 PDF(3722 KB)
PDF(3722 KB)


 PDF(3722 KB)
PDF(3722 KB)
 PDF(3722 KB)
PDF(3722 KB)
北京农业地域功能空间分异及影响因素
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Spatial differentiation of agricultural regional function in Beijing and its influencing factors
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}北京减量提质发展背景下,农业地域功能主要体现在优质农产品生产、生态保护、高端休闲娱乐供给、新业态示范、产业链拓展与融合以及就业收入拉动等方面。以184个街道、乡镇为基本研究地域单元,测算了北京农业地域功能并剖析了空间分异特征。研究发现:北京农业地域功能空间分异与城市空间开发结构密切相关,总体上表现为自城乡结合部核心区、拓展区到远郊区呈圈层递增态势;城乡结合部拓展区农业地域功能衰退趋势显著,对城市空间开发的约束变弱;远郊区农产品供给、生态保护和就业安置等基本和传统功能较强而产业融合、新业态等高级与现代功能偏低,农业地域功能仍有较大提升空间。通过OLS基本回归和分位数回归发现,土地因素是影响北京农业地域功能的关键因素,其中区位因素决定农用地规模进而影响农业地域功能,房价因素通过加速农用地流转对功能最弱地区的农业地域功能具有明显抑制作用。非农产业对农业地域功能具有促进而非挤压替代作用。
Under the background of rapid urbanization, agricultural development in Beijing has shrunk sharply and the marginalization of agriculture is becoming more and more obvious. Recently, Beijing puts forward the development model of reducing quantity and improving quality, to meet the needs of the people and improve the quality of the ecological environment. In this context, the regional function of agriculture should focus on the production of high-quality farm products, the ecological protection, the high-end leisure and entertainment supply and the popularization of agricultural science and technology, as well as the promotion of urban and rural integration, etc. By using the data of 184 streets and towns, the research calculates the regional function of agriculture in Beijing. Results show that the spatial differentiation of agricultural regional function in Beijing is closely related to the structure of urban spatial development, which is generally shown an increasing trend from the core area of urban-rural fringe to the extended area to the far suburbs, and the declining trend of agricultural regional function in the extended area of urban-rural fringe is significant, which makes the city gradually lose the constraints of spatial development. The basic functions of agricultural products supply, ecological protection and employment placement in the far suburbs are strong and industrial integration, new business type and other modern functions are at a low level. Therefore, there is still great room for improvement of agricultural regional functions. The result of basic regression and quantile regression shows that, the land factors are the key factors that affect the regional function of the agricultural region in Beijing, and the location factor determines the scale of the agricultural land and the house price factor obviously inhibit the agricultural regional function in areas with the lowest score by accelerating the circulation of agricultural land. The non-agricultural industry has the function of promoting and not squeezing the regional function of agriculture. In the future, Beijing should focus on the regional function of agriculture, protect the agricultural land and fully tap the new urban agricultural support space, promote the organic integration of the agriculture into the modern economic system of the city so as to stimulate the new potential of agriculture; and optimize the method for realizing the regional function of agriculture.
农业地域功能 / 空间分异 / 功能评价 / 北京 {{custom_keyword}} /
agricultural regional function / spatial differentiation / function evaluation / Beijing {{custom_keyword}} /
表1 北京农业地域功能评价指标体系Table 1 Evaluation index system of agricultural regional function in Beijing |
| 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 三级指标 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 农产品生产功能 | 普通农产品生产 高端农产品生产 | 人均粮食产量 人均蛋奶水产品产量 人均蔬菜干鲜果产量 有机农产品产量占比 | |
| 生态保护功能 | 生态缓冲 绿化涵养 废弃资源利用 | 农业播种面积占土地面积比例 林木绿化率 城市厨余垃圾、废弃物利用率 | |
| 休闲娱乐供给功能 | 民俗村 农业观光园 | 市级乡村旅游四、五星级民俗村占全市比例 市级星级农业观光园占全市比例 | |
| 新业态示范功能 | 国家层面示范 市级层面示范 | 国家级休闲农业和乡村旅游星级示范企业占全市比例 市级乡村旅游特色业态单位 | |
| 产业链拉动与融合功能 | 农业现代化 科技开发与推广 产业融合 | 设施农业收入占比 农业科技企业数量占全市比例 大型农业节庆会展年均接待人次占全市比例 | |
| 就业收入拉动功能 | 就业岗位提供 收入拉动 | 农业从业人员占比 第一产业从业从员平均工资 | |
表2 北京农业地域功能各评价指标权重Table 2 The weight of each evaluation index of the regional function of agriculture in Beijing |
| 指标 | 权重 | 指标 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.080944 | 0.052500 | ||
| 0.073045 | 0.084544 | ||
| 0.081472 | 0.089550 | ||
| 0.084557 | 0.045543 | ||
| 0.091846 | 0.088791 | ||
| 0.055230 | 0.091793 | ||
| 0.080184 |
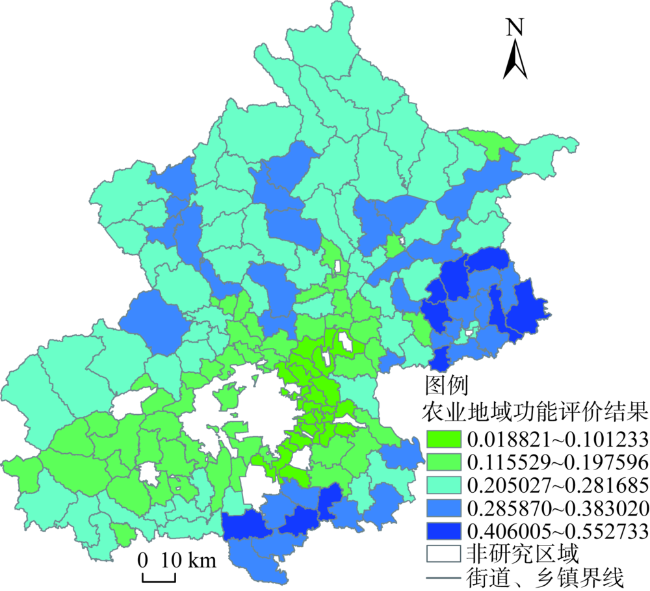
图3 2016年北京农业地域功能评价结果及类型划分Fig. 3 The evaluation results and classification of agricultural regional function in Beijing in 2016 |
表3 根据农业地域综合功能强弱划分的各区域类型数量占比分布Table 3 Distribution of the number of types according to the agricultural regional function (%) |
| 强 | 较强 | 一般 | 较弱 | 弱 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城乡结合部核心区 | 0 | 6.1 | 10.2 | 50.0 | 100 |
| 城乡结合部拓展区 | 30.0 | 33.3 | 28.8 | 33.3 | 0 |
| 远郊区 | 70.0 | 60.6 | 61.0 | 16.7 | 0 |
| 总计 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
表5 农业地域功能空间分异影响因素指标Table 5 Measurement of influencing factors of agricultural regional function |
| 变量 | 符号 | 单位 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 人均工业生产总值 | Indput | 元 | 部分样本中值为0,故该项在取值时统一在原值上加1 |
| 人口密度 | Popdense | 人/km2 | |
| 与市中心点的距离 | Dista | m | 基层地域单元中心点到市中心的直线距离 |
| 房价 | Houprice | 元 | 取2015年和2016年的均值 |
表6 北京农业地域功能影响因素回归分析结果Table 6 Results of regression analysis on the influencing factors of agricultural regional function in Beijing |
| OLS | QR_10 | QR_20 | QR_30 | QR_40 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnIndput | 0.00569** (0.00191) | 0.00342* (0.00136) | 0.00553** (0.00178) | 0.00718*** (0.00195) | 0.00699** (0.00213) |
| lnPopdense | -0.00857 (0.00680) | -0.00846 (0.00484) | -0.00868 (0.00635) | -0.00989 (0.00696) | -0.00517 (0.00758) |
| lnDistance | 0.105*** (0.0158) | 0.0777*** (0.0112) | 0.0783*** (0.0148) | 0.0866*** (0.0162) | 0.106*** (0.0176) |
| lnHouprice | -0.00473 (0.0141) | -0.0273** (0.0100) | -0.0359** (0.0132) | -0.0243 (0.0144) | -0.0155 (0.0157) |
| 常数项C | -0.843*** (0.246) | -0.392* (0.175) | -0.319 (0.230) | -0.504* (0.252) | -0.815** (0.275) |
| R2 | 0.5080 | 0.5169 | 0.4631 | 0.4160 | 0.3857 |
| 样本容量 | 184 | 184 | 184 | 184 | 184 |
| QR_50 | QR_60 | QR_70 | QR_80 | QR_90 | |
| lnIndput | 0.00673*** (0.00195) | 0.00833*** (0.00236) | 0.00736** (0.00253) | 0.00574 (0.00378) | -0.00128 (0.00585) |
| lnPopdense | -0.00224 (0.00694) | -0.00167 (0.00840) | -0.00355 (0.00900) | -0.0198 (0.0135) | -0.0338 (0.0208) |
| lnDistance | 0.111*** (0.0161) | 0.122*** (0.0195) | 0.130*** (0.0209) | 0.110*** (0.0313) | 0.113* (0.0484) |
| lnHouprice | -0.00767 (0.0144) | -0.00619 (0.0174) | 0.00803 (0.0186) | 0.0230 (0.0279) | 0.0292 (0.0432) |
| 常数项C | -0.937*** (0.251) | -1.079*** (0.304) | -1.260*** (0.326) | -1.061* (0.488) | -0.946 (0.755) |
| R2 | 0.3531 | 0.3226 | 0.2824 | 0.2477 | 0.1761 |
| 样本容量 | 184 | 184 | 184 | 184 | 184 |
| 注:***、**、*分别表示在1%、5%、10%水平下显著。 |
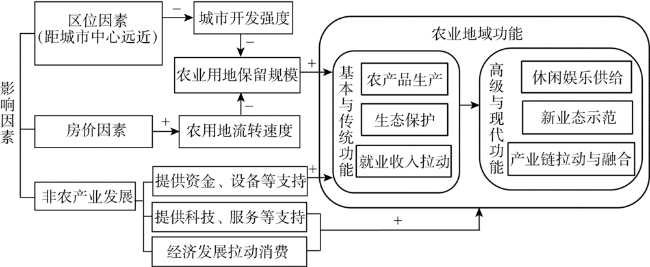
图6 北京农业地域功能影响因素及作用机制 |
| [1] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [2] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [3] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [4] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [5] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [6] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [7] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [8] |
OECD. Multifunctionality: Towards an Analytical Framework. Paris: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, 2001.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [9] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [10] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [11] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [12] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [13] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [14] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [15] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [16] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [17] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [18] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [19] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [20] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [21] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [22] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [22] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [24] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [25] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [26] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [27] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [28] |
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 PDF(3722 KB)
PDF(3722 KB)
 图1 北京农业地域功能构成
图1 北京农业地域功能构成 表1 北京农业地域功能评价指标体系
表1 北京农业地域功能评价指标体系 表2 北京农业地域功能各评价指标权重
表2 北京农业地域功能各评价指标权重 图2 研究区域与类型划分
图2 研究区域与类型划分 图3 2016年北京农业地域功能评价结果及类型划分
图3 2016年北京农业地域功能评价结果及类型划分 表3 根据农业地域综合功能强弱划分的各区域类型数量占比分布
表3 根据农业地域综合功能强弱划分的各区域类型数量占比分布 图4 2016年北京农业地域分项功能空间分布
图4 2016年北京农业地域分项功能空间分布 图5 2012—2016年北京城乡结合部拓展区农作物生产变化情况注:数据来源于北京各区统计年鉴(2013年,2017年),《中国建制镇统计年鉴2012》和《中国县域统计年鉴·乡镇卷(2017)》。
图5 2012—2016年北京城乡结合部拓展区农作物生产变化情况注:数据来源于北京各区统计年鉴(2013年,2017年),《中国建制镇统计年鉴2012》和《中国县域统计年鉴·乡镇卷(2017)》。 表4 2012—2016年北京各区域农作物生产变化情况
表4 2012—2016年北京各区域农作物生产变化情况 表5 农业地域功能空间分异影响因素指标
表5 农业地域功能空间分异影响因素指标 表6 北京农业地域功能影响因素回归分析结果
表6 北京农业地域功能影响因素回归分析结果 图6 北京农业地域功能影响因素及作用机制注:图中“+”和“-”代表作用方向,即“+”表示前者数值越大,后者数值越大;“-”表示前者数值越大,后者数值越小。
图6 北京农业地域功能影响因素及作用机制注:图中“+”和“-”代表作用方向,即“+”表示前者数值越大,后者数值越大;“-”表示前者数值越大,后者数值越小。/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |