

智慧城市人地系统理论框架与科学问题
|
甄峰(1973- ),男,陕西汉中人,博士,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为智慧城市、大数据与城市规划。E-mail: zhenfeng@nju.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2022-10-17
修回日期: 2023-04-27
网络出版日期: 2023-09-07
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(20JZD013)
国家社会科学基金项目(20AZD040)
Theoretical framework and scientific problems of smart city man-land system
Received date: 2022-10-17
Revised date: 2023-04-27
Online published: 2023-09-07
智能技术的快速发展,不仅为城市人地系统的监测与调控提供新的技术手段,更会对城市人地系统的要素结构、耦合关系及动态演进等产生深刻影响,探索并构建面向智慧城市的人地系统理论势在必行。从流空间、“人—技术—空间”一体化耦合、复杂韧性系统等方面探讨了智慧城市人地系统的理论基础,进而提出智慧城市人地系统的概念模型。面向未来,智慧城市人地系统研究需要聚焦要素时空耦合过程、要素构成及影响机理、建模方法与评价、综合调控与优化路径等内容。从智能技术带来的人类行为模式与活动变化、空间智能化、虚实关联等方面,提出智慧城市人地系统理论、方法创新与可持续调控的未来展望,以完善适应中国国情的智慧城市人地系统理论方法体系,支撑城市地理学创新及“智慧大脑”、数字孪生城市建设等现实需求。
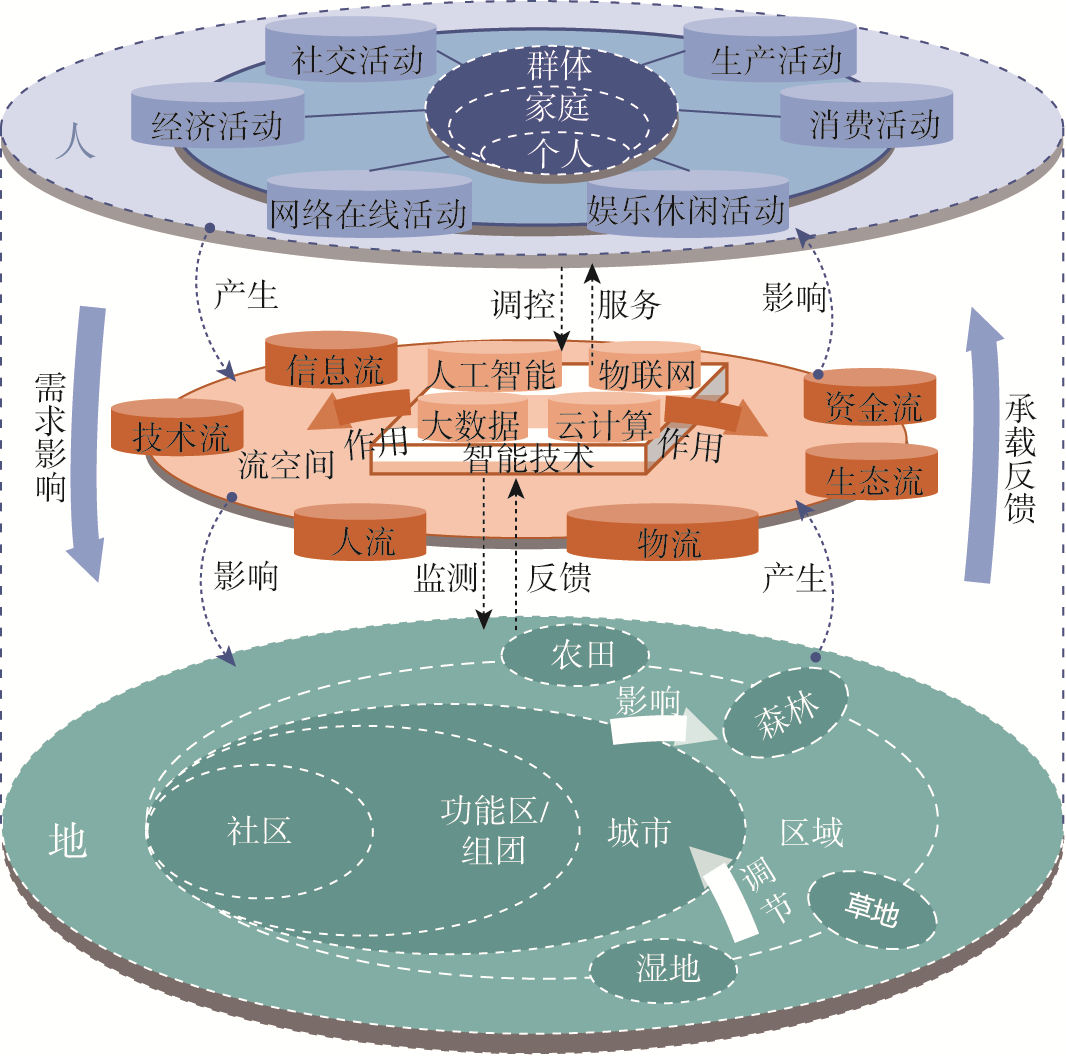
甄峰 , 席广亮 , 张姗琪 , 秦萧 . 智慧城市人地系统理论框架与科学问题[J]. 自然资源学报, 2023 , 38(9) : 2187 -2200 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20230901
The rapid development of intelligent technology not only provides new technical means for the monitoring and regulation of urban man-land system, but also has a systematic impact on the element structure, coupling relationship and dynamic evolution of urban man-land system. It is imperative to explore the theory of building a man-land system for smart cities. Based on the interpretation of the connotation of the smart city man-land system, this paper discusses the theoretical basis of the smart city man-land system from the aspects of flow space, technology-man-land coupling and resilience system, and then puts forward the conceptual model of the smart city man-land system. On the one hand, we should explore the spatial scale changes of the interactions among human activities, elemental flows, and geographic environments, and further investigate into the cross-scale collaboration, tele-coupling, and feedback between activity systems and geographic environment systems regulated by intelligent technologies. On the other hand, we should pay attention to temporal elasticity, flexibility and fragmentation of the interactive coupling between residents' activities and urban geographical environment caused by the wide application of intelligent technology. Then it is necessary to carry out the monitoring, management and dynamic optimization with the smart city man-land system. Facing the future, the research on man-land system of smart cities needs to focus on the spatio-temporal coupling process of elements, elemental composition and impact mechanism, modeling methods and evaluation, comprehensive regulation and optimization path, etc. Finally, from the aspects of human behavior patterns and activity changes brought about by smart technology, spatial intelligence, virtual reality correlation, etc., the research prospect of theoretical exploration, analysis method innovation and sustainable regulation of smart city man-land system is proposed. All in all, based on the coupling of people, technology and urban space, we build the theoretical framework of smart city man-land system adapted to China's national conditions in consideration of the trend of high penetration and integration of China's new infrastructure and smart city services in production, living and governmental management. This framework could support the innovation of urban geography theory and method and the practical needs of "smart brain", digital twin city construction.

Key words: smart cities; man-land system; coupling system; space of flow; resilience
表1 智慧城市人地耦合系统:要素、结构与尺度Table 1 Coupling system of smart city human-land: Elements, structure and scale |
| 层级尺度 | 要素 | 结构 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 节点 | 连接 | 网络 | |||
| 域外耦合 | 区域、国 家和全球 | 经济、贸易、创新、 资本等要素 | 城市、门户与枢纽 | 经济流、商品流、技术流、资金流等 | 区域、国家和全球经济网络、贸易网络、创新网络、资本网络 |
| 域内耦合 | 城市 | 社会经济、基础设施、文化、生态、治理等 要素 | 商业中心、游憩休闲中心、综合服务中心 | 经济流、交通流、能源资源流、生态流等 | 社会经济网络、基础设施网络、生态网络等 |
| 功能区 (组团) | 产业、服务、居住区、休闲、交通等要素 | 功能区/组团中心 | 居住、就业、休闲、出行等活动流 | 功能组团网络 | |
| 社区 | 居住、服务、文化等 要素 | 社区活动中心、社区服务中心 | 社区日常活动—移动 | 社区生活圈网络 | |
| 个体与家庭 | 居民活动、情感、幸 福感等 | 智慧市民、智能家庭 | 阶层流、思想流 | 个体与家庭社会网络 | |
| [1] |
德勤咨询. 超级智能城市2.0: 人工智能引领新风尚, 2020.
[
|
| [2] |
甄峰, 席广亮, 秦萧. 基于地理视角的智慧城市规划与建设的理论思考. 地理科学进展, 2015, 34(4): 402-409.
[
|
| [3] |
吴传钧. 论地理学的研究核心: 人地关系地域系统. 经济地理, 1991, 11(3): 1-6.
[
|
| [4] |
吴传钧. 人地关系与经济布局. 北京: 学苑出版社, 1998.
[
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
陆大道. 关于地理学的“人—地系统”理论研究. 地理研究, 2002, 21(2): 135-145.
[
|
| [8] |
蔡运龙. 人地关系研究范型: 地域系统实证. 人文地理, 1998, 13(2): 11-17.
[
|
| [9] |
方创琳. 中国人地关系研究的新进展与展望. 地理学报, 2004, 59(s): 21-32.
[
|
| [10] |
陆玉麒. 人文地理学科学化的总体目标与实现路径. 地理学报, 2011, 66(12): 1587-1596.
[
|
| [11] |
樊杰. 人地系统可持续过程、格局的前沿探索. 地理学报, 2014, 69(8): 1060-1068.
[
|
| [12] |
杨宇, 李小云, 董雯, 等. 中国人地关系综合评价的理论模型与实证. 地理学报, 2019, 74(6): 1063-1078.
[
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
赵生才. 社会信息化与人地关系:香山科学会议第169次学术讨论会观点摘要. 地球科学进展, 2002, 17(4): 624-627.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
马恩朴, 蔡建明, 韩燕, 等. 人地系统远程耦合的研究进展与展望. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39(2): 310-326.
[
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
吴士锋, 路紫. 网站信息流对现实人流替代函数的计算与应用: 以中国互联网络发展状况统计报告为例. 经济地理, 2007, 27(1): 22-25.
[
|
| [20] |
贺灿飞, 朱向东, 孔莹晖, 等. 集聚经济、政策激励与中国计算机制造业空间格局: 基于贸易数据的实证研究. 地理科学, 2018, 38(10): 1579-1588.
[
|
| [21] |
刘彦随. 中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴. 地理学报, 2018, 73(4): 637-650.
[
|
| [22] |
孙斌栋. 信息革命下的社会经济空间集聚与分散. 地域研究与开发, 2018, 37(2): 172-173, 180.
[
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
柴彦威, 塔娜. 中国时空间行为研究进展. 地理科学进展, 2013, 32(9): 1362-1373.
[
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
秦萧, 甄峰, 魏宗财. 未来城市研究范式探讨: 数据驱动亦或人本驱动. 地理科学, 2019, 39(1): 31-40.
[
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
龙瀛, 张宇, 崔承印. 利用公交刷卡数据分析北京职住关系和通勤出行. 地理学报, 2012, 67(10): 1339-1352.
[
|
| [35] |
潘竟虎, 赖建波. 中国城市间人口流动空间格局的网络分析: 以国庆—中秋长假和腾讯迁徙数据为例. 地理研究, 2019, 38(7): 1678-1693.
[
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
甄峰, 王波, 陈映雪. 基于网络社会空间的中国城市网络研究: 以新浪微博为例. 地理学报, 2012, 67(8): 1031-1043.
[
|
| [38] |
詹庆明, 范域立, 罗名海, 等. 基于多源大数据的武汉市区域空间格局研究. 上海城市规划, 2019, (3): 30-26.
[
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
钮心毅, 丁亮, 宋小冬. 基于手机数据识别上海中心城的城市空间结构. 城市规划学刊, 2014, (6): 61-67.
[
|
| [41] |
王德, 钟炜菁, 谢栋灿, 等. 手机信令数据在城市建成环境评价中的应用: 以上海市宝山区为例. 城市规划学刊, 2015, (5): 82-90.
[
|
| [42] |
赵渺希, 梁景宇, 郭振松. 基于多维数据的特大城市建设用地类型识别. 上海城市规划, 2018, (5): 82-87.
[
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
柴彦威, 刘伯初, 刘瑜, 等. 基于多源大数据的城市体征诊断指数构建与计算: 以上海市为例. 地理科学, 2018, 38(1): 1-10.
[
|
| [45] |
龙瀛, 张昭希, 李派, 等. 北京西城区城市区域体检关键技术研究与实践. 北京规划建设, 2019, (s2): 180-188.
[
|
| [46] |
李德仁, 姚远, 邵振峰. 智慧城市中的大数据. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2014, 39(6): 631-640.
[
|
| [47] |
甄峰, 张姗琪, 秦萧, 等. 从信息化赋能到综合赋能: 智慧国土空间规划思路探索. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(10): 2060-2072.
[
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
曹阳, 甄峰. 基于智慧城市的可持续城市空间发展模型总体架构. 地理科学进展, 2015, 34(4): 430-437.
[
|
| [50] |
吴志强, 刘晓畅. 改革开放40年来中国城乡规划知识网络演进. 城市规划学刊, 2018, (5): 11-18.
[
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
甄峰, 孔宇. “人—技术—空间”一体的智慧城市规划框架. 城市规划学刊, 2021, (6): 45-52.
[
|
| [56] |
樊杰. “人地关系地域系统”是综合研究地理格局形成与演变规律的理论基石. 地理学报, 2018, 73(4): 597-607.
[
|
| [57] |
席广亮, 甄峰. 基于可持续发展目标的智慧城市空间组织和规划思考. 城市发展研究, 2014, 21(5): 102-109.
[
|
| [58] |
郑度. 21世纪人地关系研究前瞻. 地理研究, 2002, 21(1): 9-13.
[
|
| [59] |
刘彦随. 现代人地关系与人地系统科学. 地理科学, 2020, 40(8): 1221-1234.
[
|
| [60] |
曹小曙. 基于人地耦合系统的国土空间重塑. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(10): 2051-2059.
[
|
| [61] |
郭仁忠, 林浩嘉, 贺彪, 等. 面向智慧城市的GIS框架. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2020, 45(12): 1829-1835.
[
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
崔学刚, 方创琳, 李君, 等. 城镇化与生态环境耦合动态模拟模型研究进展. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(1): 111-125.
[
|
| [67] |
方创琳, 周成虎, 顾朝林, 等. 特大城市群地区城镇化与生态环境交互耦合效应解析的理论框架及技术路径. 地理学报, 2016, 71(4): 531-550.
[
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
席广亮, 甄峰, 冷硕峰. 2022年城市数字化转型发展热点回眸. 科技导报, 2023, 41(1): 194-201.
[
|
| [71] |
姚冲, 甄峰, 席广亮. 中国智慧城市研究的进展与展望. 人文地理, 2021, 36(5): 15-23.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |