

国际粮食贸易影响下东北黑土地生产压力变化与保护策略
|
邓祥征(1971- ),男,山东日照人,博士,研究员,主要从事资源环境管理与发展地理学等相关研究。E-mail: dengxz@igsnrr.ac.cn |
收稿日期: 2021-11-08
修回日期: 2022-01-29
网络出版日期: 2022-12-28
基金资助
黑土地保护与利用科技创新工程专项(XDA28060200)
Research on changes in grain production pressure and protection strategies in the black soil region of Northeast China under the influence of international grain trade
Received date: 2021-11-08
Revised date: 2022-01-29
Online published: 2022-12-28
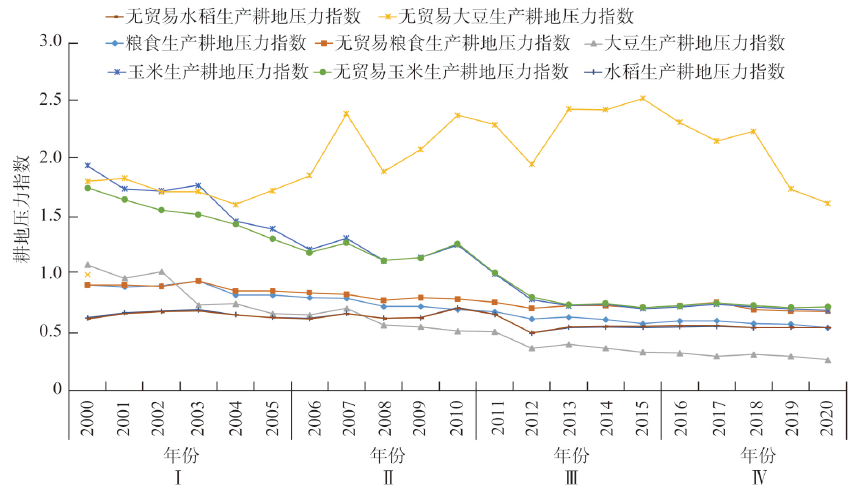
黑土地是重要的农产品生产基地之一,承担着保障国家粮食安全和维护农业生态安全的重要责任,保护好黑土地对促进我国农业可持续发展至关重要。测算与分析2000—2020年东北黑土地粮食生产耕地压力的变化情况,研究国际贸易对东北黑土地粮食生产的耕地压力的影响,利用国际市场占有率指数和贸易竞争优势指数分析东北黑土地农产品在国内及国际两个市场的竞争优势。结果表明:近20年来东北黑土地粮食生产的耕地压力基本处于安全压力区并呈逐步下降的趋势,玉米、大豆、稻谷三种主要作物生产的耕地压力分别从2000年的1.94、1.09和0.63下降至2020年的0.69、0.26和0.54。国际粮食贸易对黑土地粮食生产耕地压力减缓的作用显著且呈现出逐年上升的趋势,2020年对黑土地粮食生产耕地压力减缓的贡献率达26.22%,其中对大豆生产的耕地压力减缓的贡献率达511.48%。农产品贸易优势度分析结果显示,东北黑土地农产品在国内市场具有明显的贸易竞争优势,但在国际贸易中的竞争优势不明显。为此,提出了国际贸易粮食贸易变化背景下黑土地保护的若干建议,为东北黑土地保护及其粮食产能保障相关决策提供参考。
邓祥征 , 梁立 , 廖晓勇 , 刘玉洁 , 李志慧 , 岳天祥 , 董金玮 , 孙志刚 , 陈明星 . 国际粮食贸易影响下东北黑土地生产压力变化与保护策略[J]. 自然资源学报, 2022 , 37(9) : 2209 -2217 . DOI: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20220901
As an important agricultural production area, black soil region bears the important responsibility of ensuring national food security and maintaining agricultural ecological security. Protecting black soil is crucial to promoting sustainable agricultural development. This paper analyzes the changes of cultivated black soil pressure of grain production in Northeast China from 2000 to 2020, studies the impact of international trade on cultivated land pressure for grain production in the study area, and analyzes the competitive advantage of the agricultural products of the black soil region of Northeast China in domestic and international markets by using international market share index and trade competitive advantage index. Results show that in the past 20 years, the cultivated land pressure of grain production in the black soil region of Northeast China is basically at the safety level and presents a gradual downward trend. The cultivated land pressure of corn, soybean and rice decreased from 1.94, 1.09 and 0.63 in 2000 to 0.69, 0.26 and 0.54 in 2020, respectively. International grain trade plays a significant role in alleviating the pressure on cultivated soil for grain production and shows an increasing trend year by year. In 2020, the contribution rate to the mitigation of cultivated land pressure for grain production is 26.22%, of which the contribution rate to the mitigation of cultivated land pressure for soybean production is up to 511.48%. The results of the analysis of the agricultural product trade advantage degree show that agricultural products have obvious trade competitive advantages in the domestic market, but the competitive advantage in international trade is not obvious. Finally, this paper puts forward some suggestions on the protection of black soil under the background of changes in international grain trade, which provides a reference for the decision-making of black soil protection in Northeast China and the guarantee of grain production capacity.

表1 国际粮食贸易对于东北黑土地粮食生产耕地压力减缓作用的贡献率Table 1 Contribution of international grain trade to alleviating the pressure of cropland for grain production in the black soil region of Northeast China (%) |
| 年份 | 粮食 | 大豆 | 玉米 | 稻谷 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 26.22 | 511.48 | 4.33 | 0.04 |
| 2015 | 24.71 | 659.34 | 1.78 | 1.44 |
| 2010 | 13.31 | 362.22 | 0.81 | -0.12 |
| 2005 | 4.64 | 160.21 | -6.20 | -0.09 |
| 2000 | -0.09 | 66.24 | -9.88 | -1.46 |
| [1] |
黄汉权, 周振. 全球粮食安全新形势及我国的应对. 理论导报, 2020, (9): 55-56.
[
|
| [2] |
王晓君, 何亚萍, 蒋和平. "十四五"时期的我国粮食安全: 形势, 问题与对策. 改革, 2020, (9): 13.
[
|
| [3] |
张义博. 新时期中国粮食安全形势与政策建议. 宏观经济研究, 2020, (3): 57-66.
[
|
| [4] |
于爱芝, 杨敏. 中美贸易摩擦与我国重点农业产业走向. 华南农业大学学报: 社会科学版, 2021, 20(1): 1-8.
[
|
| [5] |
龚波. 中美贸易摩擦对中国粮食安全的影响. 求索, 2019, (4): 107-112.
[
|
| [6] |
谭砚文, 李丛希, 陈志钢. 新冠肺炎疫情对中国与东盟区域农产品供应链的影响及对策. 农业经济问题, 2020, (10): 113-121.
[
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
韩晓增, 邹文秀. 我国东北黑土地保护与肥力提升的成效与建议. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(2): 206-212.
[
|
| [9] |
韩晓增, 李娜. 中国东北黑土地研究进展与展望. 地理科学, 2018, 38(7): 1032-1041.
[
|
| [10] |
马静, 张红旗, 李慧娴, 等. 粮食国际贸易对我国水土资源利用的影响分析. 资源科学, 2008, 30(11): 1723-1728.
[
|
| [11] |
贾盼娜, 刘爱民, 成升魁, 等. 中国农产品贸易格局变化及海外农业资源利用对策. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(7): 1357-1364.
[
|
| [12] |
强文丽, 张翠玲, 刘爱民, 等. 全球农产品贸易的虚拟耕地资源流动演变及影响因素. 资源科学, 2020, 42(9): 1704-1714.
[
|
| [13] |
杨明智, 裴源生, 李旭东. 中国粮食自给率研究: 粮食、谷物和口粮自给率分析. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(4): 881-889.
[
|
| [14] |
陈彧. 中国大豆自给率与大豆供给率研究. 统计与决策, 2020, (6): 63-67.
[
|
| [15] |
刘卉芳, 单志杰, 秦伟, 等. 东北黑土区水土流失治理技术与模式研究评述. 泥沙研究, 2020, 45(4): 74-80.
[
|
| [16] |
朱红波, 张安录. 中国耕地压力指数时空规律分析. 资源科学, 2007, 29(2): 104-108.
[
|
| [17] |
罗翔, 张路, 朱媛媛. 基于耕地压力指数的中国粮食安全. 中国农村经济, 2016, (2): 83-96.
[
|
| [18] |
孟凡杰, 于晓芳, 高聚林, 等. 黑土地保护性耕作发展的制约瓶颈和突破路径. 农业经济问题, 2020, (2): 135-142.
[
|
| [19] |
敖曼, 张旭东, 关义新. 东北黑土保护性耕作技术的研究与实践. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(10): 1203-1215.
[
|
| [20] |
薛建福, 赵鑫,
[
|
| [21] |
王永军, 吕艳杰, 刘慧涛, 等. 东北春玉米高产与养分高效综合管理. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(20): 3533-3535.
[
|
| [22] |
唐亮, 吴东立, 苗微, 等. 东北地区食物安全可持续发展战略研究. 中国工程科学, 2019, 21(5): 19-27.
[
|
| [23] |
姜明, 文亚, 孙命, 等. 用好养好黑土地的科技战略思考与实施路径: 中国科学院"黑土粮仓"战略性先导科技专项的总体思路与实施方案. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(10): 1146-1154.
[
|
| [24] |
李保国, 刘忠, 黄峰, 等. 巩固黑土地粮仓保障国家粮食安全. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(10): 1184-1193.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |