雷. 中国能源安全问题探讨. 中国软科学, 2001, (4): 7-12.
[
|
| [17] |
彭忠益, 卢珊. 大数据赋能国家矿产资源安全事件预警管理研究. 情报杂志, 2023, 42(7): 65-70, 92.
[
|
| [18] |
谷树忠, 吴太平. 中国新时代自然资源治理体系的理论构想. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(8): 1802-1816.
[
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
黄健柏, 孙芳, 宋益. 清洁能源技术关键金属供应风险评估. 资源科学, 2020, 42(8): 1477-1488.
[
|
| [23] |
吴巧生, 周娜, 成金华. 战略性关键矿产资源供给安全研究综述与展望. 资源科学, 2020, 42(8): 1439-1451.
[
|
| [24] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
周娜, 吴巧生, 薛双娇. 新时代战略性矿产资源安全评价指标体系构建与实证. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2020, 30(12): 55-65.
[
|
| [31] |
郑明贵, 董娟, 钟昌标. 资本深化对中国资源型企业全要素生产率的影响. 资源科学, 2022, 44(3): 536-553.
[
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). Trend Report of Development in Materials for Substitution of Scarce Metals, 2009.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
胡森林, 鲍涵, 郝均, 等. 环境规制对长三角城市绿色发展的影响: 基于技术创新的作用路径分析. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(6): 1572-1585.
[
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
吕锋, 崔晓辉. 多目标决策灰色关联投影法及其应用. 系统工程理论与实践, 2002, 22(1): 103-107.
[
|
| [43] |
徐美, 刘春腊. 湖南省资源环境承载力预警评价与警情趋势分析. 经济地理, 2020, 40(1): 187-196.
[
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
马孝先. 中国城镇化的关键影响因素及其效应分析. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2014, 24(12): 117-124.
[
|
| [46] |
邢凯, 朱清, 邹谢华, 等. 新能源背景下锂资源产业链发展研究. 中国地质, 2023, 50(2): 395-409.
[
|
| [47] |
马哲, 李建武. 中国锂资源供应体系研究: 现状, 问题与建议. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(10): 1-7.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |